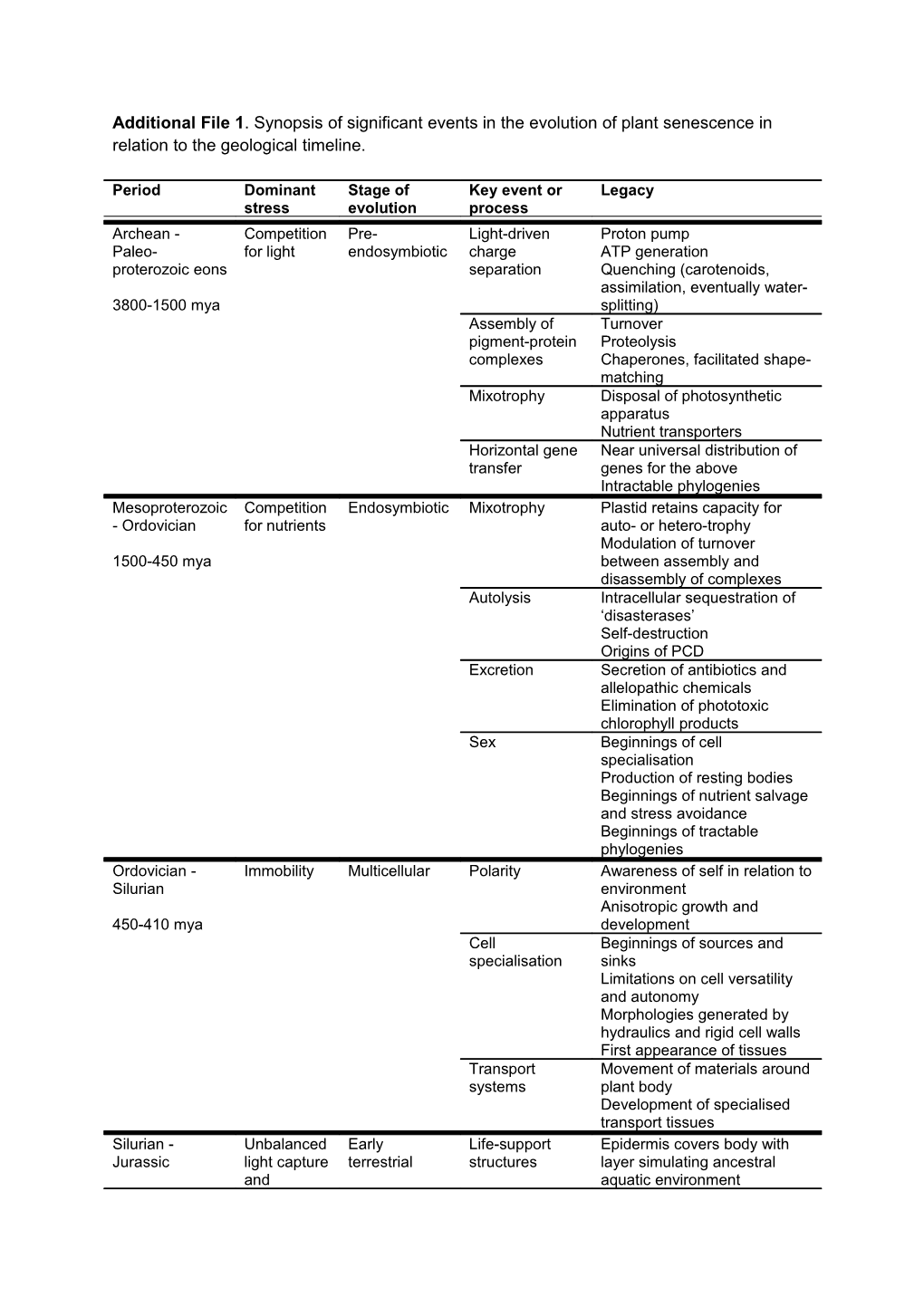
Additional File 1. Synopsis of significant events in the evolution of plant senescence in relation to the geological timeline.
Period Dominant Stage of Key event or Legacy stress evolution process Archean - Competition Pre- Light-driven Proton pump Paleo- for light endosymbiotic charge ATP generation proterozoic eons separation Quenching (carotenoids, assimilation, eventually water- 3800-1500 mya splitting) Assembly of Turnover pigment-protein Proteolysis complexes Chaperones, facilitated shape- matching Mixotrophy Disposal of photosynthetic apparatus Nutrient transporters Horizontal gene Near universal distribution of transfer genes for the above Intractable phylogenies Mesoproterozoic Competition Endosymbiotic Mixotrophy Plastid retains capacity for - Ordovician for nutrients auto- or hetero-trophy Modulation of turnover 1500-450 mya between assembly and disassembly of complexes Autolysis Intracellular sequestration of ‘disasterases’ Self-destruction Origins of PCD Excretion Secretion of antibiotics and allelopathic chemicals Elimination of phototoxic chlorophyll products Sex Beginnings of cell specialisation Production of resting bodies Beginnings of nutrient salvage and stress avoidance Beginnings of tractable phylogenies Ordovician - Immobility Multicellular Polarity Awareness of self in relation to Silurian environment Anisotropic growth and 450-410 mya development Cell Beginnings of sources and specialisation sinks Limitations on cell versatility and autonomy Morphologies generated by hydraulics and rigid cell walls First appearance of tissues Transport Movement of materials around systems plant body Development of specialised transport tissues Silurian - Unbalanced Early Life-support Epidermis covers body with Jurassic light capture terrestrial structures layer simulating ancestral and aquatic environment 410-150 mya utilisation Vacuole a souvenir of capacity ancestral environment inside every cell Enhanced Xanthophyll cycle requirement for Promiscuous CO2 fixation light energy Resource rejection dissipation Nutrient salvage Tissue differentiation in sources and sinks Elaboration of transport systems Intracellular detoxification mechanisms, including for chlorophyll catabolites Involvement of vacuole Mixotrophic Plastid transdifferentiation development network Switch between light- and respiration-dependent energy supply Elaboration of Specialisation of organs morphology and Exploitation of lysigeny and anatomy schizogeny in morphogenesis Variations on common organ development theme Organ shedding and beginnings of throw-away lifestyle Jurassic - Challenges Tracheophytic Adaptations to Mechanisms to resist excess Anthropocene from other resist abiotic light (sunblockers, quenchers) organisms stresses Repair mechanisms 150-0 mya Adaptations to Proliferation of life-forms avoid abiotic Resting and storage structures stresses Adaptations to Neighbour detection competing or Co-evolved signalling hostile mechanisms organisms Visual, chemical and other cues Mimicry Disposal of parts Adaptations to Attraction of pollinators, beneficial dispersers, defenders organisms Visual and chemical signals Rewards Human Domestication traits intervention Weed traits Hypertrophy and low competitiveness Exaggerated colours and shapes Extreme introgressive and engineered gene transfer Climate and environmental change Extinctions and loss of biodiversity