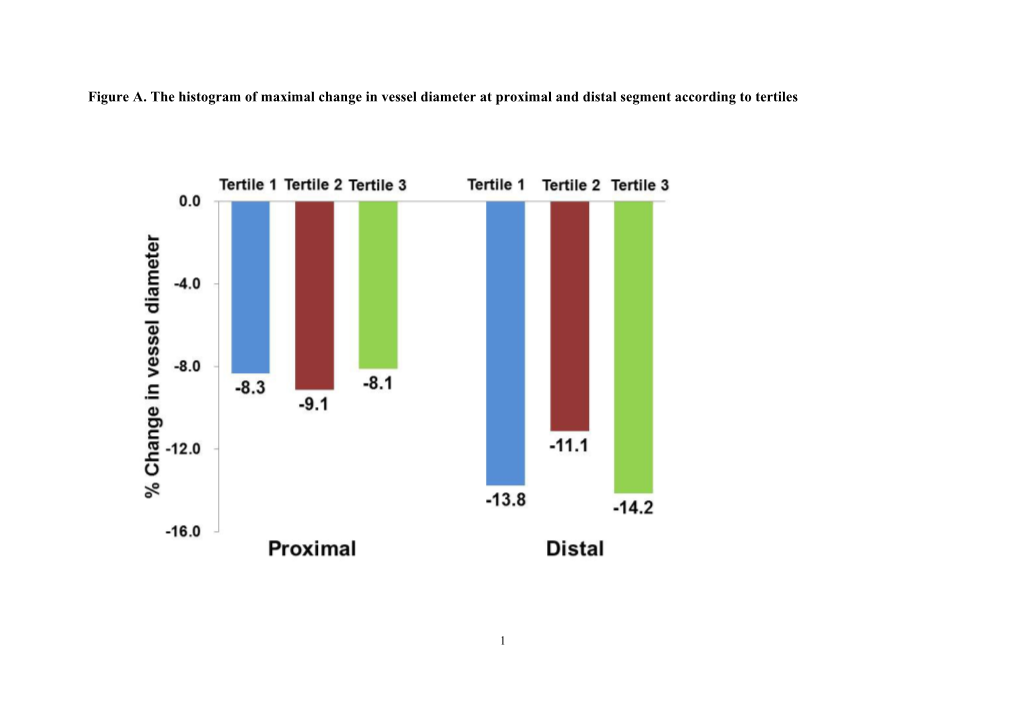
Figure A. The histogram of maximal change in vessel diameter at proximal and distal segment according to tertiles
1 Table A. Baseline clinical and procedural characteristics according to type of stent
Sirolimus-eluting stent Biolimus-eluting stent p (n=47) (n=65) Age, years 62.6 ± 9.5 61.3 ± 8.8 0.458 Male 38 (80.9) 50 (76.9) 0.649 Hypertension 26 (55.3) 35 (53.8) 0.999 Dyslipidemia 30 (63.8) 41 (63.1) 0.999 Diabetes mellitus 10 (21.3) 18 (27.7) 0.511 Current smoker 24 (51.1) 21 (32.3) 0.053 Medications Statin 45 (95.7) 61 (93.8) 0.704 ACEi or ARB 33 (70.2) 39 (60.0) 0.320 Calcium-channel blocker 14 (29.8) 27 (41.5) 0.236 Beta-blocker AHA/ACC type B2 or C 12 (25.5) 18 (27.7) 0.832 Stent deployment pressure, atm 13.7 ± 2.4 13.3 ± 3.0 0.412 Stent diameter, mm 3.1 ± 0.3 3.2 ± 0.3 0.093 Stent length, mm 18.4 ± 4.2 18.7 ± 4.8 0.715 Number of adjuvant dilation 24 (51.1) 26 (40.0) 0.256 Maximum balloon diameter 3.1 ± 0.4 3.2 ± 0.4 0.510 Maximum inflation pressure 15.5 ± 3.0 14.7 ± 3.7 0.226 Coronary artery lesion Left anterior descending artery 30 (63.8) 40 (61.5) 0.845
2 Left circumflex artery 10 (21.3) 9 (13.8) 0.319 Right coronary artery 7 (14.9) 16 (24.6) 0.243 Values are given as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation. ACEi, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker
Table B. Quantitative coronary angiographic and follow-up optical coherence tomographic findings according to type of stent
Sirolimus-eluting stent Biolimus-eluting stent p (n=47) (n=65) Reference segment diameter, mm 3.0 ± 0.4 3.2 ± 0.4 0.116 Pre-intervention minimal lumen diameter, mm 1.1 ± 0.5 1.2 ± 0.5 0.318 Post-intervention minimal lumen diameter, mm 2.7 ± 0.3 2.9 ± 0.5 0.228 Follow-up minimal lumen diameter, mm 2.5 ± 0.4 2.6± 0.5 0.410 Optical coherence tomographic findings Mean stent CSA, mm2 7.3 ± 2.3 7.8 ± 1.8 0.224 Mean lumen CSA, mm2 6.8 ± 2.1 7.4 ± 1.8 0.126 Mean neointimal hyperplasia CSA, mm2 0.5 ± 0.6 0.4 ± 0.3 0.250 Mean neointimal hyperplasia thickness, m 59.2 ± 61.7 50.8 ± 29.9 0.341 3 Percentage of neointimal hyperplasia CSA, % 6.0 ± 6.4 4.8 ± 4.0 0.253 Number of stent struts, n 7198 11501 Number of frame, n 758 1141 Percentage of uncovered strut, % 22.8 ± 19.5 21.3 ± 18.6 0.671 Cross section with uncovered strut, n 9.7 ± 5.5 10.5 ± 5.8 0.444 Percentage of malapposed strut, % 1.2 ± 2.7 1.5 ± 4.2 0.682 Values are given as mean ±standard deviation. CSA, cross-sectional area
4 Figure B. Changes in vessel diameter (%) in response to acetylcholine (Ach) and nitroglycerine (NTG) infusion by types of stent.
5 Figure C. Relationship between change in vessel diameter (%) and percentage of uncovered strut at 10-6mol/L of acetylcholine infusion in sirolimus-eluting stent
6 Figure D. Relationship between change in vessel diameter (%) and percentage of uncovered strut at 10-6mol/L of acetylcholine infusion in biolimus-eluting stent
7