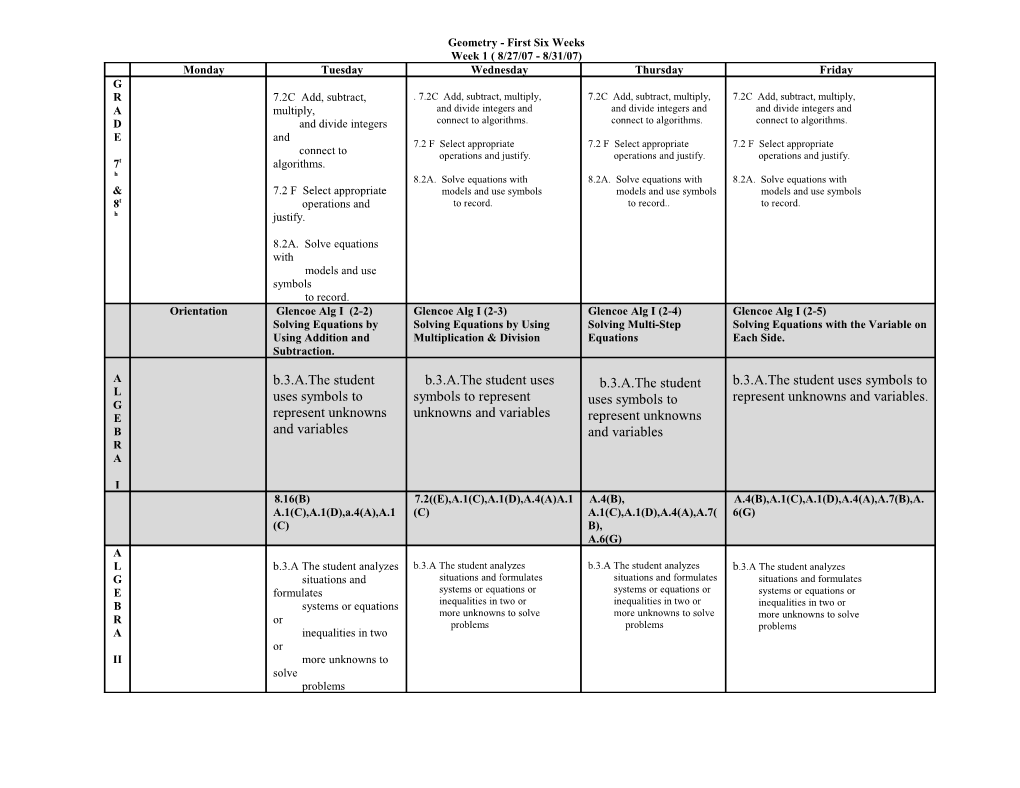
Geometry - First Six Weeks Week 1 ( 8/27/07 - 8/31/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday G R 7.2C Add, subtract, . 7.2C Add, subtract, multiply, 7.2C Add, subtract, multiply, 7.2C Add, subtract, multiply, A multiply, and divide integers and and divide integers and and divide integers and D and divide integers connect to algorithms. connect to algorithms. connect to algorithms. E and 7.2 F Select appropriate 7.2 F Select appropriate 7.2 F Select appropriate connect to operations and justify. operations and justify. operations and justify. 7t algorithms. h 8.2A. Solve equations with 8.2A. Solve equations with 8.2A. Solve equations with & 7.2 F Select appropriate models and use symbols models and use symbols models and use symbols 8t operations and to record. to record.. to record. h justify.
8.2A. Solve equations with models and use symbols to record. Orientation Glencoe Alg I (2-2) Glencoe Alg I (2-3) Glencoe Alg I (2-4) Glencoe Alg I (2-5) Solving Equations by Solving Equations by Using Solving Multi-Step Solving Equations with the Variable on Using Addition and Multiplication & Division Equations Each Side. Subtraction.
A b.3.A.The student b.3.A.The student uses b.3.A.The student b.3.A.The student uses symbols to L uses symbols to symbols to represent represent unknowns and variables. G uses symbols to E represent unknowns unknowns and variables represent unknowns B and variables and variables R A
I 8.16(B) 7.2((E),A.1(C),A.1(D),A.4(A)A.1 A.4(B), A.4(B),A.1(C),A.1(D),A.4(A),A.7(B),A. A.1(C),A.1(D),a.4(A),A.1 (C) A.1(C),A.1(D),A.4(A),A.7( 6(G) (C) B), A.6(G) A L b.3.A The student analyzes b.3.A The student analyzes b.3.A The student analyzes b.3.A The student analyzes G situations and situations and formulates situations and formulates situations and formulates E formulates systems or equations or systems or equations or systems or equations or B systems or equations inequalities in two or inequalities in two or inequalities in two or more unknowns to solve more unknowns to solve R or more unknowns to solve problems problems problems A inequalities in two or II more unknowns to solve problems Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW have TLW solve equations by TLW solve equations by using TLW solve equations TLW solve equations with the variable ORIENTATION using addition and multiplication and division. involving more than one on each side and solve equations subtraction. operation and to solve involving grouping symbols. consecutive integer problems.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
TEXTEAMS Algebra I TEXTEAMS Algebra I TEXTEAMS Algebra I TEXTEAMS Algebra I Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Mosaic Mosaic Mosaic Mosaic Bathing the Dog Bathing the Dog Bathing the Dog Bathing the Dog 600 Meter Race 600 Meter Race 600 Meter Race 600 Meter Race Swimming Pools Swimming Pools Swimming Pools Swimming Pools TEXTEAMS Alg. I 2000 and Beyond: TEXTEAMS Alg. I 2000 TEXTEAMS Alg. I 2000 and TEXTEAMS Alg. I 2000 Variables and Functions and Beyond: Beyond: and Beyond: Valentine Day Idea Variables and Variables and Functions Variables and Functions Investigate Recursively Functions Valentine Day Idea Valentine Day Idea TEXTEAMS Alg. Reasoning: Valentine Day Idea Investigate Recursively Investigate Recursively Stretching Sequences Investigate TEXTEAMS Alg. Reasoning: TEXTEAMS Alg. PH Ch. 1 - 10 Recursively Stretching Sequences Reasoning: GT I: 1, 3 TEXTEAMS Alg. PH Ch. 1 - 10 Stretching Sequences Reasoning: GT I: 1, 3 PH Ch. 1 - 10 Stretching Sequences GT I: 1, 3 PH Ch. 1 - 10 GT I: 1, 3 Vocabulary/Vocabula Vocabulary/Vocabular Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulari Vocabulary/Vocabulario rio io o
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
PH-TE, , Auditory PH-TE, , Auditory Learning, PH-TE, , Auditory PH-TE, , Auditory Learning, tactile, Learning, tactile tactile, Kinesthetic Learning Learning, tactile, Kinesthetic Learning, Kinesthetic Visual Learning Kinesthetic Learning, Visual Learning Learning Glencoe TE Visual Learning Glencoe TE Visual Learning Glencoe TE Glencoe TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT . Evaluate expression using This TEKS is developed This TEKS is developed This TEKS is developed throughout the rational numbers. throughout the Algebra I throughout the Algebra I Algebra I curriculum. Symbolic Ex: 3a – 4b when a = 5/6; curriculum. Symbolic curriculum. Symbolic manipulation is a major component of b = -2/3 manipulation is a major manipulation is a major Algebra I, and PreAP students should component of Algebra I, and component of Algebra I, have many meaningful opportunities to PreAP students should have many and PreAP students should practice these skills. meaningful opportunities to have many meaningful practice these skills. opportunities to practice these skills. Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
3-1 worksheet for Algebra 3-2 worksheet for Algebra I 3-3 worksheet for Algebra I 3-4 worksheet for Algebra I I www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.webccat.org www.webccat.org www.webccat.org www.webccat.org
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Have students calculate Assess students by asking them to Assess students by asking Small group discussion followed by their own grades justify each step as they work the them to justify each step as whole group discussion where individual (averages) and determine problems out. they work the problems out. groups share in making generalizations. grades needed to reach certain plateaus.
PH-TE, Alternative Assessment Geometry - First Six Weeks Week 2 (9/3/07 – 9/7/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A L 7.2C Add, subtract, multiply, 7.2C Add, subtract, multiply, b.1(C) Represent, interpret, b.1(C) Represent, interpret, b.1(C) Represent, interpret, and G and divide integers and and divide integers and and make inferences from and inferences from functional inferences from functional E connect to algorithms. connect to algorithms. functional relationships. relationships. relationships. B R 7.2 F Select appropriate 7.2 F Select appropriate Also, b.1(E) Also, b.1(E) Also, b.1(E) A operations and justify. operations and justify.
I 8.2A. Solve equations with 8.2A. Solve equations with models and use symbols models and use symbols to record. to record. Review Solving Equations Test Solving Equations Using Inductive Reasoning to Understanding Points, Lines, Measuring and Constructing make conjectures (2-1) and Planes. (1-1) Segments (1-2)
G b.3.A.The student uses symbols b.3.A.The student uses b.1(A). The student develops b.1(B). The student recognizes b.1(B). The student recognizes E to represent unknowns and symbols to represent an awareness of the structure that mathematics is developed that mathematics is developed O variables unknowns and variables of a mathematical system and for a variety of purposes for a variety of purposes M logical reasoning. through the historical through the historical E b.3(D). Use inductive development of geometric development of geometric T reasoning to formulate a systems; systems; R conjecture. b.1(A) The student develops an b.1(A) The student develops an Y awareness of the structure of a awareness of the structure of a mathematical system mathematical system connecting definitions and connecting definitions and logical reasoning. logical reasoning.
b.1(C), b.3(B), b.1(D), b.4(A), b.1(C), b.3(B), b.1(D), b.4(A), G.2(B),G.3(D),G.5(B) G.1(A),G.7(A), G.2(A),G.2(b),G.3(B) b.4(B), c.1(C), c.3(A).c.3(B), b.4(B), c.1(C), c.3(A).c.3(B), c3(C),b3(A) c3(C),b3(A) A L b.3.A The student analyzes b.3.A The student analyzes b.3(A) Analyze situations a.4 The student recognizes the a.4 The student recognizes the G situations and formulates situations and formulates modeled by functions relationship between algebra relationship between algebra E systems or equations or systems or equations or (quadratic, square root, and geometry. Students and geometry. Students B inequalities in two or inequalities in two or rational, and exponential) to perceive the connections perceive the connections R more unknowns to solve more unknowns to solve solve problems. between algebra and geometry between algebra and geometry A problems problems Also, c.3(A), d.4(E), e.5, f.5 and use the tools of one to help and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the other. solve problems in the other. II Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW Learner must TLW Learner will show TLW use inductive reasoning TLW identify, name, and TLW use length and midpoint demonstrate skills required for mastery of Objectives to identify patterns and make draw points, lines, segments, of a segment. (1-2) mastery of Objectives. conjectures. (2-1) rays, and planes. (1-1)
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Across the TEKS: Assessment: Assessment: PH item test generator PH item test generator Bayou City Geometry Walking the Archimedean Walking the Archimedean TEXTEAMS Geometry for Walk Walk TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 All: Talking the Archimedean Talking the Archimedean Days 1 and 3 Talk Talk Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEKS go to: TEKS go to: Assessment: All: All: www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org Going the Distance in Day 3 Day 3 Taxicab Land Geometry Sketchpad Geometry Sketchpad PH. Ch. 1 and 5 PH. Ch. 1, 6, and 11 PH. Ch. 1, 6, and 11 Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Holt - TE Holt - TE Holt - TE Holt - TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT *Use patterns involving *Involve questions that are not *Involve questions that are not fractions: PH Pp. 7 #11 necessarily drawn in the necessarily drawn in the picture, i,e, pp.. 16 #31 (line picture, i,e, pp.. 16 #31 (line TZ). TZ). *Show techniques in drawing *Show techniques in drawing 3-D figures 3-D figures
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Observation of student participation: student participation: student participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Student Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P rojects; rojects; rojects; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; or or or Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Ask students about price trends Ask students if they have ever Ask students to describe real- over the past five years in viewed a constellation. Most world examples of parallel items such as sneakers or will be familiar with the Big lines. Examples may include movie tickets. Ask them if Dipper. See if students can lane dividers, row of crops, they can predict the price a sketch the Big Dipper. Ask: streets on a map, railroad year from now and five years “How many stars are in the Big tracks, and so on. Ask them to from now based on what prices Dipper?” How many lines are describe the characteristics of have done in the past. Have used to connect the stars to these lines. them discuss their reasoning. form the Big Dipper?” Geometry - First Six Weeks Week 3 (9/10/07 – 9/14/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A G b.1(C) Represent, interpret, b.1(C) Represent, interpret, c.2(C) Investigate, describe, and c.2(C) Investigate, describe, c.2(C) Investigate, describe, E and make inferences from and make inferences from predict the effects of changes in m and predict the effects of and predict the effects of B functional relationships. functional relationships. and b or changes in m and b or changes in m and b or R Also, b.1(E) Also, b.1(E) y = mx + b y = mx + b y = mx + b A c.2(C) Investigate, describe, c.2(C) Investigate, describe, and predict the effects of and predict the effects of I changes in m and b or changes in m and b or y = mx + b y = mx + b
Quiz 2-1,1-1,1-2 Test 2-1,1-1,1-2 Measuring and constructing angles Pairs of Angles (1-4) Algebraic proof (2-5) (1-3)
G b.1(B). The student recognizes b.1(B). The student recognizes b.2(B). The student makes and b.2(B). The student makes b.2(B). The student makes E that mathematics is developed that mathematics is developed for verifies conjectures about angles and and verifies conjectures and verifies conjectures O for a variety of purposes a variety of purposes through the lines choosing from a variety of about angles and lines about angles and lines historical development of M through the historical geometric systems; approaches, such as coordinate, choosing from a variety of choosing from a variety of E development of geometric b.1(A) The student develops an transformational, or axiomatic. approaches, such as approaches, such as T systems; awareness of the structure of a b.1(A).The student develops an coordinate, transformational, coordinate, transformational, R b.1(A) The student develops mathematical system connecting awareness of the structure of a or axiomatic. or axiomatic. Y an awareness of the structure definitions and logical reasoning. mathematical system connecting b.1(A).The student develops b.1(A).The student develops of a mathematical system b.2(B). The student makes and definitions, postulates, and theorems an awareness of the structure an awareness of the structure connecting definitions and verifies conjectures about angles of a mathematical system of a mathematical system logical reasoning. and lines choosing from a variety connecting definitions, connecting definitions, of approaches, such as coordinate, transformational, or axiomatic. postulates, and theorems postulates, and theorems
b2B,b3D,b4,c1,d2A,d2B,e2D b2B,b3D,b4,c1,d2A,d2B,e2D G.1(A),G.1(B),G.2(a),G.2(B),G.3(B) G.1(A),G.2(B),G.3(B), G.1(A),G.2(B),G.3(B), b.1(B), d.2(A), b.1(A), b.1(B), d.2(A), b.1(A), G.3(C),G.3(E) G.3(C),G.3(E) b.3(B), c1 b.3(B), c1 A . . . L b.3(A) Analyze situations b.3(A) Analyze situations c.1(B) Describe graphs using parent c.1(B) Describe graphs c.1(B) Describe graphs G modeled by functions modeled by functions functions (linear, quadratic, square using parent functions using parent functions E (quadratic, square root, (quadratic, square root, roots, exponential, and logarithmic) (linear, quadratic, square (linear, quadratic, square B rational, and exponential) to rational, and exponential) to and quotients (rational); and predict roots, exponential, and roots, exponential, and R solve problems. solve problems. the effects of parameter changes. logarithmic) and quotients logarithmic) and quotients A Also, c.3(A), d.4(E), e.5, f.5 Also, c.3(A), d.4(E), e.5, f.5 Also, d.2(A), d.2(B), d.4(A), e.1, f.2 (rational); and predict the (rational); and predict the a.4 The student recognizes the a.4 The student recognizes effects of parameter changes. effects of parameter changes. II relationship between algebra the relationship between Also, d.2(A), d.2(B), d.4(A), Also, d.2(A), d.2(B), d.4(A), and geometry. Students algebra and geometry. e.1, f.2 e.1, f.2 perceive the connections Students perceive the between algebra and geometry connections between algebra and use the tools of one to and geometry and use the help solve problems in the tools of one to help solve other. problems in the other. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW demonstrate mastery of TLW show mastery of TLW name and classify angles. TLW identify adjacent, TLW Review properties of objectives. objectives. Measure and construct angles and vertical, complementary, and equality. angle bisectors. supplementary angles.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEXTEAMS Geometry Across the TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math TEKS: Across the TEKS: Across the TEKS: PH item test generator PH item test generator Bayou City Geometry Bayou City Geometry Bayou City Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Pizza Delivery Service Regions Pizza Delivery Service Pizza Delivery Service Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by More Pizza Delivery Regions Regions TEKS go to: TEKS go to: Conjecture as Discovery and Proof More Pizza Delivery More Pizza Delivery www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org as Explanation Conjecture as Discovery Conjecture as Discovery TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: and Proof as Explanation and Proof as Explanation Day 4 TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for Geometry Sketchpad All: All: Day 4 Day 4 PH. Ch. 1 Geometry Sketchpad Geometry Sketchpad Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math PH. Ch. 1 PH. Ch. 1 Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Holt- TE Holt-TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PreAP students should be given PreAP students should be PreAP students should be plenty of opportunities to explore and given plenty of opportunities given plenty of opportunities make conjectures using a variety of to explore and make to explore and make approaches. conjectures using a variety conjectures using a variety of approaches. of approaches. Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Observation of student Observation of Observation of student student participation: student student participation: participation: discussion/responses; participation: participation: discussion/response discussion/response Student demonstrations: discussion/respons discussion/respons s; s; chalkboard presentation/ es; es; Student Student oral reports/ projects ; Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: Activities: problem solving demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard Written assessment: chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projects presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Media presentations; or Activities: Activities: solving solving Technology: Applications/ problem solving problem solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Writing Written Written Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Programs assessment: assessment: Projects; Projects; Quiz/Journal/Exa Quiz/Journal/Exa Media Media m/Projects; m/Projects; presentations; or presentations; or Media Media Technology: Technology: presentations; or presentations; or Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Technology: Technology: Programs Programs Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Ask students if they have ever seen Ask students if they have Ask students if they have “mile” markers on the side of a ever seen “mile” markers on ever seen “mile” markers on highway. Ask them if they numbers the side of a highway. Ask the side of a highway. Ask on the “mile” markers increased or them if they numbers on the them if they numbers on the decreased as they went along. “mile” markers increased or “mile” markers increased or Discuss what the markers mean. decreased as they went decreased as they went along. Discuss what the along. Discuss what the markers mean. markers mean. Geometry - First Six Weeks Week 4 (9/17/07 – 9/21/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A L c.2(C) Investigate, describe, c.2(C) Investigate, describe, c.2(D) Graph equations of c.2(D) Graph equations of c.3(B) Investigate methods G and predict the effects of and predict the effects of lines given points. lines given points. and solve linear equations, E changes in m and b or changes in m and b or inequalities, and systems, B y = mx + b y = mx + b including using concrete R b.3(B) Look for patterns and b.3(B) Look for patterns and models and graphs; A represent generalizations represent generalizations b.3(A) The student uses algebraically algebraically symbols to represent I b. 1(C), b. l(E) b. 1(C), b. l(E) unknowns and variables.
Review (1-3, 1-4, 2-5, 1-6) Test 1-3,1-4,2-5,1-6 Slopes of a line (3-5) Parallel and Perpendicular Proving Lines and Related Lines (3-1) angles (3-2)
G b.1(A).The student develops an b.1(A).The student develops an d.2.(C) Develop and use b.4 The student selects an b.4 The student selects an E awareness of the structure of a awareness of the structure of a formulas including distance appropriate representation appropriate representation O mathematical system mathematical system and midpoint. (concrete, pictorial, graphical, (concrete, pictorial, graphical, M connecting definitions, connecting definitions, verbal, or symbolic) to solve verbal, or symbolic) to solve E postulates, and theorems. postulates, and theorems problems. problems. T R Y b.1B, b.2B, b.3D, b3B. b2B, b.1B, b.2B, b.3D, b3B. b2B, G.7(A),G.7(B),G.7(C) G.1,G.2,G.3,G.7,G.9 G.3(C),G.3(E),G.9(A) b3B,b3C,b3D,b3E b3B,b3C,b3D,b3E A L b.3(A.) Analyze situations b.3(A.) Analyze situations b.1(B) Collect, record, b.1(B) Collect, record, b.3(B) Solve equations, G modeled by functions modeled by functions organize data; make organize data; make inequalities, and systems E (quadratic, square root, (quadratic, square root, scatterplots and describe with a scatterplots and describe with a modeled by functions using B rational, exponential) to solve rational, exponential) to solve parent function, interpret parent function, interpret graphs and tables. R problems. problems. results and make predictions to results and make predictions to Also, d.3(D), d.4(D),e.4, f.4 A Also, c.3(A), d.4(E), e.5, f.5 Also, c.3(A), d.4(E), e.5, f.5 model and solve problems. model and solve problems. c.1(B) Describe graphs using II parent functions (linear, quadratic, square roots, exponential, and logarithmic) and quotients (rational); and predict the effects of parameter changes. Also, d.2(A), d.2(B), d.4(A), e.1, f.2
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW demonstrate skills TLW Show mastery of TLW: Find the slopes of a line. TLW Identify parallel, TLW Prove and use theorems required for mastery of Objectives. Use slopes to identify parallel perpendicular, and skew lines. about the angles formed by Objectives. and perpendicular lines. Identify the angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal. two lines and a transversal. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: PH item test generator PH item test generator Wearable Art Steiner’s Point Steiner’s Point Whitebeard’s Treasure Mad as a Hatter or Hat as a Mad as a Hatter or Hat as a TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Madder Madder PH. Ch. 1 TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Across the TEKS: Across the TEKS: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: Math TEKS toolkit: Bayou City Geometry Bayou City Geometry www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.tenet.edu/teks/math Geometry Sketchpad Geometry Sketchpad PH. Ch. 7 PH. Ch. 7 Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT Prentice hall Prentice hall Prentice hall PreAP students should be PreAP students should be *Solve problems involving Pp. 87 # 23-29 Pp. 367, #18-29 given plenty of opportunities to given plenty of opportunities to fractions explore and make conjectures explore and make conjectures ie pp. 56, #21, #24 using a variety of approaches. using a variety of approaches. Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses Student Student Student Student ; demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: Student chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard demonstrations: presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral chalkboard reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; presentation/ oral Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem reports/ projects ; solving solving solving solving Activities: problem Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: solving Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Written assessment: rojects; rojects; rojects; rojects; Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; Projects; or or or or Media presentations; Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: or Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Technology: Programs Programs Programs Programs Applications/ Writing Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Discuss with students types of Have students make a table of Draw the following diagram maps they have seen such as values to graph y = -1/2x + 5 (PH p. 363) and ask students world maps, globes, state and y = 2x – 1. Ask them how to identify all vertical angles, maps, local maps, subway the lines appear to be related. supplementary angles, and maps, bike and hiking paths, adjacent angles. and elevation maps. Geometry - First Six Weeks Week 5 (9/24/07 – 9/28/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A c.2(C) Investigate, describe, c.2(D) Graph equations of c.2(D) Graph equations of c.2(D) Graph equations of c.2(D) Graph equations of L and predict the effects of lines given points. lines given points. lines given points. lines given points. G changes in m and b or c.3(B) Investigate methods and c.3(B) Investigate methods and c.3(B) Investigate methods and c.3(B) Investigate methods and E y = mx + b solve linear equations, solve linear equations, solve linear equations, solve linear equations, B inequalities, and systems, inequalities, and systems, inequalities, and systems, inequalities, and systems, R including using concrete including using concrete including using concrete including using concrete A models and graphs; models and graphs; models and graphs; models and graphs; b.3(A) The student uses b.3(A) The student uses b.3(A) The student uses b.3(A) The student uses I symbols to represent symbols to represent symbols to represent symbols to represent unknowns and variables unknowns and variables unknowns and variables unknowns and variables Midpoint and distance in Review 1-6,3-5,3-1,3-2 Test 1-6,3-5,3-1,3-2 6 wks exam 6wks exam the coordinate plane (1-6) G E b.1(A).The student develops an d.2.(C) Develop and use d.2.(C) Develop and use d.2.(C) Develop and use d.2.(C) Develop and use O awareness of the structure of a formulas including distance formulas including distance formulas including distance formulas including distance M mathematical system and midpoint. and midpoint. and midpoint. and midpoint. E connecting definitions, e.2(A) Based on explorations e.2(A) Based on explorations e.2(A) Based on explorations e.2(A) Based on explorations T postulates, and theorems. and using concrete models, and using concrete models, and using concrete models, and using concrete models, R formulate and test conjectures formulate and test conjectures formulate and test conjectures formulate and test conjectures Y about the properties of parallel about the properties of parallel about the properties of parallel about the properties of parallel lines lines lines lines b.4 The student selects an b.4 The student selects an b.4 The student selects an b.4 The student selects an appropriate representation appropriate representation appropriate representation appropriate representation (concrete, pictorial, graphical, (concrete, pictorial, graphical, (concrete, pictorial, graphical, (concrete, pictorial, graphical, verbal, or symbolic) to solve verbal, or symbolic) to solve verbal, or symbolic) to solve verbal, or symbolic) to solve problems; problems; problems; problems; G.1(A),G.7(A),G.7(C),G.8(C) G.1(A),G.7(A),G.7(C),G.8(C) G.1(A),G.7(A),G.7(C),G.8(C) G.1(A),G.7(A),G.7(C),G.8(C) G.1(A),G.7(A),G.7(C),G.8(C) A L c.1(B) Describe graphs using b.1(B) Collect, record, b.1(B) Collect, record, b.1(B) Collect, record, b.1(B) Collect, record, G parent functions (linear, organize data; make organize data; make organize data; make organize data; make E quadratic, square roots, scatterplots and describe with a scatterplots and describe with a scatterplots and describe with a scatterplots and describe with a B exponential, and logarithmic) parent function, interpret parent function, interpret parent function, interpret parent function, interpret R and quotients (rational); and results and make predictions to results and make predictions to results and make predictions to results and make predictions to A predict the effects of parameter model and solve problem model and solve problem model and solve problem model and solve problem changes. b.3(B) Solve equations, b.3(B) Solve equations, b.3(B) Solve equations, b.3(B) Solve equations, II Also, d.2(A), d.2(B), d.4(A), inequalities, and systems inequalities, and systems inequalities, and systems inequalities, and systems e.1, f.2 modeled by functions using modeled by functions using modeled by functions using modeled by functions using graphs and tables. graphs and tables. graphs and tables. graphs and tables. Also, d.3(D), d.4(D),e.4, f.4 Also, d.3(D), d.4(D),e.4, f.4 Also, d.3(D), d.4(D),e.4, f.4 Also, d.3(D), d.4(D),e.4, f.4
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW Develop and apply the TLW Learner must TLW Learner will show TLW Find the distance TLW identify pairs of angles formula for midpoint. Use the demonstrate skills required for mastery of Objectives between two points and the formed by two lines and a distance formula and the mastery of Objectives. coordinates of the midpoint of transverse as well as relating Pythagorean Theorem to find a segment in a coordinate the measures of angles formed the distance between two plane (1-8). by parallel lines and a points. transversal (7-1);
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
TEXTEAMS Geometry Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Across the TEKS: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Bayou City Geometry PH item test generator PH item test generator PH item test generator PH item test generator TEXTEAMS Geometry Assessment: TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Pizza Delivery Service Regions Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by More Pizza Delivery TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: Conjecture as Discovery www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org and Proof as Explanation TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: Day 4 Geometry Sketchpad
PH. Ch. 5 Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Have students bring in local Attach three straws to each Visual Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning maps and develop a coordinate other with paper clips so that Cooperative Learning Kinesthetic Learning Kinesthetic Learning system and scale. Then have one straw crosses the other two Holt TE Visual Learning Visual Learning them find the coordinates of straws. Identify a pair of Holt TE Holt TE two locations on a diagonal corresponding angles formed street and find the distance by the straws. Turn the straws between the two locations until the angles appear using the distance formula. congruent. Ask what appears to be true about the straws.
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PreAP students should be PreAP students should be PreAP students should be PreAP students should be PreAP students should be given plenty of opportunities given plenty of opportunities given plenty of opportunities given plenty of opportunities given plenty of opportunities to explore and make to explore and make to explore and make to explore and make to explore and make conjectures using a variety of conjectures using a variety of conjectures using a variety of conjectures using a variety of conjectures using a variety of approaches. approaches. approaches. approaches. approaches. Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: discussion/responses discussion/responses discussion/responses discussion/responses discussion/responses ; ; ; ; ; Student Student Student Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Projects; Projects; Projects; Projects; Projects; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; or or or or or Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Ask students to share experiences about using directions to assemble something or following instructions for a recipe. Ask them what was most important about how the directions were written. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 6 (10/1/07-10/5/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A c.3(B) Students c.3(B) Students investigate c.3(B) Students investigate c.3(B) Students investigate c.3(B) Students investigate L investigate methods and methods and solve linear methods and solve linear methods and solve linear methods and solve linear G solve linear equations, equations, inequalities, and equations, inequalities, and equations, inequalities, and equations, inequalities, and E inequalities, and systems, systems, including using systems, including using concrete systems, including using concrete systems, including using concrete B including using concrete concrete models and models and graphs. models and graphs. models and graphs. R models and graphs. graphs. Also, c.4(B) Also, c.4(B) A Also, c.4(B) Also, c.4(B)
I Classifying triangles Develop the triangle sum Properties and attributes of Properties and attributes of Quiz Ch. 4-4,4-2,6-1 (4-1) theorem (4-2) polygons (6-1) polygons (6-1) c. 1. Students use numeric c. 1. Students use numeric c. 1. Students use numeric and c. 1. Students use numeric and G and geometric patterns to and geometric patterns to geometric patterns to make geometric patterns to make c. 1. Students use numeric and E make generalizations make generalizations about generalizations about geometric generalizations about geometric geometric patterns to make O about geometric geometric properties, properties, including properties of properties, including properties of generalizations about geometric M properties, including including properties of polygons and angle relationships polygons and angle relationships properties, including properties of E properties of polygons and polygons and angle in polygons. in polygons. polygons and angle relationships T angle relationships in relationships in polygons. in polygons. R polygons. Y
G.1(A), G.3(D),G.4(A),G.5(A),G.9 G.2(B),G.3(B),G.4(A),G.5(A),G. G.2(B),G.3(B),G.4(A),G.5(A),G. G.2(B),G.3(B),G.4(A),G.5(A),G.5 (B) 5(B), 5(B), (B), G.7(A) G.7(A) G.7(A) A L a.4 Students perceive the a.4 Students perceive the a.4 Students perceive the a.4 Students perceive the a.4 Students perceive the G connections between connections between connections between algebra and connections between algebra and connections between algebra and E algebra and geometry and algebra and geometry and geometry and use the tools of one geometry and use the tools of one geometry and use the tools of one B use the tools of one to use the tools of one to help to help solve problems in the to help solve problems in the to help solve problems in the R help solve problems in solve problems in the other. other. other. A the other. other.
II Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW Classify triangles TLW Use patty paper to TLW Classify polygons based on TLW Classify polygons based on TLW: Demonstrate mastery of by their angle measures discover the relationship their sides and angles. Find and their sides and angles. Find and objectives. and side lengths. between the measures of use the measures of interior and use the measures of interior and the interior angles of a exterior exterior triangle. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Across TEXTEAMS Geometry Across Math TEKS toolkit: Across the TEKS: Across the TEKS: the TEKS: the TEKS: www.tenet.edu/teks/math Stained Glass Problem Stained Glass Problem Stained Glass Problem Stained Glass Problem TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry PH item test generator Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Walking the Walking the Walking the Archimedean Walking the Archimedean TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Archimedean Walk Archimedean Walk Walk Walk Talking the Talking the Talking the Archimedean Talk Talking the Archimedean Talk Performance Assessment by TEKS Archimedean Talk Archimedean Talk TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: go to: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Day 2 Day 2 http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ for All: for All: Geometry Sketchpad Geometry Sketchpad http://www.webccat.org/ Day 2 Day 2 PH. Ch. 10 and 12 PH. Ch. 10 and 12 Geometry Sketchpad Geometry Sketchpad Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: PH. Ch. 10 and 12 PH. Ch. 10 and 12 www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Vocabulary/Vocabula Vocabulary/Vocabulari Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario rio o
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Visual Learning Tactile Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Tactile Learning Cooperative Learning Holt TE Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH, Pp. 72, #25, pp. PH, Pp. 72, #25, pp. PH, Pp. 72, #25, pp. 73 PH, Pp. 72, #25, pp. 73 PH, Pp. 72, #25, pp. 73 #27,#28 Pp. 80, #9, #26 73 #27,#28 73 #27,#28 #27,#28 #27,#28 Extension to the strategy Pp. 80, #9, #26 Pp. 80, #9, #26 Pp. 80, #9, #26 Pp. 80, #9, #26 problem: Students investigate Extension to the strategy Extension to the strategy problem: Extension to the strategy problem: Students Extension to the strategy problem: Students non-regular polygons that will problem: Students investigate Students investigate non-regular investigate non-regular polygons that will investigate non-regular polygons that will non-regular polygons that will polygons that will tile the plane tile the plane tile the plane tile the plane tile the plane AP Calculus Concept: Limits AP Calculus Concept: Limits AP Calculus Concept: Limits AP Calculus Concept: Limits AP Calculus Concept: Limits
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Observation of Observation of Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student student student participation: participation: participation: participation: participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/resp discussion/respo Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: onses; nses; chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ Student Student oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; demonstrations demonstrations: Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem : chalkboard chalkboard solving solving solving presentation/ presentation/ oral Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: oral reports/ reports/ projects ; Quiz/Journal/Exam/Proj Quiz/Journal/Exam/Proj Quiz/Journal/Exam/Proj projects ; Activities: ects; ects; ects; Activities: problem solving Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or problem Written Technology: Applications/ Technology: Applications/ Technology: Applications/ solving assessment: Writing Writing Writing Written Quiz/Journal/Exa Programs Programs Programs assessment: m/Projects; Quiz/Journal/E Media xam/Projects; presentations; or Media Technology: presentations; Applications/ Writing or Programs Technology: Applications/ Writing Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Ask students to draw one Ask students to draw one Ask students to list words Ask students to list words triangle with three sides triangle with three sides of beginning with the prefixes tri- beginning with the prefixes tri- of equal length, one with equal length, one with two quad-, pent, and oct-. Examples quad-, pent, and oct-. Examples two sides of equal length, sides of equal length, and include triathlon, quadriplegic, include triathlon, quadriplegic, and one with no sides of one with no sides of equal pentameter, and octopus. Discuss pentameter, and octopus. Discuss equal length. Then have length. Then have them the meanings of the words and the meanings of the words and them classify each angle classify each angle of the prefixes. prefixes. of the triangles. triangles. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 7 (10/8/07-10/12/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.3(A) The student uses c.3(B) Students investigate b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols L symbols to represent methods and solve linear represent unknowns and represent unknowns and to represent unknowns and G unknowns and variables. equations, inequalities, and variables. variables. variables. E systems, including using B concrete models and graphs. R b.3(A) The student uses A symbols to represent unknowns and variables. I Review Ch. 4-1,4-2,6-1 Test Ch. 4-1,4-2,6-1 The Pythagorean Theorem Applying special right Applying special right (5-7) triangles (5-8) triangles (5-8) G E e.2(B) Based on e.2(B) Based on explorations e.1(C) Students develop, use, c.3 Students identify and apply c.3 Students identify and O explorations and using and using concrete models, the and extend the Pythagorean patterns from right triangles to apply patterns from right M concrete models, the students formulate and test Theorem. solve problems, including triangles to solve problems, E students formulate and test conjectures about the properties f.3 Students develop, apply, special right triangles (45-45- including special right T conjectures about the and attributes of polygons and and justify triangle ratios and 90 and 30-60-90) and triangles (45-45-90 and R properties and attributes of their component parts. Pythagorean triples in a variety triangles whose sides are 30-60-90) and triangles Y polygons and their b.2(B) Make and verify of ways. Pythagorean triples. whose sides are Pythagorean component parts. conjectures about polygons triples. b.2(B) Make and verify using coordinate, axiomatic or conjectures about polygons transformational approaches. using coordinate, axiomatic b.4 Select an appropriate or transformational representation (concrete or approaches. symbolic) to solve problems. b.4 Select an appropriate representation (concrete or symbolic) to solve problems.
G.2(B),G.3(B),G.4(A),G.5( G.2(B),G.3(B),G.4(A),G.5(A), G.1(B),G.5(B), G.3(B),G.5(A)(D),G.7(A) G.3(B),G.5(A)(D),G.7(A) A),G.5(B), G.5(B), (D),G.8(C),G.11(C) G.7(A) G.7(A) A L a.5 Students use a variety a.5 Students use a variety of d.1(A) Students determine the d.1(A) Students determine the d.1(A) Students determine G of epresentations, tools, and epresentations, tools, and reasonable domain and range reasonable domain and range the reasonable domain and E technology and model technology and model values of quadratic functions, values of quadratic functions, range values of quadratic B mathematical situations to mathematical situations to solve as well as interprets and as well as interprets and functions, as well as R solve meaningful problems. meaningful problems. determines the reasonableness determines the reasonableness interprets and determines the A of solutions to quadratic of solutions to quadratic reasonableness of solutions equations and inequalities. equations and inequalities. to quadratic equations and II inequalities. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Show mastery of TLW: Use the Pythagorean TLW Justify and apply TLW Justify and apply required for mastery of Objectives. Theorem and its converse to properties of 45-45-90 and 30- properties of 45-45-90 and Objectives. solve problems 60-90 triangles. 30-60-90 triangles.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Assessment: Assessment: Perfume Packaging Perfume Packaging PH item test generator PH item test generator PH item test generator Playing with Pipes Playing with Pipes The Slice is Right The Slice is Right TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: All: Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Day 2 Day 2 TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmark http://www.mathbenchmarks.or http://www.mathbenchmarks.or PH. Ch. 5 and 11 PH. Ch. 5 and 11 s.org/ g/ g/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall - TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Cooperative Learning; Q & Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Visual Learning Tactile Learning A session Holt TE Holt TE Cooperative Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH. Pp. 313, #20-#25, Pp. PH. Pp. 313, #20-#25, Pp. 320, PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. 262 PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. 262 PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. 320, #17, #24, #26 #17, #24, #26 #58 #58 262 #58 Pp. 267 #20-#23 Pp. 267 #20-#23 Pp. 267 #20-#23
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of student student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; participation: discussion/respons Student Student Student discussion/respons es; demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: es; Student chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard Student demonstrations: presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral demonstrations: chalkboard reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; chalkboard presentation/ oral Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; solving solving solving reports/ projects ; Activities: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Activities: problem problem solving Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P Quiz/Journal/Exam/P solving Written rojects; rojects; rojects; Written assessment: Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exa or or or Quiz/Journal/Exam m/Projects; Technology: Technology: Technology: /Projects; Media Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Media presentations; or Programs Programs Programs presentations; or Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Ask students to use the Ask students to use the Ask students if the following Pythagorean Theorem to find Pythagorean Theorem to find can be the lengths of sides of a the missing lengths of the the missing lengths of the triangle. If yes, ask them to following right triangles if a, b, following right triangles if a, identify the lengths of the sides and c, represent the lengths of b, and c, represent the opposite the greatest and the sides. lengths of the sides. smallest angles. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 8 ( 10/15/07-10/19/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.3A Students use symbols b.3A Students use symbols b.3A Students use symbols a4 Relationship between equations and a4 Relationship between L to represent unknowns and to represent unknowns and to represent unknowns and functions. Equations arise as a way of equations and functions. G variables. variables. variables. asking and answering questions involving Equations arise as a way of asking E functional relationships. Students work in and answering questions B many situations to set up equations and involving functional relationships. R use a variety of methods to solve these Students work in many situations A equations. to set up equations and use a variety of methods to solve these I equations. Quiz sec. 5-7 5-8 Review sec. 5-7 5-8 Test sec. 5-7 5-8 Properties of Parallelograms (6-2) Conditions for parallelograms (6-3)
G c.3 Students identify and c.3 Students identify and c.3 Students identify and b3(B) The student constructs and justifies b2(A) The student uses E apply patterns from right apply patterns from right apply patterns from right statements about geometric figures and constructions to explore attributes O triangles to solve triangles to solve triangles to solve their properties. of geometric figures and to make M problems, including problems, including problems, including conjectures about geometric E special right triangles special right triangles special right triangles relationships. T (45-45-90 and 30-60- (45-45-90 and 30-60- (45-45-90 and 30-60- R 90) and triangles whose 90) and triangles whose 90) and triangles whose Y sides are Pythagorean sides are Pythagorean sides are Pythagorean triples. triples. triples. e.1(C) Students develop, e.1(C) Students develop, e.1(C) Students develop, use, and extend the use, and extend the use, and extend the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem. f.3 Students develop, f.3 Students develop, f.3 Students develop, apply, and justify triangle apply, and justify triangle apply, and justify triangle ratios and Pythagorean ratios and Pythagorean ratios and Pythagorean triples in a variety of ways. triples in a variety of ways. triples in a variety of ways. G.3(B),G.5(A)(D),G.7(A) G.3(B),G.5(A)(D),G.7(A) G.3(B),G.5(A)(D),G.7(A) G.2(B),G.3(b),G.7(B),G.10(B),G.3€,G.7( G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) C) (C) A L d.1(A) Students determine d.1(A) Students determine d.1(A) Students determine a4 Relationship between Algebra and a4 Relationship between Algebra G the reasonable domain and the reasonable domain and the reasonable domain and Geometry. Equations and functions are and Geometry. Equations and E range values of quadratic range values of quadratic range values of quadratic algebraic tools that can be used to functions are algebraic tools that B functions, as well as functions, as well as functions, as well as represent geometric curves and figures; can be used to represent geometric R interprets and determines interprets and determines interprets and determines similarly, geometric figures can illustrate curves and figures; similarly, A the reasonableness of the reasonableness of the reasonableness of algebraic relationships. Students perceive geometric figures can illustrate solutions to quadratic solutions to quadratic solutions to quadratic the connections between Algebra and algebraic relationships. Students II equations and inequalities. equations and inequalities. equations and inequalities. Geometry and use the tools of one to help perceive the connections between solve problems in the other. Algebra and Geometry and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the other. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations TLW Demonstrate TLW Demonstrate skills TLW Show mastery of TLW Prove and apply properties of TLW prove that a given mastery of objectives. required for master of objectives. parallelograms. Use properties of quadrilateral is a parallelogram. objectives. parallelograms to solve problems. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook
Performance Assessment Performance Assessment Performance Assessment Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: Performance Assessment by by TEKS go to: by TEKS go to: by TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ TEKS go to: www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ Vocabulary/Vocabular Vocabulary/Vocabular Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario io io
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Visual Learning Visual Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Cooperative Learning Kinesthetic Learning. Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Visual Learning Independent learning Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. PH, Pp. 260 #22, #36, pp. PH p. 451 #11-13, 25-27 PH p. 466 # 16-19 262 #58 262 #58 262 #58 Pp. 267 #20-#23 Pp. 267 #20-#23 Pp. 267 #20-#23 Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Written Observation of student Observation of student student student assessment: participation: participation: participation: participation: Quiz/Journal/Ex discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/respo discussion/respo am/Projects; Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: nses; nses; chalkboard presentation/ oral chalkboard presentation/ Student Student reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ presentation/ oral reports/ oral reports/ projects ; projects ; Activities: Activities: problem solving problem solving Written Written assessment: assessment: Quiz/Journal/Ex Quiz/Journal/Ex am/Projects; am/Projects; Media Media presentations; or presentations; or Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Draw the following quadrilaterals (PH TE Copy the Venn diagram from p. 448). Ask students which appear to be page 93 omitting the labels. Ask parallelograms and have them find the students to add the labels: missing angle measures. Quadrilaterals, Parallelograms, Rectangles, Squares, Rhombuses, Kites, and Trapezoids. Have them justify the placement of each by giving the definition of the figure. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 9 (10/22/07-10/26/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between L equations and functions. equations and functions. equations and functions. equations and functions. equations and functions. G Equations arise as a way of Equations arise as a way of Equations arise as a way of Equations arise as a way Equations arise as a way of E asking and answering questions asking and answering questions asking and answering questions of asking and answering asking and answering questions B involving functional involving functional involving functional questions involving involving functional R relationships. Students work in relationships. Students work in relationships. Students work in functional relationships. relationships. Students work in A many situations to set up many situations to set up many situations to set up Students work in many many situations to set up equations and use a variety of equations and use a variety of equations and use a variety of situations to set up equations and use a variety of I methods to solve these methods to solve these methods to solve these equations and use a methods to solve these equations. equations. equations. equations. variety of methods to solve these equations. Properties of Special Quiz 6-2,6-3,6-4 Review 6-2,6-3,6-4 Test 6-2,6-3,6-4 Conditions for special Parallelograms (6-4) parallelograms (6-5) G E b2(A) The student uses b2(A) The student uses b2(A) The student uses b2(A) The student uses b2(A) The student uses O constructions to explore constructions to explore constructions to explore constructions to explore constructions to explore M attributes of geometric figures attributes of geometric figures attributes of geometric figures attributes of geometric attributes of geometric figures E and to make conjectures about and to make conjectures about and to make conjectures about figures and to make and to make conjectures about T geometric relationships. geometric relationships. geometric relationships. conjectures about geometric relationships. R geometric relationships. Y
G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) (C) (B)(C (B)(C ,G.7(A)(B)(C (C) A L a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between a4 Relationship between G Algebra and Geometry. Algebra and Geometry. Algebra and Geometry. Algebra and Geometry. Algebra and Geometry. E Equations and functions are Equations and functions are Equations and functions are Equations and functions Equations and functions are B algebraic tools that can be used algebraic tools that can be used algebraic tools that can be used are algebraic tools that algebraic tools that can be used R to represent geometric curves to represent geometric curves to represent geometric curves can be used to represent to represent geometric curves A and figures; similarly, geometric and figures; similarly, geometric and figures; similarly, geometric geometric curves and and figures; similarly, geometric figures can illustrate algebraic figures can illustrate algebraic figures can illustrate algebraic figures; similarly, figures can illustrate algebraic II relationships. Students perceive relationships. Students perceive relationships. Students perceive geometric figures can relationships. Students perceive the connections between Algebra the connections between the connections between illustrate algebraic the connections between Algebra and Geometry and use the tools Algebra and Geometry and use Algebra and Geometry and use relationships. Students and Geometry and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the tools of one to help solve the tools of one to help solve perceive the connections of one to help solve problems in the other. problems in the other. problems in the other. between Algebra and the other. Geometry and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the other. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW prove and apply TLW Demonstrate mastery of TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Show mastery of TLW Prove that a given properties of rectangles and objectives. required for mastery of Objectives. quadrilateral is a rectangle, rhombuses and squares. Use Objectives. rhombus or square. properties of rectangles rhombuses and squares to solve problems. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math PH item test generator PH item test generator Prentice Hall TE, workbook PH item test generator Prentice Hall TE, workbook TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Performance Assessment by TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: by TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org / TEKS go to: www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.or / http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.or g http://www.webccat.org/ g/ www.webccat.org http://www.webccat.org/ www.webccat.org Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabula Vocabulary/Vocabulario rio www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH p. 466 # 16-19 PH p. 474 # 9-12
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of student Observation of Written assessment: Written Observation of student participation: student participation: Quiz/Journal/Exam/ assessment: participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Projects; Quiz/Journal/E discussion/responses; Student Student xam/ Projects; Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Copy the Venn diagram from Draw the following figures (PH page 93 omitting the labels. Ask TE p. 470). Have the students students to add the labels: name them and describe how Quadrilaterals, Parallelograms, they are alike and how they are Rectangles, Squares, different. Rhombuses, Kites, and Trapezoids. Have them justify the placement of each by giving the definition of the figure. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 10 (10/29/07-11/2/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A a4 Relationship between b.1(A) The student gathers and b.1(A) The student gathers and b.1(A) The student gathers b.1(A) The student gathers and L equations and functions. records data, or uses date sets. to records data, or uses date sets. to and records data, or uses records data, or uses date sets. G Equations arise as a way of asking determine functional relationships determine functional relationships date sets. to determine to determine functional E and answering questions between quantities. between quantities. functional relationships relationships between B involving functional relationships. between quantities. quantities. R Students work in many situations A to set up equations and use a variety of methods to solve these I equations.
Properties and Trapezoids Review 6-5, 6-6 Test 6-5,6-6 Using formulas in Developing formulas for (6-6) Geometry (1-5) triangles and quadrilaterals (9-1)
G b2(A) The student uses e.1(A)Students find areas of e.1(A)Students find areas of e.1(A)Students find areas e.1(A)Students find areas of E constructions to explore attributes polygons and composite figures. polygons and composite figures. of polygons and composite polygons and composite O of geometric figures and to make figures. figures. M conjectures about geometric E relationships. T R Y
G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B) G.(A)(B),G.8(A), G.(B),G.3(C) (C) (C) (C) (E),G.5(A),G.8(C)
A a4 Relationship between a.6 Students use problem-solving, a.6 Students use problem-solving, a.6 Students use problem- a.6 Students use problem- L Algebra and Geometry. computation in problem-solving computation in problem-solving solving, computation in solving, computation in G Equations and functions are contexts, language and contexts, language and problem-solving contexts, problem-solving contexts, E algebraic tools that can be used to communication, connections communication, connections language and language and communication, B represent geometric curves and within and outside mathematics, within and outside mathematics, communication, connections within and outside R figures; similarly, geometric and reasoning, as well as multiple and reasoning, as well as multiple connections within and mathematics, and reasoning, as A figures can illustrate algebraic representations, applications and representations, applications and outside mathematics, and well as multiple relationships. Students perceive modeling, and justification and modeling, and justification and reasoning, as well as representations, applications II the connections between Algebra proof. proof. multiple representations, and modeling, and justification and Geometry and use the tools of applications and modeling, and proof. one to help solve problems in the and justification and proof. other. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW Use properties of kites and TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Show mastery of TLW Apply formulas for TLW Develop and apply the trapezoids to solve problems. required for mastery of Objectives perimeter, area and formulas for the areas of Objectives. circumference.(1-5) triangles and special quadrilaterals. Solve problems involving perimeter and area of triangles and special quadrilaterals.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Assessment: Assessment: PH item test generator PH item test generator Boxing Basketballs Boxing Basketballs Prentice Hall TE, workbook Greenhouse Greenhouse TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 Flowers Flowers Performance Assessment by Walter and Juanita’s Walter and Juanita’s Water TEKS go to: Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Water Troughs Troughs http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry for http://www.webccat.org/ www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org for All: All: Day 3 Day 3 www.webccat.org www.webccat.org TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Across the TEKS: Across the TEKS: Stained Glass Circles Stained Glass Circles
PH. Ch. 5, 6, and 7 PH. Ch. 5, 6, and 7
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabular Vocabulary/Vocabulario io www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Visual Learning Visual Learning Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH p. 474 # 9-12 PH. Pp. 246 #16-#19, pp. PH. Pp. 252 #11, #14, pp. 253 247 #35-#38 #27, #30 Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of student Written assessment: Written assessment: Observation of Observation of participation: Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ student student participation: discussion/responses; Projects; Projects; participation: discussion/responses; Student demonstrations: discussion/respo Student chalkboard presentation/ nses; demonstrations: oral reports/ projects ; Student chalkboard demonstrations: presentation/ oral chalkboard reports/ projects ; presentation/ Activities: problem oral reports/ solving projects ; Written assessment: Activities: Quiz/Journal/Exam/P problem solving rojects; Written Media presentations; assessment: or Quiz/Journal/Ex Technology: am/Projects; Applications/ Writing Media Programs presentations; or Technology: Applications/ Writing Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Draw the following figures (PH Review with students the Draw a parallelogram, a TE p. 470). Have the students properties of squares, rectangle, a square, and a name them and describe how they rectangles, and rhombus. Have students name are alike and how they are parallelograms. Have each figure in as many ways as different. students use calculators to they can. find the perimeter of rectangles with dimensions sq.rt.7 cm by sq.rt. 13 cm, sq.rt.21 in. by sq.rt. 21in., and sq.rt. 37 m by sq.rt. 5 m. Geometry - Second Six Weeks Week 11 (11/5/07-11/9/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.1(A) The student gathers and b.1(A) The student gathers and L records data, or uses date sets. to records data, or uses date sets. to G determine functional relationships determine functional relationships E between quantities. between quantities. B R A
I
Review 1-5 9-1 Test 1-5 9-1
G e.1(A)Students find areas of e.1(A)Students find areas of E polygons and composite figures. polygons and composite figures. O M BENCHMARK TESTING BENCHMARK TESTING BENCHMARK E WINDOW WINDOW TESTING T WINDOW R Y
G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B)(C) G.2(A)(B),G.3(B)(E),G.7(A)(B)(C)
A a.6 Students use problem-solving, a.6 Students use problem-solving, L computation in problem-solving computation in problem-solving G contexts, language and contexts, language and E communication, connections within communication, connections within B and outside mathematics, and and outside mathematics, and R reasoning, as well as multiple reasoning, as well as multiple A representations, applications and representations, applications and modeling, and justification and modeling, and justification and II proof. proof.
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW: Demonstrate skills required TLW: Show mastery of Objectives for mastery of Objectives.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math PH item test generator PH item test generator
TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7
Performance Assessment by TEKS Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: go to: www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.webccat.org www.webccat.org
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Projects; Projects;
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 12 (11/12/07 – 11/16/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.3(A) Students use symbols to b.3(A) Students use symbols to a1 Foundation concepts for high a.1 Students use the basic a.1 Students use the basic L represent unknowns and represent unknowns and school mathematics. As understanding of number, understanding of number, G variables. variables. presented in grades K-8, the operation, and quantitative operation, and quantitative E basic understandings of number, reasoning, patterns, relationships, reasoning, patterns, relationships, B operation, and quantitative algebraic reasoning, geometry algebraic reasoning, geometry R reasoning; patterns relationships, and continue to build on this and continue to build on this A and algebraic thinking; foundation as they expand their foundation as they expand their geometry; measurement; and understanding through other understanding through other I probability and statistics are mathematical experiences. mathematical experiences. essential foundations for all work in high school mathematics. Students will continue to build on this foundation as they expand their understanding through other mathematical experiences. Developing Formulas for Developing Formulas for Sector Area and Arc Length Representations of Three- Quiz 9-1, 9-2, 11-3, 10-2 Triangles and Quadrilaterals Circles and Regular Polygons (11-3) Dimensional Figures (10-2) (9-1) (9-2) G E e.1(C) Students develop, use, and e.1(C) Students develop, use, and e1(b) The student finds areas d.1(A) The student describes and d.1(A) The student describes and O extend the Pythagorean extend the Pythagorean of sectors and arc lengths of draws cross sections and other draws cross sections and other M Theorem; Theorem; circles using proportional slices of three-dimensional slices of three-dimensional E e.1(A) Students find the areas of e.1(A) Students find the areas of reasoning. objects. objects. T regular polygons. regular polygons. d.1(C) Use top, front, side, and d.1(C) Use top, front, side, and R corner views of 3-D objects to corner views of 3-D objects to Y create accurate and complete create accurate and complete representations and solve representations and solve problems. problems. G.1B, G.3C, G.3E, G.5A, G.8C G.5A, G.8A, G.8C G.8B, G.9C, G.1A, G.1B G.6C, G.9D G.1B, G.3C, G.3E, G.5A, G.8C A L b.1(A) Students identify the b.1(A) Students identify the a4 Relationship between a.4 Students perceive the a.4 Students perceive the G mathematical domains and mathematical domains and algebra and geometry. Equations connections between algebra and connections between algebra and E ranges and determine reasonable ranges and determine reasonable and functions are algebraic tools geometry and use the tools of one geometry and use the tools of one B domain and range values for domain and range values for hat can be used to represent to help solve problems in the to help solve problems in the R given situations. given situations. geometric curves and figures; other. other. A similarly, geometric figures can illustrate algebraic relationships. II Students perceive the connections between algebra and geometry and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the other. Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations TLW Develop and apply the TLW Develop and apply the TLW Find the area of sectors. TLW Draw representations of TLW Demonstrate skills formulas for the areas of formulas for the area and Find arc lengths. three-dimensional figures. required for mastery of triangles and special circumference of a circle. Recognize a three-dimensional Objectives. quadrilaterals. Solve problems Develop and apply the formula figure from a given involving perimeters and areas of for the area of a regular polygon. representation. triangles and special quadrilaterals. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Assessment: Assessment: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Boxing Basketballs Boxing Basketballs www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Walter and Juanita’s Water Walter and Juanita’s Water Troughs Troughs Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook Nesting Hexagons Nesting Hexagons Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/
Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH. Pp. 272 #17-#21, pp. 277 #19, PH. Pp. 272 #17-#21, pp. 277 #19, PH. Pp. 282 #14-18, Pp. 283 PH. Pp. 289 #18-29 PH. Pp. 114, #12-15, #21-#24 #20 #20 #19-27 Pp. 278 #23-#26 Pp. 278 #23-#26 AP Cal. concept: Optimization AP Cal. concept: Optimization
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student participation: participation: participation: participation: participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Student Student Student Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro jects; jects; jects; jects; jects; Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs Programs Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Draw an isosceles trapezoid, a Present students with the Draw the following circle on the Draw a circle and a diameter. Have students create a scale trapezoid with two right angles, following diagram. Ask them board (p.279). Have students Label it 12 cm. Ask students to drawing of the classroom or a and two other trapezoids in what they can say about give an example of each arc and identify the following: room in their home. Have them different orientations on the segments AD and DB and angle its measure. a. d include objects like furniture, board. Ask students to name the DCB and why. a. minor arc b. r appliances, and fixtures. Discuss figures and describe their b. major arc c. 2r how they represented three- similarities and differences. c. semicircle d. r2 dimensional objects. Did they draw the objects from a front view, side view, or top view? Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 13 (11/19/07 – 11/23/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A a1 Foundation concepts for high a1 Foundation concepts for high L school mathematics. As school mathematics. As G presented in grades K-8, the presented in grades K-8, the E basic understandings of number, basic understandings of number, B operation, and quantitative operation, and quantitative R reasoning; patterns relationships, reasoning; patterns relationships, A and algebraic thinking; and algebraic thinking; geometry; measurement; and geometry; measurement; and I probability and statistics are probability and statistics are essential foundations for all work essential foundations for all work in high school mathematics. in high school mathematics. Students will continue to build Students will continue to build on this foundation as they expand on this foundation as they expand their understanding through other their understanding through other mathematical experiences. mathematical experiences. Review 9-1, 9-2, 11-3, 10-2 Test 9-1, 9-2, 11-3, 10-2 Thanksgiving Thanksgiving Thanksgiving Holiday Holiday Holiday G E e.1(C) Students develop, use, and e.1(C) Students develop, use, and O extend the Pythagorean extend the Pythagorean M Theorem; Theorem; E e.1(A) Students find the areas of e.1(A) Students find the areas of T regular polygons. regular polygons. R e1(b) The student finds areas of e1(b) The student finds areas of Y sectors and arc lengths of circles sectors and arc lengths of circles using proportional reasoning. using proportional reasoning. G.1B, G.3C, G.3E, G.5A, G.8C G.1B, G.3C, G.3E, G.5A, G.8C A L a4 Relationship between algebra a4 Relationship between algebra G and geometry. Equations and and geometry. Equations and E functions are algebraic tools hat functions are algebraic tools hat B can be used to represent can be used to represent R geometric curves and figures; geometric curves and figures; A similarly, geometric figures can similarly, geometric figures can illustrate algebraic relationships. illustrate algebraic relationships. II Students perceive the Students perceive the connections between algebra and connections between algebra and geometry and use the tools of one geometry and use the tools of one to help solve problems in the to help solve problems in the other. other.
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Show mastery of required for mastery of Objectives. Objectives. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook
Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of student Observation of student participation: participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro jects; jects; Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 14 (11/26/07 – 11/30/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A L a.6 Students use problem- b.3(A) Students use symbols to b.3(A) Students use symbols a.6 Students use problem- a.6 Students use problem- G solving, computation in represent unknowns and to represent unknowns and solving, computation in solving, computation in E problem-solving contexts, variables. variables. problem-solving contexts, problem-solving contexts, B language and communication, language and communication, language and communication, R connections within and outside connections within and outside connections within and A mathematics. mathematics. outside mathematics. b.3(A) Students use symbols to b.3(A) Students use symbols I represent unknowns and to represent unknowns and variables. variables. Solid Geometry (10-1) Surface Areas of Prisms and Surface Areas of Pyramids Review Ch. 10-1, 10-4, 10-5 Test Ch. 10-1, 10-4, 10-5 Cylinders (10-4) and Cones (10-5)
G d.1(B) Students use nets to e.2(D) Students analyze the f.4 Students describe the effect d.1(B) Students use nets to d.1(B) Students use nets to E represent and construct three- characteristics of three- on perimeter and area when represent and construct three- represent and construct three- O dimensional objects. dimensional figures and their length, width, or height of a 3- dimensional objects. dimensional objects. M component parts. D solid is changed and applies e.2(D) Students analyze the e.2(D) Students analyze the E e.1(D) Students find the this idea in solving problems characteristics of three- characteristics of three- T surface areas of prisms, dimensional figures and their dimensional figures and their R pyramids, cones, and cylinders. component parts. component parts. Y e.1(D) Students find the e.1(D) Students find the surface areas of prisms, surface areas of prisms, pyramids, cones, and cylinders pyramids, cones, and cylinders f.4 Students describe the effect f.4 Students describe the effect on perimeter and area when on perimeter and area when length, width, or height of a 3- length, width, or height of a 3- D solid is changed and applies D solid is changed and applies this idea in solving problems this idea in solving problems G.2B, G.6A, G.6B, G.9D G.6B, G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.6B, G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.6B, G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.6B, G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.5B G.5B G.5B G.5B A L a.5 Students use a variety of a.2 Students study algebraic a.2 Students study algebraic a.2 Students study algebraic a.2 Students study algebraic G representations, tools, and concepts and the relationships concepts and the relationships concepts and the relationships concepts and the relationships E technology to solve among them to better among them to better among them to better among them to better B meaningful problems. understand the structure of understand the structure of understand the structure of understand the structure of R algebra. algebra. algebra. algebra. A
II
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations TLW Classify three- TLW Learn and apply the TLW Learn and apply the TLW Demonstrate skills TLW Demonstrate skills dimensional figures according formula for the surface area of formula for the surface area of required for mastery of required for mastery of to their properties. Use nets a prism. Learn and apply the a pyramid. Learn and apply objectives. objectives. and cross sections to analyze formula for the surface area of the formula for the surface area three-dimensional figures. a cylinder. of a cone. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math Perfume Packaging The Most Juice The Most Juice Different Views TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TEXTEAMS Geometry PH. Ch. 6 PH. Ch. 6 Across the TEKS: Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Dwellings Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org Construction of polyhedrons
Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Visual Learning Tactile Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Tactile Learning Cooperative Learning Holt TE Cooperative Learning Cooperative Learning Kinesthetic Learning. Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Visual Learning Independent Test Taking Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH. Pp. 305, #`17 PH. Pp. 313, #20-#25, Pp. 320, PH. Pp. 313, #20-#25, Pp. 320, PH. Pp. 313, #20-#25, Pp. 320, #17, #24, #26 #17, #24, #26 #17, #24, #26
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Written assessment: participation: participation: participation: participation: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Proje discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; cts; Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: Media presentations; or chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ Technology: oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; Applications/ Writing Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Programs solving solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec ts; ts; ts; ts; Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Ask students to give examples Ask students to find the area of Give students the following net of three-dimensional objects in each of the following nets. for a square pyramid. Ask the classroom. Have them them to identify the solid and describe the objects using find the area of the net. geometric terms. Then have them create a classification system for the objects using “objects with a square side,” “ objects with a circular side,” “objects that have points,” etc. Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 15 (12/03/07 – 12/07/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to L represent unknowns and represent unknowns and represent unknowns and represent unknowns and represent unknowns and G variables. variables. variables. variables. variables. E B R A
I
Volume of Prisms and Volume of Pyramids and Spheres (10-8) Composite Figures Quiz 10-6, 10-7, 10-8, 9-3 Cylinders (10-6) Cones (10-7) (9-3)
G e.1(D) Students find surface e.1(D) Students find volumes e.1(D) Students find surface e.1(D) Students find surface e.1(D) Students find surface E areas of prisms, pyramids, of prisms, pyramids, spheres, areas of prisms, pyramids, areas and volumes of prisms, areas and volumes of prisms, O spheres, cones, and cylinders cones, and cylinders in spheres, cones, and cylinders pyramids, spheres, cones, and pyramids, spheres, cones, and M in problem situations. problem situations. in problem situations. cylinders in problem cylinders in problem situations. E Describe the effect on volume Describe the effect on volume Describe the effect on volume situations. Describe the effect on volume T when length, width, or height when length, width, or height when length, width, or height Describe the effect on volume when length, width, or height R of a 3-D solid is changed and of a 3-D solid is changed and of a 3-D solid is changed and when length, width, or height of a 3-D solid is changed and Y applies this idea in solving applies this idea in solving applies this idea in solving of a 3-D solid is changed and applies this idea in solving problems. problems. problems. applies this idea in solving problems. problems.
G.1B, G.5A, G.5B, G.8D, G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.5B G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.5B G.8D, G.11D, G.5A, G.5B G.1B, G.5A, G.5B, G.8D, G.11D G.11D
A a.5 Students use a variety of a.5 Students use a variety of a.5 Students use a variety of a.5 Students use a variety of a.5 Students use a variety of L representations, tools, and representations, tools, and representations, tools, and representations, tools, and representations, tools, and G technology to model technology to model technology to model technology to model technology to model E mathematical situations to mathematical situations to mathematical situations to mathematical situations to mathematical situations to B solve meaningful problems. solve meaningful problems. solve meaningful problems. solve meaningful problems. solve meaningful problems. R A
II
Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW: Learn and apply the TLW Learn and apply the TLW Learn and apply the TLW Recognize composite TLW Demonstrate mastery of formula for the volume of a formula for the volume of a formula for the volume of a space figures, which combine objectives. prism. Learn and apply the pyramid. Learn and apply the sphere. Learn and apply the two or more simple figures formula for the volume of a formula for the volume of a formula for the surface area of (6-7) cylinder. cone. a sphere. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry TEXTEAMS Geometry Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Tiling with Four Congruent Tiling with Four Congruent Tiling with Four Congruent Tiling with Four Congruent Triangles Triangles Triangles Triangles Ancient Ruins Ancient Ruins Ancient Ruins Ancient Ruins Sightseeing Walk Sightseeing Walk Sightseeing Walk Sightseeing Walk TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for TEXTEAMS Geometry for All: All: All: All: Day 5 Day 5 Day 5 Day 5
PH. Ch. 2, 3, 10, and 11 PH. Ch. 2, 3, 10, and 11 PH. Ch. 2, 3, 10, and 11 PH. Ch. 2, 3, 10, and 11
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
PH, Pp. 328, #21-#23 PH, Pp. 334, #9, #14, #17, #22 PH, Pp. 341, #12, #13, #17, PH, Pp. 341, #12, #13, #14, #21, #23, #27 #15, #16, #17 Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of Observation of Observation of Observation of student participation: student participation: student participation: student participation: discussion/responses discussion/responses discussion/responses discussion/responses ; ; ; ; Student Student Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Quiz/Journal/Exam/ Projects; Projects; Projects; Projects; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; Media presentations; or or or or Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions
Present students with the Have students find the volume Have students calculate the Have students identify three- following bases of prisms and of a prism with a square base volume of the following: dimensional objects in the ask them to calculate the area of length 5 cm and height 8 cm A. a cylinder with diameter 4 classroom that are not prisms, of each. See TE p.323 and the volume of a cylinder cm and height 16 cm cylinders, pyramids, or cones. with a diameter of 5 cm and B. a regular square pyramid Ask what space figure or height 8 cm. with base length 8 in. and figures they resemble. height 14 in. Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 16 (12/10/07 – 12/14/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A b.3A Students use symbols to b.3A Students use symbols to L represent unknowns and represent unknowns and G variables. variables. E B R A
I Review 10-6, 10-7, 10-8, 9-3 Test 10-6, 10-7, 10-8, 9-3 Review – Semester Exams Review – Semester Exams Review – Semester Exams G E e.1(D) Students find surface e.1(D) Students find surface O areas and volumes of prisms, areas and volumes of prisms, M pyramids, spheres, cones, and pyramids, spheres, cones, and E cylinders in problem situations. cylinders in problem situations. T Describe the effect on volume Describe the effect on volume R when length, width, or height when length, width, or height Y of a 3-D solid is changed and of a 3-D solid is changed and applies this idea in solving applies this idea in solving problems. problems.
G.1B, G.5A, G.5B, G.8D, G.1B, G.5A, G.5B, G.8D, G.11D G.11D A L a.5 Students use a variety of a.5 Students use a variety of G representations, tools, and representations, tools, and E technology to model technology to model B mathematical situations to mathematical situations to R solve meaningful problems. solve meaningful problems. A
II Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Show mastery of TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Demonstrate skills TLW: Demonstrate skills required for mastery of Objectives. required for mastery of required for mastery of required for mastery of Objectives. semester objectives. semester objectives. semester objectives. Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math PH item test generator PH item test generator
TAKS Objectives 6 and 7 TAKS Objectives 6 and 7
Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: TEKS go to: www.mathbenchmarks.org www.mathbenchmarks.org www.webccat.org www.webccat.org
Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Kinesthetic Learning. Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Visual Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student participation: Observation of student participation: participation: participation: discussion/responses; participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Student demonstrations: discussion/responses; Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: Student demonstrations: chalkboard presentation/ Student demonstrations: chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ chalkboard presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; chalkboard presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; oral reports/ projects ; Activities: problem oral reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving Activities: problem solving solving solving Written assessment: solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec Quiz/Journal/Exam/Proje ts; Quiz/Journal/Exam/Projec ts; ts; cts; Media presentations; or ts; Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Technology: Media presentations; or Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Geometry - Third Six Weeks Week 17 (12/17/07 – 12/21/07) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
A L G E B R A
I Semester Semester Semester Semester Teacher Preparation Exam Exam Exam Exam G E O M E T R Y
A L G E B R A
II Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations Learner Expectations
TLW Take the Semester Exam. TLW Take the Semester Exam. TLW Take the Semester Exam. TLW Take the Semester Exam.
Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources Suggested Resources
Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: Math TEKS toolkit: www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math www.tenet.edu/teks/math
Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook Prentice Hall TE, workbook
Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by Performance Assessment by TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: TEKS go to: http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.mathbenchmarks.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ http://www.webccat.org/ Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario Vocabulary/Vocabulario
www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com www.glencoe.com
Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies Strategies
Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Prentice Hall -TE Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Tactile Learning Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE Holt TE
PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT PreAP/GT
Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student Observation of student participation: participation: participation: participation: discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; discussion/responses; Student Student Student Student demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: demonstrations: chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard chalkboard presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral presentation/ oral reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; reports/ projects ; Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem Activities: problem solving solving solving solving Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Written assessment: Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro Quiz/Journal/Exam/Pro jects; jects; jects; jects; Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Media presentations; or Technology: Technology: Technology: Technology: Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Applications/ Writing Programs Programs Programs Programs
Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions Scaffolding Questions