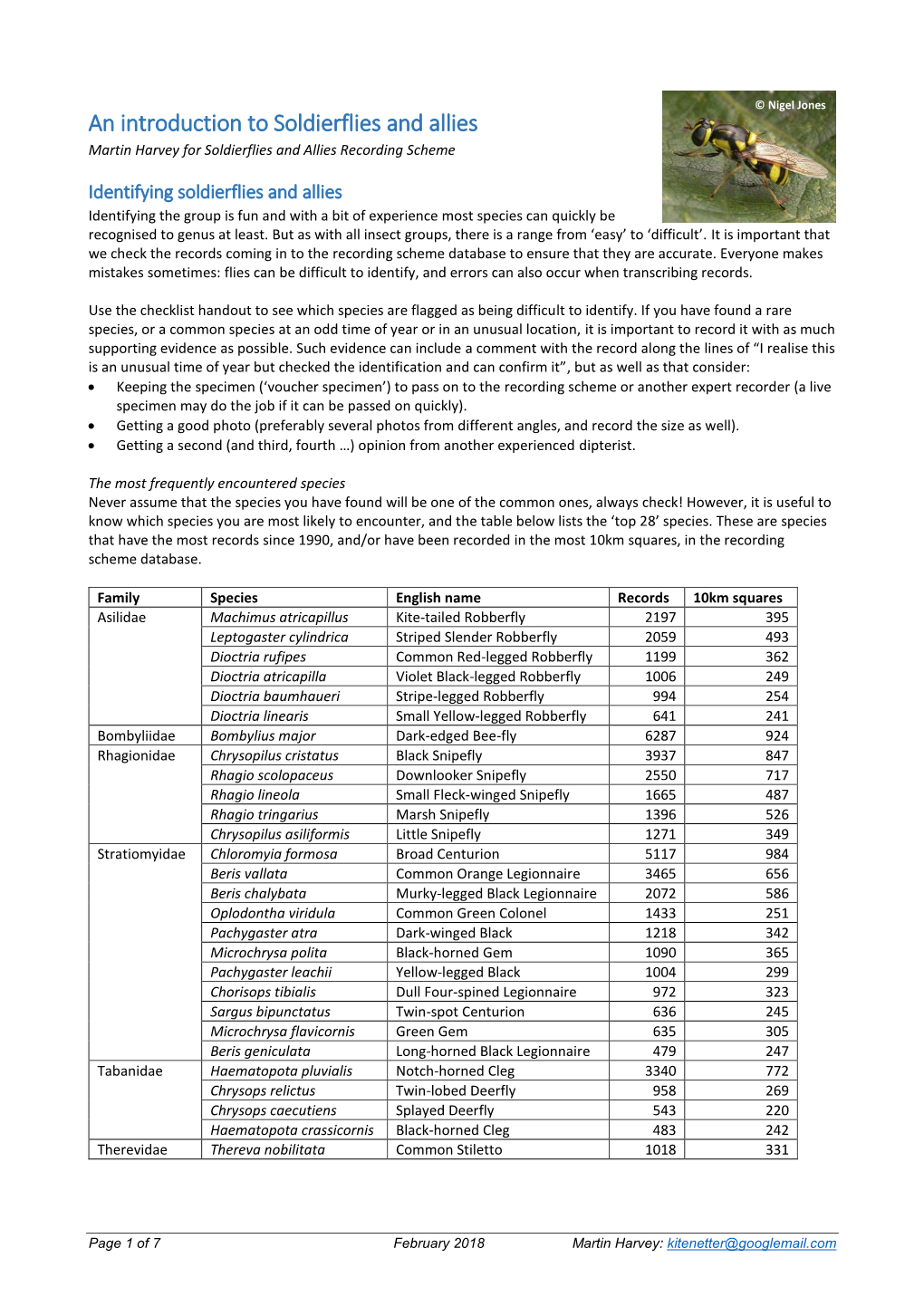
An Introduction to Soldierflies and Allies Martin Harvey for Soldierflies and Allies Recording Scheme
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

R. P. LANE (Department of Entomology), British Museum (Natural History), London SW7 the Diptera of Lundy Have Been Poorly Studied in the Past
Swallow 3 Spotted Flytcatcher 28 *Jackdaw I Pied Flycatcher 5 Blue Tit I Dunnock 2 Wren 2 Meadow Pipit 10 Song Thrush 7 Pied Wagtail 4 Redwing 4 Woodchat Shrike 1 Blackbird 60 Red-backed Shrike 1 Stonechat 2 Starling 15 Redstart 7 Greenfinch 5 Black Redstart I Goldfinch 1 Robin I9 Linnet 8 Grasshopper Warbler 2 Chaffinch 47 Reed Warbler 1 House Sparrow 16 Sedge Warbler 14 *Jackdaw is new to the Lundy ringing list. RECOVERIES OF RINGED BIRDS Guillemot GM I9384 ringed 5.6.67 adult found dead Eastbourne 4.12.76. Guillemot GP 95566 ringed 29.6.73 pullus found dead Woolacombe, Devon 8.6.77 Starling XA 92903 ringed 20.8.76 found dead Werl, West Holtun, West Germany 7.10.77 Willow Warbler 836473 ringed 14.4.77 controlled Portland, Dorset 19.8.77 Linnet KC09559 ringed 20.9.76 controlled St Agnes, Scilly 20.4.77 RINGED STRANGERS ON LUNDY Manx Shearwater F.S 92490 ringed 4.9.74 pullus Skokholm, dead Lundy s. Light 13.5.77 Blackbird 3250.062 ringed 8.9.75 FG Eksel, Belgium, dead Lundy 16.1.77 Willow Warbler 993.086 ringed 19.4.76 adult Calf of Man controlled Lundy 6.4.77 THE DIPTERA (TWO-WINGED FLffiS) OF LUNDY ISLAND R. P. LANE (Department of Entomology), British Museum (Natural History), London SW7 The Diptera of Lundy have been poorly studied in the past. Therefore, it is hoped that the production of an annotated checklist, giving an indication of the habits and general distribution of the species recorded will encourage other entomologists to take an interest in the Diptera of Lundy. -

On the Microscope As an Aid to the Study of Biology in Entomology
JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL MICROSCOPICAL SOCIETY. AUGUST, 1908. TRANSACTIONS OF THE SOCIETY. XI.-On the Microscop as an Aid to the fltudy of Biology in Entomology, with particular reference to the Food of Insects. By W. WESCHE,F.R.M.S. (Read January 15, 1908.) PLATESV. TO X. ENTOMOLOGISTSare generally satisfied with the identification and classification of their specimens ; connected with this work are many points of the greatest interest, such as variation and mimicry, and in the phylogeny new points are constantly arising and give little leisure for other work. So the large majority of the life-histories still remain unstudied, and the habits of many well known species _-- -I__- EXPLANATION OF PLATE V. Fig. 1.-Fore leg of Chrysops cecutiens L. 0. To illustrate the simple type of limb. This insect belongs to the family of the Tabanids, and is a well known and keen blood-sucker. It is mot with in our English woods and meadows. Fig. 2.-Middle leg of Chrysopilus aureus Mg. 0. Simple type. Belongs to the Leptids, and is not uncommon in long grass and meadows. Fig. 3.-Hind leg of Beris vallata Forst. 0. Simple type. Belongs to the Stratiomyidse ; is very common, and found on the hedges. Fig. 4.-Fore leg of Hydrophorus ; species undetermined ( 8 ). To illustrate the raptorial or predaceous type. Belongs to the Dolichopodidze, and resembles Aphrosylus in the structure of the legs, but has dissimilar mouth-parts. It is a small Australian insect, which I captured at Geelong, Vic. Fig. B.-Fore leg of Notiphila cincrea Fln. -

Ecological Survey of Land at Beesley Green, Salford, Greater Manchester
Peel Investments (North) Ltd ECOLOGICAL SURVEY OF LAND AT BEESLEY GREEN, SALFORD, GREATER MANCHESTER DRAFT V1 SEPTEMBER 2013 ESL (Ecological Services) Ltd, 1 Otago House, Allenby Business Village, Crofton Road, Lincoln, LN3 4NL Ecological Survey of Land at Beesley Green, Salford, Greater Manchester SCS.PH Peel Investments (North) Ltd DOCUMENT CONTROL TITLE: Ecological Survey of Land at Beesley Green, Salford, Greater Manchester VERSION: Draft V1 DATE: September 2013 ISSUED BY: Brian Hedley AUTHORS: Brian Hedley, Emily Cook, Pete Morrell, Jackie Nicholson and Andy Jukes CHECKED BY: Andrew Malkinson APPROVED BY: Vanessa Tindale ISSUED TO: Peel Investments (North) Ltd Peel Dome The Trafford Centre Manchester M17 8PL This report has been prepared by ESL with all reasonable skill, care and diligence, within the terms of the contract with the Client. The report is confidential to the Client. ESL accepts no responsibility of whatever nature to third parties to whom this report may be made known. No part of this document may be reproduced without the prior written approval of ESL. ESL (Ecological Services) Ltd, 1 Otago House, Allenby Business Village, Crofton Road, Lincoln, LN3 4NL Ecological Survey of Land at Beesley Green, Salford, Greater Manchester SCS.PH Peel Investments (North) Ltd CONTENTS Page 1 INTRODUCTION 1 2 INITIAL SCOPING STUDY 1 2.1 Desk-based Study 1 2.2 Walkover Survey 3 2.3 Summary of Walkover and Recommendations for Further Survey 4 3 HABITATS, PLANT COMMUNITIES AND SPECIES 6 3.1 Survey Methods 6 3.2 Results 6 3.3 Discussion -

Dipterists Forum
BULLETIN OF THE Dipterists Forum Bulletin No. 76 Autumn 2013 Affiliated to the British Entomological and Natural History Society Bulletin No. 76 Autumn 2013 ISSN 1358-5029 Editorial panel Bulletin Editor Darwyn Sumner Assistant Editor Judy Webb Dipterists Forum Officers Chairman Martin Drake Vice Chairman Stuart Ball Secretary John Kramer Meetings Treasurer Howard Bentley Please use the Booking Form included in this Bulletin or downloaded from our Membership Sec. John Showers website Field Meetings Sec. Roger Morris Field Meetings Indoor Meetings Sec. Duncan Sivell Roger Morris 7 Vine Street, Stamford, Lincolnshire PE9 1QE Publicity Officer Erica McAlister [email protected] Conservation Officer Rob Wolton Workshops & Indoor Meetings Organiser Duncan Sivell Ordinary Members Natural History Museum, Cromwell Road, London, SW7 5BD [email protected] Chris Spilling, Malcolm Smart, Mick Parker Nathan Medd, John Ismay, vacancy Bulletin contributions Unelected Members Please refer to guide notes in this Bulletin for details of how to contribute and send your material to both of the following: Dipterists Digest Editor Peter Chandler Dipterists Bulletin Editor Darwyn Sumner Secretary 122, Link Road, Anstey, Charnwood, Leicestershire LE7 7BX. John Kramer Tel. 0116 212 5075 31 Ash Tree Road, Oadby, Leicester, Leicestershire, LE2 5TE. [email protected] [email protected] Assistant Editor Treasurer Judy Webb Howard Bentley 2 Dorchester Court, Blenheim Road, Kidlington, Oxon. OX5 2JT. 37, Biddenden Close, Bearsted, Maidstone, Kent. ME15 8JP Tel. 01865 377487 Tel. 01622 739452 [email protected] [email protected] Conservation Dipterists Digest contributions Robert Wolton Locks Park Farm, Hatherleigh, Oakhampton, Devon EX20 3LZ Dipterists Digest Editor Tel. -

Final Report 1
Sand pit for Biodiversity at Cep II quarry Researcher: Klára Řehounková Research group: Petr Bogusch, David Boukal, Milan Boukal, Lukáš Čížek, František Grycz, Petr Hesoun, Kamila Lencová, Anna Lepšová, Jan Máca, Pavel Marhoul, Klára Řehounková, Jiří Řehounek, Lenka Schmidtmayerová, Robert Tropek Březen – září 2012 Abstract We compared the effect of restoration status (technical reclamation, spontaneous succession, disturbed succession) on the communities of vascular plants and assemblages of arthropods in CEP II sand pit (T řebo ňsko region, SW part of the Czech Republic) to evaluate their biodiversity and conservation potential. We also studied the experimental restoration of psammophytic grasslands to compare the impact of two near-natural restoration methods (spontaneous and assisted succession) to establishment of target species. The sand pit comprises stages of 2 to 30 years since site abandonment with moisture gradient from wet to dry habitats. In all studied groups, i.e. vascular pants and arthropods, open spontaneously revegetated sites continuously disturbed by intensive recreation activities hosted the largest proportion of target and endangered species which occurred less in the more closed spontaneously revegetated sites and which were nearly absent in technically reclaimed sites. Out results provide clear evidence that the mosaics of spontaneously established forests habitats and open sand habitats are the most valuable stands from the conservation point of view. It has been documented that no expensive technical reclamations are needed to restore post-mining sites which can serve as secondary habitats for many endangered and declining species. The experimental restoration of rare and endangered plant communities seems to be efficient and promising method for a future large-scale restoration projects in abandoned sand pits. -

Biologie, Vývoj a Zoogeografie Vybraných Saproxylických Skupin
1 Masarykova univerzita Přírodovědecká fakulta Katedra zoologie a ekologie Biologie, vývoj a zoogeografie vybraných saproxylických skupin orientálních druhů čeledi Stratiomyidae Diplomová práce 2007 Prof. RNDr. R. Rozkošný, Dr. Sc. Alena Bučánková 2 Biologie, vývoj a zoogeografie vybraných saproxylických skupin orientálních druhů čeledi Stratiomyidae Abstrakt Je popsána morfologie, biologie a zoogeografie larev čtyř druhů z čeledi Stratiomyidae. Dva z nich, Pegadomyia pruinosa a Craspedometopon sp. n., patří do podčeledi Pachygasterinae, další dva, Adoxomyia bistriata a Cyphomyia bicarinata , patří do podčeledi Clitellariinae. Larvy byly sbírány Dr. D. Kovacem pod kůrou padlých stromů v Malysii a Thajsku. Saproxylický způsob života larev v rámci celé čeledi je zde diskutován jako původní stav. Byly vytypovány morfologické a biologické znaky larev s možným fylogenetickým významem a jejich platnost byla vyzkoušena v kladistických programech Nona a Winclada. Zjištěný fylogenetický vztah hlavních podčeledí odpovídá v podstatě současnému systému čeledi. Překážkou detailnímu vyhodnocení jsou zatím jen nedostatečné popisy larev a jejich malá znalost, zvláště v tropických oblastech. Biology, development and zoogeography of some saproxylic Oriental species of Stratiomyidae (Diptera) Abstract The morphology, biology and zoogeography of four larvae of Stratiomyidae are described. Two of them, Pegadomyia pruinosa , Craspedometopon sp. n. belong to the subfamily Pachygasteinae, the others, Adoxomyia bistriata and Cyphomyia bicarinata are placed to the subfamily Clitellariinae. The larvae were collected under the bark of fallen trees in Malaysia and Thailand by Dr. D. Kovac. The saproxylic habitat of stratiomyid larvae is discussed in this thesis as an original state. The morphological and biological characters of possible phylogenetic significance are evaluated and their value was verified with use of Nona and Winclada programs. -

Ad Hoc Referees Committee for This Issue Thomas Dirnböck
COMITATO DI REVISIONE PER QUESTO NUMERO – Ad hoc referees committee for this issue Thomas Dirnböck Umweltbundesamt GmbH Studien & Beratung II, Spittelauer Lände 5, 1090 Wien, Austria Marco Kovac Slovenian Forestry Institute, Vecna pot 2, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenija Susanna Nocentini Università degli Studi di Firenze, DISTAF, Via S. Bonaventura 13, 50145 Firenze Ralf Ohlemueller Department of Biology, University of York, PO Box 373, York YO10 5YW, UK Sandro Pignatti Orto Botanico di Roma, Dipartimento di Biologia Vegetale, L.go Cristina di Svezia, 24, 00165 Roma Stergios Pirintsos Department of Biology, University of Crete, P.O.Box 2208, 71409 Heraklion, Greece Matthias Plattner Hintermann & Weber AG, Oeko-Logische Beratung Planung Forschung, Hauptstrasse 52, CH-4153 Reinach Basel Arne Pommerening School of Agricultural & Forest Sciences, University of Wales, Bangor, Gwynedd LL57 2UW, DU/ UK Roberto Scotti Università degli Studi di Sassari, DESA, Nuoro branch, Via C. Colombo 1, 08100 Nuoro Franz Starlinger Forstliche Bundesversuchsanstalt Wien, A 1131 Vienna, Austria Silvia Stofer Eidgenössische Forschungsanstalt für Wald, Schnee und Landschaft – WSL, Zürcherstrasse 111, CH-8903 Birmensdorf, Switzerland Norman Woodley Systematic Entomology Lab-USDA , c/o Smithsonian Institution NHB-168 , O Box 37012 Washington, DC 20013-7012 CURATORI DI QUESTO NUMERO – Editors Marco Ferretti, Bruno Petriccione, Gianfranco Fabbio, Filippo Bussotti EDITORE – Publisher C.R.A. - Istituto Sperimentale per la Selvicoltura Viale Santa Margherita, 80 – 52100 Arezzo Tel.. ++39 0575 353021; Fax. ++39 0575 353490; E-mail:[email protected] Volume 30, Supplemento 2 - 2006 LIST OF CONTRIBUTORS C.R.A.A - ISTITUTO N SPERIMENTALE N A PER LA LSELVICOLTURA I (in alphabetic order) Allegrini, M. C. -

6. Bremsen Als Parasiten Und Vektoren
DIPLOMARBEIT / DIPLOMA THESIS Titel der Diplomarbeit / Title of the Diploma Thesis „Blutsaugende Bremsen in Österreich und ihre medizini- sche Relevanz“ verfasst von / submitted by Manuel Vogler angestrebter akademischer Grad / in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Magister der Naturwissenschaften (Mag.rer.nat.) Wien, 2019 / Vienna, 2019 Studienkennzahl lt. Studienblatt / A 190 445 423 degree programme code as it appears on the student record sheet: Studienrichtung lt. Studienblatt / Lehramtsstudium UF Biologie und Umweltkunde degree programme as it appears on UF Chemie the student record sheet: Betreut von / Supervisor: ao. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Andreas Hassl Danksagung Hiermit möchte ich mich sehr herzlich bei Herrn ao. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Andreas Hassl für die Vergabe und Betreuung dieser Diplomarbeit bedanken. Seine Unterstützung und zahlreichen konstruktiven Anmerkungen waren mir eine ausgesprochen große Hilfe. Weiters bedanke ich mich bei meiner Mutter Karin Bock, die sich stets verständnisvoll ge- zeigt und mich mein ganzes Leben lang bei all meinen Vorhaben mit allen ihr zur Verfügung stehenden Kräften und Mitteln unterstützt hat. Ebenso bedanke ich mich bei meiner Freundin Larissa Sornig für ihre engelsgleiche Geduld, die während meiner zahlreichen Bremsenjagden nicht selten auf die Probe gestellt und selbst dann nicht überstrapaziert wurde, als sie sich während eines Ausflugs ins Wenger Moor als ausgezeichneter Bremsenmagnet erwies. Auch meiner restlichen Familie gilt mein Dank für ihre fortwährende Unterstützung. -

A Review of the Status of Larger Brachycera Flies of Great Britain
Natural England Commissioned Report NECR192 A review of the status of Larger Brachycera flies of Great Britain Acroceridae, Asilidae, Athericidae Bombyliidae, Rhagionidae, Scenopinidae, Stratiomyidae, Tabanidae, Therevidae, Xylomyidae. Species Status No.29 First published 30th August 2017 www.gov.uk/natural -england Foreword Natural England commission a range of reports from external contractors to provide evidence and advice to assist us in delivering our duties. The views in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of Natural England. Background Making good decisions to conserve species This report should be cited as: should primarily be based upon an objective process of determining the degree of threat to DRAKE, C.M. 2017. A review of the status of the survival of a species. The recognised Larger Brachycera flies of Great Britain - international approach to undertaking this is by Species Status No.29. Natural England assigning the species to one of the IUCN threat Commissioned Reports, Number192. categories. This report was commissioned to update the threat status of Larger Brachycera flies last undertaken in 1991, using a more modern IUCN methodology for assessing threat. Reviews for other invertebrate groups will follow. Natural England Project Manager - David Heaver, Senior Invertebrate Specialist [email protected] Contractor - C.M Drake Keywords - Larger Brachycera flies, invertebrates, red list, IUCN, status reviews, IUCN threat categories, GB rarity status Further information This report can be downloaded from the Natural England website: www.gov.uk/government/organisations/natural-england. For information on Natural England publications contact the Natural England Enquiry Service on 0300 060 3900 or e-mail [email protected]. -

Pick Your Poison: Molecular Evolution of Venom Proteins in Asilidae (Insecta: Diptera)
toxins Article Pick Your Poison: Molecular Evolution of Venom Proteins in Asilidae (Insecta: Diptera) Chris M. Cohen * , T. Jeffrey Cole and Michael S. Brewer * Howell Science Complex, East Carolina University, 1000 E 5th St., Greenville, NC 27858, USA; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] (C.M.C.); [email protected] (M.S.B.) Received: 5 November 2020; Accepted: 20 November 2020; Published: 24 November 2020 Abstract: Robber flies are an understudied family of venomous, predatory Diptera. With the recent characterization of venom from three asilid species, it is possible, for the first time, to study the molecular evolution of venom genes in this unique lineage. To accomplish this, a novel whole-body transcriptome of Eudioctria media was combined with 10 other publicly available asiloid thoracic or salivary gland transcriptomes to identify putative venom gene families and assess evidence of pervasive positive selection. A total of 348 gene families of sufficient size were analyzed, and 33 of these were predicted to contain venom genes. We recovered 151 families containing homologs to previously described venom proteins, and 40 of these were uniquely gained in Asilidae. Our gene family clustering suggests that many asilidin venom gene families are not natural groupings, as delimited by previous authors, but instead form multiple discrete gene families. Additionally, robber fly venoms have relatively few sites under positive selection, consistent with the hypothesis that the venoms of older lineages are dominated by negative selection acting to maintain toxic function. Keywords: Asilidae; transcriptome; positive selection Key Contribution: Asilidae venoms have relatively few sites under positive selection, consistent with the hypothesis that the venoms of older lineages are dominated by negative selection acting to maintain toxic function. -

Insects and Related Arthropods Associated with of Agriculture
USDA United States Department Insects and Related Arthropods Associated with of Agriculture Forest Service Greenleaf Manzanita in Montane Chaparral Pacific Southwest Communities of Northeastern California Research Station General Technical Report Michael A. Valenti George T. Ferrell Alan A. Berryman PSW-GTR- 167 Publisher: Pacific Southwest Research Station Albany, California Forest Service Mailing address: U.S. Department of Agriculture PO Box 245, Berkeley CA 9470 1 -0245 Abstract Valenti, Michael A.; Ferrell, George T.; Berryman, Alan A. 1997. Insects and related arthropods associated with greenleaf manzanita in montane chaparral communities of northeastern California. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-167. Albany, CA: Pacific Southwest Research Station, Forest Service, U.S. Dept. Agriculture; 26 p. September 1997 Specimens representing 19 orders and 169 arthropod families (mostly insects) were collected from greenleaf manzanita brushfields in northeastern California and identified to species whenever possible. More than500 taxa below the family level wereinventoried, and each listing includes relative frequency of encounter, life stages collected, and dominant role in the greenleaf manzanita community. Specific host relationships are included for some predators and parasitoids. Herbivores, predators, and parasitoids comprised the majority (80 percent) of identified insects and related taxa. Retrieval Terms: Arctostaphylos patula, arthropods, California, insects, manzanita The Authors Michael A. Valenti is Forest Health Specialist, Delaware Department of Agriculture, 2320 S. DuPont Hwy, Dover, DE 19901-5515. George T. Ferrell is a retired Research Entomologist, Pacific Southwest Research Station, 2400 Washington Ave., Redding, CA 96001. Alan A. Berryman is Professor of Entomology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164-6382. All photographs were taken by Michael A. Valenti, except for Figure 2, which was taken by Amy H. -

Scottish Pollinating Flies
Scottish Pollinating Flies Introduction to True flies True flies form one of the largest and most diverse orders of insects called Diptera (meaning two wings). There are around 160,000 species worldwide in 150 families, with 7,200 species from over 90 families recorded in the UK. They inhabit every continent and almost every terrestrial and freshwater niche on the planet which is testament to their adaptability. True flies differ from other insects in that they have retained only their front pair of wings, with the hind pair having evolved into small club-shaped appendages called ‘halteres’ which act as gyroscopes and facilitate greater aerobatic agility. They provide a range of ecological services including pollination, controlling pest species, the decomposition of organic material, and supplementing the dietary requirements of a wide range of other organisms. Pollinating flies and other dipterans Of the four most significant orders of pollinating insects, flies are the most abundant. Approximately 1,500 of the 7,200 British species are thought to contribute to pollination. Hoverflies (family Syrphidae) are especially significant pollinators, but some other families (the house flies and their relatives) are just as important. The remainder of the 90+ families contribute relatively few, or no pollinating species. True flies contribute to more pollination in Scotland than any other order of insects, mainly due to the sparsity, absence or selectiveness of bees in colder, northern upland habitats. Below are some examples that demonstrate the diversity of true flies that may be encountered. Common dronefly (Eristalis tenax) Splayed deerfly Chrysops( caecutiens) © Steven Falk © Steven © Steven Falk © Steven Cranefly Tipula lateralis Orange-legged robberfly (Dioctria oelandica) © Steven Falk © Steven Falk © Steven Buglife—The Invertebrate Conservation Trust is a company limited by guarantee.