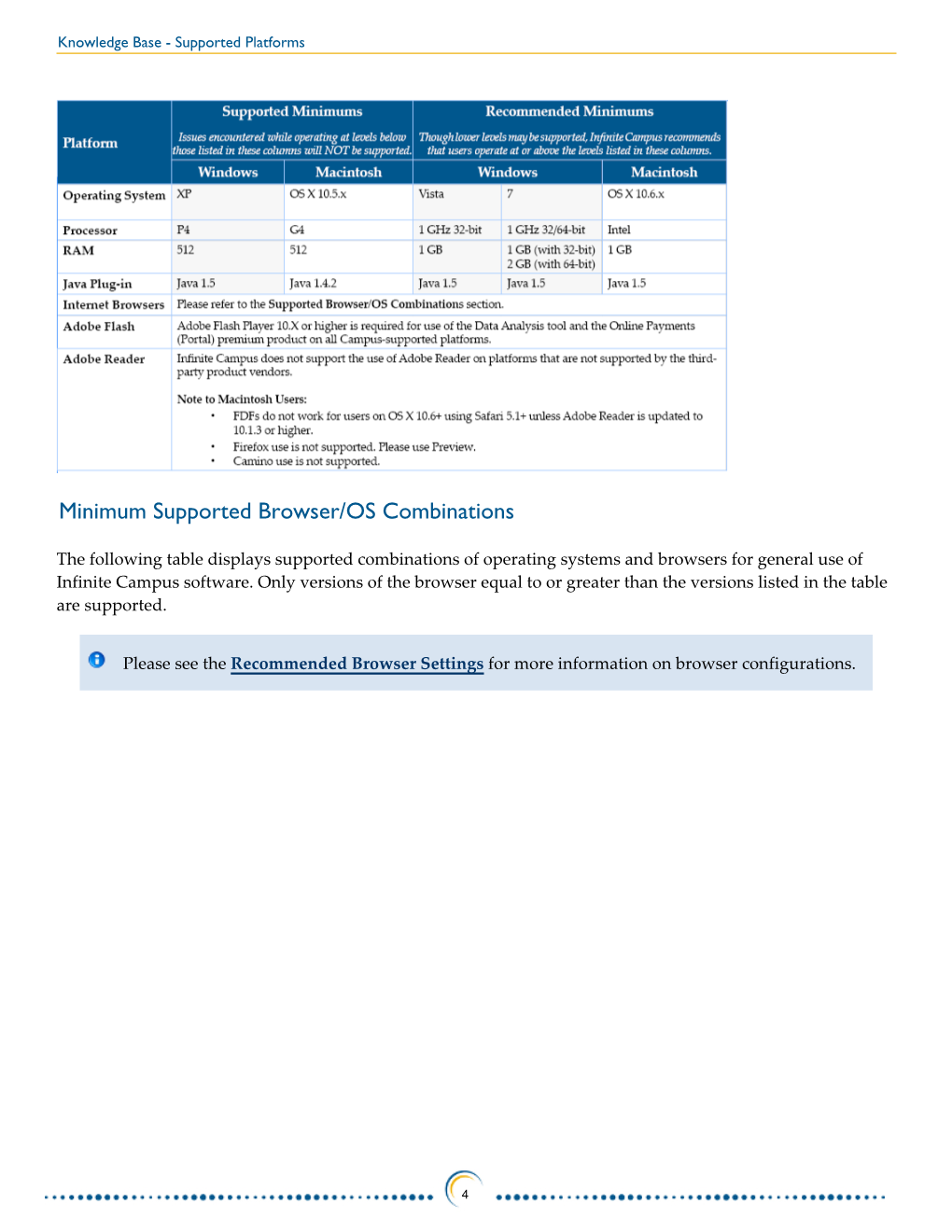
Minimum Supported Browser/OS Combinations
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cache Files Detect and Eliminate Privacy Threats
Award-Winning Privacy Software for OS X Every time you surf the web or use your computer, bits of Recover Disk Space data containing sensitive information are left behind that Over time, the files generated by web browsers can start could compromise your privacy. PrivacyScan provides to take up a large amount of space on your hard drive, protection by scanning for these threats and offers negatively impacting your computer’s performance. multiple removal options to securely erase them from PrivacyScan can locate and removes these space hogs, your system. freeing up valuable disk space and giving your system a speed boost in the process. PrivacyScan can seek and destroy internet files used for tracking your online whereabouts, including browsing history, cache files, cookies, search history, and more. Secure File Shredding Additionally, PrivacyScan can eliminate Flash Cookies, PrivacyScan utilizes advanced secure delete algorithms which are normally hidden away on your system. that meet and exceed US Department of Defense recommendations to ensure complete removal of Privacy Threat: Cookies sensitive data. Cookies can be used to track your usage of websites, determining which pages you visited and the length Intuitive Interface of time you spent on each page. Advertisers can use PrivacyScan’s award-winning design makes it easy to cookies to track you across multiple sites, building up track down privacy threats that exist on your system and a “profile” of who you are based on your web browsing quickly eliminate them. An integrated setup assistant and habits. tip system provide help every step of the way to make file cleaning a breeze. -

Kemble Z3 Ephemera Collection
http://oac.cdlib.org/findaid/ark:/13030/c818377r No online items Kemble Ephemera Collection Z3 Finding aid prepared by Jaime Henderson California Historical Society 678 Mission Street San Francisco, CA, 94105-4014 (415) 357-1848 [email protected] 2013 Kemble Ephemera Collection Z3 Kemble Z3 1 Title: Kemble Z3 Ephemera Collection Date (inclusive): 1802-2013 Date (bulk): 1900-1970 Collection Identifier: Kemble Z3 Extent: 185 boxes, 19 oversize boxes, 4 oversize folder (137 linear feet) Repository: California Historical Society 678 Mission Street San Francisco, CA 94105 415-357-1848 [email protected] URL: http://www.californiahistoricalsociety.org Location of Materials: Collection is stored onsite. Language of Materials: Collection materials are primarily in English. Abstract: The collection comprises a wide variety of ephemera pertaining to printing practice, culture, and history in the Western Hemisphere. Dating from 1802 to 2013, the collection includes ephemera created by or relating to booksellers, printers, lithographers, stationers, engravers, publishers, type designers, book designers, bookbinders, artists, illustrators, typographers, librarians, newspaper editors, and book collectors; bookselling and bookstores, including new, used, rare and antiquarian books; printing, printing presses, printing history, and printing equipment and supplies; lithography; type and type-founding; bookbinding; newspaper publishing; and graphic design. Types of ephemera include advertisements, announcements, annual reports, brochures, clippings, invitations, trade catalogs, newspapers, programs, promotional materials, prospectuses, broadsides, greeting cards, bookmarks, fliers, business cards, pamphlets, newsletters, price lists, bookplates, periodicals, posters, receipts, obituaries, direct mail advertising, book catalogs, and type specimens. Materials printed by members of Moxon Chappel, a San Francisco-area group of private press printers, are extensive. Access Collection is open for research. -

HTTP Cookie - Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia 14/05/2014
HTTP cookie - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 14/05/2014 Create account Log in Article Talk Read Edit View history Search HTTP cookie From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Navigation A cookie, also known as an HTTP cookie, web cookie, or browser HTTP Main page cookie, is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored in a Persistence · Compression · HTTPS · Contents user's web browser while the user is browsing that website. Every time Request methods Featured content the user loads the website, the browser sends the cookie back to the OPTIONS · GET · HEAD · POST · PUT · Current events server to notify the website of the user's previous activity.[1] Cookies DELETE · TRACE · CONNECT · PATCH · Random article Donate to Wikipedia were designed to be a reliable mechanism for websites to remember Header fields Wikimedia Shop stateful information (such as items in a shopping cart) or to record the Cookie · ETag · Location · HTTP referer · DNT user's browsing activity (including clicking particular buttons, logging in, · X-Forwarded-For · Interaction or recording which pages were visited by the user as far back as months Status codes or years ago). 301 Moved Permanently · 302 Found · Help 303 See Other · 403 Forbidden · About Wikipedia Although cookies cannot carry viruses, and cannot install malware on 404 Not Found · [2] Community portal the host computer, tracking cookies and especially third-party v · t · e · Recent changes tracking cookies are commonly used as ways to compile long-term Contact page records of individuals' browsing histories—a potential privacy concern that prompted European[3] and U.S. -

How to Check Your Browser Version on a PC
How to Check Your Browser Version on a PC Google Chrome (PC) 1) Click on the Menu Icon ( ) in the upper right corner of your browser window. 2) Click on Settings 3) Click on the About tab on the left-hand side of the page. 4) If you are not running the most recent version of Chrome available for your Operating System, you will be prompted to update Chrome. For your security, we recommend that you install all Security, App and Operating System updates as they become available. Mozilla Firefox (PC) 1) Click on the Help menu at the top of your browser window. 2) Click on About Firefox at the bottom of the menu. 3) A small window will pop up showing your Firefox version number, and will tell you whether you are on the most recent version, or not. For your security, we recommend that you install all Security, App and Operating System updates as they become available. Internet Explorer (PC) 1) Click on the Gear Icon at the top of your browser window. 2) Click on the About Internet Explorer option. 3) A window will pop up showing you your Internet Explorer version. 4) If you are using Internet Explorer 9 or 10, you will need to make sure that you have TLS 1.2 enabled by: A) Clicking on the Gear Icon again. B) Click on Internet Options. C) Click on the Advanced Tab and scroll down to the option titled “Use TLS 1.2”. (This should be found at the bottome of the list of options.) The box next to this should be checked. -

Discontinued Browsers List
Discontinued Browsers List Look back into history at the fallen windows of yesteryear. Welcome to the dead pool. We include both officially discontinued, as well as those that have not updated. If you are interested in browsers that still work, try our big browser list. All links open in new windows. 1. Abaco (discontinued) http://lab-fgb.com/abaco 2. Acoo (last updated 2009) http://www.acoobrowser.com 3. Amaya (discontinued 2013) https://www.w3.org/Amaya 4. AOL Explorer (discontinued 2006) https://www.aol.com 5. AMosaic (discontinued in 2006) No website 6. Arachne (last updated 2013) http://www.glennmcc.org 7. Arena (discontinued in 1998) https://www.w3.org/Arena 8. Ariadna (discontinued in 1998) http://www.ariadna.ru 9. Arora (discontinued in 2011) https://github.com/Arora/arora 10. AWeb (last updated 2001) http://www.amitrix.com/aweb.html 11. Baidu (discontinued 2019) https://liulanqi.baidu.com 12. Beamrise (last updated 2014) http://www.sien.com 13. Beonex Communicator (discontinued in 2004) https://www.beonex.com 14. BlackHawk (last updated 2015) http://www.netgate.sk/blackhawk 15. Bolt (discontinued 2011) No website 16. Browse3d (last updated 2005) http://www.browse3d.com 17. Browzar (last updated 2013) http://www.browzar.com 18. Camino (discontinued in 2013) http://caminobrowser.org 19. Classilla (last updated 2014) https://www.floodgap.com/software/classilla 20. CometBird (discontinued 2015) http://www.cometbird.com 21. Conkeror (last updated 2016) http://conkeror.org 22. Crazy Browser (last updated 2013) No website 23. Deepnet Explorer (discontinued in 2006) http://www.deepnetexplorer.com 24. Enigma (last updated 2012) No website 25. -

Tutorial URL Manager Pro Tutorial
Tutorial URL Manager Pro Tutorial Version 3.3 Summer 2004 WWW http://www.url-manager.com Email mailto:[email protected] Copyright © 2004 Alco Blom All Rights Reserved - 1 - Tutorial Installation Requirements URL Manager Pro 3.3 requires Mac OS X 10.2 or higher. On Mac OS X 10.1 you can use URL Manager Pro 3.1.1. URL Manager Pro 2.8 is still available for Mac OS 8 users. The bundle size of URL Manager Pro 3.3 is around 8 MB, including this user manual and localizations for English, Japanese, German, French, Spanish and Italian, which are all included in the default package. Installing Installation is very easy, just move URL Manager Pro into the Applications folder. To start using URL Manager Pro, simply double-click the application icon. Optional: You may want to install the Add Bookmark Contextual Menu Item plug-in. The Add Bookmark plug-in can be installed using the URLs tab of the Preferences Window of URL Manager Pro. The plug-in will then be copied to: ~/Library/Contextual Menu Items/ Where ~ is the customary Unix shorthand to indicate the user's home directory. For more information, go to the Add Bookmark Web page or the Contextual Menu Item section in the Special Features chapter. The Bookmark Menu Extra While URL Manager Pro is running, it automatically adds the Bookmark Menu Extra to the menu bar. With the Bookmark Menu Extra you have access to your bookmarks from within any application, including your web browser. The Bookmark Menu Extra is located in the right part of your menu bar (see below). -

One Page Series: Mac OS X -- Ipv6 and Browsing the Web Via Firefox, Camino, Opera and Safari
One Page Series: Mac OS X -- IPv6 and Browsing the Web Via Firefox, Camino, Opera and Safari [If you haven t already done so, begin with One Page Series: Mac OS X -- Enabling Native IPv6 Via Stateless Autoconfiguration ] If you don t already have Firefox on your Mac, you can download it for free from http://www.mozilla.com/firefox/ If you don t already have Camino on your Mac, you can download it for free from http://caminobrowser.org/ If you don t already have Opera on your Mac, you can download it for free from http://www.opera.com/ Safari is another option, bundled for free with Mac OS X. You can find Safari in your Mac s Applications folder. Browsing the IPv6 Web With Firefox (or Camino) Firefox (and Camino) are both IPv6 aware, but need one tweak to work properly with IPv6. Launch Firefox (or Camino) and go to about:config Filter on ipv6 Click on network.dns.disableIPv6 to set the value for that preference item to false You only need to adjust this setting once -- it will be remembered from then on Now try using IPv6 by going to http://ipv6.google.com/ You should see a dancing Google Browsing the IPv6 Web With Opera Opera is all set to work with IPv6 web sites, just launch Opera and stick in an IPv6 URL and Opera will go to that site. Browsing the IPv6 Web With Safari There is one key thing to know about Safari and IPv6, and that is that in some versions of OS X and Safari, it likes IPv4 more than it likes IPv6. -

Web Browsers
WEB BROWSERS Page 1 INTRODUCTION • A Web browser acts as an interface between the user and Web server • Software application that resides on a computer and is used to locate and display Web pages. • Web user access information from web servers, through a client program called browser. • A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web Page 2 FEATURES • All major web browsers allow the user to open multiple information resources at the same time, either in different browser windows or in different tabs of the same window • A refresh and stop buttons for refreshing and stopping the loading of current documents • Home button that gets you to your home page • Major browsers also include pop-up blockers to prevent unwanted windows from "popping up" without the user's consent Page 3 COMPONENTS OF WEB BROWSER 1. User Interface • this includes the address bar, back/forward button , bookmarking menu etc 1. Rendering Engine • Rendering, that is display of the requested contents on the browser screen. • By default the rendering engine can display HTML and XML documents and images Page 4 HISTROY • The history of the Web browser dates back in to the late 1980s, when a variety of technologies laid the foundation for the first Web browser, WorldWideWeb, by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991. • Microsoft responded with its browser Internet Explorer in 1995 initiating the industry's first browser war • Opera first appeared in 1996; although it have only 2% browser usage share as of April 2010, it has a substantial share of the fast-growing mobile phone Web browser market, being preinstalled on over 40 million phones. -

Why Websites Can Change Without Warning
Why Websites Can Change Without Warning WHY WOULD MY WEBSITE LOOK DIFFERENT WITHOUT NOTICE? HISTORY: Your website is a series of files & databases. Websites used to be “static” because there were only a few ways to view them. Now we have a complex system, and telling your webmaster what device, operating system and browser is crucial, here’s why: TERMINOLOGY: You have a desktop or mobile “device”. Desktop computers and mobile devices have “operating systems” which are software. To see your website, you’ll pull up a “browser” which is also software, to surf the Internet. Your website is a series of files that needs to be 100% compatible with all devices, operating systems and browsers. Your website is built on WordPress and gets a weekly check up (sometimes more often) to see if any changes have occured. Your site could also be attacked with bad files, links, spam, comments and other annoying internet pests! Or other components will suddenly need updating which is nothing out of the ordinary. WHAT DOES IT LOOK LIKE IF SOMETHING HAS CHANGED? Any update to the following can make your website look differently: There are 85 operating systems (OS) that can update (without warning). And any of the most popular roughly 7 browsers also update regularly which can affect your site visually and other ways. (Lists below) Now, with an OS or browser update, your site’s 18 website components likely will need updating too. Once website updates are implemented, there are currently about 21 mobile devices, and 141 desktop devices that need to be viewed for compatibility. -

Software Management Full Installers Guide
Software Management Full Installers Guide Supported Platforms and Applications | Q1 2020 Software Management Full Installers Guide Release 9.5 | Q1 2020 www.kaseya.com 2 Software Management Full Installers Guide Release 9.5 | Q1 2020 Copyright Agreement The purchase and use of all Software and Services is subject to the Agreement as defined in Kaseya’s “Click-Accept” EULATOS as updated from time to time by Kaseya at http://www.kaseya.com/legal.aspx. If Customer does not agree with the Agreement, please do not install, use or purchase any Software and Services from Kaseya as continued use of the Software or Services indicates Customer’s acceptance of the Agreement. www.kaseya.com Software Management Full Installers 3 Guide Release 9.5 | Q1 2020 Contents Installers Available 4 www.kaseya.com 4 Software Management Full Installers Guide Release 9.5 | Q1 2020 Installers Available Title Vendor URL 7-Zip File Archiver (Full Install) for Igor Pavlov http://www.7-zip.org/ Windows Adobe Acrobat Reader DC Adobe http://acrobat.adobe.com/us/en/products/pdf-reader.html (Continuous) (Full Install) for Mac Systems, Inc OS X Adobe Acrobat Reader DC Adobe http://acrobat.adobe.com/us/en/products/pdf-reader.html (Continuous) (de-DE) (Full Install) Systems, Inc for Windows Adobe Acrobat Reader DC Adobe http://acrobat.adobe.com/us/en/products/pdf-reader.html (Continuous) (en-US) (Full Install) Systems, Inc for Windows Adobe Acrobat Reader DC Adobe http://acrobat.adobe.com/us/en/products/pdf-reader.html (Continuous) (es-ES) (Full Install) Systems, Inc for Windows -

How to Download and Install Firefox on Windows
How to download and install Firefox on Windows This article explains how to download and install Firefox on Windows using a simplified online installer. (Advanced users: see the For advanced users section at the end of the article.) To update Firefox from a previous version, see Update Firefox to the latest version. Before installing Firefox, see the Firefox System Requirements to make sure that your computer has the required operating system and recommended hardware. 1. Visit this Firefox download page in any browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge. o Alternatively, use this download link for the latest English (U.S.) Firefox version. 2. Click the Download Now button. The Firefox Installer that downloads will automatically offer you the best available version of Firefox for your computer. For example, if you have a 64-bit version of Windows, you are offered the 64-bit version of Firefox (details here). o If you use Microsoft Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge, a notification bar will appear at the bottom of the page with the options to run the installer or save the file to your computer. Click Run to start the process. o In other browsers, you may need to first save the Firefox installer to your computer, then open the file you downloaded. Note: If you see an Open File - Security Warning dialog, click Open or Run . 3. The User Account Control dialog may open, to ask you to allow the Firefox Installer to make changes to your computer. If this dialog appears, click Yes to start the installation. -

Internet Explorer and Firefox: Web Browser Features Comparision and Their Future
https://doi.org/10.48009/2_iis_2007_478-483 INTERNET EXPLORER AND FIREFOX: WEB BROWSER FEATURES COMPARISION AND THEIR FUTURE Siwat Saibua, Texas A&M University-Kingsville, [email protected] Joon-Yeoul Oh, Texas A&M University-Kingsville, [email protected] Richard A. Aukerman, Texas A&M University-Kingsville, [email protected] ABSTRACT Next to Netscape, which was introduced to the Internet technology is one of the utmost inventions of market in 1998, Mozilla Firefox was released in 2004 our era and has contributed significantly in to compete with IE. The software codes of Firefox distributing and collecting data and information. are in the open source format, and any software Effectiveness and efficiency of the process depends developers around the world can put their own ideas on the performance of the web browser. Internet into this browser. As a result, Firefox’s performance Explorer is the leader of the competitive browser effectiveness and efficiency improved every day and market with Mozzilla Fox as its strongest rival, which gained popularity rapidly. has been and is gaining a substantial level of popularity among internet users. Choosing the 100.00% superlative web browser is a difficult task due to the considerably large selection of browser programs and lack of tangible comparison data. This paper 90.00% describes and compares vital features of Internet Firefox Explorer and Mozzilla Firefox, which represent over 90% of the browser market. The performance of each 80.00% IE browser is evaluated based on the general features, operating system support, browser features, protocol 70.00% support and language support.