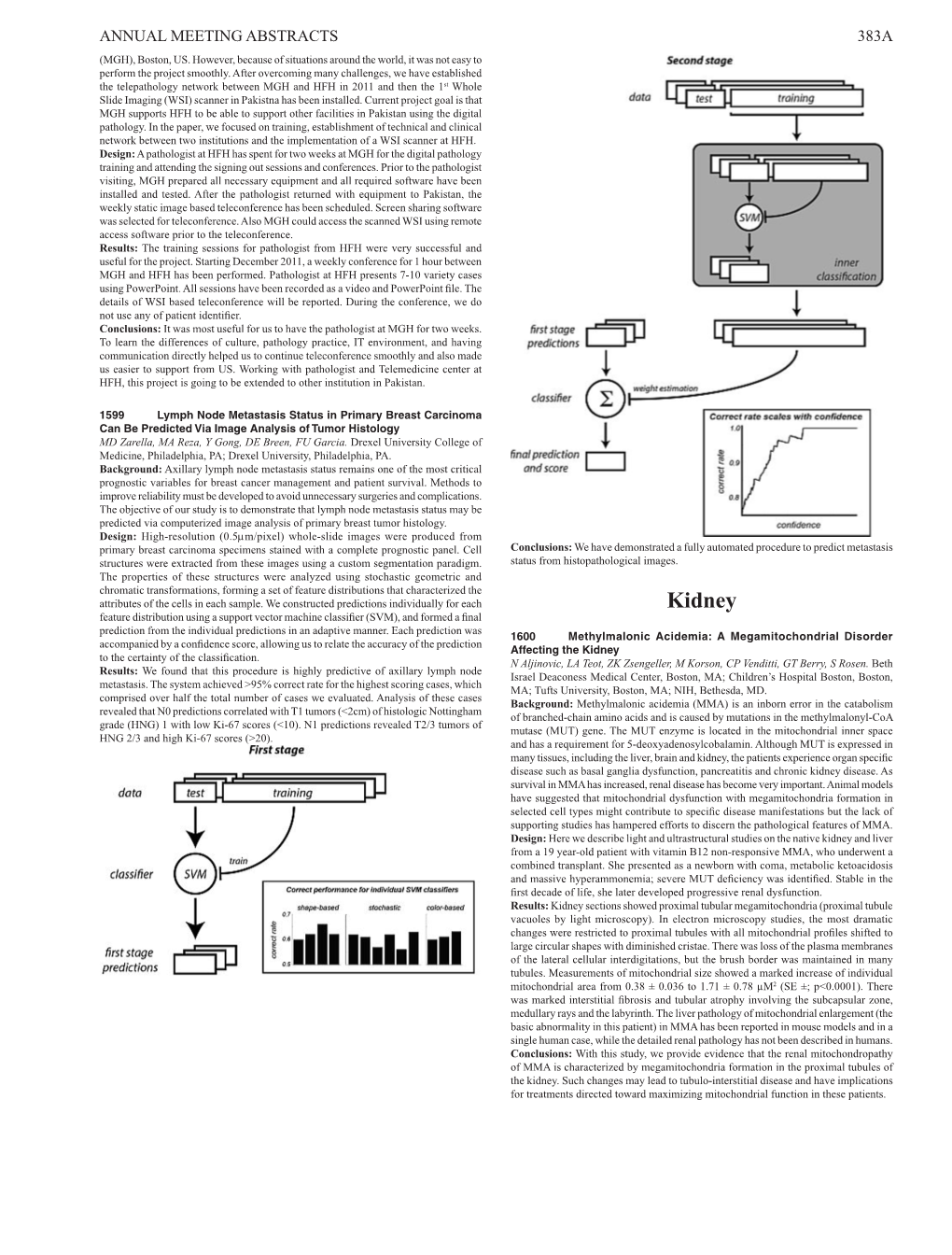
Kidney Feature Distribution Using a Support Vector Machine Classifier (SVM), and Formed a Final Prediction from the Individual Predictions in an Adaptive Manner
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Perturbation of Mitochondrial Dynamics in Alcoholic Liver Disease
EXTENDED ABSTRACT Journal of the World Mitochondria Society Vol. 2, Issue n°2 DOI 10.18143/JWMS_v2i2_1948 Perturbation of mitochondrial dynamics in alcoholic liver disease Elena PALMA(1, 2), Antonio RIVA(1, 2), Satvinder MUDAN(3), Nikolai MANYAKIN(3), Dawn MORRISON(3), Christophe MORENO(4, 5), Delphine DEGRÉ(4, 5), Eric TREPO(4, 5), Pau SANCHO- BRU(6, 7), Jose ALTAMIRANO(6, 8), Juan CABALLERIA(6, 7), Gemma ODENA(9), Ramon BATALLER(9), Roger WILLIAMS(1, 2), Shilpa CHOKSHI(1, 2) 1Institute of Hepatology, Foundation for Liver Research, London, United Kingdom. 2King’s College London, Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, London, United Kingdom. 3The London Clinic, London, United Kingdom. 4CUB Hôpital Erasme, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatopancreatology and Digestive Oncology, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium. 5Laboratory of Experimental Gastroenterology, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium. 6Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain. 7Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBERehd), Barcelona, Spain. 8Liver Unit -Internal Medicine Department Vall d'Hebron University Hospital. Vall d'Hebron Institut de Recerca (VHIR), Barcelona, Spain. 9Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Departments of Medicine and Nutrition, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. Corresponding author: Elena Palma Institute of Hepatology, Foundation for Liver Research 111 Coldharbour Lane, London, SE5 9NT (UK) [email protected] Abstract Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) is a global issue that causes increasing number of deaths annually. In the complex pathogenesis of ALD the involvement of mitochondria is well established and gross morphological alterations (mega-mitochondria) in the liver biopsies of patients are recognised as hallmarks of ALD. -

Review Article Alcohol Induced Liver Disease
J Clin Pathol: first published as 10.1136/jcp.37.7.721 on 1 July 1984. Downloaded from J Clin Pathol 1984;37:721-733 Review article Alcohol induced liver disease KA FLEMING, JO'D McGEE From the University of Oxford, Nuffield Department ofPathology, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford OX3 9DU, England SUMMARY Alcohol induces a variety of changes in the liver: fatty change, hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. The histopathological appearances of these conditions are discussed, with special atten- tion to differential diagnosis. Many forms of alcoholic liver disease are associated with Mallory body formation and fibrosis. Mallory bodies are formed, at least in part, from intermediate filaments. Associated changes in intermediate filament organisation in alcoholic liver disease also occur. Their significance in the pathogenesis of hepatocyte death may be related to abnormalities in messenger RNA function. The mechanisms underlying hepatic fibrogenesis are also discussed. Although alcohol has many effects on the liver, all formed after some period of alcohol abstinence, except cirrhosis are potentially reversible on cessa- alcohol related changes may not be seen. Accord- tion of alcohol ingestion. Cirrhosis is irreversible ingly, we shall consider the morphological changes and usually ultimately fatal. It is therefore important associated with alcohol abuse under the headings in to determine what factors are responsible for Table 1. development of alcohol induced cirrhosis, especially In the second part, the pathogenesis of alcohol since only 17-30% of all alcoholics become' cirrho- induced liver disease will be discussed, but this will tic.' This is of some urgency now, since there has deal only with the induction of alcoholic hepatitis, been an explosive increase in alcohol consumption fibrosis, and cirrhosis-that is, chronic alcoholic http://jcp.bmj.com/ in the Western World, particularly affecting young liver disease-and not with fatty change, for two people, resulting in a dramatic increase in the inci- reasons. -

1 Pathology Week 1 – Cellular Adaptation, Injury and Death
Pathology week 1 – Cellular adaptation, injury and death Cellular responses to injury Cellular Responses to Injury Nature and Severity of Injurious Stimulus Cellular Response Altered physiologic stimuli: Cellular adaptations: • ↑demand, ↑ trophic stimulation (e.g. growth factors, hormones) • Hyperplasia, hypertrophy • ↓ nutrients, stimulation • Atrophy • Chronic irritation (chemical or physical) • Metaplasia Reduced oxygen supply; chemical injury; microbial infection Cell injury: • Acute and self-limited • Acute reversible injury • Progessive and severe (including DNA damage) • Irreversible injury → cell death Necrosis Apoptosis • Mild chronic injury • Subcellular alterations in organelles Metabolic alterations, genetic or acquired Intracell accumulations; calcifications Prolonged life span with cumulative sublethal injury Cellular aging Hyperplasia - response to increased demand and external stimulation - ↑ number cells - ↑ volume of organ - often occurs with hypertrophy - occurs if cells able to synthesize DNA – mitotic division - physiologic or pathologic Physiological hyperplasia A) hormonal – ↑ functional capacity tissue when needed (breast in puberty, uterus in pregnancy) B) compensatory - ↑ tissue mass after damage/resection (post-nephrectomy) Mechanisms: - ↑ local production growth factors or activation intracellular signaling pathways o both → production transcription factors that turn on cellular genes incl those encoding growth factors, receptors for GFs, cell cycle regulators →→ cellular proli feration - in hormonal hyperplasia -

Liver Giant Mitochondria Revisited
412 J Clin Pathol 1992;45:412-415 Liver giant mitochondria revisited N J Robertson, C H Kendall J Clin Pathol: first published as 10.1136/jcp.45.5.412 on 1 May 1992. Downloaded from Abstract alcohol induced liver damage and the presence Aims: To examine the correlation be- of ICRBs. In a study by Chedid et al' in 1986, tween the severity of alcohol induced ICRBs were observed most frequently in liver liver damage and the presence of biopsies exhibiting mild degrees of alcohol intracytoplasmic red bodies (defined as induced damage. Junge et al2 in 1987 obtained periodic acid-Schiff diastase negative, similar results. However, in a study by globular, hyaline cytoplasmic inclusions Bruguera et al' in 1977 the frequency of larger in size than the hepatocyte ICRBs in liver biopsies from alcoholic nucleolus). To investigate the incidence patients was found to be unrelated to the of intracytoplasmic red bodies (ICRBs) nature of the histological changes present. in non-alcoholic liver disease. The significance of ICRBs with respect to Methods: Liver biopsy specimens from non-alcoholic liver disease remains equally 53 patients with alcoholic liver disease unclear. The main purposes of this study are and 50 patients with a variety of non- therefore: (1) to examine the correlation be- alcohol related liver diseases were tween the severity of alcohol induced liver examined by light microscopy for the damage and the presence of ICRBs; (2) to presence of ICRBs. For the 53 patients investigate the incidence of ICRBs in non- with alcoholic liver disease an assess- alcoholic liver disease. -

Session 2 Cellular and Tissue Response to Damage
Session 2 Cellular and Tissue Response to Damage B.M.C.Randika Wimalasiri B.Sc in MLS(Peradeniya) Lecturer(Probationary) Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences • The changes that occur in the various cellular organelles and cytoskeleton Cellular response to damage • Non lethal damage- changes in organelles and in the cytoskeleton. • The type of response - type of the injurious agent. • Different cellular organelles - different types of damage. • More common reactions. Changes in Mitochondria • Function: mediate cellular respiration • Non lethal damage to mitochondria -alterations in number, size, shape and function. • Examples 1. Hypertrophy - increased demand causes increase in workload ad increase in the number of mitochondria. 2. Atrophy - decrease the number of mitochondria in a cell 3. Megamitochondria - are very large, sometimes abnormally shaped. Ex : alcoholic liver disease nutritional deficiencies 4. Mitochondrial myopathies - group of genetic disorders causing metabolic disease of skeletal muscle. • Increased numbers of unusually large mitochondria containing abnormal cristae filled with crystalloids • muscle fibers do not work due to mitochondrial defects) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum • Functions - detoxification and metabolism of various drugs and chemicals including alcohol, barbiturates, insecticides, steroids etc. • Examples 1. Barbiturates- • metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P-450 oxidase system found in the SER. • Prolonged usage leads to a state of tolerance, with a decrease in the effects of the drug and the need to use increasing doses. This adaptation is due to increased volume (hypertrophy) of the SER of hepatocytes and increased P-450 enzymatic activity. • More of the enzyme is produced the drugs and toxins are metabolized quicker and the patients ‘adapt’ to the drug . -

Communications Between Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum in the Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis
cells Review Communications between Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum in the Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis Pengcheng Zhang, Daniels Konja, Yiwei Zhang and Yu Wang * The State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China; [email protected] (P.Z.); [email protected] (D.K.); [email protected] (Y.Z.) * Correspondence: [email protected] Abstract: Mitochondria associated membranes (MAM), which are the contact sites between en- doplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria, have emerged as an important hub for signaling molecules to integrate the cellular and organelle homeostasis, thus facilitating the adaptation of energy metabolism to nutrient status. This review explores the dynamic structural and functional features of the MAM and summarizes the various abnormalities leading to the impaired insulin sensitivity and metabolic diseases. Keywords: mitochondria; endoplasmic reticulum; MAM; energy metabolism 1. Introduction Citation: Zhang, P.; Konja, D.; Zhang, In mammalian cells, the mitochondrion is the organelle specialized for energy produc- Y.; Wang, Y. Communications tion through the processes of oxidative phosphorylation, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle between Mitochondria and and fatty acid β-oxidation [1]. Approximately 90% of cellular reactive oxygen species Endoplasmic Reticulum in the (ROS) are produced from mitochondria during the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis. (OXPHOS) -

Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Apoptosis Christophe Fleury, Bernard Mignotte, Jean-Luc Vayssière
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and apoptosis Christophe Fleury, Bernard Mignotte, Jean-Luc Vayssière To cite this version: Christophe Fleury, Bernard Mignotte, Jean-Luc Vayssière. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and apoptosis. Mitochondrial Ubiquinone (Coenzyme Q10): Biochemical, Functional, Medical and Therapeutic Aspects in Human Health and Disease, 2002. hal-03002776 HAL Id: hal-03002776 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03002776 Submitted on 12 Nov 2020 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. - 1 - Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and apoptosis Christophe Fleury1, Bernard Mignotte1,2 and Jean-Luc Vayssière1 1 CNRS - UPRES-A 8087, Université de Versailles/Saint-Quentin, Bâtiment Fermat, 45 avenue des Etats-Unis, 78035 VERSAILLES cedex 2 Laboratoire de Génétique Moléculaire et Physiologique de l’EPHE, Université de Versailles/Saint-Quentin, Bâtiment Fermat, 45 avenue des Etats-Unis, 78035 VERSAILLES cedex - 2 - 1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ -

Role and Mechanisms of Mitophagy in Liver Diseases
cells Review Role and Mechanisms of Mitophagy in Liver Diseases Xiaowen Ma 1, Tara McKeen 1, Jianhua Zhang 2 and Wen-Xing Ding 1,* 1 Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutics, University of Kansas Medical Center, 3901 Rainbow Blvd., Kansas City, KS 66160, USA; [email protected] (X.M.); [email protected] (T.M.) 2 Department of Pathology, Division of Molecular Cellular Pathology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 901 19th street South, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +1-913-588-9813 Received: 13 February 2020; Accepted: 28 March 2020; Published: 31 March 2020 Abstract: The mitochondrion is an organelle that plays a vital role in the regulation of hepatic cellular redox, lipid metabolism, and cell death. Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with both acute and chronic liver diseases with emerging evidence indicating that mitophagy, a selective form of autophagy for damaged/excessive mitochondria, plays a key role in the liver’s physiology and pathophysiology. This review will focus on mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy regulation, and their roles in various liver diseases (alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, drug-induced liver injury, hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury, viral hepatitis, and cancer) with the hope that a better understanding of the molecular events and signaling pathways in mitophagy regulation will help identify promising targets for the future treatment of liver diseases. Keywords: alcohol; autophagy; mitochondria; NAFLD; Parkin; Pink1 1. Introduction Autophagy (or macroautophagy) involves the formation of a double membrane structure called an autophagosome. Autophagosomes bring the enveloped cargoes to the lysosomes to form autolysosomes where the lysosomal enzymes consequently degrade the cargos [1,2]. -

What Information Can a Liver Biopsy Provide?
Basic patterns of liver damage: What information can a liver biopsy provide? RCPath, March 2019 Rob Goldin [email protected] @robdgol Fatty liver disease: Core features • Fat • Ballooning • Inflammation • Fibrosis Bedossa P. Diagnosis of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease/non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis: Why liver biopsy is essential. Liver International. 2018 Feb;38:64-6. Roth NC, Qin J. Histopathology of Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases. Clinics in liver disease. 2019 Feb 1;23(1):11-23. Large droplet fatty change Ballooning Bedossa, Pierre, et al. "Histopathological algorithm and scoring system for evaluation of liver lesions in morbidly obese patients." Hepatology 56.5 (2012): 1751-1759. Fibrosis Differentiating ALD from NAFLD • Hepatocellular injury and fibrosis are often more severe in ALD • Some lesions of ALD are very rare or have not been described in patients with pure NAFLD: 1. nuclear vacuolation 2. cholestasis 3. microvesicular steatosis 4. fibro-obliterative changes in hepatic veins (sclerosing hyaline necrosis) EASL Guidelines: ALD Guidelines Thursz M, et al. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. Journal of Hepatology. 2018 Jul 1;69(1):154-81. Fig. 1 European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL clinical practical guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. Journal of Hepatology. 2012 Aug 1;57(2):399-420. ALD: Indications for liver biopsy •Establish the definite diagnosis of ALD •Assess the exact stage and prognosis of liver disease •Predict response to treatment •Exclude alternative or additional causes of liver injury •Trials EASL CPG ALD. J Hepatol 2018;69:154–81 Predicting Response to Treatment in Alcoholic Hepatitis Points Stage of fibrosis No fibrosis or portal fibrosis 0 The AHHS categories: Expansive fibrosis 0 mild, 0–3; Bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis +3 intermediate, 4–5; Bilirubinostasis severe, 6–9. -

What Information Can a Liver Biopsy Provide and What Clinical Information Does the Pathologist Need? Rob Goldin [email protected] @Robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Basic patterns of liver damage – what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin [email protected] @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt EM Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the ongoing role of liver biopsy evaluation. Hepatol Commun. 2017 Jun 7;1(5):370-378. Types of fatty change: Large droplet Types of fatty change: Small droplet Fatty liver disease: • Ballooning and inflammation Recognising ballooning (B) Normal hepatocytes, ballooning, grade 0. Cytoplasm is pink and granular and liver cells have sharp angles. (C) Ballooning, grade 1. Hepatocytes have rounded contours with clear reticular cytoplasm. Size is quite similar to that of normal hepatocytes. (D) Ballooning, grade 2. Cells are rounded with clear cytoplasm and twice as large as normal hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2012 Nov 1;56(5):1751-9 Nuclear vacuolation Predicting Response to Treatment in Alcoholic Hepatitis Points Stage of fibrosis No fibrosis or portal fibrosis 0 Expansive fibrosis 0 Bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis +3 Bilirubinostasis No 0 Hepatocellular only 0 Canalicular or ductular +1 Canalicular or ductular plus +2 hepatocellular PMN infiltration No/Mild +2 Severe 0 Megamitochondria No megamitochondria +2 Megamitochondria 0 The AHHS categories are as follows: mild, 0–3; intermediate, 4–5; severe, 6–9. Gastroenterology. 2014 May 1;146(5):1231-9. ( A ) Hepatocellular and canalicular bilirubinostasis ( arrow ). ( B ) Ductular bilirubinostasis ( arrow ). ( C ) Megamitochondria ( arrows ). NAFLD Activity Score Steatosis grade Lobular Hepatocellular inflammation ballooning 0: <5% 0: None 0: None 1: 5-33% 1:<2 foci/20x field 1: Mild, few 2: 34-66% 2: 2-4 foci/20x 2: Moderate – field marked, 3: >66% 3: >4 foci/20x many field NAFLD activity score (NAS): 0-8 Steatosis (0-3) + Lobular + Ballooning (0- Inflammation (0- 2) 3) Hepatology. -

Alcohol-Related Sudden Death with Hepatic Fatty Metamorphosis
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 32, No. 6, pp. 745-752, 1997 ALCOHOL-RELATED SUDDEN DEATH WITH HEPATIC FATTY METAMORPHOSIS: A COMPREHENSIVE CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL INQUIRY INTO ITS PATHOGENESIS TAKEFUMI YUZURIHA1-2*, MASAHIKO OKUDAIRA2, ITARU TOMINAGA2, SfflNGO HORI3, HIROMICHI SUZUKI4, YOSHIHIRO MATSUO2, MUNESUKE SHOJI2, AKIRA YOKOYAMA1, SATOSHI TAKAGI1 and MOTOI HAYASHIDA1 Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/alcalc/article/32/6/745/204822 by guest on 02 October 2021 'National Institute on Alcoholism, Kurihama National Hospital, Kanagawa, ^okyo Metropolitan Medical Examiner's Office, Tokyo, 3Emergency Department, Keio University Hospital, Tokyo and 4Renal Disease and Dialysis Centre, Saitama Medical College, Saitama, Japan (Received 15 November 1996; in revised form 28 June 1997; accepted 7 July 1997) Abstract — To clarify the pathogenesis of the widely known but obscure syndrome of sudden death with hepatic fatty metamorphosis observed in alcohol abusers, we have scrutinized both the clinical and pathological data of 11 subjects who died under such circumstances between 1987 and 1993. Death followed several days of uninterrupted drinking often with little dietary intake. The notable clinical features on arrival at the emergency room were disturbance of consciousness (11/11), hypotension (4/6), hypothermia (3/5), hypoglycaemia (8/11), metabolic acidosis (676), renal dysfunction (11/11), and hyperammonaemia (5/5). The common hepatic pathology was the extensive appearance of numerous microvesicular fatty droplets in the hepatocytes together -

Permeabilization of the Mitochondrial Inner Membrane During Apoptosis: Impact of the Adenine Nucleotide Translocator
Cell Death and Differentiation (2000) 7, 1146 ± 1154 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 1350-9047/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/cdd Review Permeabilization of the mitochondrial inner membrane during apoptosis: impact of the adenine nucleotide translocator HLA Vieira1, D Haouzi1, C El Hamel1, E Jacotot1, Abbreviations: ANT, adenine nucleotide translocator; IM, inner A-S Belzacq2, C Brenner2 and G Kroemer*,1 membrane; OM, outer membrane; PTPC, permeability transition pore complex; SIMPs, soluble intermembrane space proteins; 1 Centre National de la Recherche Scienti®que, UMR1599, Institut Gustave VDAC, voltage dependent anion channel Roussy, 39 rue Camille-Desmoulins, F-94805 Villejuif, France 2 Centre National de la Recherche Scienti®que, UMR6022, Universite Technologique de CompieÁgne, F-60205 CompieÁgne, France * Corresponding author: G Kroemer, 19 rue Guy MoÃquet, B.P. 8, F-94801 Introduction Villejuif, France. Tel: 33-1-49 58 35 13; Fax: 33-1-49 58 35 09; Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP) appears to E-mail: [email protected] be a near-to-general phenomenon associated with apopto- 1±3 Received 15.7.00; accepted 14.9.00 sis. Schematically, three phases of the apoptotic process Edited by G Kroemer can be distinguished. During a pre-mitochondrial phase pro- apoptotic second messengers are activated and factors acting on mitochondrial membranes accumulate and/or Abstract translocate to mitochondria. Prominent pro-apoptotic pro- teins directly acting on mitochondria include the pro-apoptotic Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization can be a rate members of the Bcl-2/Bax family, as well as kinases and limiting step of apoptotic as well as necrotic cell death.