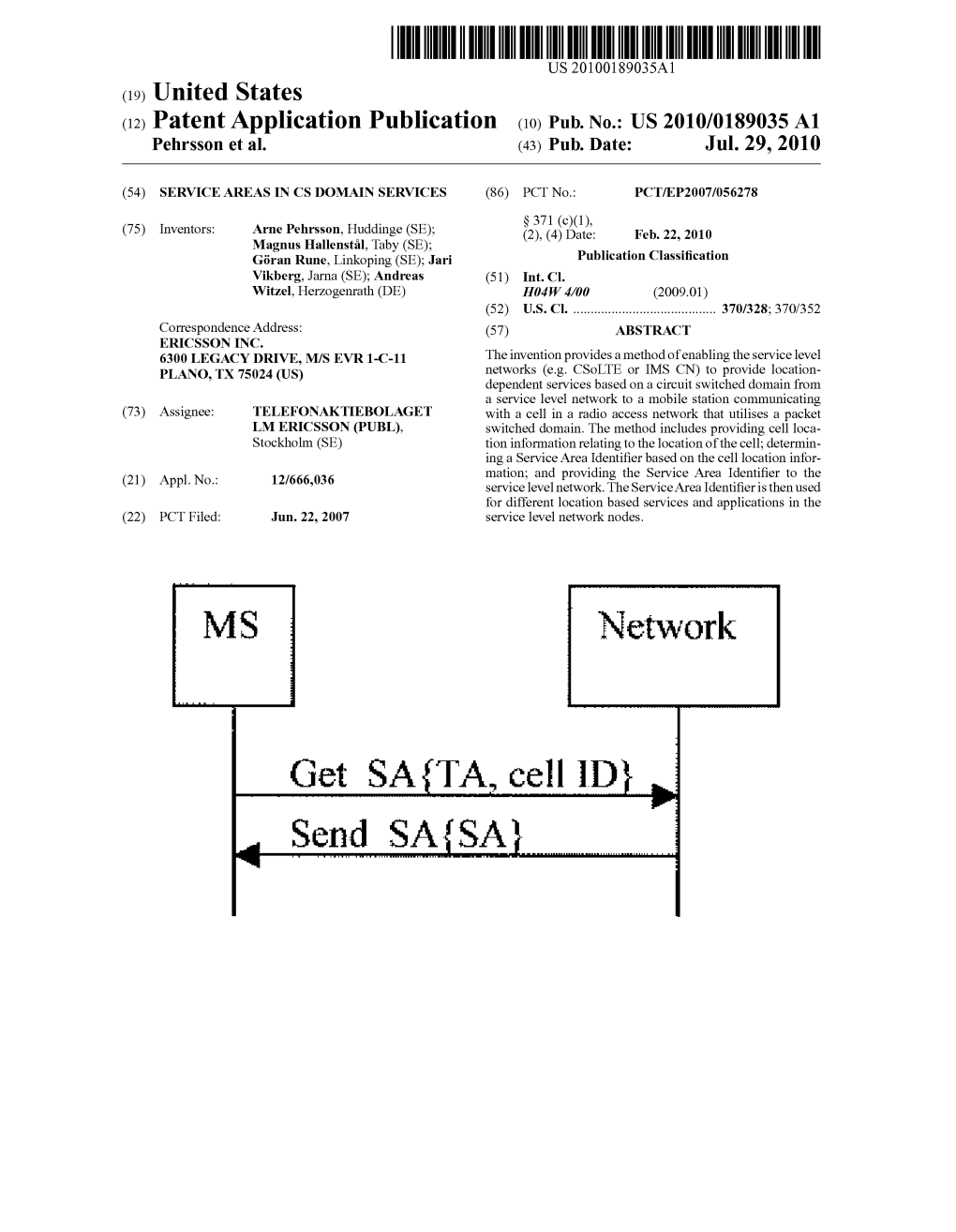
Get SATA Cell D
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

LTE-M Deployment Guide to Basic Feature Set Requirements
LTE-M DEPLOYMENT GUIDE TO BASIC FEATURE SET REQUIREMENTS JUNE 2019 LTE-M DEPLOYMENT GUIDE TO BASIC FEATURE SET REQUIREMENTS Table of Contents 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4 2 INTRODUCTION 5 2.1 Overview 5 2.2 Scope 5 2.3 Definitions 6 2.4 Abbreviations 6 2.5 References 9 3 GSMA MINIMUM BAseLINE FOR LTE-M INTEROPERABILITY - PROBLEM STATEMENT 10 3.1 Problem Statement 10 3.2 Minimum Baseline for LTE-M Interoperability: Risks and Benefits 10 4 LTE-M DATA ARCHITECTURE 11 5 LTE-M DePLOYMENT BANDS 13 6 LTE-M FeATURE DePLOYMENT GUIDE 14 7 LTE-M ReLEAse 13 FeATURes 15 7.1 PSM Standalone Timers 15 7.2 eDRX Standalone 18 7.3 PSM and eDRX Combined Implementation 19 7.4 High Latency Communication 19 7.5 GTP-IDLE Timer on IPX Firewall 20 7.6 Long Periodic TAU 20 7.7 Support of category M1 20 7.7.1 Support of Half Duplex Mode in LTE-M 21 7.7.2 Extension of coverage features (CE Mode A / B) 21 7.8 SCEF 22 7.9 VoLTE 22 7.10 Connected Mode Mobility 23 7.11 SMS Support 23 7.12 Non-IP Data Delivery (NIDD) 24 7.13 Connected-Mode (Extended) DRX Support 24 7.14 Control Plane CIoT Optimisations 25 7.15 User Plane CIoT Optimisations 25 7.16 UICC Deactivation During eDRX 25 7.17 Power Class 26 LTE-M DEPLOYMENT GUIDE TO BASIC FEATURE SET REQUIREMENTS 8 LTE-M ReLEAse 14 FeATURes 27 8.1 Positioning: E-CID and OTDOA 27 8.2 Higher data rate support 28 8.3 Improvements of VoLTE and other real-time services 29 8.4 Mobility enhancement in Connected Mode 29 8.5 Multicast transmission/Group messaging 29 8.6 Relaxed monitoring for cell reselection 30 8.7 Release Assistance Indication -

Cell Oscillation Resolution in Mobility Profile Building Cell Oscillation
Cell oscillation resolution in mobility profile building Shafqat Ali Shad 1, Enhong Chen 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Technology University of Science and Technology of China Huangshan Road, Hefei, 230027 Anhui, China [email protected] 2 Department of Computer Science and Technology University of Science and Technology of China Huangshan Road, Hefei, 230027 Anhui, China [email protected] Abstract depending on its configuration and methods used. As for Mobility profile building became extensively examined mobile users GPS is discouraging in term of high power area in Location based services (LBS) through extraction consumption and extra equipment installation in network. of significant locations. Mobility traces are recorded under This makes its use limited for positioning or location three reference positioning systems that are Satellite based extraction. While in case of Local positioning systems i.e. i.e. GPS, Network based i.e. GSM and Local positioning Bluetooth, RFID, Infrared, Wifi, IrDA they operate in i.e. WLAN, RFID, IrDA. Satellite based and local limited space area due to of its short range signal positioning due to of high power consumption, additional capabilities. So only viable solution for position extraction resource installation, low accuracy and space limitation are widely spread and examined is Network position system less encouraging. So network based positioning i.e. GSM i.e. GSM. While in case of GSM, location exaction can be is only viable solution for mobility tracing through Cell done through Assisted-GPS (A-GPS), Time difference of global identity (CGI). CGI presents the Cell-ids to extract arrival (TDOA) and Enhanced observed time difference the significant locations from mobility history. -

Miot Location in Roaming Version 1.0 20 May 2020
GSM Association Confidential - Full, Rapporteur, Associate and Affiliate Members Official Document NG.120 - MIoT Location in Roaming MIoT Location in Roaming Version 1.0 20 May 2020 This is a Non-binding Permanent Reference Document of the GSMA Security Classification: Confidential - Full, Rapporteur, Associate and Affiliate Members Access to and distribution of this document is restricted to the persons permitted by the security classification. This document is confidential to the Association and is subject to copyright protection. This document is to be used only for the purposes for which it has been supplied and information contained in it must not be disclosed or in any other way made available, in whole or in part, to persons other than those permitted under the security classification without the prior written approval of the Association. Copyright Notice Copyright © 2020 GSM Association Disclaimer The GSM Association (“Association”) makes no representation, warranty or undertaking (express or implied) with respect to and does not accept any responsibility for, and hereby disclaims liability for the accuracy or completeness or timeliness of the information contained in this document. The information contained in this document may be subject to change without prior notice. Antitrust Notice The information contain herein is in full compliance with the GSM Association’s antitrust compliance policy. V1.0 Page 1 of 37 GSM Association Confidential - Full, Rapporteur, Associate and Affiliate Members Official Document NG.120 - MIoT Location -

Physical Cell ID Allocation in Cellular Networks
Linköping University | Department of Computer Science Master thesis, 30 ECTS | Informationsteknologi 2016 | LIU-IDA/LITH-EX-A--16/039--SE Physical Cell ID Allocation in Cellular Networks Sofia Nyberg Supervisor : Kaj Holmberg Examiner : Niklas Carlsson Linköpings universitet SE–581 83 Linköping +46 13 28 10 00 , www.liu.se Upphovsrätt Detta dokument hålls tillgängligt på Internet – eller dess framtida ersättare – under 25 år från publiceringsdatum under förutsättning att inga extraordinära omständigheter uppstår. Tillgång till dokumentet innebär tillstånd för var och en att läsa, ladda ner, skriva ut enstaka kopior för enskilt bruk och att använda det oförändrat för ickekommersiell forskning och för undervisning. Överföring av upphovsrätten vid en senare tidpunkt kan inte upphäva detta tillstånd. All annan användning av dokumentet kräver upphovsmannens medgivande. För att garantera äktheten, säkerheten och tillgängligheten finns lösningar av teknisk och admin- istrativ art. Upphovsmannens ideella rätt innefattar rätt att bli nämnd som upphovsman i den omfattning som god sed kräver vid användning av dokumentet på ovan beskrivna sätt samt skydd mot att dokumentet ändras eller presenteras i sådan form eller i sådant sam- manhang som är kränkande för upphovsmannenslitterära eller konstnärliga anseende eller egenart. För ytterligare information om Linköping University Electronic Press se förlagets hemsida http://www.ep.liu.se/. Copyright The publishers will keep this document online on the Internet – or its possible replacement – for a period of 25 years starting from the date of publication barring exceptional circum- stances. The online availability of the document implies permanent permission for anyone to read, to download, or to print out single copies for his/hers own use and to use it unchanged for non-commercial research and educational purpose. -

UMTS); LTE; Nq and Nq' Application Protocol (Nq-AP); Stage 3 (3GPP TS 29.405 Version 15.0.0 Release 15
ETSI TS 129 405 V15.0.0 (2018-07) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Nq and Nq' Application Protocol (Nq-AP); Stage 3 (3GPP TS 29.405 version 15.0.0 Release 15) 3GPP TS 29.405 version 15.0.0 Release 15 1 ETSI TS 129 405 V15.0.0 (2018-07) Reference RTS/TSGC-0429405vf00 Keywords LTE,UMTS ETSI 650 Route des Lucioles F-06921 Sophia Antipolis Cedex - FRANCE Tel.: +33 4 92 94 42 00 Fax: +33 4 93 65 47 16 Siret N° 348 623 562 00017 - NAF 742 C Association à but non lucratif enregistrée à la Sous-Préfecture de Grasse (06) N° 7803/88 Important notice The present document can be downloaded from: http://www.etsi.org/standards-search The present document may be made available in electronic versions and/or in print. The content of any electronic and/or print versions of the present document shall not be modified without the prior written authorization of ETSI. In case of any existing or perceived difference in contents between such versions and/or in print, the only prevailing document is the print of the Portable Document Format (PDF) version kept on a specific network drive within ETSI Secretariat. Users of the present document should be aware that the document may be subject to revision or change of status. Information on the current status of this and other ETSI documents is available at https://portal.etsi.org/TB/ETSIDeliverableStatus.aspx If you find errors in the present document, please send your comment to one of the following services: https://portal.etsi.org/People/CommiteeSupportStaff.aspx Copyright Notification No part may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm except as authorized by written permission of ETSI. -

ETSI TS 123 060 V3.6.0 (2001-01) Technical Specification
ETSI TS 123 060 V3.6.0 (2001-01) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 23.060 version 3.6.0 Release 1999) R GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS 3GPP TS 23.060 version 3.6.0 Release 1999 1 ETSI TS 123 060 V3.6.0 (2001-01) Reference RTS/TSGS-0223060UR4 Keywords GSM, UMTS ETSI 650 Route des Lucioles F-06921 Sophia Antipolis Cedex - FRANCE Tel.:+33492944200 Fax:+33493654716 Siret N° 348 623 562 00017 - NAF 742 C Association à but non lucratif enregistrée à la Sous-Préfecture de Grasse (06) N° 7803/88 Important notice Individual copies of the present document can be downloaded from: http://www.etsi.org The present document may be made available in more than one electronic version or in print. In any case of existing or perceived difference in contents between such versions, the reference version is the Portable Document Format (PDF). In case of dispute, the reference shall be the printing on ETSI printers of the PDF version kept on a specific network drive within ETSI Secretariat. Users of the present document should be aware that the document may be subject to revision or change of status. Information on the current status of this and other ETSI documents is available at http://www.etsi.org/tb/status/ If you find errors in the present document, send your comment to: [email protected] Copyright Notification No part may be reproduced except as authorized by written permission. -

Handbook on the Use of Mobile Phone Data for Official Statistics
Handbook on the Use of Mobile Phone Data for Official Statistics UN Global Working Group on Big Data for Official Statistics September 2019 1 Table of Contents Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 4 List of Definitions and Abbreviations .................................................................................... 5 1 Applications ................................................................................................................... 9 1.1 Mobile positioning data used in official statistics production ................................... 9 Travel statistics in Estonia .............................................................................................. 9 Inbound cross-border visitor arrival statistics in Indonesia .............................................. 9 1.2 Mobile positioning data used in research and pilots applicable for statistics ........... 10 Domain: Tourism and event statistics ........................................................................... 10 Domain: Population statistics ........................................................................................ 12 Domain: Migration statistics ......................................................................................... 14 Domain: Commuting statistics ...................................................................................... 15 Domain: Traffic flow statistics ..................................................................................... -

We Know Where You Are!
2016 8th International Conference on Cyber Conflict Permission to make digital or hard copies of this publication for internal use within NATO and for personal or educational use when for non-profit or non-commercial Cyber Power purposes is granted providing that copies bear this notice and a full citation on the N.Pissanidis, H.Rõigas, M.Veenendaal (Eds.) first page. Any other reproduction or transmission requires prior written permission by NATO CCD COE. 2016 © NATO CCD COE Publications, Tallinn We Know Where You Are! Siddharth Prakash Rao Dr Silke Holtmanns Department of Computer Science Bell Labs, Nokia Aalto University, Finland Espoo, Finland [email protected] [email protected] Dr Ian Oliver Dr Tuomas Aura Bell Labs, Nokia Department of Computer Science Espoo, Finland Aalto University, Finland [email protected] [email protected] Abstract: Mobile network technologies require some degree of tracking of user location, specifically user equipment tracking, as part of their fundamental mechanism of working. Without this basic function, features such as hand-over between cells would not work. Since mobile devices are typically associated with a single person, this provides a potential mechanism for user location surveillance. Network operators are bound by strict privacy legislation. However, spying by certain agencies, hackers and even advertisers without the users’ or operators’ knowledge has become a serious issue. In this article, we introduce and explain all known recent attacks on mobile networks that compromised user privacy. We focus on attacks using the Signalling System 7 (SS7) protocol as the interconnection interface between operators mainly in GSM networks. -

2. an Optimized Cellular Network Design Using Various Technologies
International Journal of Engineering Research and General Science Volume 3, Issue 2, March-April, 2015 ISSN 2091-2730 An optimized cellular network design using various technologies within a service area N. Anish 1, A. Neelima 2, G. Deepti 2 Student, M.Sc., Telecommunication Engineering, Staffordshire University, Staffordshire, United Kingdom1 Student, M. Tech, Dept. of ECE, Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla, India2 Abstract— this paper deals with Optimized Cellular Network with different access technologies with in the Staffordshire country. The main aim is to provide good coverage to the customers in the prescribed area as per the customers‟ utilization. For the cause of poor coverage probability and higher call blocking rates the network has been redefined. So the cellular network was designed with the target coverage probability of 0.98 and blocking probability of 1% which covers entire Staffordshire country. For designing practically we use a tool called ''MENTUM PLANET'' software providing capacity, coverage and frequency planning and analysis of Staffordshire County according to the customers‟ utilization. Keywords— Global Systems for Mobile Communications, Universal Mobile Telecommunications Systems, Long Term Evolution, Core Network, UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, Radio Network Controller, Frequency Division duplex.. 1. INTRODUCTION In present day technology, mobile world plays a high flying role in every individual day to day life. There has been drastic change in the field of cellular technology since few decades. Even today the network technologies are developing with new requirements depending upon the usage of traffic, but in early days it was utilized for minimum and limited requirements. Here we are designing optimized cellular network and obtaining network constraints and parameters. -

Report “GSM ARCHITECTURE”
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION GSM ARCHITECTURE Gyan Vihar School of Engineering & Technology Jagatpura, Jaipur A Report on “GSM ARCHITECTURE” Based on the training at Session (2010-2011) Rajasthan Technical University, Kota B.TECH-2007 Submitted To : Submitted By Mr. Rashid Hussain Puneet Gupta hod (e&c deptt.) elelctronics &comm. 1 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION GSM ARCHITECTURE INDEX SR.NO. CONTENTS PAGE NO. 1. Certificate 1.................................................................................. 4 2. Certificate 2.................................................................................. 5 3. Acknowledgement........................................................................ 6 4. Preface................................................................................ .......... 7 5. Declaration.................................................................................... 8 6. Company Profile........................................................................... 9-10 7. History of GSM............................................................................ 11-12 8. GSM System Specification........................................................... 13-14 i. Frequency Ranges 9. GSM Abbreviations...................................................................... 15-19 10. Some Facts about GSM................................................................ 20 i. Access Method ii. Narrow Band Vs Broad Band iii. Performance Characteristics Of GSM 11. GSM Services............................................................................... -

Ts 132 423 V12.1.0 (2015-01)
ETSI TS 132 423 V12.1.0 (2015-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Telecommunication management; Subscriber and equipment trace; Trace data definition and management (3GPP TS 32.423 version 12.1.0 Release 12) 3GPP TS 32.423 version 12.1.0 Release 12 1 ETSI TS 132 423 V12.1.0 (2015-01) Reference RTS/TSGS-0532423vc10 Keywords GSM,LTE,UMTS ETSI 650 Route des Lucioles F-06921 Sophia Antipolis Cedex - FRANCE Tel.: +33 4 92 94 42 00 Fax: +33 4 93 65 47 16 Siret N° 348 623 562 00017 - NAF 742 C Association à but non lucratif enregistrée à la Sous-Préfecture de Grasse (06) N° 7803/88 Important notice The present document can be downloaded from: http://www.etsi.org The present document may be made available in electronic versions and/or in print. The content of any electronic and/or print versions of the present document shall not be modified without the prior written authorization of ETSI. In case of any existing or perceived difference in contents between such versions and/or in print, the only prevailing document is the print of the Portable Document Format (PDF) version kept on a specific network drive within ETSI Secretariat. Users of the present document should be aware that the document may be subject to revision or change of status. Information on the current status of this and other ETSI documents is available at http://portal.etsi.org/tb/status/status.asp If you find errors in the present document, please send your comment to one of the following services: http://portal.etsi.org/chaircor/ETSI_support.asp Copyright Notification No part may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm except as authorized by written permission of ETSI. -

MME Administration Guide, Staros Release 21.24
MME Administration Guide, StarOS Release 21.24 First Published: 2021-06-30 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS. THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY. The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California. NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE. IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.