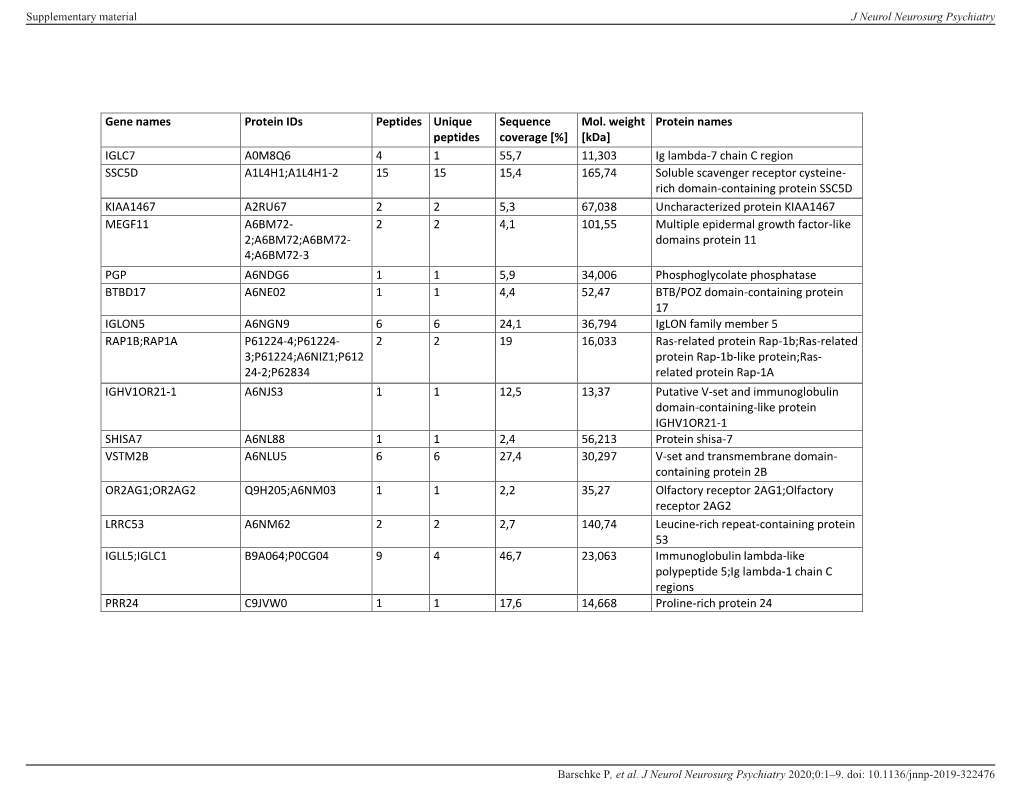
Protein Names IGLC7 A0M8Q6 4 1 55,7 11,3
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Supplemental Figure 1. Vimentin
Double mutant specific genes Transcript gene_assignment Gene Symbol RefSeq FDR Fold- FDR Fold- FDR Fold- ID (single vs. Change (double Change (double Change wt) (single vs. wt) (double vs. single) (double vs. wt) vs. wt) vs. single) 10485013 BC085239 // 1110051M20Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1110051M20 gene // 2 E1 // 228356 /// NM 1110051M20Ri BC085239 0.164013 -1.38517 0.0345128 -2.24228 0.154535 -1.61877 k 10358717 NM_197990 // 1700025G04Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1700025G04 gene // 1 G2 // 69399 /// BC 1700025G04Rik NM_197990 0.142593 -1.37878 0.0212926 -3.13385 0.093068 -2.27291 10358713 NM_197990 // 1700025G04Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1700025G04 gene // 1 G2 // 69399 1700025G04Rik NM_197990 0.0655213 -1.71563 0.0222468 -2.32498 0.166843 -1.35517 10481312 NM_027283 // 1700026L06Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1700026L06 gene // 2 A3 // 69987 /// EN 1700026L06Rik NM_027283 0.0503754 -1.46385 0.0140999 -2.19537 0.0825609 -1.49972 10351465 BC150846 // 1700084C01Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1700084C01 gene // 1 H3 // 78465 /// NM_ 1700084C01Rik BC150846 0.107391 -1.5916 0.0385418 -2.05801 0.295457 -1.29305 10569654 AK007416 // 1810010D01Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1810010D01 gene // 7 F5 // 381935 /// XR 1810010D01Rik AK007416 0.145576 1.69432 0.0476957 2.51662 0.288571 1.48533 10508883 NM_001083916 // 1810019J16Rik // RIKEN cDNA 1810019J16 gene // 4 D2.3 // 69073 / 1810019J16Rik NM_001083916 0.0533206 1.57139 0.0145433 2.56417 0.0836674 1.63179 10585282 ENSMUST00000050829 // 2010007H06Rik // RIKEN cDNA 2010007H06 gene // --- // 6984 2010007H06Rik ENSMUST00000050829 0.129914 -1.71998 0.0434862 -2.51672 -

Peking University-Juntendo University Joint Symposium on Cancer Research and Treatment ADAM28 (A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 28) in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Progression
Whatʼs New from Juntendo University, Tokyo Juntendo Medical Journal 2017. 63(5), 322-325 Peking University - Juntendo University Joint Symposium on Cancer Research and Treatment ADAM28 (a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 28) in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Progression YASUNORI OKADA* *Department of Pathophysiology for Locomotive and Neoplastic Diseases, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan A disintegrinandmetalloproteinase 28 (ADAM28) is overexpressedpredominantlyby carcinoma cells in more than 70% of the non-small cell lung carcinomas, showing positive correlations with carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis. ADAM28 cleaves insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in the IGF-I/IGFBP-3 complex, leading to stimulation of cell proliferation by intact IGF-I released from the complex. ADAM28 also degrades von Willebrand factor (VWF), which induces apoptosis in human carcinoma cell lines with negligible ADAM28 expression, andthe VWF digestionby ADAM28-expressing carcinoma cells facilitates them to escape from VWF-induced apoptosis, resulting in promotion of metastasis. We have developed human antibodies against ADAM28 andshown that one of them significantly inhibits tumor growth andmetastasis using lung adenocarcinoma cells. Our data suggest that ADAM28 may be a new molecular target for therapy of the patients with ADAM28-expressing non-small cell lung carcinoma. Key words: a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 28 (ADAM28), cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, human antibody inhibitor Introduction human cancers 2). However, development of the synthetic inhibitors of MMPs andtheir application Cancer cell proliferation andprogression are for treatment of the cancer patients failed 3). modulated by proteolytic cleavage of tissue micro- On the other hand, members of the ADAM (a environmental factors such as extracellular matrix disintegrin and metalloproteinase) gene family, (ECM), growth factors andcytokines, receptors another family belonging to the metzincin gene andcell adhesionmolecules. -

Human ADAM12 Quantikine ELISA
Quantikine® ELISA Human ADAM12 Immunoassay Catalog Number DAD120 For the quantitative determination of A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase domain- containing protein 12 (ADAM12) concentrations in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma, and urine. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE INTRODUCTION .....................................................................................................................................................................1 PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY ...................................................................................................................................................2 LIMITATIONS OF THE PROCEDURE .................................................................................................................................2 TECHNICAL HINTS .................................................................................................................................................................2 MATERIALS PROVIDED & STORAGE CONDITIONS ...................................................................................................3 OTHER SUPPLIES REQUIRED .............................................................................................................................................3 PRECAUTIONS .........................................................................................................................................................................4 -

Quantikine® ELISA
Quantikine® ELISA Human ADAMTS13 Immunoassay Catalog Number DADT130 For the quantitative determination of human A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with Thombospondin type 1 motif, 13 (ADAMTS13) concentrations in cell culture supernates, serum, and plasma. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE INTRODUCTION .....................................................................................................................................................................1 PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY ...................................................................................................................................................2 LIMITATIONS OF THE PROCEDURE .................................................................................................................................2 TECHNICAL HINTS .................................................................................................................................................................2 MATERIALS PROVIDED & STORAGE CONDITIONS ...................................................................................................3 OTHER SUPPLIES REQUIRED .............................................................................................................................................4 PRECAUTIONS .........................................................................................................................................................................4 -

Defining Functional Interactions During Biogenesis of Epithelial Junctions
ARTICLE Received 11 Dec 2015 | Accepted 13 Oct 2016 | Published 6 Dec 2016 | Updated 5 Jan 2017 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13542 OPEN Defining functional interactions during biogenesis of epithelial junctions J.C. Erasmus1,*, S. Bruche1,*,w, L. Pizarro1,2,*, N. Maimari1,3,*, T. Poggioli1,w, C. Tomlinson4,J.Lees5, I. Zalivina1,w, A. Wheeler1,w, A. Alberts6, A. Russo2 & V.M.M. Braga1 In spite of extensive recent progress, a comprehensive understanding of how actin cytoskeleton remodelling supports stable junctions remains to be established. Here we design a platform that integrates actin functions with optimized phenotypic clustering and identify new cytoskeletal proteins, their functional hierarchy and pathways that modulate E-cadherin adhesion. Depletion of EEF1A, an actin bundling protein, increases E-cadherin levels at junctions without a corresponding reinforcement of cell–cell contacts. This unexpected result reflects a more dynamic and mobile junctional actin in EEF1A-depleted cells. A partner for EEF1A in cadherin contact maintenance is the formin DIAPH2, which interacts with EEF1A. In contrast, depletion of either the endocytic regulator TRIP10 or the Rho GTPase activator VAV2 reduces E-cadherin levels at junctions. TRIP10 binds to and requires VAV2 function for its junctional localization. Overall, we present new conceptual insights on junction stabilization, which integrate known and novel pathways with impact for epithelial morphogenesis, homeostasis and diseases. 1 National Heart and Lung Institute, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. 2 Computing Department, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. 3 Bioengineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. 4 Department of Surgery & Cancer, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. -

An Investigation of ADAM-Like Decysin 1 in Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation and Crohn’S Disease
An Investigation of ADAM-like Decysin 1 in Macrophage-mediated Inflammation and Crohn’s Disease By Nuala Roisin O’Shea A thesis submitted to UCL for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Division of Medicine Declaration I, Nuala Roisin O’Shea, confirm that the work presented in this thesis is my own. Where information has been derived from other sources, I confirm that this has been indicated in the thesis. 2 Abstract Crohn’s disease (CD) is now recognised as a defective host response to bacteria in genetically susceptible individuals. The role of innate immunity and impaired bacterial clearance are widely accepted. In this thesis the role of ADAM-like, Decysin-1 (ADAMDEC1) in macrophage-mediated inflammation and gut mucosal immunity is explored. Using transcriptomic analysis of monocyte derived macrophages (MDM) ADAMDEC1 was identified as grossly under expressed in a subset of patients with CD. ADAMDEC1 was found to be highly selective to the intestine, peripheral blood monocyte-derived and lamina propria macrophages. It was shown to be an inflammatory response gene, upregulated in response to bacterial antigens and inflammation. ADAMDEC1 was expressed in prenatal and germ free mice, demonstrating exposure to a bacterial antigen is not a prerequisite for expression. Adamdec1 knock out mice were used to investigate the role of ADAMDEC1 in vivo. Adamdec1-/- mice displayed an increased susceptibility to dextran sodium sulphate (DSS), Citrobacter rodentium and Salmonella typhimurium induced colitis. In Adamdec1-/- mice, bacterial translocation and systemic infection were increased in bacterial models of colitis. These results suggest that individuals with grossly attenuated expression of ADAMDEC1 may be at an increased risk of developing intestinal inflammation as a consequence of an impaired ability to handle enteric bacterial pathogens. -

NICU Gene List Generator.Xlsx
Neonatal Crisis Sequencing Panel Gene List Genes: A2ML1 - B3GLCT A2ML1 ADAMTS9 ALG1 ARHGEF15 AAAS ADAMTSL2 ALG11 ARHGEF9 AARS1 ADAR ALG12 ARID1A AARS2 ADARB1 ALG13 ARID1B ABAT ADCY6 ALG14 ARID2 ABCA12 ADD3 ALG2 ARL13B ABCA3 ADGRG1 ALG3 ARL6 ABCA4 ADGRV1 ALG6 ARMC9 ABCB11 ADK ALG8 ARPC1B ABCB4 ADNP ALG9 ARSA ABCC6 ADPRS ALK ARSL ABCC8 ADSL ALMS1 ARX ABCC9 AEBP1 ALOX12B ASAH1 ABCD1 AFF3 ALOXE3 ASCC1 ABCD3 AFF4 ALPK3 ASH1L ABCD4 AFG3L2 ALPL ASL ABHD5 AGA ALS2 ASNS ACAD8 AGK ALX3 ASPA ACAD9 AGL ALX4 ASPM ACADM AGPS AMELX ASS1 ACADS AGRN AMER1 ASXL1 ACADSB AGT AMH ASXL3 ACADVL AGTPBP1 AMHR2 ATAD1 ACAN AGTR1 AMN ATL1 ACAT1 AGXT AMPD2 ATM ACE AHCY AMT ATP1A1 ACO2 AHDC1 ANK1 ATP1A2 ACOX1 AHI1 ANK2 ATP1A3 ACP5 AIFM1 ANKH ATP2A1 ACSF3 AIMP1 ANKLE2 ATP5F1A ACTA1 AIMP2 ANKRD11 ATP5F1D ACTA2 AIRE ANKRD26 ATP5F1E ACTB AKAP9 ANTXR2 ATP6V0A2 ACTC1 AKR1D1 AP1S2 ATP6V1B1 ACTG1 AKT2 AP2S1 ATP7A ACTG2 AKT3 AP3B1 ATP8A2 ACTL6B ALAS2 AP3B2 ATP8B1 ACTN1 ALB AP4B1 ATPAF2 ACTN2 ALDH18A1 AP4M1 ATR ACTN4 ALDH1A3 AP4S1 ATRX ACVR1 ALDH3A2 APC AUH ACVRL1 ALDH4A1 APTX AVPR2 ACY1 ALDH5A1 AR B3GALNT2 ADA ALDH6A1 ARFGEF2 B3GALT6 ADAMTS13 ALDH7A1 ARG1 B3GAT3 ADAMTS2 ALDOB ARHGAP31 B3GLCT Updated: 03/15/2021; v.3.6 1 Neonatal Crisis Sequencing Panel Gene List Genes: B4GALT1 - COL11A2 B4GALT1 C1QBP CD3G CHKB B4GALT7 C3 CD40LG CHMP1A B4GAT1 CA2 CD59 CHRNA1 B9D1 CA5A CD70 CHRNB1 B9D2 CACNA1A CD96 CHRND BAAT CACNA1C CDAN1 CHRNE BBIP1 CACNA1D CDC42 CHRNG BBS1 CACNA1E CDH1 CHST14 BBS10 CACNA1F CDH2 CHST3 BBS12 CACNA1G CDK10 CHUK BBS2 CACNA2D2 CDK13 CILK1 BBS4 CACNB2 CDK5RAP2 -

Gene Symbol Category ACAN ECM ADAM10 ECM Remodeling-Related ADAM11 ECM Remodeling-Related ADAM12 ECM Remodeling-Related ADAM15 E
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 Gene symbol Category ACAN ECM ADAM10 ECM remodeling-related ADAM11 ECM remodeling-related ADAM12 ECM remodeling-related ADAM15 ECM remodeling-related ADAM17 ECM remodeling-related ADAM18 ECM remodeling-related ADAM19 ECM remodeling-related ADAM2 ECM remodeling-related ADAM20 ECM remodeling-related ADAM21 ECM remodeling-related ADAM22 ECM remodeling-related ADAM23 ECM remodeling-related ADAM28 ECM remodeling-related ADAM29 ECM remodeling-related ADAM3 ECM remodeling-related ADAM30 ECM remodeling-related ADAM5 ECM remodeling-related ADAM7 ECM remodeling-related ADAM8 ECM remodeling-related ADAM9 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS1 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS10 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS12 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS13 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS14 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS15 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS16 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS17 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS18 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS19 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS2 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS20 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS3 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS4 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS5 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS6 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS7 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS8 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTS9 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTSL1 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTSL2 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTSL3 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTSL4 ECM remodeling-related ADAMTSL5 ECM remodeling-related AGRIN ECM ALCAM Cell-cell adhesion ANGPT1 Soluble factors and receptors -

Conservation and Divergence of ADAM Family Proteins in the Xenopus Genome
Wei et al. BMC Evolutionary Biology 2010, 10:211 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2148/10/211 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access ConservationResearch article and divergence of ADAM family proteins in the Xenopus genome Shuo Wei*1, Charles A Whittaker2, Guofeng Xu1, Lance C Bridges1,3, Anoop Shah1, Judith M White1 and Douglas W DeSimone1 Abstract Background: Members of the disintegrin metalloproteinase (ADAM) family play important roles in cellular and developmental processes through their functions as proteases and/or binding partners for other proteins. The amphibian Xenopus has long been used as a model for early vertebrate development, but genome-wide analyses for large gene families were not possible until the recent completion of the X. tropicalis genome sequence and the availability of large scale expression sequence tag (EST) databases. In this study we carried out a systematic analysis of the X. tropicalis genome and uncovered several interesting features of ADAM genes in this species. Results: Based on the X. tropicalis genome sequence and EST databases, we identified Xenopus orthologues of mammalian ADAMs and obtained full-length cDNA clones for these genes. The deduced protein sequences, synteny and exon-intron boundaries are conserved between most human and X. tropicalis orthologues. The alternative splicing patterns of certain Xenopus ADAM genes, such as adams 22 and 28, are similar to those of their mammalian orthologues. However, we were unable to identify an orthologue for ADAM7 or 8. The Xenopus orthologue of ADAM15, an active metalloproteinase in mammals, does not contain the conserved zinc-binding motif and is hence considered proteolytically inactive. We also found evidence for gain of ADAM genes in Xenopus as compared to other species. -

Gene-Expression Signature Regulated by the KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 Axis Is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer Akhileshwar Namani1†, Md
Namani et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:46 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3907-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gene-expression signature regulated by the KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 axis is associated with a poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell cancer Akhileshwar Namani1†, Md. Matiur Rahaman2†, Ming Chen2* and Xiuwen Tang1* Abstract Background: NRF2 is the key regulator of oxidative stress in normal cells and aberrant expression of the NRF2 pathway due to genetic alterations in the KEAP1 (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1)-NRF2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2 like 2)-CUL3 (cullin 3) axis leads to tumorigenesis and drug resistance in many cancers including head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSCC). The main goal of this study was to identify specific genes regulated by the KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 axis in HNSCC patients, to assess the prognostic value of this gene signature in different cohorts, and to reveal potential biomarkers. Methods: RNA-Seq V2 level 3 data from 279 tumor samples along with 37 adjacent normal samples from patients enrolled in the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-HNSCC study were used to identify upregulated genes using two methods (altered KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 versus normal, and altered KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 versus wild-type). We then used a new approach to identify the combined gene signature by integrating both datasets and subsequently tested this signature in 4 independent HNSCC datasets to assess its prognostic value. In addition, functional annotation using the DAVID v6.8 database and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis using the STRING v10 databasewereperformedonthesignature. Results: A signature composed of a subset of 17 genes regulated by the KEAP1-NRF2-CUL3 axis was identified by overlapping both the upregulated genes of altered versus normal (251 genes) and altered versus wild-type (25 genes) datasets. -

Supplementary Table S4. FGA Co-Expressed Gene List in LUAD
Supplementary Table S4. FGA co-expressed gene list in LUAD tumors Symbol R Locus Description FGG 0.919 4q28 fibrinogen gamma chain FGL1 0.635 8p22 fibrinogen-like 1 SLC7A2 0.536 8p22 solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 DUSP4 0.521 8p12-p11 dual specificity phosphatase 4 HAL 0.51 12q22-q24.1histidine ammonia-lyase PDE4D 0.499 5q12 phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific FURIN 0.497 15q26.1 furin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) CPS1 0.49 2q35 carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1, mitochondrial TESC 0.478 12q24.22 tescalcin INHA 0.465 2q35 inhibin, alpha S100P 0.461 4p16 S100 calcium binding protein P VPS37A 0.447 8p22 vacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) SLC16A14 0.447 2q36.3 solute carrier family 16, member 14 PPARGC1A 0.443 4p15.1 peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha SIK1 0.435 21q22.3 salt-inducible kinase 1 IRS2 0.434 13q34 insulin receptor substrate 2 RND1 0.433 12q12 Rho family GTPase 1 HGD 0.433 3q13.33 homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase PTP4A1 0.432 6q12 protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA, member 1 C8orf4 0.428 8p11.2 chromosome 8 open reading frame 4 DDC 0.427 7p12.2 dopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) TACC2 0.427 10q26 transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 MUC13 0.422 3q21.2 mucin 13, cell surface associated C5 0.412 9q33-q34 complement component 5 NR4A2 0.412 2q22-q23 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 EYS 0.411 6q12 eyes shut homolog (Drosophila) GPX2 0.406 14q24.1 glutathione peroxidase -

Proteomic Analysis of Human Osteoarthritis Synovial Fluid
Balakrishnan et al. Clinical Proteomics 2014, 11:6 http://www.clinicalproteomicsjournal.com/content/11/1/6 CLINICAL PROTEOMICS RESEARCH Open Access Proteomic analysis of human osteoarthritis synovial fluid Lavanya Balakrishnan1,2, Raja Sekhar Nirujogi1,3, Sartaj Ahmad1,4, Mitali Bhattacharjee1,5, Srikanth S Manda1,3, Santosh Renuse1,5, Dhanashree S Kelkar1,5, Yashwanth Subbannayya1,6, Rajesh Raju1, Renu Goel1,2, Joji Kurian Thomas1,5, Navjyot Kaur7, Mukesh Dhillon7, Shantal Gupta Tankala7, Ramesh Jois8, Vivek Vasdev9, YL Ramachandra2, Nandini A Sahasrabuddhe1, TS Keshava Prasad1,3,4, Sujatha Mohan10, Harsha Gowda1, Subramanian Shankar7* and Akhilesh Pandey11,12,13,14* Abstract Background: Osteoarthritis is a chronic musculoskeletal disorder characterized mainly by progressive degradation of the hyaline cartilage. Patients with osteoarthritis often postpone seeking medical help, which results in the diagnosis being made at an advanced stage of cartilage destruction. Sustained efforts are needed to identify specific markers that might help in early diagnosis, monitoring disease progression and in improving therapeutic outcomes. We employed a multipronged proteomic approach, which included multiple fractionation strategies followed by high resolution mass spectrometry analysis to explore the proteome of synovial fluid obtained from osteoarthritis patients. In addition to the total proteome, we also enriched glycoproteins from synovial fluid using lectin affinity chromatography. Results: We identified 677 proteins from synovial fluid of patients