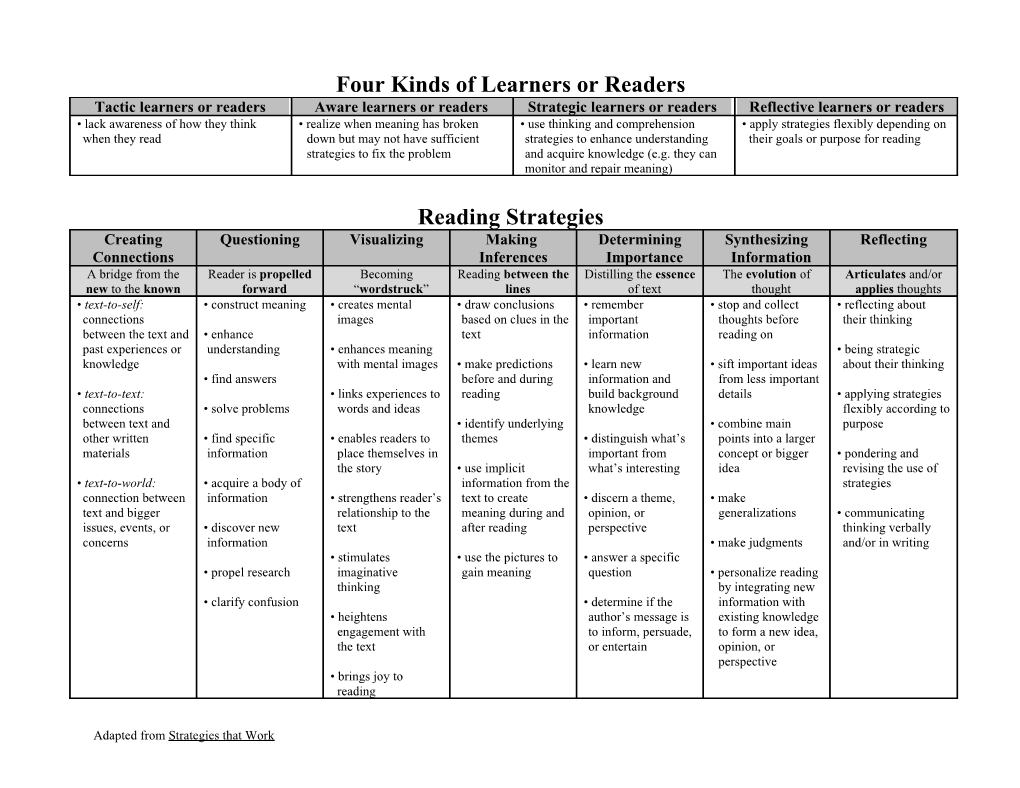
Four Kinds of Learners or Readers Tactic learners or readers Aware learners or readers Strategic learners or readers Reflective learners or readers • lack awareness of how they think • realize when meaning has broken • use thinking and comprehension • apply strategies flexibly depending on when they read down but may not have sufficient strategies to enhance understanding their goals or purpose for reading strategies to fix the problem and acquire knowledge (e.g. they can monitor and repair meaning)
Reading Strategies Creating Questioning Visualizing Making Determining Synthesizing Reflecting Connections Inferences Importance Information A bridge from the Reader is propelled Becoming Reading between the Distilling the essence The evolution of Articulates and/or new to the known forward “wordstruck” lines of text thought applies thoughts • text-to-self: • construct meaning • creates mental • draw conclusions • remember • stop and collect • reflecting about connections images based on clues in the important thoughts before their thinking between the text and • enhance text information reading on past experiences or understanding • enhances meaning • being strategic knowledge with mental images • make predictions • learn new • sift important ideas about their thinking • find answers before and during information and from less important • text-to-text: • links experiences to reading build background details • applying strategies connections • solve problems words and ideas knowledge flexibly according to between text and • identify underlying • combine main purpose other written • find specific • enables readers to themes • distinguish what’s points into a larger materials information place themselves in important from concept or bigger • pondering and the story • use implicit what’s interesting idea revising the use of • text-to-world: • acquire a body of information from the strategies connection between information • strengthens reader’s text to create • discern a theme, • make text and bigger relationship to the meaning during and opinion, or generalizations • communicating issues, events, or • discover new text after reading perspective thinking verbally concerns information • make judgments and/or in writing • stimulates • use the pictures to • answer a specific • propel research imaginative gain meaning question • personalize reading thinking by integrating new • clarify confusion • determine if the information with • heightens author’s message is existing knowledge engagement with to inform, persuade, to form a new idea, the text or entertain opinion, or perspective • brings joy to reading
Adapted from Strategies that Work