THE COLLAPSE OF INTERNATIONAL PEACE (1930S)
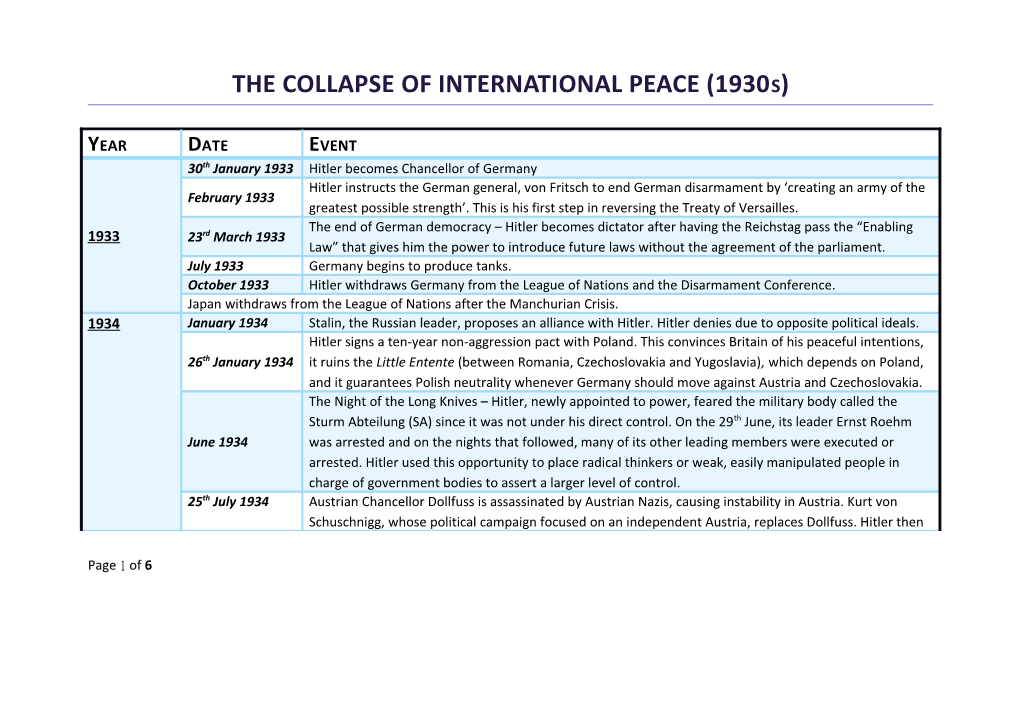
YEAR DATE EVENT 30th January 1933 Hitler becomes Chancellor of Germany Hitler instructs the German general, von Fritsch to end German disarmament by ‘creating an army of the February 1933 greatest possible strength’. This is his first step in reversing the Treaty of Versailles. The end of German democracy – Hitler becomes dictator after having the Reichstag pass the “Enabling 1933 23rd March 1933 Law” that gives him the power to introduce future laws without the agreement of the parliament. July 1933 Germany begins to produce tanks. October 1933 Hitler withdraws Germany from the League of Nations and the Disarmament Conference. Japan withdraws from the League of Nations after the Manchurian Crisis. 1934 January 1934 Stalin, the Russian leader, proposes an alliance with Hitler. Hitler denies due to opposite political ideals. Hitler signs a ten-year non-aggression pact with Poland. This convinces Britain of his peaceful intentions, 26th January 1934 it ruins the Little Entente (between Romania, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia), which depends on Poland, and it guarantees Polish neutrality whenever Germany should move against Austria and Czechoslovakia. The Night of the Long Knives – Hitler, newly appointed to power, feared the military body called the Sturm Abteilung (SA) since it was not under his direct control. On the 29th June, its leader Ernst Roehm June 1934 was arrested and on the nights that followed, many of its other leading members were executed or arrested. Hitler used this opportunity to place radical thinkers or weak, easily manipulated people in charge of government bodies to assert a larger level of control. 25th July 1934 Austrian Chancellor Dollfuss is assassinated by Austrian Nazis, causing instability in Austria. Kurt von Schuschnigg, whose political campaign focused on an independent Austria, replaces Dollfuss. Hitler then
Page 1 of 6 Timeline [Type the date]
tries to take advantage of the instability, but is prevented by Mussolini who sends Italian troops to the Austrian border (Brenner Pass). Soviet Union joins League of Nations, and starts building relations with the Western powers (Britain and September 1934 France) after being rejected by Germany. France leaves the Geneva Disarmament Conference and builds a line of fortifications along its border (Maginot Line). Germany begins to produce warships and aircraft. The number of aircrafts reaches from an initial of 36 in 1932 to 5,112 in 1936. 1935 A plebiscite is held in the Saarland, an area that was taken away from Germany during the Treaty of 13th January 1935 Versailles. The vote is a success for Hitler with 90% votes in favor of a union with Germany. Hitler introduces conscription to increase the size of the German army and holds a massive ‘Proclamation 16th March 1935 of Freedom to rearm’ rally to boost morale. Italian leader, Benito Mussolini, meets the leaders of France and Britain. They form the Stresa Pact, an April 1935 agreement to work against and resist German breaches of the Treaty of Versailles, particularly rearmament. France and Russia sign the Franco–Soviet Mutual Assistance Pact after Germany declares its rearmament May 1935 in order to contain German aggression. Germany uses this ‘encirclement’ as an excuse to remilitarize the Rhineland in 1936. Britain signs the Anglo-German naval pact with Germany, allowing Germany to increase the size of its 18th June 1935 navy to 35% of Britain’s and to build submarines. This caused a sense of betrayal between the other two members of the Stresa Front, France and Italy, weakening the Stresa Pact greatly. 3rd October 1935 Italy invades Abyssinia (now Ethiopia), endangering the Stresa Front even further.
Page 2 of 6 Britain and France design a compromise called the Hoare-Laval Pact under which Italy would be given the larger and richer part of Abyssinia. This marked the beginning of French and British appeasement. December 1935 However, the pact is leaked to the press, causing uproar among civilians – the pact was scrapped. Hitler, who had previously declared German neutrality, now condemns the actions of France and Britain. France is caught in a financial crisis. The treasury has insufficient cash reserves and the value of the Franc Late 1935 is on the verge of collapsing. 1936 Hitler marches German troops into the Rhineland with orders to withdraw on encountering minimum resistance since the German army was not yet strong enough to resist a possible French or British attack. 7th March 1936 Even though this is a breach of the Locarno and Versailles Treaties, no active resistance is offered. To pacify the British and French, Hitler proposes a 25-year long peace pact. German nationwide referendum reveals a 98.8% vote in favour of Hitler’s remlitarization of the 29th March 1936 Rhineland. March 1936 The League of Nations introduces oil and petrol sanctions against Italy. May 1936 Italy wins the war and takes control of Abyssinia. The League of Nations ends the sanctions against Italy. Having failed, for the second time now, the 15th July 1936 League is discredited. The Spanish Civil War begins. Italy and Germany combine their military forces to help the fascist anti- 17th July 1936 government side, lead by Fransisco Franco. In the process, Hitler tests out the newly remilitarized German army. 21st October 1936 Italy and Germany sign the Rome-Berlin Axis, an agreement of fascist states. 25th November Germany and Japan sign the Anti-Comintern Pact, an alliance of expansionist countries directed towards
Page 3 of 6 Timeline [Type the date]
1936 the event of a military confrontation with communist USSR. Stalin has almost all the Soviet army generals executed due to paranoia. This is the greatest military January 1937 purge yet, but it leaves the Russian army crippled, causing Britain and France to doubt the value of an alliance with communist Russia. 27th February France extends the Maginot Line along its border with Germany. 1937 German air force (the Luftwaffe) bombs Guernica in Spain. Guernica, located in the Basque market town, 26th April 1937 1937 is defenceless. Hitler adopts the Four-Year Plan, proposed by Hermann Goering. It argues that Germany invest money mainly in rearmament to provide military strength and leave Germany in a position to conquer foreign territory and resources within four years. In the Hossbach Memorandum of 1937, Hitler calls a meeting of his generals and tells them that the only way of stopping a drastic fall in living standards in Germany was to embark on a policy of aggression to provide sufficient Lebensraum (living space) by seizing Austria and Czechoslovakia. Italy joins the Anti-Comintern Pact and leaves the League of Nations. 1938 Austrian authorities discover a plot by Austrian Nazis to assassinate the German ambassador in order to Early 1938 increase the instability to pave way for a German invasion. Austrian Chancellor Kurt Schuschnigg goes to meet Hitler for ‘peace talks’, and gets humiliated and badly February 1938 treated. 9th March 1938 Schuschnigg announces a plebiscite in Austria to decide whether it wants to remain independent or be united under a common German rule. He sets the age limit at 24, so that most of the young Nazi members are unable to vote.
Page 4 of 6 German army invades Austria and arrests more than 76000 Nazi enemies. This rigs the plebiscite; the 11th March 1938 majority vote in Hitler’s favor is 99.75%. Konrad Henlein, leader of the Sudeten Nazis is given instructions from Hitler to make impossible 28th March 1938 demands from the Czechoslovakian government in order to increase instability. 30th March 1938 Hitler decides to “smash Czechoslovakia by military action in the near future”. 7th April 1938 Spain joins the Anti-Comintern Pact. British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain, is told that South African and Australian governments will 1st September not give military support if war breaks out. Thus showing that if Britain adopts an aggressive policy, they 1938 would split their Empire. Chamberlain meets Hitler at the Berchtesgaden Conference. They agree to allow Hitler to annex parts of 15th September Sudetenland, but without the use of force. A plebiscite will be held in any area containing more than 50% 1938 of a German population. French leaders Daladier and Bonnet support partition of Czechoslovakia in return for a British promise to 18th September defend the rest of Czechoslovakia. The Czech president, Benes, feels betrayed, as France had promised to 1938 protect Czechoslovakia under the 1925 Locarno Treaties. 22nd September Hitler refuses to compromise. He reverts on what was decided during the Berchtesgaden Conference and 1938 makes more unreasonable demands. 28th September Hitler agrees to a Munich conference with Britain, France, and Italy for a peaceful solution over 1938 Czechoslovakia and the Sudetenland. 29th September British and French Prime Ministers agree to let Hitler annex the entire region of the Sudetenland on 1938 condition that he will leave the rest of Czechoslovakia alone. War, which had become very likely, is now
Page 5 of 6 Timeline [Type the date]
averted. Czechoslovakia loses its industrial resources and military defenses against Germany. German troops marched unopposed into Sudetenland. 1st October 1938 At the same time, Hungarians and Poles enter Czech territory that was taken from them during the Treaty of Versailles. 1939 Germany invades the rest of Czechoslovakia, going against what was agreed during the Munich 15th March 1939 Conference. Chamberlain realizes that Hitler and his promises cannot be trusted. British government agrees to support Poland in case of a German invasion in order to stop Hitler before 31st March 1939 he challenges British Empire. Soviet Foreign Minister Maxim Litvinov, outlines the basis for a treaty with Britain and France in which all 17th April 1939 three promise to defend existing borders of Eastern Europe from German attack, and each promises to help other in case of German attack. May 1939 Germany and Italy sign the Pact of Steel, a guarantee by each nation to support the other in case of war. British, French and Soviet military leaders meet for talks in Leningrad. British and French do not send 12th August 1939 leaders powerful enough to sign treaties. This angers Russian leader, Stalin, and makes him doubt the allies’ sincerity in case of an alliance. Litvinov is sacked, Molotov replaces him as foreign minister. The pact between the Allies and USSR fails. Decision is announced one day after Hitler sends Stalin a 21st August 1939 personal written letter regarding a Soviet-German alliance. German foreign Minister Ribbentrop meets Stalin in Moscow, and bargains with him. A pact is signed 23rd August 1939 called the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, in which both nations agree to carve up most of the territory that lay between their two countries, specifically Poland. 1st September German army invades Poland from the west.
Page 6 of 6 1939 3rd September Britain and France declare war on Germany. World War Two begins. 1939
Page 7 of 6