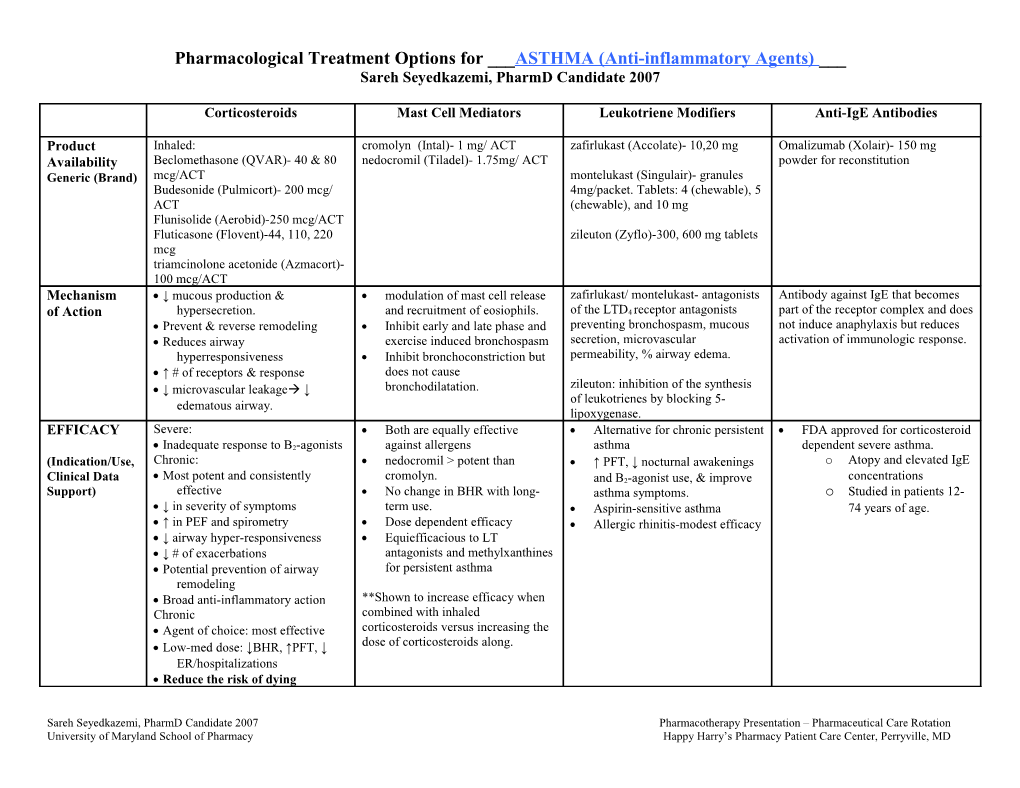
Pharmacological Treatment Options for ___ASTHMA (Anti-inflammatory Agents) ___ Sareh Seyedkazemi, PharmD Candidate 2007
Corticosteroids Mast Cell Mediators Leukotriene Modifiers Anti-IgE Antibodies
Product Inhaled: cromolyn (Intal)- 1 mg/ ACT zafirlukast (Accolate)- 10,20 mg Omalizumab (Xolair)- 150 mg Availability Beclomethasone (QVAR)- 40 & 80 nedocromil (Tiladel)- 1.75mg/ ACT powder for reconstitution Generic (Brand) mcg/ACT montelukast (Singulair)- granules Budesonide (Pulmicort)- 200 mcg/ 4mg/packet. Tablets: 4 (chewable), 5 ACT (chewable), and 10 mg Flunisolide (Aerobid)-250 mcg/ACT Fluticasone (Flovent)-44, 110, 220 zileuton (Zyflo)-300, 600 mg tablets mcg triamcinolone acetonide (Azmacort)- 100 mcg/ACT Mechanism ↓ mucous production & modulation of mast cell release zafirlukast/ montelukast- antagonists Antibody against IgE that becomes of Action hypersecretion. and recruitment of eosiophils. of the LTD4 receptor antagonists part of the receptor complex and does Prevent & reverse remodeling Inhibit early and late phase and preventing bronchospasm, mucous not induce anaphylaxis but reduces Reduces airway exercise induced bronchospasm secretion, microvascular activation of immunologic response. hyperresponsiveness Inhibit bronchoconstriction but permeability, % airway edema. ↑ # of receptors & response does not cause zileuton: inhibition of the synthesis ↓ microvascular leakage ↓ bronchodilatation. of leukotrienes by blocking 5- edematous airway. lipoxygenase. EFFICACY Severe: Both are equally effective Alternative for chronic persistent FDA approved for corticosteroid Inadequate response to B2-agonists against allergens asthma dependent severe asthma. (Indication/Use, Chronic: nedocromil > potent than ↑ PFT, ↓ nocturnal awakenings o Atopy and elevated IgE Clinical Data Most potent and consistently cromolyn. and B2-agonist use, & improve concentrations Support) effective No change in BHR with long- asthma symptoms. o Studied in patients 12- ↓ in severity of symptoms term use. Aspirin-sensitive asthma 74 years of age. ↑ in PEF and spirometry Dose dependent efficacy Allergic rhinitis-modest efficacy ↓ airway hyper-responsiveness Equiefficacious to LT ↓ # of exacerbations antagonists and methylxanthines Potential prevention of airway for persistent asthma remodeling Broad anti-inflammatory action **Shown to increase efficacy when Chronic combined with inhaled Agent of choice: most effective corticosteroids versus increasing the dose of corticosteroids along. Low-med dose: ↓BHR, ↑PFT, ↓ ER/hospitalizations Reduce the risk of dying
Sareh Seyedkazemi, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD SAFETY Adverse Effects: Adverse Effects: Cough and Adverse Effects: Adverse Effects: headache, injection- Low-Med Dose- delayed growth; not wheezing zileuton: elevated liver enzymes, site reaction, URI, sinusitis, (Major Drug significant. Nedocromil only: bad taste headache, pain, dyspepsia, nausea, pharyngitis, viral infection, Interactions, High Dose- osteoporosis/ glaucoma/ and headache abdominal pain. Drug Interactions: Pre-cautions, cataracts in the elderly, adrenal Contraindications: hypersensitivity; zafirlukast/montelukast: Pregnancy Category: (B) Contra- insufficiency acute asthma attack Churg Strauss Syndrome; dizziness, Contraindications: hypersensitivity, indications, Local Effects: oropharyngeal Precautions: children <6 yo, fatigue, fever, rash acute bronchospasm, status Adverse Effects, candidiasis, dysphonia breastfeeding, cardiac arrythmias Drug Interactions: asthmaticus. Pregnancy Risk Contraindications- viral TB, bacterial Pregnancy Category: Zileuton- inhibitor of 1A2, warfarin, Precautions: risk for parasitic Category) respiratory infection, cromolyn (B) theophylline, and propanolol. infections (helminth), Safety and Drug Interactions- CYP 3A4 nedocromil (B) Zafirlukast/montelukast- substrate of efficacy in children <12 yo not inhibitors, grapefruit juice, 2C19 and inhibitor of 2C9 mod, ASA established. salmeterol. Pregnancy Category: Pregnancy Category: zafirlukast (B) Beclomethasone- (C) montelukast (B) Budesonide- (C/B) zileuton (C) Flunisolide- (C) Contraindications: hypersensitivity. Fluticasone- (C) Zileuton- LFT ≥3 x’s ULN Triamcinolone- (C) Precautions: safety and efficacy unknown in children <5 yo, chewable form of Singulair contains phenylalanine. Females >65 yo at greater risk of liver AE with zileuton- caution with hx of liver disease and/or alcohol abuse. Dosage & **See Dosing Chart** Only effective by Inhalation!!! zileuton: Administered SubQ Administration Severe: Cromolyn- available MDI & ≥12 yo: 600mg QID Oral or systemic indicated; no nebulizer zafirlukast: Dose determined by baseline (Include renal therapeutic advantage of either Nedocromil- MDI only 5-11 yo: 10 mg BID total serum IgE levels and body and/or hepatic Full course continued until PF Cromolyn: >12 yo: 20 mg BID weight adjustments) reaches 80% or predicted. Nebulizer: >2 & adults Hepatic: 50-60%↓ Systemic multiple daily dosing oInitial- 20 mg QID 1 hr before 2 hr after meals Range (150-375 mg) more effective than high doses or MDI: >5 -12 yo montelukast: very high pulse dosing. oInitial: 2 inhalations QID 12-23 mo: 4 mg QHS 2-4 week intervals 4-12 hours for effects to be seen oUsual: 1-2 Inhalations 3- (granules) 4 times per day 2-5 yo: 4mg QHS (granules Consistent dose for duration of Chronic: delivery method alters MDI: >12 yo or chewable) therapy. comparable dose oInitial: 2 inhalations QID 6-14 yo: chew 5 mg/d QHS Mild- QD oUsual:2-4 inhalations 3-4 >15 yo: 10mg/d QHS Most controlled with BID, less times per day No hepatic/renal toxicity Nedocromil: adjustments, severe hepatic Severe- multiple daily dosing, start >6 yo: 2 inhalations QID; ↓ when cases where not studied. high then taper down stable (BID-TID) Unlabeled use in acute
Sareh Seyedkazemi, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD Corticosteroids Mast Cell Mediators Leukotriene Modifiers Anti-IgE Antibodies
Monitoring Efficacy: PFT, coughing, wheezing, Efficacy: PFT, coughing, wheezing, Efficacy: PFT, coughing, wheezing, Efficacy: FEV1, Peak Flow, cough, dyspnea, beta agonist use dyspnea, beta agonist use dyspnea, beta agonist use wheezing, dyspnea, NOT IgE levels!! (Efficacy and Toxicity Toxicity: difficulty/ change in voice Toxicity: c/o change in taste, c/o Toxicity: symptoms of hepatic Toxicity: # of headaches, signs and Parameters) quality, wheezing, cough. injury (right upper quadrant pain, symptoms of infection, nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, flu-like symptoms), LFT (ALT/AST) Patient Use dose as directed. Do not stop Use as instructed. Do not Take on empty stomach and do not Proper use. Potential Adverse Education use abruptly. discontinue. Proper use. discontinue despite improvement. Reaction response and reporting. Prime pump (if applicable) Montelukast granules can be mixed Reconstitution: SWFI 1.4 ml to Proper Use of inhalers with food. Must be administered 15 upright vial and swirl gently for 5-10 Rinse mouth with water after use min after opening package. seconds every 5 minutes until Wipe off mouth piece with dry tissue dissolved. Storage: after reconstitution, lasts 8 hrs if refrigerated and 4 hrs if not refrigerated. Cost beclomethasone: cromolyn- 8.1gm $65.39 – 112 ACT zileuton- 600 mg (120)$92.99 Range $541- $2,706 depending on (1-month) 40 mcg (7.3gm) $60.84 14.2gm $90.47- 200 ACT the dosage. 80 mcg (7.3gm) $73.57 zafirlukast- 10 mg (60) $80.50 budesonide: nedocromil- 16.2 gm $71.62 20 mg (60) $74.99 1 inhaler (104 gm) $148.12 flunisolide: montelukast- 4 mg (30) $91.14 (7gm) $74.57 5 mg (30) $89.99 fluticasone: 10 mg (30) $89.99 triamcinolone References Pharmacotherapy, Dipiro 2005 See below See below See below** (Guidelines, Lexicomp-Online Drug Info Sources) Kelly HW, Sorkness CA. Asthma. In: Dipiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM, editors. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach 6th Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc;2005. p. 503-35.
Lexi-Comp OnlineTM [database on the Internet]. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp. c1978-2006 [cited: 2006 July]. Lexi-Drugs. Available from: www.crlonline.com
** https://www.clevelandclinicmeded.com/medical_info/pharmacy/janfeb2004/omalizumab.htm
Sareh Seyedkazemi, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD