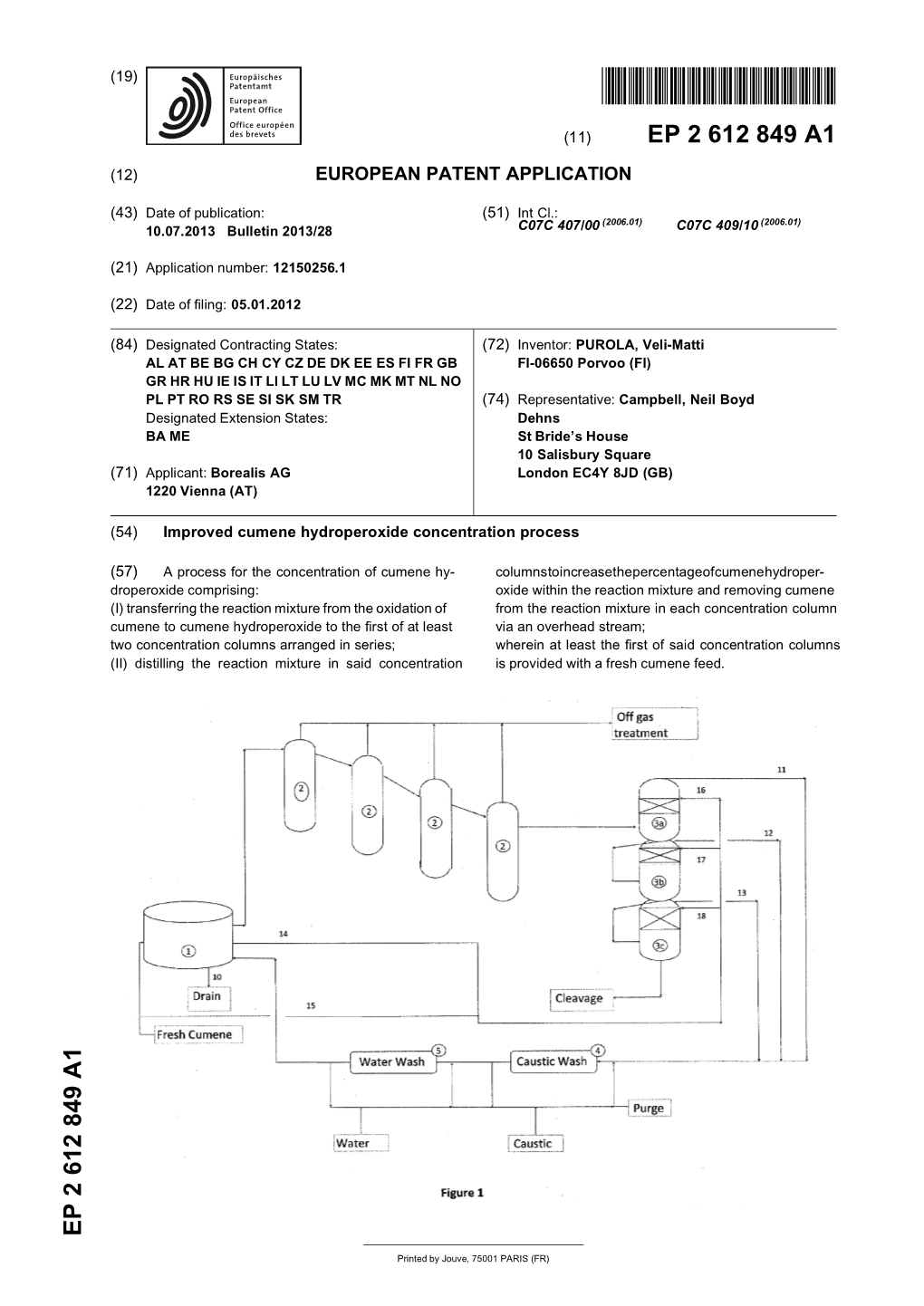
Improved Cumene Hydroperoxide Concentration Process
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Oxidation Processes: Experimental Study and Theoretical Investigations
Oxidation Processes: Experimental Study and Theoretical Investigations By Nada Mohammed Al-Ananzeh A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Chemical Engineering April 2004 Approved by: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Robert Thompson, Ph.D., Advisor Professor of Chemical Engineering Worcester Polytechnic --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- John Bergendahl, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering Worcester Polytechnic Institute -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Fabio H. Ribeiro, Ph.D. Professor of Chemical Engineering Purdue University i Abstract Oxidation reactions are of prime importance at an industrial level and correspond to a huge market. Oxidation reactions are widely practiced in industry and are thoroughly studied in academic and industrial laboratories. Achievements in oxidation process resulted in the development of many new selective oxidation processes. Environmental protection also relies mainly on oxidation reactions. Remarkable results obtained in this field contributed to promote the social image of chemistry which gradually changes from being the enemy of nature to becoming its friend and savior. This study dealt with two aspects regarding oxidation process. The first aspect represented an experimental study for the catalytic -

Process for Preparing Phenol and Acetone from Cumene
Europaisches Patentamt 0 1 64 568 J) European Patent Office Publication number: B1 Office europeen des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION Date of publication of patent specification: 06.07.88 (g) int. ci.4: C 07 C 45/53, C 07 C 37/08, C 07 C 27/00, C 07 C 39/04, Application number: 85105584.8 C 07 C 49/08 Date of filing: 07.05.85 Process for preparing phenol and acetone from cumene. (§) Priority: 24.05.84 US 614124 Proprietor: GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY 1 River Road Schenectady New York 12305 (US) Date of publication of application: 18.12.85 Bulletin 85/51 Inventor: Fulmer, John William 78 Park Ridge Drive Publication of the grant of the patent: Mt. Vernon Indiana 47620 (US) 06.07.88 Bulletin 88/27 Representative: Catherine, Alain Designated Contracting States: General Electric France Service de Propriete DEFRGBIT Industrielle 18 Rue Horace Vernet B.P. 76 F-92134 Issy-les-Moulineaux Cedex (FR) References cited: EP-A-0 008 869 EP-A-0 028 522 EP-A-0028910 EP-A-0 032 255 AT-B-205490 AT-B- 219 029 00 DE-A-2 756026 DE-A-3 222 533 US-A-2715145 US-A-4480134 <0 Note: Within nine months from the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to the European patent granted. Notice of opposition shall shall be deemed have been filed until the opposition fee has been Q. be filed in a written reasoned statement. -

Ni-DOPED Cu-BTC for DIRECT HYDROXYLATION of BENZENE to PHENOL”
1 UNIVERSIDAD DE INVESTIGACIÓN DE TECNOLOGÍA EXPERIMENTAL YACHAY School of Chemical Sciences and Engineering TITTLE: “Ni-DOPED Cu-BTC FOR DIRECT HYDROXYLATION OF BENZENE TO PHENOL”. Trabajo de integración curricular presentado como requisito para la obtención del título de Ingeniero en Polímeros Author: Zenteno Sanchez Jeremee Paul Advisor: PhD Terencio Thibault Urcuquí, September 2019 2 3 4 5 6 Acknowledgments For god, family, and friends. For my family that has always been there to support me every day especially my mother who believes and supports me in the good and bad moments. For my friends and the special people who are an excellent company through these years and the good moments that I shared with them. For all the teachers that teach me in every class, especially Thibault Terencio excellent mentor that support and guiding me throughout the last year of this project. For all of them, thank you so much. 7 Abstract Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are novel materials with vast applications such as catalysis, dye adsorption, drug retention, or gas storage.1 MOFs can retain molecules inside their microporosity or onto its surface due to its 3D structure. One of the main advantages of the MOFs is the chemical diversity present at their surface because they consist of an organic ligand and a metal center. In this case, Copper (II) acts as the metal center and benzene-1, 3, 5 tricarboxylic acid BTC as the organic ligand, to form HKUST-1 (also known as Cu-BTC or MOF-199). Despite the diversity of existing inorganic and organic parts, each MOF usually contains only one type of transition metal. -

Presidential Green Chemistry Challenge Awards Program Summary of 1998 Award Entries and Recipients
awrd98final.qxd 8/24/99 1:13 PM Page a United States Pollution Prevention and EPA744-R-98-001 Environmental Protection Toxics (7406) November 1998 Agency www.epa.gov/greenchemistry 1EPA The Presidential Green Chemistry Challenge Awards Program Summary of 1998 Award Entries and Recipients 2 Printed on paper that contains at least 20 percent postconsumer fiber. awrd98final.qxd 8/24/99 1:13 PM Page i The Presidential Green Chemistry Challenge Awards Program Contents Summary of 1998 Award Entries and Recipients . 1 Awards . 2 Academic Awards . 2 Small Business Award . 4 Alternative Synthetic Pathways Award . 5 Alternative Solvents/Reaction Conditions Award . 6 Designing Safer Chemicals Award . 7 Entries From Academia . 8 Entries From Small Businesses . 27 Entries From Industry and Government . 38 Index . 70 i awrd98final.qxd 8/24/99 1:13 PM Page ii ii awrd98final.qxd 8/24/99 1:13 PM Page 1 The Presidential Green Chemistry Challenge Awards Program Summary of 1998 Award Entries and Recipients President Clinton announced the Green Chemistry Challenge on March 16, 1995, as one of his Reinventing Environmental Regulations Initiatives. According to President Clinton, the Green Chemistry Challenge was established to “promote pollution prevention and indus- trial ecology through a new U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Design for the Environment partnership with the chemical industry.” More specifically, the program was established to recognize and support fundamental and innovative chemical methodolo- gies that are useful to industry and that accomplish pollution prevention through source reduction. EPA Administrator Carol Browner announced the Green Chemistry Challenge Awards Program on October 30, 1995. -

Acetone from Singapore and Spain
CONTENTS Page Determinations .............................................................................................................................. 1 Views of the Commission ............................................................................................................... 3 Part I: Introduction .............................................................................................................. I-1 Background ................................................................................................................................ I-1 Statutory criteria ....................................................................................................................... I-2 Organization of report ............................................................................................................... I-3 Market summary ....................................................................................................................... I-3 Summary data and data sources ............................................................................................... I-4 Previous and related investigations .......................................................................................... I-4 Nature and extent of sales at LTFV ........................................................................................... I-5 Sales at LTFV .......................................................................................................................... I-5 The subject merchandise ......................................................................................................... -

Page 1-21.FH10
CHAPTER I GENERAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER I GENERAL INTRODUCTION 1.1 Alkylation Reactions of Aromatic Hydrocarbons: The importance of alkylation in organic preparations was realized as early as 1877 with the reaction of benzene and amyl chloride, to produce amyl benzene, by Charles Friedel and James Mason Crafts-^. This was apparently the first typical alkylation reaction and came to be known as the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction. Friedel-Crafts reactions now find a number of industrial applications such as m the manufacture of high octane gasoline, synthetic rubber, plastics, synthetic fibers, synthetic detergents etc. Besides its commercial importance, the area of organic chemistry dealing with this reaction encompasses classic examples of some of the most interesting aspects of modern organic chemistry: electrophilic aromatic substitution, carbocation formation and rearrangement. In the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the alkylating or acylating agent and the catalyst, such as aluminium chloride and hydrogen chloride, react to form either carbonium or acylium ion or complex. The ion or complex then attacks the aromatic ring^. Thus in the alkylation of olefins in the presence of the catalyst, the following reactions take place. R-CH=CHo+ AICI^ + HCI R-CH-CH3AlC I4 CH-CH3 r -1- + R-CH-CH3AICI4 AlCl ^ +AICI4 + HCl The aromatic ring to which the olefin gets attached may be that of benzene, substituted benzene or more complicated ring systems like naphthalene or anthracene. Friedel-Crafts reactions are complicated by the rearrangement of the attacking agent and in some cases of the aromatic starting materials . There is a tendency for a carbonium ion formed during the reaction, to rearrange to a stable secondary or tertiary carbonium ion. -

Immediate Hydroxylation of Arenes to Phenols Via V-Containing All-Silica ZSM-22 Zeolite Triggered Non-Radical Mechanism
ARTICLE DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05351-w OPEN Immediate hydroxylation of arenes to phenols via V-containing all-silica ZSM-22 zeolite triggered non-radical mechanism Yu Zhou1, Zhipan Ma1, Junjie Tang1, Ning Yan 2, Yonghua Du 3, Shibo Xi3, Kai Wang1, Wei Zhang1, Haimeng Wen1 & Jun Wang1 – 1234567890():,; Hydroxylation of arenes via activation of aromatic Csp2 H bond has attracted great attention for decades but remains a huge challenge. Herein, we achieve the ring hydroxylation of various arenes with stoichiometric hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into the corresponding phenols on a robust heterogeneous catalyst series of V–Si–ZSM-22 (TON type vanadium silicalite zeolites) that is straightforward synthesized from an unusual ionic liquid involved dry-gel- conversion route. For benzene hydroxylation, the phenol yield is 30.8% (selectivity >99%). Ring hydroxylation of mono-/di-alkylbenzenes and halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons cause the yields up to 26.2% and selectivities above 90%. The reaction is completed within 30 s, the fastest occasion so far, resulting in ultra-high turnover frequencies (TOFs). Sys- tematic characterization including 51V NMR and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analyses suggest that such high activity associates with the unique non-radical hydroxylation mechanism arising from the in situ created diperoxo V(IV) state. 1 State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering, College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University (former Nanjing University of Technology), Nanjing 210009, P.R. China. 2 Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore 117585, Singapore. 3 Institute of Chemical and Engineering Sciences, 1 Pesek Road, Jurong Island, Singapore 627833, Singapore. -

Process for Preparing Phenol and Acetone from Cumene
Patentamt JEuropSischesEuropean Patent Office (5) Publication number: 0 164 568 Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION @ Application number: 85105584.8 © mt.ci.4: C 07 C 45/53 C 07 C 37/08, C 07 C 27/00 © Date of filing: 07.05.85 C 07 C 39/04, C 07 C 49/08 (S3) Priority: 24.05.84 US 614124 © Applicant: GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY 1 River Road Schenectady New York 12305(US) © Date of publication of application: 18.12.85 Bulletin 85/51 @ Inventor: Fulmer, John William 78 Park Ridge Drive © Designated Contracting States: Mfc Vernon Indiana 47620IUS) DE FR GB rr © Representative: Catherine, Alain General Electric - Deutschland Munich Patent Operations Frauenstrasse 32 D-8000Munchen5(DE) @ Process for preparing phenol and acetone from cumene. Benzene, toluene and ethylbenzene is removed from the heavy residues of a phenol distillation in a phenol and ace- tone from cumene process. r- DO S BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Phenol is a basic commodity chemical with many end uses. Most of the phenol manufactured is prepared from isopropyl benzene, hereafter referred to as cumene. The reaction sequence is short and entails the follow- ing steps: 1. Air oxidation of cumene to give cumene hydro- peroxide. 2. Acid cleavage of the hydroperoxide to provide phenol and acetone. The phenol and acetone are separated and each one purified to the degree necessary to satisfy its ulti- mate use. As is readily observed, for every mole of phenol that is produced, a mole of acetone is also theoretically produced. Acetone is also a commodity chemical with various end uses. -

Phenol/Acetone/Cumene December 2015 Report Contents
Phenol/Acetone/Cumene December 2015 Report Contents Phenol/Acetone/Cumene Table of Contents A Report by NexantThinking™ Process Evaluation/Research Planning (PERP) Program PERP Report 2015-6 – Published December 2015 www.nexantthinking.com Section Page 1 Executive Summary ............................................................................................................... 1 1.1 INDUSTRY OVERVIEW AND TECHNOLOGY LICENSORS ................................... 1 1.2 BUSINESS AND STRATEGIC ANALYSIS REVIEW ................................................ 2 1.3 COMMERCIAL PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGIES ................................................... 4 Cumene Consumption.................................................................................. 4 Selection of Phenol Technologies by Customers for Grassroots and Retrofitting Projects ...................................................................................... 6 1.4 ALTERNATIVE AND “DEVELOPING” TECHNOLOGIES ........................................ 7 SBB to Phenol Process ................................................................................ 7 Benzene Oxidation (with Nitrous Oxide) to Phenol Process ........................ 7 Green Technology Developments ................................................................ 8 1.5 PROCESS ECONOMICS.......................................................................................... 9 Sensitivity Analyses ...................................................................................... 10 Concluding Remarks ................................................................................... -

(C2 & C3) Olefins in Liquid Phase Epoxidation Systems and Experimental Determination
Modeling of the phase behavior of light (C2 & C3) olefins in liquid phase epoxidation systems and experimental determination of gas/liquid mass transfer coefficients By Madhav Ghanta Submitted to the graduate degree program in Chemical Engineering and Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas. in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Masters of Science ________________________________ Dr. Bala Subramaniam, Committee Chairman _____________________________________ Dr. Daryle H. Busch, Committee Member _____________________________________ Dr. R. V. Chaudhari, Committee Member _____________________________________ Date Thesis Defended The thesis committee for Madhav Ghanta certifies that this is the approved version of this thesis Modeling of the phase behavior of light (C2 &C3) olefins in liquid phase epoxidation systems and experimental determination of gas/liquid mass transfer coefficients Committee: _________________________________ Dr. Bala Subramaniam, Committee Chairman* ______________________________________ Dr. Daryle H. Busch, Committee Member* ______________________________________ Dr. R. V. Chaudhari, Committee Member ______________________________________ Date Thesis Defended i ABSTRACT Conventional technologies for the selective epoxidation of olefins such as ethylene and propylene to form their corresponding epoxides are either non selective and/or produce much waste. A novel biphasic process for the epoxidation of olefins has been developed by the researchers at Center for Environmentally Beneficial -
![Cumene Hydroperoxide [80-15-9]](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/9185/cumene-hydroperoxide-80-15-9-3939185.webp)
Cumene Hydroperoxide [80-15-9]
Cumene Hydroperoxide [80-15-9] Review of Toxicological Literature Prepared for Errol Zeiger, Ph.D. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences P.O. Box 12233 Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709 Contract No. N01-ES-65402 Submitted by Raymond Tice, Ph.D. (Principal Investigator) Brigette Brevard, M.A. (Co-Principal Investigator) Integrated Laboratory Systems P.O. Box 13501 Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709 September 1998 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Cumene hydroperoxide was identified by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences as a possible candidate for toxicity and carcinogenicity testing. Cumene hydroperoxide is produced at ~130°C via the oxidation of cumene with air in the presence of aqueous sodium carbonate as a catalyst and is analyzed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Thirteen companies have been identified as producers of cumene hydroperoxide in the United States. In 1985, ~1.1 million pounds (514,000 kg) were produced in the United States. About 7 billion pounds of cumene hydroperoxide are consumed yearly in the United States, indicating that the majority of cumene hydroperoxide used is imported. No current data on import volumes were located. Over 95% of the cumene hydroperoxide produced in this country is used in the production of acetone and phenol. Additional applications include use as a catalyst, a curing agent, and as an initiator for polymerization. Cumene hydroperoxide may enter the environment from industrial discharges and spills, and also as a by-product of fuel oil slicks exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. It has been found in rivers and wastewaters in Illinois, Delaware, and Pennsylvania at levels as high as 0.25 ppm. -

Phenol and Cumene Process Summary
IHS Chemical Process Economics Program Review 2013-11 Phenol and Cumene Process Summary By Girish Ballal December 2013 ihs.com/chemical IHS Chemical Process Economics Program | Review 2013-11 IHS Chemical agrees to assign professionally qualified personnel to the preparation of the Process Economics Program’s reports and will perform the work in conformance with generally accepted professional standards. No other warranties expressed or implied are made. Because the reports are of an advisory nature, neither IHS Chemical nor its employees will assume any liability for the special or consequential damages arising from the Client’s use of the results contained in the reports. The Client agrees to indemnify, defend, and hold IHS Chemical, its officers, and employees harmless from any liability to any third party resulting directly or indirectly from the Client’s use of the reports or other deliverables produced by IHS Chemical pursuant to this agreement. For detailed marketing data and information, the reader is referred to one of the IHS Chemical programs specializing in marketing research. THE IHS CHEMICAL ECONOMICS HANDBOOK Program covers most major chemicals and chemical products produced throughout the world. In addition the IHS DIRECTORY OF CHEMICAL PRODUCERS services provide detailed lists of chemical producers by company, product, and plant for the United States, Europe, East Asia, China, India, South & Central America, the Middle East & Africa, Canada, and Mexico. December 2013 © 2013 IHS IHS Chemical Process Economics Program | Review 2013-11 PEP Review 2013-11 Phenol and Cumene Process Summary By Girish Ballal December 2013 Abstract Phenol is an important chemical intermediate, which is mostly consumed in the production of phenolic resins and polycarbonates via bisphenol A.