Zoonotic Diseases
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Genetic Engineering and Sustainable Crop Disease Management: Opportunities for Case-By-Case Decision-Making
sustainability Review Genetic Engineering and Sustainable Crop Disease Management: Opportunities for Case-by-Case Decision-Making Paul Vincelli Department of Plant Pathology, 207 Plant Science Building, College of Agriculture, Food and Environment, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40546, USA; [email protected] Academic Editor: Sean Clark Received: 22 March 2016; Accepted: 13 May 2016; Published: 20 May 2016 Abstract: Genetic engineering (GE) offers an expanding array of strategies for enhancing disease resistance of crop plants in sustainable ways, including the potential for reduced pesticide usage. Certain GE applications involve transgenesis, in some cases creating a metabolic pathway novel to the GE crop. In other cases, only cisgenessis is employed. In yet other cases, engineered genetic changes can be so minimal as to be indistinguishable from natural mutations. Thus, GE crops vary substantially and should be evaluated for risks, benefits, and social considerations on a case-by-case basis. Deployment of GE traits should be with an eye towards long-term sustainability; several options are discussed. Selected risks and concerns of GE are also considered, along with genome editing, a technology that greatly expands the capacity of molecular biologists to make more precise and targeted genetic edits. While GE is merely a suite of tools to supplement other breeding techniques, if wisely used, certain GE tools and applications can contribute to sustainability goals. Keywords: biotechnology; GMO (genetically modified organism) 1. Introduction and Background Disease management practices can contribute to sustainability by protecting crop yields, maintaining and improving profitability for crop producers, reducing losses along the distribution chain, and reducing the negative environmental impacts of diseases and their management. -

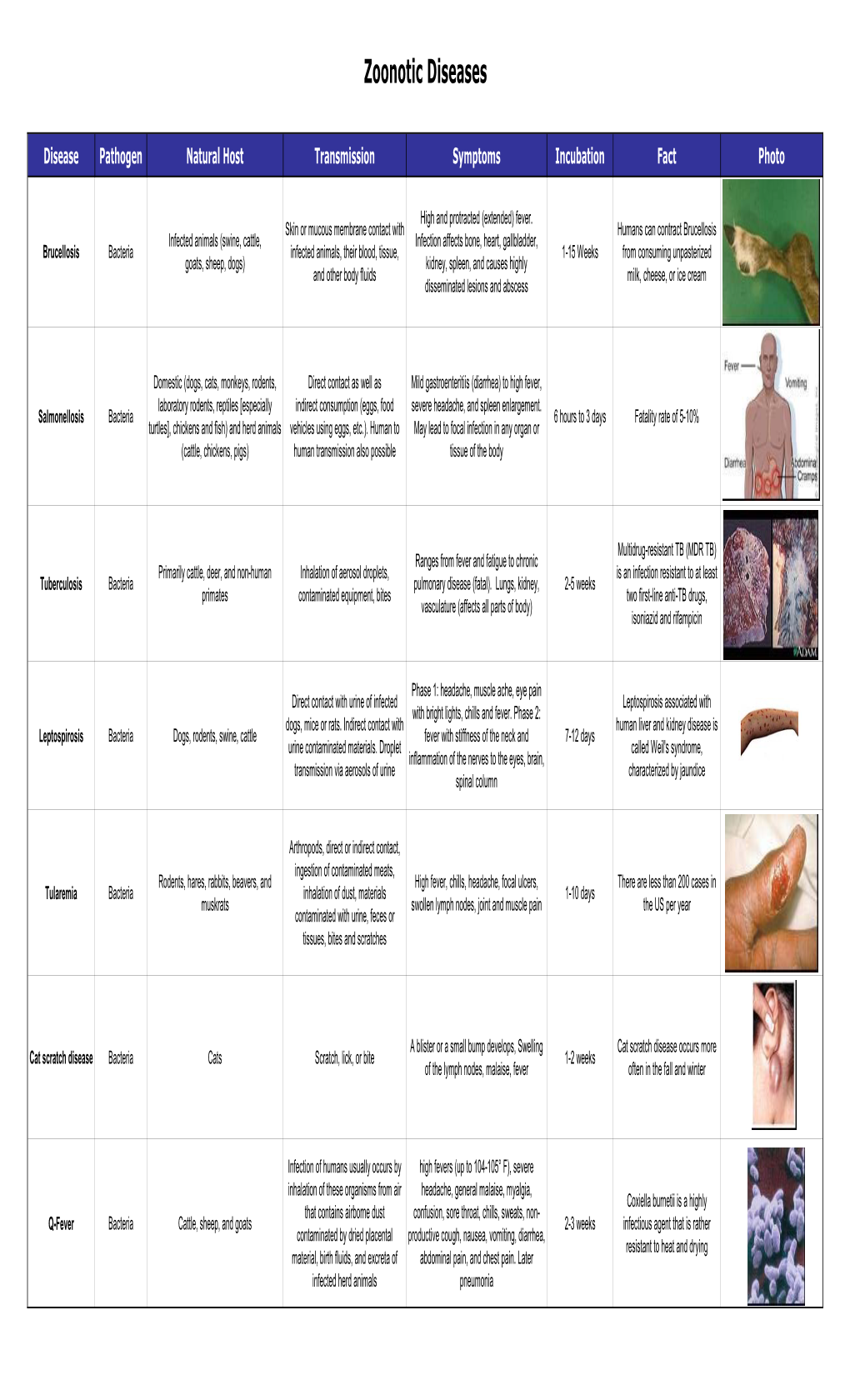
Zoonotic Diseases Fact Sheet
ZOONOTIC DISEASES FACT SHEET s e ion ecie s n t n p is ms n e e s tio s g s m to a a o u t Rang s p t tme to e th n s n m c a s a ra y a re ho Di P Ge Ho T S Incub F T P Brucella (B. Infected animals Skin or mucous membrane High and protracted (extended) fever. 1-15 weeks Most commonly Antibiotic melitensis, B. (swine, cattle, goats, contact with infected Infection affects bone, heart, reported U.S. combination: abortus, B. suis, B. sheep, dogs) animals, their blood, tissue, gallbladder, kidney, spleen, and laboratory-associated streptomycina, Brucellosis* Bacteria canis ) and other body fluids causes highly disseminated lesions bacterial infection in tetracycline, and and abscess man sulfonamides Salmonella (S. Domestic (dogs, cats, Direct contact as well as Mild gastroenteritiis (diarrhea) to high 6 hours to 3 Fatality rate of 5-10% Antibiotic cholera-suis, S. monkeys, rodents, indirect consumption fever, severe headache, and spleen days combination: enteriditis, S. labor-atory rodents, (eggs, food vehicles using enlargement. May lead to focal chloramphenicol, typhymurium, S. rep-tiles [especially eggs, etc.). Human to infection in any organ or tissue of the neomycin, ampicillin Salmonellosis Bacteria typhi) turtles], chickens and human transmission also body) fish) and herd animals possible (cattle, chickens, pigs) All Shigella species Captive non-human Oral-fecal route Ranges from asymptomatic carrier to Varies by Highly infective. Low Intravenous fluids primates severe bacillary dysentery with high species. 16 number of organisms and electrolytes, fevers, weakness, severe abdominal hours to 7 capable of causing Antibiotics: ampicillin, cramps, prostration, edema of the days. -

Chapter 2 Disease and Disease Transmission
DISEASE AND DISEASE TRANSMISSION Chapter 2 Disease and disease transmission An enormous variety of organisms exist, including some which can survive and even develop in the body of people or animals. If the organism can cause infection, it is an infectious agent. In this manual infectious agents which cause infection and illness are called pathogens. Diseases caused by pathogens, or the toxins they produce, are communicable or infectious diseases (45). In this manual these will be called disease and infection. This chapter presents the transmission cycle of disease with its different elements, and categorises the different infections related to WES. 2.1 Introduction to the transmission cycle of disease To be able to persist or live on, pathogens must be able to leave an infected host, survive transmission in the environment, enter a susceptible person or animal, and develop and/or multiply in the newly infected host. The transmission of pathogens from current to future host follows a repeating cycle. This cycle can be simple, with a direct transmission from current to future host, or complex, where transmission occurs through (multiple) intermediate hosts or vectors. This cycle is called the transmission cycle of disease, or transmission cycle. The transmission cycle has different elements: The pathogen: the organism causing the infection The host: the infected person or animal ‘carrying’ the pathogen The exit: the method the pathogen uses to leave the body of the host Transmission: how the pathogen is transferred from host to susceptible person or animal, which can include developmental stages in the environment, in intermediate hosts, or in vectors 7 CONTROLLING AND PREVENTING DISEASE The environment: the environment in which transmission of the pathogen takes place. -

Ask a Scientist: How Do People Become Infected with Germs?
One way to think about how living things get sick is to imagine a triangle. The three corners represent the environment... ...the host... All three aspects of this triangle must come ...and the cause of the disease, together for disease to occur. Disease the Agent. agents can be non-infectious or infectious. Non-infectious agents are non-living things that are toxic to the host, like radiation or chemicals... ...while infectious agents are organisms that invade a host to survive. Only infectious agents can spread, or transmit, between hosts. Infectious disease agents, otherwise known as pathogens, A person can become infected with a must infect a host pathogen when in the same environment in order to grow, or as the agent... replicate. Human pathogens, like viruses, bacteria, and parasites, evolved to infect people. Their survival is dependent on quickly invading, making more of themselves, and efficiently transmitting to others. If a pathogen gets past a host’s defenses, it will attempt to infect the host and begin replicating itself. ...and don’t have enough protection in the form The subsequent battle between Many cells will be destroyed as of physical barriers or the germs and the body’s germs kill them through replicating pre-existing immunity. immune system will cause the and as collateral damage from the symptoms of illness. activated immune cells. That’s just how one person gets infected, but how does disease spread? Well, if sick people go around sneezing and coughing without covering their mouth or frequently washing their hands... ...they are actually spreading pathogens all over the environment around them. -

Neglected Tropical Diseases in The
Qian et al. Infectious Diseases of Poverty (2019) 8:86 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-019-0599-4 SCOPING REVIEW Open Access Neglected tropical diseases in the People’s Republic of China: progress towards elimination Men-Bao Qian1, Jin Chen1, Robert Bergquist2, Zhong-Jie Li3, Shi-Zhu Li1, Ning Xiao1, Jürg Utzinger4,5 and Xiao-Nong Zhou1* Abstract Since the founding of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, considerable progress has been made in the control and elimination of the country’s initial set of 11 neglected tropical diseases. Indeed, elimination as a public health problem has been declared for lymphatic filariasis in 2007 and for trachoma in 2015. The remaining numbers of people affected by soil-transmitted helminth infection, clonorchiasis, taeniasis, and echinococcosis in 2015 were 29.1 million, 6.0 million, 366 200, and 166 100, respectively. In 2017, after more than 60 years of uninterrupted, multifaceted schistosomiasis control, has seen the number of cases dwindling from more than 10 million to 37 600. Meanwhile, about 6000 dengue cases are reported, while the incidence of leishmaniasis, leprosy, and rabies are down at 600 or fewer per year. Sustained social and economic development, going hand-in-hand with improvement of water, sanitation, and hygiene provide the foundation for continued progress, while rigorous surveillance and specific public health responses will consolidate achievements and shape the elimination agenda. Targets for poverty elimination and strategic plans and intervention packages post-2020 are important opportunities for further control and elimination, when remaining challenges call for sustainable efforts. Keywords: Control, Elimination, People's Republic of China, Neglected tropical diseases Multilingual abstracts deprived urban settings [1, 2]. -

Working to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases Annexe I
Working to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases Annexe I Working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases First WHO report on neglected tropical diseases WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data First WHO report on neglected tropical diseases: working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases. 1 Tropical medicine - trends. 2 Endemic diseases. 3 Poverty areas. 4. Parasitic diseases. 5 Developing countries. 6. Annual reports. I. World Health Organization ISBN 978 92 4 1564090 (NLM Classification: WC 680) Working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases was produced under the overall direction and supervision of Dr Lorenzo Savioli (Director, WHO Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases) and Dr Denis Daumerie (Programme Manager, WHO Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases), with contributions from staff serving in the department. Regional directors and members of their staff provided support and advice. Valuable inputs in the form of contributions, peer reviews and suggestions were received by members of the Strategic and Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases. The report was edited by Professor David W.T. Crompton, assisted by Mrs Patricia Peters. © World Health Organization 2010 All rights reserved. Publications of the World Health Organization can be obtained from WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland (tel.: +41 22 791 3264; fax: +41 22 791 4857; e-mail: [email protected]). Requests for permission to reproduce or translate WHO publications – whether for sale or for noncommercial distribution – should be addressed to WHO Press, at the above address (fax: +41 22 791 4806; e-mail: [email protected]). -

Neglected Tropical Diseases: Epidemiology and Global Burden
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease Review Neglected Tropical Diseases: Epidemiology and Global Burden Amal K. Mitra * and Anthony R. Mawson Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Jackson State University, Jackson, PO Box 17038, MS 39213, USA; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +1-601-979-8788 Received: 21 June 2017; Accepted: 2 August 2017; Published: 5 August 2017 Abstract: More than a billion people—one-sixth of the world’s population, mostly in developing countries—are infected with one or more of the neglected tropical diseases (NTDs). Several national and international programs (e.g., the World Health Organization’s Global NTD Programs, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Global NTD Program, the United States Global Health Initiative, the United States Agency for International Development’s NTD Program, and others) are focusing on NTDs, and fighting to control or eliminate them. This review identifies the risk factors of major NTDs, and describes the global burden of the diseases in terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Keywords: epidemiology; risk factors; global burden; DALYs; NTDs 1. Introduction Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of bacterial, parasitic, viral, and fungal infections that are prevalent in many of the tropical and sub-tropical developing countries where poverty is rampant. According to a World Bank study, 51% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa, a major focus for NTDs, lives on less than US$1.25 per day, and 73% of the population lives on less than US$2 per day [1]. In the 2010 Global Burden of Disease Study, NTDs accounted for 26.06 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) (95% confidence interval: 20.30, 35.12) [2]. -

7 Microbial Aspects
7 Microbial aspects he greatest risk from microbes in water is associated with consumption of Tdrinking-water that is contaminated with human and animal excreta, although other sources and routes of exposure may also be significant. This chapter focuses on organisms for which there is evidence, from outbreak studies or from prospective studies in non-outbreak situations, of disease being caused by ingestion of drinking-water, inhalation of droplets or contact with drinking-water; and their control. 7.1 Microbial hazards associated with drinking-water Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria, viruses and parasites (e.g., proto- zoa and helminths) are the most common and widespread health risk associated with drinking-water. The public health burden is determined by the severity of the illness(es) associated with pathogens, their infectivity and the population exposed. Breakdown in water supply safety may lead to large-scale contamination and potentially to detectable disease outbreaks. Other breakdowns and low-level, poten- tially repeated contamination may lead to significant sporadic disease, but is unlikely to be associated with the drinking-water source by public health surveillance. Quantified risk assessment can assist in understanding and managing risks, espe- cially those associated with sporadic disease. 7.1.1 Waterborne infections The pathogens that may be transmitted through contaminated drinking-water are diverse. Table 7.1 and Figure 7.1 provide general information on pathogens that are of relevance for drinking-water supply management. The spectrum changes in response to variables such as increases in human and animal populations, escalating use of wastewater, changes in lifestyles and medical interventions, population move- ment and travel and selective pressures for new pathogens and mutants or recombi- nations of existing pathogens. -

Monitoring for Microbial Pathogens and Indicators
Through the National Nonpoint Source Monitoring Program (NNPSMP), states monitor and evaluate a subset of watershed projects funded by the Clean Water Act Section 319 Nonpoint Source Control Program. The program has two major objectives: 1. To scientifically evaluate the effectiveness of watershed technologies designed to control nonpoint source pollution September 2013 Revised, originally published August 2013 2. To improve our understanding of nonpoint source pollution Donald W. Meals, Jon B. Harcum, and Steven A. Dressing. 2013. Monitoring for microbial pathogens and indicators. Tech Notes 9, NNPSMP Tech Notes is a series of publications that shares this unique September 2013. Developed for U.S. Environmental Protection Agency research and monitoring effort. It offers guidance on data collection, by Tetra Tech, Inc., Fairfax, VA, 29 p. Available online at https://www.epa. implementation of pollution control technologies, and monitoring design, gov/polluted-runoff-nonpoint-source-pollution/nonpoint-source-monitoring- as well as case studies that illustrate principles in action. technical-notes. Monitoring for Microbial Pathogens and Indicators Introduction The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) 2010 A 1993 outbreak of cryptosporidiosis in National Water Quality Assessment lists pathogens (including Milwaukee is the largest waterborne disease indicators) as the leading cause of impairment for rivers and outbreak ever reported in the U.S. An streams, the number two cause of wetland impairment, and the estimated 400,000 people were reported ill. High tributary flows into Lake Michigan third-ranked cause of impairments in the nation’s bays and estuaries because of rain and snow runoff may have (USEPA 2012b). Pathogens have been the focus of more than transported the parasites great distances 11,000 total maximum daily load (TMDL) determinations since into the lake from its watershed, and from there to the water plant intake. -

Human Activity and Spread of the Pathogen That Causes Sudden Oak Death1
Human Activity and Spread of the Pathogen 1 That Causes Sudden Oak Death Hall Cushman2 and Ross Meentemeyer3 Abstract A striking consequence of globalization is the tremendous influx of infectious diseases and invasive, non-natives species worldwide. One invader of great concern is the fungus-like pathogen, Phytophthora ramorum, which causes a devastating forest disease known as Sudden Oak Death (SOD) in many coastal regions of California and Oregon. In addition, P. ramorum has been found in nurseries and managed landscapes throughout Europe (11 countries so far) and recent laboratory studies have indicated that numerous oak species in the eastern United States are extremely susceptible to attack by the pathogen, should it reach these areas in the future. Here, we evaluate the influence of human activity on the distribution of this pathogen at three spatial scales in California. At the local scale, we found that P. ramorum was significantly more common in soil found on hiking trails at Fairfield Osborn Preserve than from adjacent areas off trail. At the landscape scale, forests on public lands in eastern Sonoma County open to recreation had significantly higher proportions of diseased host trees than those on private lands. And at the regional scale, forested areas in northern and central California surrounded by large human populations were significantly more likely to have infected host trees. Collectively, these findings suggest that humans are important dispersal agents of a destructive pathogen and promote its spread. Efforts to address this epidemic may thus require aggressive management of human activity, which could be logistically and politically difficult to achieve. -

Flowering Plant Composition Shapes Pathogen Infection Intensity and Reproduction in Bumble Bee Colonies
Flowering plant composition shapes pathogen infection intensity and reproduction in bumble bee colonies Lynn S. Adlera,1, Nicholas A. Barberb, Olivia M. Billerc, and Rebecca E. Irwind aDepartment of Biology, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003; bEcology Program Area, Department of Biology, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA 92182; cDepartment of Occupational Therapy, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA 19107; and dDepartment of Applied Ecology, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 27695 Edited by Nils Chr. Stenseth, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, and approved April 10, 2020 (received for review January 3, 2020) Pathogens pose significant threats to pollinator health and food the number of trees and shrubs was positively correlated with security. Pollinators can transmit diseases during foraging, but the phorid fly parasitism in both honey and bumble bees (18). In consequences of plant species composition for infection is un- another study, the prevalence of deformed wing virus and black known. In agroecosystems, flowering strips or hedgerows are queen cell virus was higher in bumble bees and on flowers near often used to augment pollinator habitat. We used canola as a honey bee apiaries, suggesting that flowers are the site of virus focal crop in tents and manipulated flowering strip composition transmission from commercial honey bees to wild bumble bees using plant species we had previously shown to result in higher or (19). All of these studies suggest that floral resources can in- lower bee infection in short-term trials. We also manipulated ini- crease both bee abundance and risks of pathogen or parasite tial colony infection to assess impacts on foraging behavior. -

The Tragedy of Viral Diagnosis
Postgrad Med J: first published as 10.1136/pgmj.46.539.545 on 1 September 1970. Downloaded from Postgraduate Medical Journal (September 1970) 46, 545-550. The tragedy of viral diagnosis ERNEST C. HERRMANN, JR Ph.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Department ofMicrobiology and Immunology Rochester, Minnesota Summary Retrospective diagnosis The shortcomings of the methods commonly recom- Perhaps one can obtain a clue to the problem in mended for the diagnosis of viral infections are what Lennette, a recognized leader in viral diagnosis, emphasized. says: 'Isolation and identification of an agent are Most of them are laborious and expensive, and are still, in most cases, relatively costly procedures and of very little practical value to the clinician. seldom give information which cannot be more Nine years' experience has confirmed that the simply, more rapidly, and less expensively (albeit use of a single swab, obtained during the acute stage retrospectively) obtained by serologic methods' of the illness, for bacterial culture and viral isolation (Lennette, 1964). Lennette is also the chief editor (looking for cytopathic effects or haemadsorption) of the latest version of another manual purporting copyright. provides the diagnosis quickly in the great majority to show how viral disease should be diagnosed, and of viral infections. he is consistent (Blair, Lennette & Truant, 1970). The serological approach is emphasized in virtually every presentation on the subject. As will be shown, Introduction this emphasis is wrong. The key words in Lennette's Most infectious disease suffered by humans remarks are, of course, 'albeit retrospectively'. affects the upper respiratory tract. If, as has been A retrospective diagnosis is largely an academic shown in a variety of studies (Dingle et al., 1953; exercise, not very useful in the practice of medicine.