NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

4 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Chapter 4, page 1 4 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Pieter Zeeman observed in 1896 the splitting of optical spectral lines in the field of an electromagnet. Since then, the splitting of energy levels proportional to an external magnetic field has been called the "Zeeman effect". The "Zeeman resonance effect" causes magnetic resonances which are classified under radio frequency spectroscopy (rf spectroscopy). In these resonances, the transitions between two branches of a single energy level split in an external magnetic field are measured in the megahertz and gigahertz range. In 1944, Jevgeni Konstantinovitch Savoiski discovered electron paramagnetic resonance. Shortly thereafter in 1945, nuclear magnetic resonance was demonstrated almost simultaneously in Boston by Edward Mills Purcell and in Stanford by Felix Bloch. Nuclear magnetic resonance was sometimes called nuclear induction or paramagnetic nuclear resonance. It is generally abbreviated to NMR. So as not to scare prospective patients in medicine, reference to the "nuclear" character of NMR is dropped and the magnetic resonance based imaging systems (scanner) found in hospitals are simply referred to as "magnetic resonance imaging" (MRI). 4.1 The Nuclear Resonance Effect Many atomic nuclei have spin, characterized by the nuclear spin quantum number I. The absolute value of the spin angular momentum is L =+h II(1). (4.01) The component in the direction of an applied field is Lz = Iz h ≡ m h. (4.02) The external field is usually defined along the z-direction. The magnetic quantum number is symbolized by Iz or m and can have 2I +1 values: Iz ≡ m = −I, −I+1, ..., I−1, I. -

Effect of Electronegative Elements on the NMR Chemical Shift in Some Simple R-X Organic Compounds
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-ISSN: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul-Aug. 2014), PP 45-56 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of electronegative elements on the NMR chemical shift in some simple R-X organic compounds Muhammad A. AL-Jalali1, Yahia M. Mahzia2 1Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Taif University, Taif, AL-Haweiah, , P. O. Box 888, Zip code 21974, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 2Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Damascus University, Damascus, Syrian Arab Republic. Abstract: Organic halides and other organic compounds that contain electronegative elements, have a strong chemical shift and a brilliant NMR spectrum will prevail. Relationship between 1H, 13C NMR chemical shift and Electronegativity in some simple R-X organic compounds (X=F, Cl, Br, I, O, H, ...R=CH3 or CH3-CH2-) give nonlinear equation, as well as a power series equation appears between nuclear magnetogyric ratio, magnetic shielding constant and chemical shift, which are not included in the theoretical expressions. More investigations required to remove the discrepancy between the theoretical and the experimental results. Keywords: Electronegativity, chemical shift, shielding constant, magnetogyric ratio. I. Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance, or NMR is a physical phenomenon was observed in 1945[1,2], which occurs when the nuclei of certain atoms, firstly, subject to nuclear Zeeman effect[3,4,5]will Precession with the Larmor frequency [6, 7]. Secondly, exposed to an oscillating electromagnetic field (radio waves), then if the radio wave frequency exactly matches the precession frequency, the resonance phenomenon will happen and this is the so-called nuclear magnetic resonance. However, experimentally, it has been noticed [8, 9, 10] that a nucleus may have a different resonant frequency for a given applied magnetic field in different chemical compounds, this difference in resonant frequency is called the chemical shift or sometimes fine structure. -

The Chemical Shift Chem 117 the Chemical Shift Key Questions (1) What Controls Proton Chemical Shifts? Eugene E
E. Kwan Lecture 2: The Chemical Shift Chem 117 The Chemical Shift Key Questions (1) What controls proton chemical shifts? Eugene E. Kwan January 26, 2012. H H H H 0.86 ppm 5.28 2.88 Br Scope of Lecture 16.4 proton chemical problem shift trends diamagnetic vs. (2) What controls carbon chemical shifts? solving paramagnetic O O shielding O CH2 H C OH the chemical 3 H3C CH3 basic DEPT 49.2 49.2 40.5 69.2 and COSY shift H-bonding and solvent (3) What are COSY and DEPT? What useful information effects spin-orbit coupling, can they give about a structure? carbon chemical effect of unsaturation shift trends 123 Helpful References 10 0 1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy... Lambert, J.B.; 1 Mazzola, E.P. Prentice-Hall, 2004. (Chapter 3) 2 2. The ABCs of FT-NMR Roberts, J.D. University Science Books, 2000. (Chapter 10) 3 3. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds (7th ed.) Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Wiley, 2005. (useful charts in the appendices of chapters 2-4) 10 4. Organic Structural Spectroscopy Lambert, J.B.; Shurvell, H.F.; Lightner, D.A.; Cooks, R.G. Prentice-Hall, 1998. I thank Professors William F. Reynolds (Toronto) and Gene Mazzola (Maryland/FDA) for providing some useful 5. Organic Structure Analysis Crews, P. Rodriguez, J.; Jaspars, material for this lecture. The section on chemical shifts M. Oxford University Press, 1998. is based on the discussion in Chapter 3 of reference 1. E. Kwan Lecture 2: The Chemical Shift Chem 117 Proton Chemical Shifts Clearly, the regions overlap: reference: Lambert and Mazzola, Chapter 3. -

NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents As Trace Impurities
7512 J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512-7515 NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities Hugo E. Gottlieb,* Vadim Kotlyar, and Abraham Nudelman* Department of Chemistry, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan 52900, Israel Received June 27, 1997 In the course of the routine use of NMR as an aid for organic chemistry, a day-to-day problem is the identifica- tion of signals deriving from common contaminants (water, solvents, stabilizers, oils) in less-than-analyti- cally-pure samples. This data may be available in the literature, but the time involved in searching for it may be considerable. Another issue is the concentration dependence of chemical shifts (especially 1H); results obtained two or three decades ago usually refer to much Figure 1. Chemical shift of HDO as a function of tempera- more concentrated samples, and run at lower magnetic ture. fields, than today’s practice. 1 13 We therefore decided to collect H and C chemical dependent (vide infra). Also, any potential hydrogen- shifts of what are, in our experience, the most popular bond acceptor will tend to shift the water signal down- “extra peaks” in a variety of commonly used NMR field; this is particularly true for nonpolar solvents. In solvents, in the hope that this will be of assistance to contrast, in e.g. DMSO the water is already strongly the practicing chemist. hydrogen-bonded to the solvent, and solutes have only a negligible effect on its chemical shift. This is also true Experimental Section for D2O; the chemical shift of the residual HDO is very NMR spectra were taken in a Bruker DPX-300 instrument temperature-dependent (vide infra) but, maybe counter- (300.1 and 75.5 MHz for 1H and 13C, respectively). -

Article Is Available Online Is One of the Most Comprehensive Ways to Envision Such at Doi:10.5194/Bg-13-2257-2016-Supplement
Biogeosciences, 13, 2257–2277, 2016 www.biogeosciences.net/13/2257/2016/ doi:10.5194/bg-13-2257-2016 © Author(s) 2016. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter from subtropical wetlands: a comparative study through the analysis of optical properties, NMR and FTICR/MS Norbert Hertkorn1, Mourad Harir1, Kaelin M. Cawley2, Philippe Schmitt-Kopplin1, and Rudolf Jaffé2 1Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health, Research Unit Analytical Biogeochemistry (BGC), Ingolstädter Landstrasse 1, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany 2Southeast Environmental Research Center, and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Florida International University, 11200 SW 8th Street, Miami, FL 33199, USA Correspondence to: Rudolf Jaffé (jaffer@fiu.edu) Received: 23 July 2015 – Published in Biogeosciences Discuss.: 25 August 2015 Revised: 22 December 2015 – Accepted: 7 February 2016 – Published: 19 April 2016 Abstract. Wetlands provide quintessential ecosystem ser- relative disparity was largest between the Everglades long- vices such as maintenance of water quality, water supply and short-hydroperiod samples, whereas Pantanal and Oka- and biodiversity, among others; however, wetlands are also vango samples were more alike among themselves. Other- among the most threatened ecosystems worldwide. Natural wise, molecular divergence was most obvious in the case dissolved organic matter (DOM) is an abundant and criti- of unsaturated protons (δH > 5 ppm). 2-D NMR spectroscopy cal component in wetland biogeochemistry. This study de- for a particular sample revealed a large richness of aliphatic scribes the first detailed, comparative, molecular characteri- and unsaturated substructures, likely derived from microbial zation of DOM in subtropical, pulsed, wetlands, namely the sources such as periphyton in the Everglades. -

Measuring T1 and T2 Relaxation Times
Relaxation Measurements Two Relaxation Mechanisms 90° pulse T1: Spin‐lattice or longitudinal relaxation is the average lifetime of the nuclei in the higher spin state T2: Spin‐spin or transverse relaxation corresponds to a de‐coherence of the transverse nuclear spin magnetization Spin‐Lattice Relaxation Time or T1 • Any factor which slows molecular motion (e.g. increasing solution viscosity, aggregation, or rigidifying the molecule) shortens the spin‐lattice relaxation time • A short T1 favors sensitivity but too short can result in line broadening and degradation of resolution since T2 cannot be longer than T1 • 3 principal magnetic interactions that contribute to T1 relaxation of spin ½ nuclei: o Dipole‐dipole interaction ‐ the nucleus experiences a fluctuating field due to the motions of neighboring dipoles, unpaired electrons, or other nuclei o Chemical shift anisotropy ‐ chemical shielding of the nucleus is a function of molecular orientation with respect to B0 field direction o Spin rotation interaction –small magnetic fields are induced at the nucleus as a molecule reorients; this field fluctuates because the motions are not uniform but proceed by a series of small jumps • Small amounts of paramagnetic substances speed up relaxation • Inversion recovery experiment measures T1 T1 Measurement: Inversion Recovery Parameters to note & Optimize • To change the value of the delay, d7, a variable delay list must be created. • In the acquisition parameters a VDLIST can be generated which contains values that typically cover a time range which extends past vdlist the expected T1 value. 0.05 0.5 Iz = I0(1‐2exp(‐d7/T1) 1.0 1.5 ln(I0‐Iz) = ln(2I0)‐d7/T1 2 Tnull = T1*ln2 4 6 8 Spin‐Spin Relaxation Time or T2 • T1 = T2 when molecular tumbling is fast compared with the Larmor frequency; this is the condition for small molecules. -

NMR Spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy • Not a single technique but a large set of related techniques • “simple” 1H-NMR • 13C NMR • 2D experiments 1 Nuclear Spin Angular momentum of spinning charge described by quantum spin number “I” Intrinsic magnitude of generated dipole = I = 0, 1/2, 1, 3/2… Spinning nucleus generates a magnetic dipole (µ) Criteria for spin: Atomic mass Atomic # I Example even even 0 12C, 16O, 34S odd odd or even half integer 1H (1/2); 13C (1/2); 15N (3/2) even odd integer 14N (1), 2H (1) Spin ½ nuclei in magnetic field (e.g. 1H and 13C) In the absence of a magnetic field, these spins have the same energy and are randomly aligned #orientations with respect to an applied B = 2I+1 B0 In an external magnetic field (B0) spin ½ can align with the magnetic field or against it (2)(1/2)+1 = 2 ΔE energy difference magnetogyric ratio hγB0 γB0 γ ΔE= ν= resonant frequency 2π 2π ν The difference in energy between the two spin states depends on B: ΔE increases with B β-spin hν ΔE depends on B, so the frequency of light needed to flip the nuclei will depend on Energy B α-spin applied magnetic field (B) 4 Common NMR active nuclei 2πµ γ = hI 7 -1 -1 Nucleus Natural Abundance γ (10 radT s ) 1H 99.9844 26 753 13C 1.108 6 728 19F 100 25 179 31P 100 10 840 1 13 νC = 0.25νΗ For a B0 where ν=200 MHz ( H) ν ≈ 50 MHz ( C) Energy difference and population The number of nuclei in the two states α and β are determined by Boltzmann distribution: N upper = e-ΔE/kT Nlower Since the α-spin state is lower in energy, it is more populated (more nuclei have α than β). -

Origin of Chemical Shifts
Origin of Chemical Shifts BCMB/CHEM 8190 Empirical Properties of Chemical Shift υi (Hz) = γB0 (1-σi) /2π • The Larmor frequencies of nuclei depend on the electronic structure of the molecule and the electronic environments of the nuclei, and reflect the chemical properties • The adjustments to the resonance frequencies to account for electronic structure and electronic shielding of nuclei from the magnetic field are embodied in the shielding constant, σ • The values of σ are small (10-6), and reduce the effective field strength by parts per million (ppm) (Beff = B0(1-σ)) Measurements are made relative to a reference peak (TMS). Offsets given in terms of δ in parts per million, ppm, + downfield. 6 δi = (σref - σi ) x 10 or 6 δi = (( υi - υref )/υref) x 10 Ranges: 1H, 2H, 10 ppm; 13C, 15N, 31P, 300 ppm; 19F, 1000 ppm Importance of Chemical Shifts and Their Origins • Shieldings are tensor quantities: magnitudes depend on orientation to magnetic field (chemical shift anisotropy) • In the solid state, different orientations give different shifts • In solution (rapid molecular tumbling) an average value results • However, in solution some orientation can be reintroduced in order to exploit available structural information • Chemical shifts reflect chemical environment, so there is potentially lots of structural information in chemical shifts themselves if we can understand the relationship with structure Ramsey’s Equation for Chemical Shift Reference: Webb, G. A. in "Nuclear Magnetic Shielding and Molecular Structure", J. A. Tossel, Ed., NATO -

Xenon NMR: Chemical Shifts of a General Anesthetic in Common Solvents, Proteins, and Membranes ("9Xe/'31Xe/Myoglobin/Lipid Bilayers/Biomembranes) KEITH W
Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 78, No. 8, pp. 4946-4949, August 1981 Biophysics Xenon NMR: Chemical shifts of a general anesthetic in common solvents, proteins, and membranes ("9Xe/'31Xe/myoglobin/lipid bilayers/biomembranes) KEITH W. MILLER*, NICHOLAS V. REOt, ANTONIUS J. M. SCHOOT UITERKAMPt, DIANE P. STENGLE§, THOMAS R. STENGLEt, AND KENNETH L. WILLIAMSON§ *Departments of Pharmacology and Anesthesia, Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114; tDepartment of Chemistry, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, Massachusetts 01003; *Interdisciplinary Programs in Health, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02115; and IDepartment ofChemistry, Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley, Massachusetts 01075 Communicated by Donald F. Hornig, April 20, 1981 ABSTRACT The rare gas xenon contains two NMR-sensitive published data). Its most striking pharmacological property is isotopes in high natural abundance. The nuclide '"Xe has a spin its ability to induce general anesthesia; its efficacy is comparable of 'h; '31Xe is quadrupolar with a spin of 3/2. The complementary to that ofnitrous oxide (7). The physicochemical mechanism of NMR characteristics ofthese nuclei provide a unique opportunity anesthetic action is controversial, but it is likely that the locus for probing their environment. The method is widely applicable ofaction is either in the lipid or the protein region ofexcitable because xenon interacts with a useful range of condensed phases membranes (8). If the NMR characteristics of xenon in these including pure liquids, protein solutions, and suspensions oflipid environments differ widely, then this would have obvious im- and biological membranes. Although xenon is chemically inert, it plications fordistinguishing among action. does interact with living systems; it is an effective general anes- theories ofanesthetic thetic. -

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Graphics from http://fs512.fshn.uiuc.edu/3D-NMR-chazin.gif Presentation Outline • Introduction – What is NMR Good Gor? • Brief Theory – Quantum Chemistry, Magnetization • NMR Concepts – – Frequency, Relaxation, Chemical Shift, Coupling, Integration • 1-Dimension NMR Experiments • 2-D NMR – COSY, HMQC/HSQC, NOESY • ********************BREAK************************* • Biomolecular NMR – 3-D • NMR Application Examples – Dynamic NMR, Solid State NMR, Inorganic, Diffusion • Spectrometer Description – Probes and Gradients • Structure Determination with NMR Introduction – NMR, What is it Good for? • Determine Solution Structure of Small Molecules • DNA and Protein Structure Determination • Molecular Dynamics – Quantifying Motional Properties – Exchange Rate/Activation Energy/∆H/ ∆S • Diffusion Measurements • Hydrogen Bonding Determination/pKa Measurements • Drug Screening • Metabolite Analysis - Metabolomics • Natural Product Chemistry • Polymer Chemistry • Environmental Chemistry The Nuclear Magnetic Moment • All atomic nuclei can be characterized by a nuclear spin quantum number, I. I can be ≥ 0 and any multiple of ½. • Nuclei with I = 0 do not possess nuclear spin and consequently are termed ‘NMR silent’. • All nuclei with I ≠ 0 possess spin, charge, and angular momentum P, resulting in a nuclear magnetic moment µ. µ = γP Where γ is the magnetogyric ratio of the nucleus. NMR- Quantum Chemistry I = the nuclear spin quantum number For Nuclei of: I = Example Odd Mass Half Integer 1H, 13C Even Mass/Even Charge -

NMR Solvents Chart
Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. www.isotope.com unit NMR Solvent Data CHart Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. www.isotope.com NMRRESEARCH SOLVENTS PRODUCTS NMR Solvent Data Chart More Solvents, More Sizes, More Solutions NMR Solvents 1H Chemical Shift 13C Chemical Shift 1H Chemical Shift Density at Melting point Boiling point Dielectric Molecular 20°C (°C) (°C) Weight (ppm from TMS) JCD(Hz) (ppm from TMS) JCD(Hz) of HOD Constant (multiplicity) (multiplicity) (ppm from TMS) � � � � � � � 11.65 (1) 178.99 (1) Acetic Acid-d4 20 11.5 1.12 16.7 118 6.1 64.08 2.04 (5) 2.2 20.0 (7) 206.68 (1) 0.9 Acetone-d6 2.8 * 0.87 -94 56.5 20.7 64.12 2.05 (5) 2.2 29.92 (7) 19.4 118.69 (1) Acetonitrile-d3 2.1 * 0.84 -45 81.6 37.5 44.07 1.94 (5) 2.5 1.39 (7) 21 Benzene-d6 7.16 (1) 128.39 (3) 24.3 0.4 0.95 5.5 80.1 2.3 84.15 Chloroform-d 7.24 (1) 77.23 (3) 32.0 1.5 * 1.50 -63.5 61-62 4.8 120.38 Cyclohexane-d12 1.38 (1) 26.43 (5) 19 0.8 0.89 6.47 80.7 2.0 96.24 4.80 (DSS) NA NA 4.8 1.11 3.81 101.42 78.5 Deuterium Oxide 4.81 (TSP) 20.03 8.03 (1) 163.15 (3) 29.4 3.5 1.03 -61 153 36.7 80.14 N, N-Dimethyl-formamide-d7 2.92 (5) 1.9 34.89 (7) 21.0 2.75 (5) 1.9 29.76 (7) 21.1 Dimethyl Sulfoxide-d6 2.50 (5) 1.9 39.51 (7) 21.0 3.3 * 1.19 18.45 189 46.7 84.17 1,4-Dioxane-d8 3.53 (m) 66.66 (5) 21.9 2.4 1.13 11.8 101.1 2.2 96.16 5.19 (1) 5.3 0.89 -114.1 78.5 24.5 52.11 Ethanol-d6 3.56 (1) 56.96 (5) 22 1.11 (m) 17.31 (7) 19 4.78 (1) 4.9 0.89 -97.8 64.7 32.7 36.07 Methanol-d4 3.31 (5) 1.7 49.15 (7) 21.4 Methylene Chloride-d2 5.32 (3) 1.1 54.00 (5) 27.2 1.5 1.35 -95 -

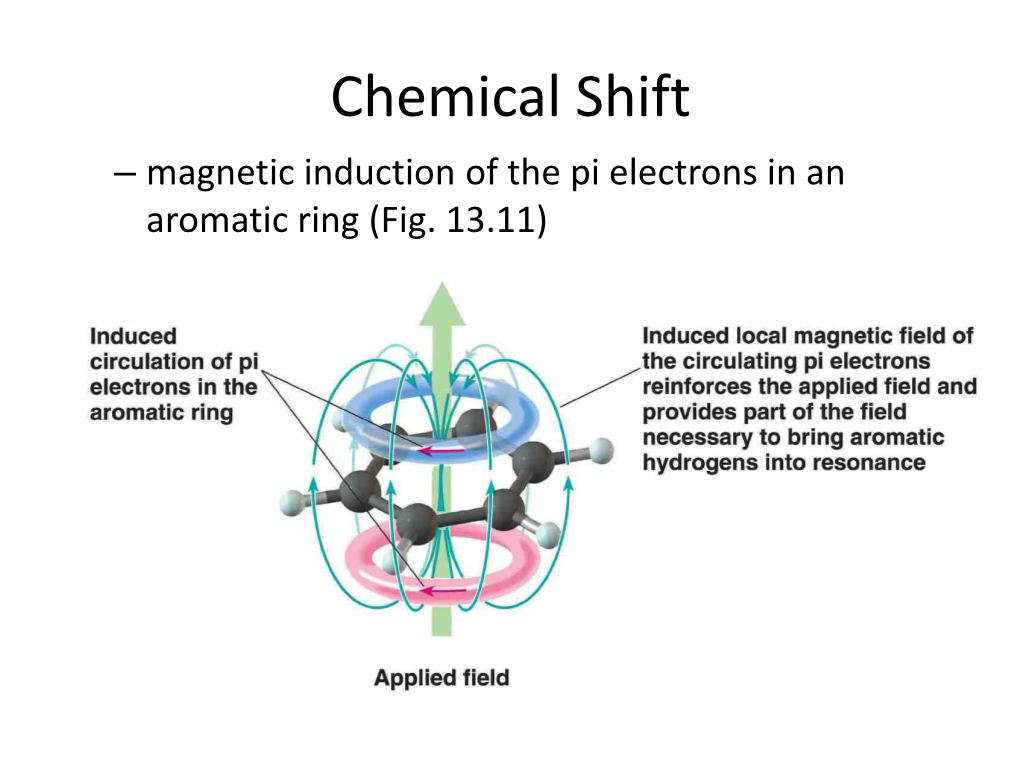
Chemical Shifts
Chemical shifts Discovered in 1950 by Proctor and Yu based on solution 14N NMR studies of NH4NO3 1 H chemical shifts Empirical correlations between chemical shifts and structure Typical 1H chemical shift values. Proton / ppm Proton / ppm Aldehyde 9.5 - 10.5 CH3 attached to double Aromatic 6.5 - 8.2 bonds/aromatics 1.8 - 2.5 Alkene 4.5 - 6.1 Methyl (CH3–CO) 1.8 - 2.7 Alkyne 2.0 - 3.2 Methylene (CH2–O) ~3.6 - 4.7 Acetal 4.5 - 6.0 Methylene (CH2– R1R2) ~1.3 Alkoxy 3.4 - 4.8 Methine (CH–R1R2R3) ~1.5 Methyl (CH3–R) ~0.9 Cyclopropane 0.22 N-methyl 3.0 - 3.5 Me4Si (TMS) 0.0 Methoxy 3.3 - 3.8 Metal hydride –5 to –20 The influence of the electron density at the proton (Diamagnetic) Shielding of Nucleus by Electrons B o Nucleus Electron (lines of force arising from electron motion) NMR Spectroscopy 1 The applied magnetic field, B0, induces circulations in the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus such that a magnetic moment , opposed to B0, is produced (Lenz's law). Nuclei in a region of high electron density are more shielded from the applied field than those in regions of lower electron density. If inductive effects present in a molecule reduce the electron density in the hydrogen 1s orbital, dishielding (shift to higher frequencies) is expected. CH3F CH3Cl CH3Br CH3I CH3H (CH3) 4.13 2.84 2.45 1.98 0.13 Electonegativity (Pauling) 4.0 3.0 2.8 2.5 2.1 TMS Less screened than TMS More screened than TMS Low field High Field High frequency Low frequency {Most organic protons} {Metal Hydrides} +10 0 -10 Substituents, such as OR or NR2, can act both as an electron withdrawing group (due to electronegativity, thus causing a shift to higher frequencies) and as a donor of lone pairs (if double bonds are present, thus causing a shift to lower frequency).