How Do All the Systems Work Together
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Lung Transplantation with the OCS (Organ Care System)
Lung Transplantation with the OCSTM (Organ Care System) Lung System Bringing Breathing Lung Preservation to Transplant Patients A Guide for You and Your Family DRAFT ABOUT THIS BOOKLET This booklet was created for patients like you who have been diagnosed with end-stage lung failure and are candidates for a lung transplant. It contains information that will help you and your family learn about options available to you for a transplant. This booklet includes information on your lungs, how they function, and respiratory failure. In addition, you will learn about a new way to preserve lungs before transplantation, called breathing lung preservation. Your doctor is the best person to explain your treatment options and their risks and to help you decide which option is right for you. The booklet explains: • Breathing lung preservation with the OCS™ Lung System • How the OCS™ Lung System works • Who is eligible for the OCS™ Lung System • Lung transplant complications • How the lungs function • What is respiratory failure and the treatment options • What to expect during your treatment • Summary of clinical data for the OCS™ Lung System • Contact Information Please read this booklet carefully and share it with your family and caregivers. For your convenience, a glossary is provided in the front of this booklet. Terms in the text in bold italics are explained in the glossary. If you have questions about the OCS™ Lung System that are not answered in this booklet, please ask your physician. This booklet is intended for general information only. It is not intended to tell you everything you need to know about a lung transplant. -

Case Report AJNT
Arab Journal of Nephrology and Transplantation. 2011 Sep;4(3):155-8 Case Report AJNT High Ureteric Injury Following Multiorgan Recovery: Successful Kidney Transplant with Boari Flap Ureterocystostomy Reconstruction Michael Charlesworth*, Gabriele Marangoni, Niaz Ahmad Department of Transplantation, Division of Surgery, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds, United Kingdom Abstract Keywords: Kidney; Transplant; Ureter; Donor efficiency Introduction: Despite increased utilization of marginal organs, there is still a marked disparity between organ The authors declared no conflict of interest supply and demand for transplantation. To maximize resources, it is imperative that procured organs are in Introduction good condition. Surgical damage at organ recovery can happen and organs are sometimes discarded as a result. Despite the extension of the donor pool with the inclusion We describe a damaged recovered kidney with high of marginal organs and the use of organs donated after ureteric transection that was successfully transplanted cardiac death, there is still a great disparity between the using a primary Boari flap ureterocystostomy. number of patients on the transplant waiting list and the number of kidney transplants performed each year. Case report: The donor kidney was procured form a It is therefore of paramount importance to maximize deceased donor and sustained damage by transection our scarce resources and avoid the discard of otherwise of the ureter just distal to the pelvi-ureteric junction at functional kidneys due to iatrogenic injuries at the time organ recovery. The recipient had been on the transplant of multi-organ recovery. Essentially, three types of organ waiting list for eight years and not accepting this kidney damage can potentially occur: vascular, parenchymal would have seriously jeopardized her chance of future and ureteric. -

Pelvic Anatomyanatomy
PelvicPelvic AnatomyAnatomy RobertRobert E.E. Gutman,Gutman, MDMD ObjectivesObjectives UnderstandUnderstand pelvicpelvic anatomyanatomy Organs and structures of the female pelvis Vascular Supply Neurologic supply Pelvic and retroperitoneal contents and spaces Bony structures Connective tissue (fascia, ligaments) Pelvic floor and abdominal musculature DescribeDescribe functionalfunctional anatomyanatomy andand relevantrelevant pathophysiologypathophysiology Pelvic support Urinary continence Fecal continence AbdominalAbdominal WallWall RectusRectus FasciaFascia LayersLayers WhatWhat areare thethe layerslayers ofof thethe rectusrectus fasciafascia AboveAbove thethe arcuatearcuate line?line? BelowBelow thethe arcuatearcuate line?line? MedianMedial umbilicalumbilical fold Lateralligaments umbilical & folds folds BonyBony AnatomyAnatomy andand LigamentsLigaments BonyBony PelvisPelvis TheThe bonybony pelvispelvis isis comprisedcomprised ofof 22 innominateinnominate bones,bones, thethe sacrum,sacrum, andand thethe coccyx.coccyx. WhatWhat 33 piecespieces fusefuse toto makemake thethe InnominateInnominate bone?bone? PubisPubis IschiumIschium IliumIlium ClinicalClinical PelvimetryPelvimetry WhichWhich measurementsmeasurements thatthat cancan bebe mademade onon exam?exam? InletInlet DiagonalDiagonal ConjugateConjugate MidplaneMidplane InterspinousInterspinous diameterdiameter OutletOutlet TransverseTransverse diameterdiameter ((intertuberousintertuberous)) andand APAP diameterdiameter ((symphysissymphysis toto coccyx)coccyx) -

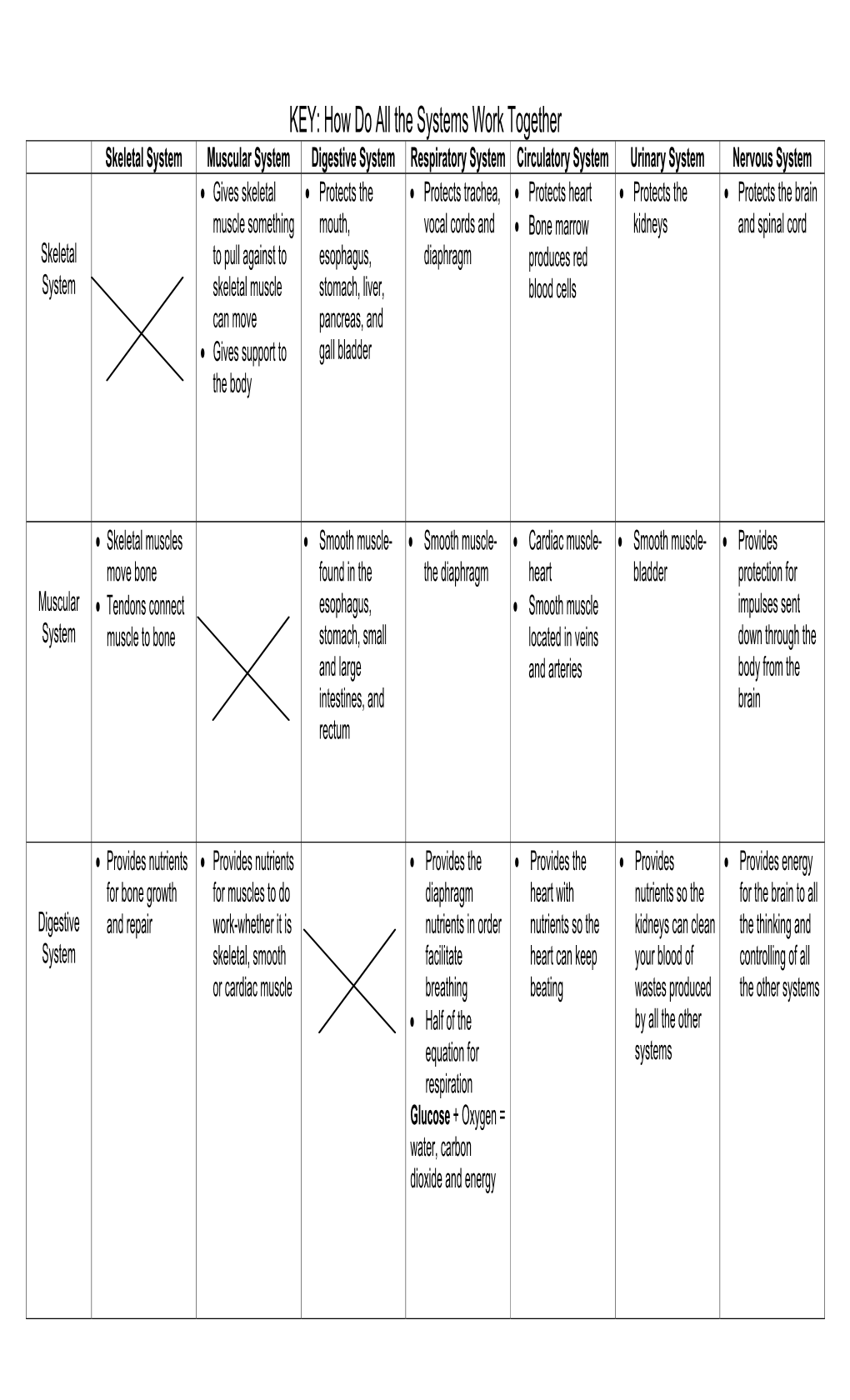
The Human Body Systems for Kids
1 Maine Regional School Unit #67 Chester, Lincoln, Mattawamkeag The Human Body Systems for Kids KidsKonnect.com and kidshealth.org provide links to more detailed information about each of the systems listed below. The first group of systems are commonly taught in the elementary grades. Teachers wishing more detailed information should consult sources beyond this handout. There are many systems in the human body. • Skeletal System (bones) • Respiratory System (nose, trachea, lungs) • Circulatory System (heart, blood, vessels) • Digestive System (mouth, esophogus, stomach, intestines) • Muscular System (muscles) • Nervous System (brain, spinal cord, nerves) • Excretory System (lungs, large intestine, kidneys) • Urinary System (bladder, kidneys) • Endocrine System (glands) • Reproductive System (male and female reproductive organs) • Immune System (many types of protein, cells, organs, tissues) 2 The Skeletal System has three major jobs: • It protects our vital organs such as the brain, the heart, and the lungs. • It gives us the shape that we have. • It allows us to move. Because muscles are attached to bones, when muscles move, they move the bones and the body moves. http://kidshealth.org/kid/htbw/bones.html The Respiratory System is the system of the body that deals with breathing. When we breathe, the body takes in the oxygen that it needs and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesn't need. The organ most closely connected with this system is the lung. The human body has two lungs. http://kidshealth.org/kid/htbw/lungs.html 3 The Circulatory System is the system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the body's cells, and waste materials are carried away. -

The Muscular System
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM COMPILED BY HOWIE BAUM 1 Muscles make up the bulk of the body and account for 1/3 of its weight.!! Blood vessels and nerves run to every muscle, helping control and regulate each muscle’s function. The muscular system creates body heat and also moves the: Bones of the Skeletal system Food through Digestive system Blood through the Circulatory system Fluids through the Excretory system MUSCLE TISSUE The body has 3 main types of muscle tissue 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth, and 3) Cardiac SKELETAL MUSCLE SMOOTH MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE Skeletal muscles attach to and move bones by contracting and relaxing in response to voluntary messages from the nervous system. Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of long cells called muscle fibers that have a striated appearance. Muscle fibers are organized into bundles supplied by blood vessels and innervated by motor neurons. Muscle structure Skeletal (striated or voluntary) muscle consists of densely packed groups of hugely elongated cells known as myofibers. These are grouped into bundles (fascicles). A typical myofiber is 2–3 centimeters ( 3/4–1 1/5 in) long and 0.05millimeters (1/500 inch) in diameter and is composed of narrower structures – myofibrils. These contain thick and thin myofilaments made up mainly of the proteins actin and myosin. Numerous capillaries keep the muscle supplied with the oxygen and glucose needed to fuel contraction. Skeletal Muscles • Skeletal muscles attach to bones by tendons (connective tissue) and enable movement. • Skeletal muscles are mostly voluntary Feel the back of your ankle to feel your Achilles tendon - the largest tendon in your body. -

Skin Is Not the Largest Organ
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE providedRD by Elsevier Sontheimer - Publisher Connector Skin is Not the Largest Organ 3 content. CHS, JNB, and MAS were involved in Paris, France; Division of Genetics and susceptibility to psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest study supervision. Molecular Medicine, St John’s Institute of Dermatol 134:271–3 Dermatology, Guy’s Hospital, London, UK; Martin MA, Klein TE, Dong BJ et al. (2012) Clinical 1,8 4 Alexander A. Navarini , Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation pharmacogenetics implementation consortium Trust, Skin Therapy Research Unit, St John’s Laurence Valeyrie-Allanore2,8, guidelines for HLA-B genotype and abacavir 1 Institute of Dermatology, St Thomas’ Hospital, dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther 91:734–8 Niovi Setta-Kaffetzi , London, UK; 5King’s College Hospital, London, Jonathan N. Barker1,3,4, UK; 6University Medical Center Freiburg, Navarini AA, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Setta-Kaffetzi N et al. (2013) Rare variations in IL36RN in 1 5 Institute of Medical Biometry and Medical Francesca Capon , Daniel Creamer , severe adverse drug reactions manifesting as 2 6 Informatics, Freiburg, Germany and Jean-Claude Roujeau , Peggy Sekula , 7 acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. 1 Department of Dermatology, J Invest Dermatol 133:1904–7 Michael A. Simpson , Dokumentationszentrum Schwerer 1 Richard C. Trembath , Hautreaktionen (dZh), Universita¨ts-Hautklinik, Setta-Kaffetzi N, Navarini AA, Patel VM et al. (2013) Maja Mockenhaupt7,8 and Freiburg, Germany Rare pathogenic variants in IL36RN underlie a spectrum of psoriasis-associated 1,3,4,8 8 Catherine H. Smith These authors contributed equally to this work. -

GLOSSARY of MEDICAL and ANATOMICAL TERMS
GLOSSARY of MEDICAL and ANATOMICAL TERMS Abbreviations: • A. Arabic • abb. = abbreviation • c. circa = about • F. French • adj. adjective • G. Greek • Ge. German • cf. compare • L. Latin • dim. = diminutive • OF. Old French • ( ) plural form in brackets A-band abb. of anisotropic band G. anisos = unequal + tropos = turning; meaning having not equal properties in every direction; transverse bands in living skeletal muscle which rotate the plane of polarised light, cf. I-band. Abbé, Ernst. 1840-1905. German physicist; mathematical analysis of optics as a basis for constructing better microscopes; devised oil immersion lens; Abbé condenser. absorption L. absorbere = to suck up. acervulus L. = sand, gritty; brain sand (cf. psammoma body). acetylcholine an ester of choline found in many tissue, synapses & neuromuscular junctions, where it is a neural transmitter. acetylcholinesterase enzyme at motor end-plate responsible for rapid destruction of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. acidophilic adj. L. acidus = sour + G. philein = to love; affinity for an acidic dye, such as eosin staining cytoplasmic proteins. acinus (-i) L. = a juicy berry, a grape; applied to small, rounded terminal secretory units of compound exocrine glands that have a small lumen (adj. acinar). acrosome G. akron = extremity + soma = body; head of spermatozoon. actin polymer protein filament found in the intracellular cytoskeleton, particularly in the thin (I-) bands of striated muscle. adenohypophysis G. ade = an acorn + hypophyses = an undergrowth; anterior lobe of hypophysis (cf. pituitary). adenoid G. " + -oeides = in form of; in the form of a gland, glandular; the pharyngeal tonsil. adipocyte L. adeps = fat (of an animal) + G. kytos = a container; cells responsible for storage and metabolism of lipids, found in white fat and brown fat. -

Human Anatomy and Physiology
LECTURE NOTES For Nursing Students Human Anatomy and Physiology Nega Assefa Alemaya University Yosief Tsige Jimma University In collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, The Carter Center, the Ethiopia Ministry of Health, and the Ethiopia Ministry of Education 2003 Funded under USAID Cooperative Agreement No. 663-A-00-00-0358-00. Produced in collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, The Carter Center, the Ethiopia Ministry of Health, and the Ethiopia Ministry of Education. Important Guidelines for Printing and Photocopying Limited permission is granted free of charge to print or photocopy all pages of this publication for educational, not-for-profit use by health care workers, students or faculty. All copies must retain all author credits and copyright notices included in the original document. Under no circumstances is it permissible to sell or distribute on a commercial basis, or to claim authorship of, copies of material reproduced from this publication. ©2003 by Nega Assefa and Yosief Tsige All rights reserved. Except as expressly provided above, no part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission of the author or authors. This material is intended for educational use only by practicing health care workers or students and faculty in a health care field. Human Anatomy and Physiology Preface There is a shortage in Ethiopia of teaching / learning material in the area of anatomy and physicalogy for nurses. The Carter Center EPHTI appreciating the problem and promoted the development of this lecture note that could help both the teachers and students. -

THE 6 MAJOR BODY SYSTEMS and How They Interact with Each Other to Keep the “Body Machine” Alive and Working Well
THE 6 MAJOR BODY SYSTEMS And how they interact with each other to keep the “body machine” alive and working well. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM / CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PRIMARY PURPOSE: transport blood throughout the body by circulating PRIMARY ORGANS/PARTS: Heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) (1) Transports/carries nutrients and oxygen through the blood to most parts of the body (2) Transports/carries waste in cells and carbon-dioxide (CO2) away from the parts: (a) Cell waste goes to the kidneys for filter and disposal (b) Carbon-dioxide (CO2) goes to the lungs to exhale (breathe out) Kidneys and Lungs have a close relationship with Cardiovascular system Kidneys: filter through blood to take out the waste and get it eventually out of the body Lungs: breathes in oxygen and gives it to the blood for Circulatory system to carry throughout the body; and takes unneeded carbon-dioxide (CO2) from the blood and breathes that out. Circulatory/Cardiovascular System through the blood to most parts of the body provides nutrients and oxygen which is needed for our bodies to have ENERGY! RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PRIMARY PURPOSE: Breathing - taking in Oxygen, pushing out Carbon-Dioxide (CO2) PRIMARY ORGANS: Lungs, trachea (tube going from lungs to nose/mouth) (1) Inhales (breathes in) Oxygen - good for the body - gives it to the Circulatory System to be transported throughout the body through the blood. (2) Exhales (breathes out) Carbon-Dioxide (CO2) - lungs get this gas from the blood (Circ. Sys.) and pushes it out of the body DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PRIMARY PURPOSE: take in food; break down food into nutrients (good) and waste (unneeded) PRIMARY ORGANS: Stomach, large and small intestines, esophagus (tube from stomach to mouth) (1) Digestive System gets nutrients (good) from food and hands it over to the blood and Circulatory System then carries those nutrients where they need to go. -

Human Organ Matching and Labelling Cut out the Organ Names and Descriptions and Stick Them Down in the Correct Boxes on the Diagram
Human Organ Matching and Labelling Cut out the organ names and descriptions and stick them down in the correct boxes on the diagram. Page 1 of 3 visit twinkl.com Maintains body temperature using Receives food from the oesophagus sweat and goosebumps. and begins to break it down with digestive juices (enzymes). Controls all of our necessary bodily functions, sends the Transports air from the nose and impulses which allow us to move mouth to the lungs. and enables you to think and learn. Pumps oxygenated blood around your body and receives de- oxygenated blood back. Filters water and salt out of your oesophagus blood and creates urine. bladder Makes bile for digestion, filters out toxins and regulates blood sugar. liver Produces enzymes necessary for large intestine digestion. gall bladder Digests food using enzymes and absorbs nutrients for the blood. kidneys Continues the digestion process, stomach absorbs as much water as possible and expels excess fibre and waste. heart Stores and concentrates bile pancreas produced by the liver. lungs Takes in oxygen, which reaches the blood via the heart. small intestine Stores urine so that we can decide trachea when we want to go to the toilet. skin Transports food and drink from the mouth to the stomach. brain Page 2 of 3 visit twinkl.com Answers brain oesophagus Controls all of our necessary bodily Transports food and drink from the functions, sends the impulses which mouth to the stomach. allow us to move and enables you to think and learn. trachea Transports air from the nose and liver mouth to the lungs. -

Body Systems Work Together by Cindy Grigg
Body Systems Work Together By Cindy Grigg 1 You know that your body is made of cells. When groups of cells do the same kind of work, they are called tissues. The word tissue comes from a Latin word meaning to "weave." Cells that make up tissues are sometimes "woven" together. 2 You have four main types of tissues: epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the outside of the body. It also lines organs and cavities. Nervous tissue sends electrical signals. Muscle tissue helps you move. Connective tissue joins bones and cushions organs. 3 When groups of tissues work together, they are called organs. Some examples of organs are the heart, lungs, skin, and stomach. When organs work together, they are called systems. For example, your heart, lungs, blood, and blood vessels work together. They make up the circulatory system. 4 There are eleven systems in the human body: muscular system, respiratory system, digestive system, integumentary system (skin), skeletal system, circulatory (or cardiovascular) system, excretory (or urinary) system, reproductive system, nervous system, lymphatic system, and endocrine system. Each system has a special job. 5 All of your body systems have to work together to keep you healthy. Your bones and muscles work together to support and move your body. Your respiratory system takes in oxygen from the air. It also gets rid of carbon dioxide. 6 Your digestive system absorbs water and nutrients from the food you eat. 7 Your circulatory system carries oxygen, water, and nutrients to cells throughout your body. Wastes from the cells are eliminated by your respiratory system, your excretory system, and your skin. -

A Case Study in Organ Allocation Policy and Administrative Law
139 Journal of Health & Biomedical Law, XIV (2018) 139-148 © 2018 Journal of Health & Biomedical Law Suffolk University Law School THE LUNG LAWSUIT: A CASE STUDY IN ORGAN ALLOCATION POLICY AND ADMINISTRATIVE LAW Alexandra K. Glazier, J.D., M.P.H.* In November 2017, twenty-one-year-old Miriam Holman, was waiting for a lung transplant.1 Miriam was suffering from a rare form of pulmonary hypertension for which there is no medical therapy, and which is rapidly fatal without lung transplantation. Miriam was on an artificial lung machine in the ICU at Columbia Medical Center in New York where she was listed for organ transplantation.2 Organ allocation policies are, under federal law, designed to balance equity and utility principles based on medical criteria to rank order patients waiting for suitable organs to be available that are a biological match.3 Allocation policy therefore, incorporates factors such as (1) how critically ill the patient waiting is; (2) how long the patient has been waiting; and (3) for some organs allocation policies, the relative magnitude of the * Ms. Glazier is President and CEO of New England Donor Services, the two OPOs serving Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont, a member of the OPTN Board of Directors, previously chaired the OPTN Ethics Committee and has twice been appointed to the U.S. Secretary of HHS, Advisory Committee on Organ Transplantation. 1 Complaint at 18, Holman v. Secretary of HHS, No. 17-cv-09041 (S.D.N.Y. filed Nov. 11, 2017) (describing the plaintiff’s medical history). 2 Id.