(Ph OH N N Me O YO O YO
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cell Line Descriptions Geneblazer® M1-NFAT
Version No.: GeneBLAzer ® Validation Packet Page 1 of 5 01Sep08 Optimization of the GeneBLazer ® M1-NFAT-bla Jurkat Cell Line GeneBLAzer ® M1 NFAT-bla Jurkat Cells Catalog Numbers – K1710 Cell Line Descriptions GeneBLAzer ® M1-NFAT-bla Jurkat cells contain the human Acetylcholine (muscarinic) subtype 1 receptor (M1), (Accession # NM_000738 ) stably integrated into the CellSensor ® NFAT-bla Jurkat cell line. CellSensor ® NFAT-bla Jurkat cells (Cat. no. K1671) contain a beta-lactamase (bla ) reporter gene under control of the Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells (NFAT) response element. M1-NFAT-bla Jurkat cells are functionally validated for Z’-factor and EC 50 concentrations of carbachol (Figure 1). In addition, GeneBLAzer ® M1-NFAT-bla CHO-K1 cells have been tested for assay performance under variable conditions. Target Description Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are members of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. Muscarinic receptors are widely distributed and mediate the actions of acetylcholine in both the CNS and peripheral tissues. Five muscarinic receptor subtypes have been identified and are referred to as M 1-M5 (1-5). The five genes that encode the muscarinic receptors all belong to the rhodopsin-line family (Family A) and share strong sequence homology but have unique regions located at the amino terminus (extracellular) and in the third intracellular loop. The M 1, M3, and M 5 receptor subtypes couple through the G q/11 class of G-proteins and activate the phopholipase C pathway. Activation of this pathway in turn leads to increases in free intracellular calcium levels as inositol triphosphate mediates release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0110449 A1 Lorber Et Al
US 200601 10449A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0110449 A1 LOrber et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2006 (54) PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION Publication Classification (76) Inventors: Richard R. Lorber, Scotch Plains, NJ (US); Heribert W. Staudinger, Union, (51) Int. Cl. NJ (US); Robert E. Ward, Summit, NJ A6II 3/473 (2006.01) (US) A6II 3L/24 (2006.01) Correspondence Address: A6IR 9/20 (2006.01) SCHERING-PLOUGH CORPORATION (52) U.S. Cl. ........................... 424/464; 514/290: 514/540 PATENT DEPARTMENT (K-6-1, 1990) 2000 GALLOPNG HILL ROAD KENILWORTH, NJ 07033-0530 (US) (57) ABSTRACT (21) Appl. No.: 11/257,348 (22) Filed: Oct. 24, 2005 The present invention relates to formulations useful for Related U.S. Application Data treating respiratory disorders associated with the production of mucus glycoprotein, skin disorders, and allergic conjunc (60) Provisional application No. 60/622,507, filed on Oct. tivitis while substantially reducing adverse effects associ 27, 2004. Provisional application No. 60/621,783, ated with the administration of non-selective anti-cholin filed on Oct. 25, 2004. ergic agents and methods of use thereof. US 2006/01 10449 A1 May 25, 2006 PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION example, Weinstein and Weinstein (U.S. Pat. No. 6,086,914) describe methods of treating allergic rhinitis using an anti CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED cholinergic agent with a limited capacity to pass across lipid APPLICATION membranes, such as the blood-brain barrier, in combination with an antihistamine that is limited in both sedating and 0001. This application claims benefit of priority to U.S. -

Cerebellar Toxicity of Phencyclidine
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1995, 75(3): 2097-2108 Cerebellar Toxicity of Phencyclidine Riitta N&kki, Jari Koistinaho, Frank Ft. Sharp, and Stephen M. Sagar Department of Neurology, University of California, and Veterans Affairs Medical Center, San Francisco, California 94121 Phencyclidine (PCP), clizocilpine maleate (MK801), and oth- Phencyclidine (PCP), dizocilpine maleate (MK801), and other er NMDA antagonists are toxic to neurons in the posterior NMDA receptor antagonistshave attracted increasing attention cingulate and retrosplenial cortex. To determine if addition- becauseof their therapeutic potential. These drugs have neuro- al neurons are damaged, the distribution of microglial ac- protective properties in animal studies of focal brain ischemia, tivation and 70 kDa heat shock protein (HSP70) induction where excitotoxicity is proposedto be an important mechanism was studied following the administration of PCP and of neuronal cell death (Dalkara et al., 1990; Martinez-Arizala et MK801 to rats. PCP (10-50 mg/kg) induced microglial ac- al., 1990). Moreover, NMDA antagonists decrease neuronal tivation and neuronal HSP70 mRNA and protein expression damage and dysfunction in other pathological conditions, in- in the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortex. In ad- cluding hypoglycemia (Nellgard and Wieloch, 1992) and pro- dition, coronal sections of the cerebellar vermis of PCP (50 longed seizures(Church and Lodge, 1990; Faingold et al., 1993). mg/kg) treated rats contained vertical stripes of activated However, NMDA antagonists are toxic to certain neuronal microglial in the molecular layer. In the sagittal plane, the populations in the brain. Olney et al. (1989) demonstratedthat microglial activation occurred in irregularly shaped patch- the noncompetitive NMDA antagonists,PCP, MK801, and ke- es, suggesting damage to Purkinje cells. -

Euphoric Non-Fentanil Novel Synthetic Opioids on the Illicit Drugs Market
Forensic Toxicology (2019) 37:1–16 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0454-5 REVIEW ARTICLE The search for the “next” euphoric non‑fentanil novel synthetic opioids on the illicit drugs market: current status and horizon scanning Kirti Kumari Sharma1,2 · Tim G. Hales3 · Vaidya Jayathirtha Rao1,2 · Niamh NicDaeid4,5 · Craig McKenzie4 Received: 7 August 2018 / Accepted: 11 November 2018 / Published online: 28 November 2018 © The Author(s) 2018 Abstract Purpose A detailed review on the chemistry and pharmacology of non-fentanil novel synthetic opioid receptor agonists, particularly N-substituted benzamides and acetamides (known colloquially as U-drugs) and 4-aminocyclohexanols, developed at the Upjohn Company in the 1970s and 1980s is presented. Method Peer-reviewed literature, patents, professional literature, data from international early warning systems and drug user fora discussion threads have been used to track their emergence as substances of abuse. Results In terms of impact on drug markets, prevalence and harm, the most signifcant compound of this class to date has been U-47700 (trans-3,4-dichloro-N-[2-(dimethylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-methylbenzamide), reported by users to give short- lasting euphoric efects and a desire to re-dose. Since U-47700 was internationally controlled in 2017, a range of related compounds with similar chemical structures, adapted from the original patented compounds, have appeared on the illicit drugs market. Interest in a structurally unrelated opioid developed by the Upjohn Company and now known as BDPC/bromadol appears to be increasing and should be closely monitored. Conclusions International early warning systems are an essential part of tracking emerging psychoactive substances and allow responsive action to be taken to facilitate the gathering of relevant data for detailed risk assessments. -

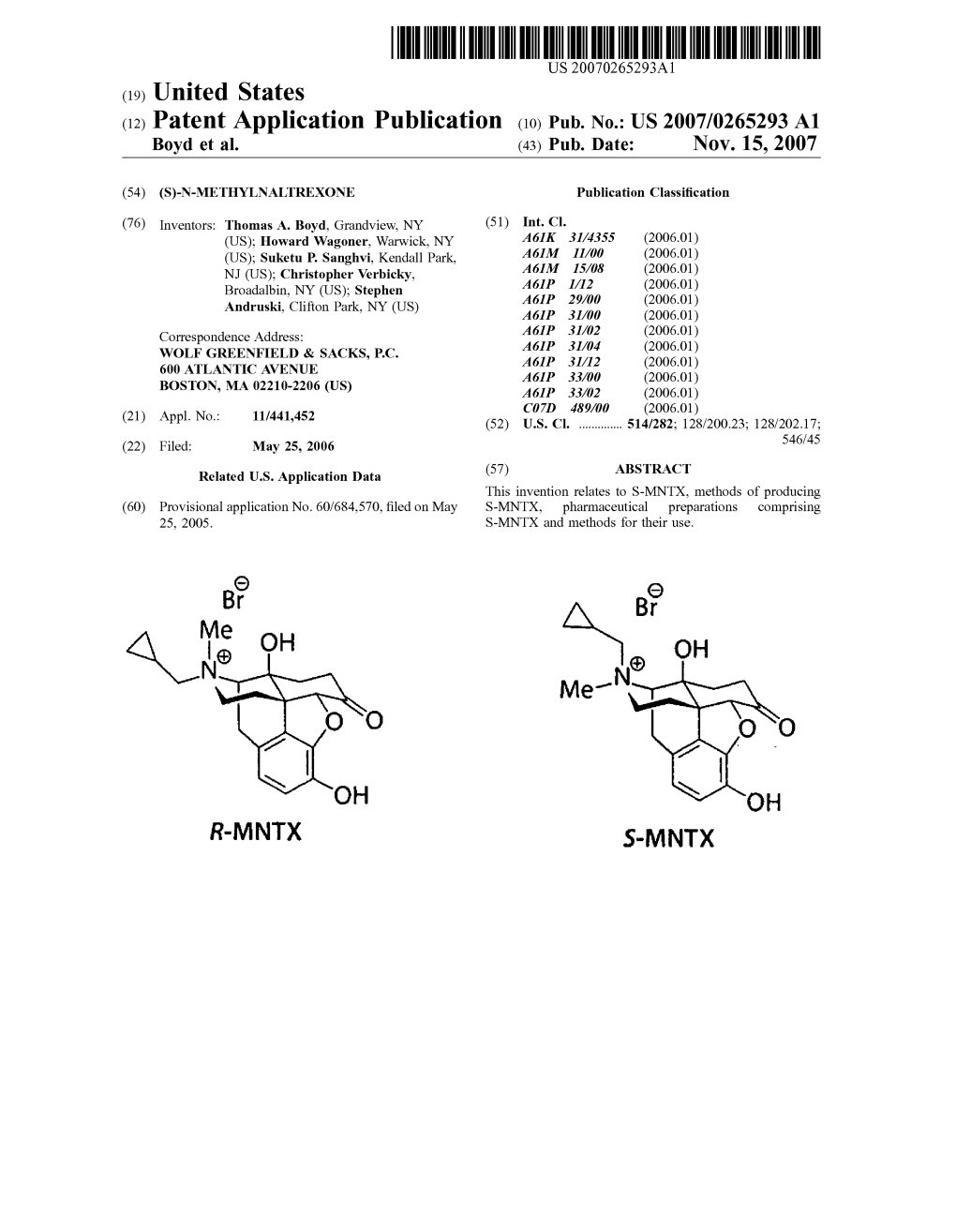
United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,916,581 B2 Boyd Et Al
USOO891 6581 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,916,581 B2 Boyd et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 23, 2014 (54) (S)-N-METHYLNALTREXONE 4,194,045 A 3, 1980 Adelstein 4,203,920 A 5, 1980 Diamond et al. (75) Inventors: Thomas A. Boyd, Grandview, NY (US); 4,241,066 A 12, 1980 Kobylecki et al. H OW d Wagoner,goner, Warwick,s NY (US);s 4,311,833.4,277,605 A T.1/1982 1981 NamikoshiBuyniski et etal. al. Suketu P. Sanghvi, Kendall Park, NJ 4.322,426 A 3/1982 Hermann et al. (US); Christopher Verbicky, 4.326,074 A 4, 1982 Diamond et al. Broadalbin, NY (US); Stephen 4.326,075 A 4, 1982 Diamond et al. “. s 4,377.568 A 3/1983 Chopra et al. Andruski, Clifton Park, NY (US) 4.385,078 A 5/1983 Onda et al. 4.427,676 A 1/1984 White et al. (73) Assignee: Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 4,430,327 A 2, 1984 Frederickson et al. Tarrytown, NY (US) 4,452,775 A 6/1984 Kent 4,457,907 A 7/1984 Porteret al. (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 4,462.839 A 7/1984 McGinley et al. patent is extended or adjusted under 35 4,518.4334,466,968 A 5/19858, 1984 McGinleyBernstein et al. U.S.C. 154(b) by 344 days. 4,533,739 A 8/1985 Pitzele et al. This patent is Subject to a terminal dis- 4,606,9094,556,552 A 12/19858/1986 PorterBechgaard et al. -

)&F1y3x PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX to THE
)&f1y3X PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX TO THE HARMONIZED TARIFF SCHEDULE )&f1y3X PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX TO THE TARIFF SCHEDULE 3 Table 1. This table enumerates products described by International Non-proprietary Names (INN) which shall be entered free of duty under general note 13 to the tariff schedule. The Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) registry numbers also set forth in this table are included to assist in the identification of the products concerned. For purposes of the tariff schedule, any references to a product enumerated in this table includes such product by whatever name known. Product CAS No. Product CAS No. ABAMECTIN 65195-55-3 ACTODIGIN 36983-69-4 ABANOQUIL 90402-40-7 ADAFENOXATE 82168-26-1 ABCIXIMAB 143653-53-6 ADAMEXINE 54785-02-3 ABECARNIL 111841-85-1 ADAPALENE 106685-40-9 ABITESARTAN 137882-98-5 ADAPROLOL 101479-70-3 ABLUKAST 96566-25-5 ADATANSERIN 127266-56-2 ABUNIDAZOLE 91017-58-2 ADEFOVIR 106941-25-7 ACADESINE 2627-69-2 ADELMIDROL 1675-66-7 ACAMPROSATE 77337-76-9 ADEMETIONINE 17176-17-9 ACAPRAZINE 55485-20-6 ADENOSINE PHOSPHATE 61-19-8 ACARBOSE 56180-94-0 ADIBENDAN 100510-33-6 ACEBROCHOL 514-50-1 ADICILLIN 525-94-0 ACEBURIC ACID 26976-72-7 ADIMOLOL 78459-19-5 ACEBUTOLOL 37517-30-9 ADINAZOLAM 37115-32-5 ACECAINIDE 32795-44-1 ADIPHENINE 64-95-9 ACECARBROMAL 77-66-7 ADIPIODONE 606-17-7 ACECLIDINE 827-61-2 ADITEREN 56066-19-4 ACECLOFENAC 89796-99-6 ADITOPRIM 56066-63-8 ACEDAPSONE 77-46-3 ADOSOPINE 88124-26-9 ACEDIASULFONE SODIUM 127-60-6 ADOZELESIN 110314-48-2 ACEDOBEN 556-08-1 ADRAFINIL 63547-13-7 ACEFLURANOL 80595-73-9 ADRENALONE -

Self-Administration of Abused Substances: Methods for Study
Self-Administration of Abused Substances: Methods for Study U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH, EDUCATION AND WELFARE Public Health Service Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration Self-Administration of Abused Substances: Methods for Study Editor: Norman A. Krasnegor, Ph.D. NIDA Research Monograph 20 July 1978 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH. EDUCATION, AND WELFARE Public Health Service Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration National Institute on Drug Abuse Division of Research 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, Maryland 20857 For sale by the Superintendent of Documents U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402 Stock No. 017-024-00794-3 The NIDA Research Monograph series is prepared by the Division of Research of the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Its primary objective is to provide critical re- views of research problem areas and techniques, the content of state-of-the-art conferences, integrative research reviews and significant original research. Its dual publication emphasis is rapid and targeted dissemination to the scientific and professional community. Editorial Advisory Board Avram Goldstein, M.D. Addiction Research Foundation Polo Alto, California Jerome Jaffe, M.D. College of Physicians and Surgeons Columbia University New York Reese T. Jones, M.D. Langley Porter Neuropsychiatric Institute University of California San Francisco, California William McGlothlin, Ph.D. Department of Psychology. UCLA Los Angeles, California Jack Mendelson, M.D. Alcohol and Drug Abuse Research Center Harvard Medical School McLean Hospital Belmont, Massachusetts Helen Nowlis, Ph.D. Office of Drug Education, DHEW Washington, D C Lee Robins, Ph.D. Washington University School of Medicine St Louis, Missouri NIDA Research Monograph series William Pollin, M.D. -

Problems of Drug Dependence 1980 Proceedings of the 42Nd Annual Scientific Meeting the Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence
National Institute on Drug Abuse MONOGRAPH SERIES Problems of Drug Dependence 1980 Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Scientific Meeting The Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence, Inc. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES • Public Health Service • Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration Problems of Drug Dependence, 1980 Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Scientific Meeting, The Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence, Inc. Editor: Louis S. Harris, Ph.D. NIDA Research Monograph 34 February 1981 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration National Institute on Drug Abuse Division of Research 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, Maryland 20857 For sale by the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office Washington, D.C. 20402 The NIDA Research Monograph series is prepared by the Division of Research of the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Its primary objective is to provide critical reviews of research problem areas and techniques, the content of state-of-the-art conferences, integrative research reviews and significant original research. Its dual publication emphasis is rapid and targeted dissemination to the scientific and professional community. Editorial Advisory Board Avram Goldstein, M.D. Addiction Research Foundation Palo Alto, California Jerome Jaffe, M.D. College of Physicians and Surgeons Columbia University, New York Reese T. Jones, M.D. Langley Porter Neuropsychiatric Institute University of California San Francisco, California William McGlothlin, Ph.D. Deportment of Psychology, UCLA Los Angeles, California Jack Mendelson, M.D. Alcohol and Drug Abuse Research Center Harvard Medical School McLean Hospital Belmont, Massachusetts Helen Nowlis, Ph.D. Office of Drug Education, DHHS Washington, D.C Lee Robins, Ph.D. -

PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX to the TARIFF SCHEDULE 2 Table 1
Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (2020) Revision 19 Annotated for Statistical Reporting Purposes PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX TO THE HARMONIZED TARIFF SCHEDULE Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (2020) Revision 19 Annotated for Statistical Reporting Purposes PHARMACEUTICAL APPENDIX TO THE TARIFF SCHEDULE 2 Table 1. This table enumerates products described by International Non-proprietary Names INN which shall be entered free of duty under general note 13 to the tariff schedule. The Chemical Abstracts Service CAS registry numbers also set forth in this table are included to assist in the identification of the products concerned. For purposes of the tariff schedule, any references to a product enumerated in this table includes such product by whatever name known. -

1 to the Stomach Inhibits Gut-Brain Signalling by the Satiety Hormone Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Targeted Expression of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor (PAI)-1 to the Stomach Inhibits Gut-Brain Signalling by the Satiety Hormone Cholecystokinin (CCK) Thesis submitted in accordance with the requirements of the University of Liverpool for the degree of Doctor in Philosophy By Joanne Gamble October 2013 I For Lily, you are the sunshine in my life…. II Table of Contents Figures and tables VII Acknowledgements XI Publications XIII Abstract XIV Chapter 1 ................................................................................................................................ 1 1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................... 2 1.2 The Gastrointestinal Tract and Digestive Function ...................................................... 4 1.2.1 Distribution, Structure and Biology of Enteroendocrine (EEC) Cells ........................ 5 1.2.2 Luminal Sensing ......................................................................................................... 6 1.3 Energy Homeostasis ......................................................................................................... 7 1.3.1 Gut Hormones ........................................................................................................... 10 1.3.1.1 The Gastrin Family ............................................................................................ 11 1.3.2 PP-fold Family ......................................................................................................... -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,264,917 B1 Klaveness Et Al
USOO6264,917B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,264,917 B1 Klaveness et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2001 (54) TARGETED ULTRASOUND CONTRAST 5,733,572 3/1998 Unger et al.. AGENTS 5,780,010 7/1998 Lanza et al. 5,846,517 12/1998 Unger .................................. 424/9.52 (75) Inventors: Jo Klaveness; Pál Rongved; Dagfinn 5,849,727 12/1998 Porter et al. ......................... 514/156 Lovhaug, all of Oslo (NO) 5,910,300 6/1999 Tournier et al. .................... 424/9.34 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (73) Assignee: Nycomed Imaging AS, Oslo (NO) 2 145 SOS 4/1994 (CA). (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 19 626 530 1/1998 (DE). patent is extended or adjusted under 35 O 727 225 8/1996 (EP). U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. WO91/15244 10/1991 (WO). WO 93/20802 10/1993 (WO). WO 94/07539 4/1994 (WO). (21) Appl. No.: 08/958,993 WO 94/28873 12/1994 (WO). WO 94/28874 12/1994 (WO). (22) Filed: Oct. 28, 1997 WO95/03356 2/1995 (WO). WO95/03357 2/1995 (WO). Related U.S. Application Data WO95/07072 3/1995 (WO). (60) Provisional application No. 60/049.264, filed on Jun. 7, WO95/15118 6/1995 (WO). 1997, provisional application No. 60/049,265, filed on Jun. WO 96/39149 12/1996 (WO). 7, 1997, and provisional application No. 60/049.268, filed WO 96/40277 12/1996 (WO). on Jun. 7, 1997. WO 96/40285 12/1996 (WO). (30) Foreign Application Priority Data WO 96/41647 12/1996 (WO). -

Stems for Nonproprietary Drug Names
USAN STEM LIST STEM DEFINITION EXAMPLES -abine (see -arabine, -citabine) -ac anti-inflammatory agents (acetic acid derivatives) bromfenac dexpemedolac -acetam (see -racetam) -adol or analgesics (mixed opiate receptor agonists/ tazadolene -adol- antagonists) spiradolene levonantradol -adox antibacterials (quinoline dioxide derivatives) carbadox -afenone antiarrhythmics (propafenone derivatives) alprafenone diprafenonex -afil PDE5 inhibitors tadalafil -aj- antiarrhythmics (ajmaline derivatives) lorajmine -aldrate antacid aluminum salts magaldrate -algron alpha1 - and alpha2 - adrenoreceptor agonists dabuzalgron -alol combined alpha and beta blockers labetalol medroxalol -amidis antimyloidotics tafamidis -amivir (see -vir) -ampa ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors (AMPA and/or KA receptors) subgroup: -ampanel antagonists becampanel -ampator modulators forampator -anib angiogenesis inhibitors pegaptanib cediranib 1 subgroup: -siranib siRNA bevasiranib -andr- androgens nandrolone -anserin serotonin 5-HT2 receptor antagonists altanserin tropanserin adatanserin -antel anthelmintics (undefined group) carbantel subgroup: -quantel 2-deoxoparaherquamide A derivatives derquantel -antrone antineoplastics; anthraquinone derivatives pixantrone -apsel P-selectin antagonists torapsel -arabine antineoplastics (arabinofuranosyl derivatives) fazarabine fludarabine aril-, -aril, -aril- antiviral (arildone derivatives) pleconaril arildone fosarilate -arit antirheumatics (lobenzarit type) lobenzarit clobuzarit -arol anticoagulants (dicumarol type) dicumarol