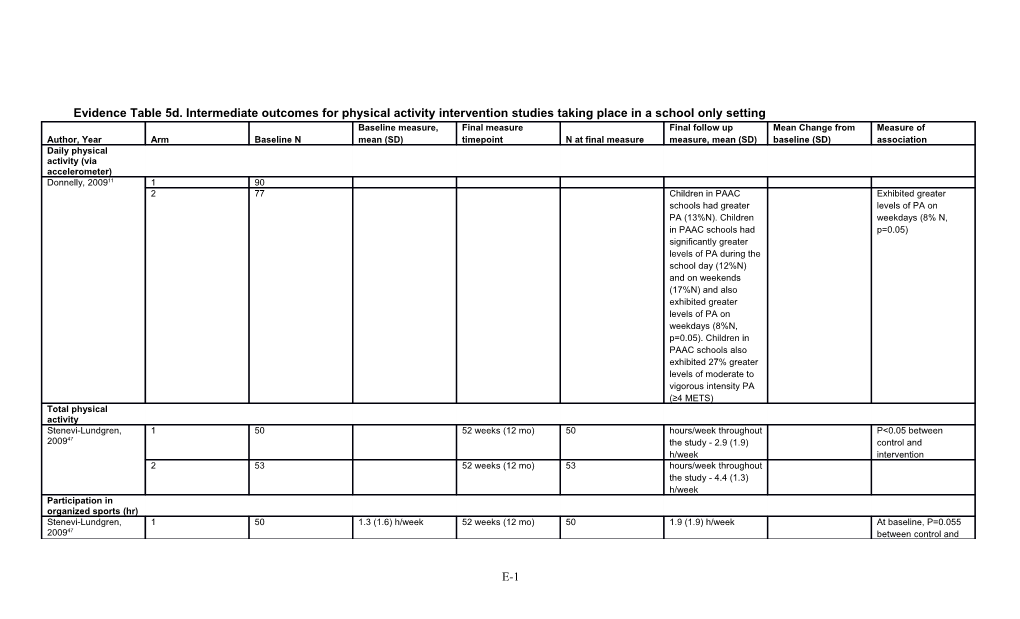
Evidence Table 5d. Intermediate outcomes for physical activity intervention studies taking place in a school only setting Baseline measure, Final measure Final follow up Mean Change from Measure of Author, Year Arm Baseline N mean (SD) timepoint N at final measure measure, mean (SD) baseline (SD) association Daily physical activity (via accelerometer) Donnelly, 200911 1 90 2 77 Children in PAAC Exhibited greater schools had greater levels of PA on PA (13%N). Children weekdays (8% N, in PAAC schools had p=0.05) significantly greater levels of PA during the school day (12%N) and on weekends (17%N) and also exhibited greater levels of PA on weekdays (8%N, p=0.05). Children in PAAC schools also exhibited 27% greater levels of moderate to vigorous intensity PA (≥4 METS) Total physical activity Stenevi-Lundgren, 1 50 52 weeks (12 mo) 50 hours/week throughout P<0.05 between 200947 the study - 2.9 (1.9) control and h/week intervention 2 53 52 weeks (12 mo) 53 hours/week throughout the study - 4.4 (1.3) h/week Participation in organized sports (hr) Stenevi-Lundgren, 1 50 1.3 (1.6) h/week 52 weeks (12 mo) 50 1.9 (1.9) h/week At baseline, P=0.055 200947 between control and
E-1 Baseline measure, Final measure Final follow up Mean Change from Measure of Author, Year Arm Baseline N mean (SD) timepoint N at final measure measure, mean (SD) baseline (SD) association intervention.
At follow up, P<0.05 between control and intervention. 2 53 0.7 (1.2) h/week 52 weeks (12 mo) 53 1.1 (1.3) h/week Salmon, 200843* 2 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and Female maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 11.1 (3.8 to 18.4) P value <0.01 3 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 10.2 (4.7 to 25.1) 4 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 0.3 (7.7 to 8.3) Salmon, 200843 2 66 52 60 b-coefficients (95% CI); 4.3 (3.6 to 12.2) 3 74 52 69 b-coefficients (95% CI); 9.5 (1.4 to 17.6) P<0.05 4 93 52 84 b-coefficients (95% CI); 6.7 (6.4 to 19.8) Moderate to Vigorous physical activity (min/day) Howe, 2012 20 1 27 0.91 (0.14) 43 28 1.49 (0.12) 0.58 P<0.04 2 22 0.83 (0.13) 43 23 0.98 (0.13) 0.15 NS 3 36 0.83 (0.10) 43 36 0.91 (0.12) 0.08 NS Vigorous physical activity Salmon, 200843 2 66 52 60 b-coefficients (95%
E-2 Baseline measure, Final measure Final follow up Mean Change from Measure of Author, Year Arm Baseline N mean (SD) timepoint N at final measure measure, mean (SD) baseline (SD) association CI); 2.8 (0.2 to 5.4) P value<0.05 3 74 52 69 b-coefficients (95% CI); 7.7 (3.2 to 12.2) p value <0.01 4 93 52 84 b-coefficients (95% CI); 3.0 (0.59 to 6.6) Salmon, 200843 2 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and Male maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 4.4 (0.44 to 8.4) P value <0.05 3 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 13.8 (8.4 to 19.1) P value <0.001 4 52 Baseline to follow up Intervention and maintenance effects (coefficient, 95% CI); 4.8 (1.2 to 10.7) TV viewing (min/d) Salmon, 200843 2 66 52 60 -6 b-coefficients (95% CI); 239.9 (27.6 to 452.2) p value<0.05 3 74 52 69 -5 b-coefficients (95% CI); 142.6 (33.6 to 318.9) 4 93 52 84 -9 b-coefficients (95% CI); 141.9 (15.6 to 299.5) %N = Percent Sample Size; B-Coefficient = Beta Coefficients; CI = Confidence Interval; Hr = Hour; METS = metabolic equivalent; Min/day = Minutes/Day; Mo = month; N = Sample Size; NS = Not Significant; P = P-value; PA = Physical Activity; PAAC = Physical Activity Across the Curriculum; SD = Standard Deviation
E-3