Chapter 8 Alcohol and Ether
Nomenclature of Ethers
The functional group of ether is an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms
R—O—R
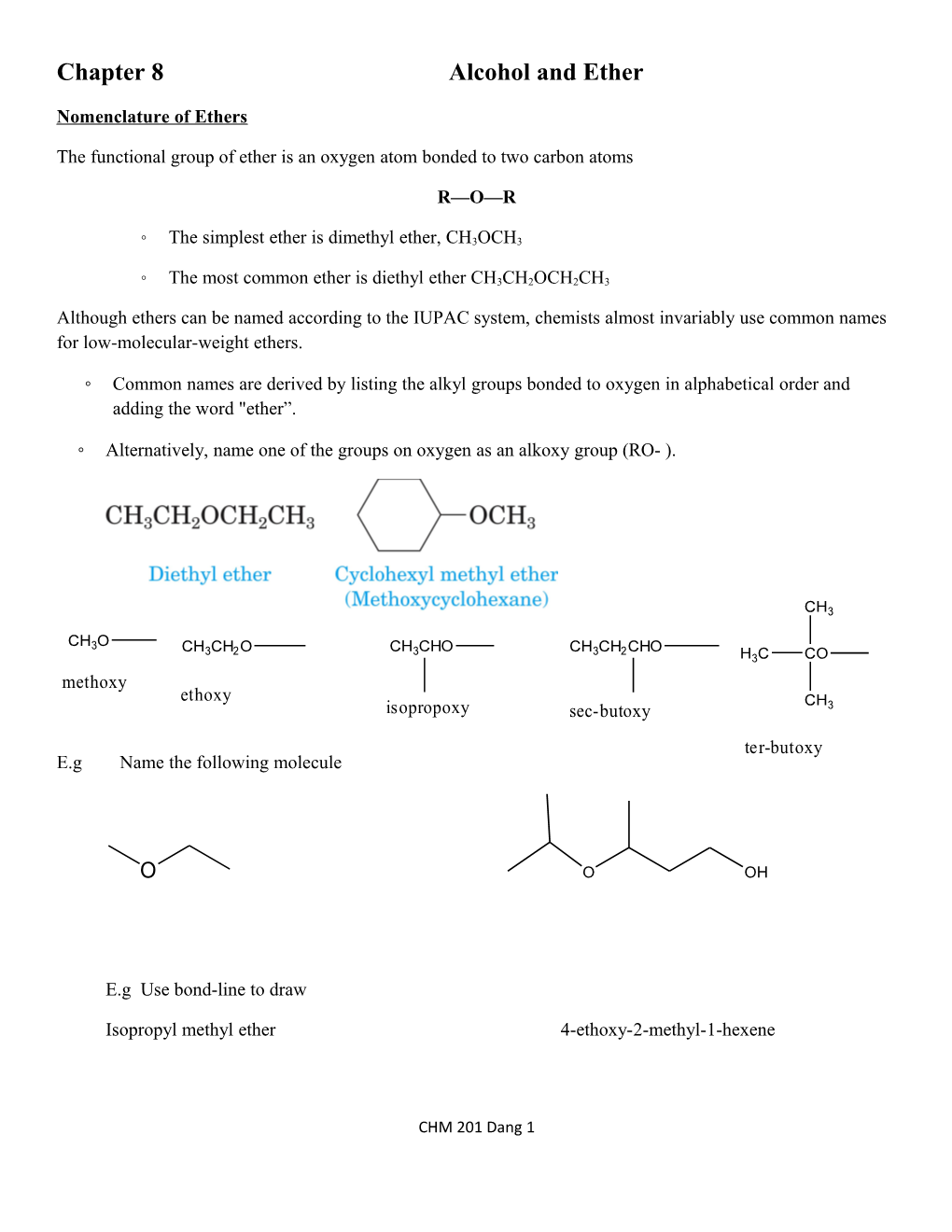
◦ The simplest ether is dimethyl ether, CH3OCH3
◦ The most common ether is diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3
Although ethers can be named according to the IUPAC system, chemists almost invariably use common names for low-molecular-weight ethers.
◦ Common names are derived by listing the alkyl groups bonded to oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word "ether”.
◦ Alternatively, name one of the groups on oxygen as an alkoxy group (RO- ).
CH3
CH O 3 CH3CH2O CH3CHO CH3CH2CHO H3C CO methoxy ethoxy CH isopropoxy sec-butoxy 3 ter-butoxy E.g Name the following molecule
O O OH
E.g Use bond-line to draw
Isopropyl methyl ether 4-ethoxy-2-methyl-1-hexene
CHM 201 Dang 1 Substitution of Alcohols (ROH RX)
- - CH3Cl + OH CH3OH + Cl
- - CH3OH + Cl CH3Cl + OH
-OH is strongly basic, unstable, not a good LG
Must convert into a weaker base, in the protonated form (R OH2 )
ROH + NaCl NR (no LG)
ROH + HCl RCl + H2O
ROH + HBr RBr + H2O
ROH + HI RI + H2O
H Br + CH3 OH + H Br CH3 O H3C Br H2O H SN2
poor LG weak good LG base
o o SN1 mechanism (2 and 3 )
H2O H Br + H Br OH OH Br + H2O
3o alcohol + Br
o SN2 mechanism (1 ) Br
H + H2O + H Br Br OH O H H O 1o alcohol 2
Explain why (S)-2-butanol forms a racemic mixture when it is heated in aqueous sulfuric acid?
CHM 201 Dang 2 E.g Predict the product and provide a mechanism
CH3
OH + HI
Elimination reactions of Alcohols
Aka dehydration of alcohol lost of H2O
Required strong acid catalyst
Formation of alkene follows Zaitsev’s rule: More substituted alkene is the major product
More stable carbocation will be formed faster
Benzylic/allylic/3o ROH > 2oROH >> 1oROH
OSO3H OSO3H E1 mechanism
HB HA A minor H OSO3H heat O OH H H B + major OSO3H
CHM 201 Dang 3 E2 mechanism H H O + H2O OH H OSO3H H heat + H2SO4
OSO3H
Ether is also obtained; it is the product of a competing SN2 reaction
H O H OSO H O O OH 3 H H o 1 H O ether HO 2
E.g Give the major product formed when each of the following alcohols is heated in presence of H2SO4
OH
H2SO4
OH
H2SO4
Oxidation of Alcohols
CHM 201 Dang 4 Oxidation: increases # C-O bonds and decreases the # of C-H bonds
O O
CH4 CH3OH HCH HCOH O C O
Reduction: decreases # C-O bonds and increases the # C-H bonds
Common reagents: chromic acid, chromate salt, dichromate salt, permanganate
Oxidation of a 1° alcohol to a carboxylic acid is commonly carried out using potassium
dichromate, K2Cr2O7, in aqueous sulfuric acid.
Further oxidation OH O O K2Cr2O7 K2Cr2O7 R C H C C H SO OH H2SO4 R H 2 4 R H 1o alcohol Aldehyde carboxylic
Or using pyridium chlorochromate (PCC) as the oxidizing agent in an anhydrous solvent OH O PCC R C H C CH2Cl2 R H H 1o alcohol Aldehyde
◦ Oxidation of a 2° alcohol and cyclic alcohol gives a ketone. OH O K Cr O 2 2 7 C R1 C H R1 R2 H2SO4 R2 Ketone 2o alcohol
OH O
K Cr O 2 2 7 CHM 201 Dang 5
H2SO4
cyclohexanol cyclohexanone Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation R H2CrO4 R OH NR
R
Consider the following reaction
OH O LiAlH4 a reaction
a agent
Predict the product(s)
H2CrO4
OH
OH
H2CrO4
O reagents? alcohol ???? OH
CHM 201 Dang 6