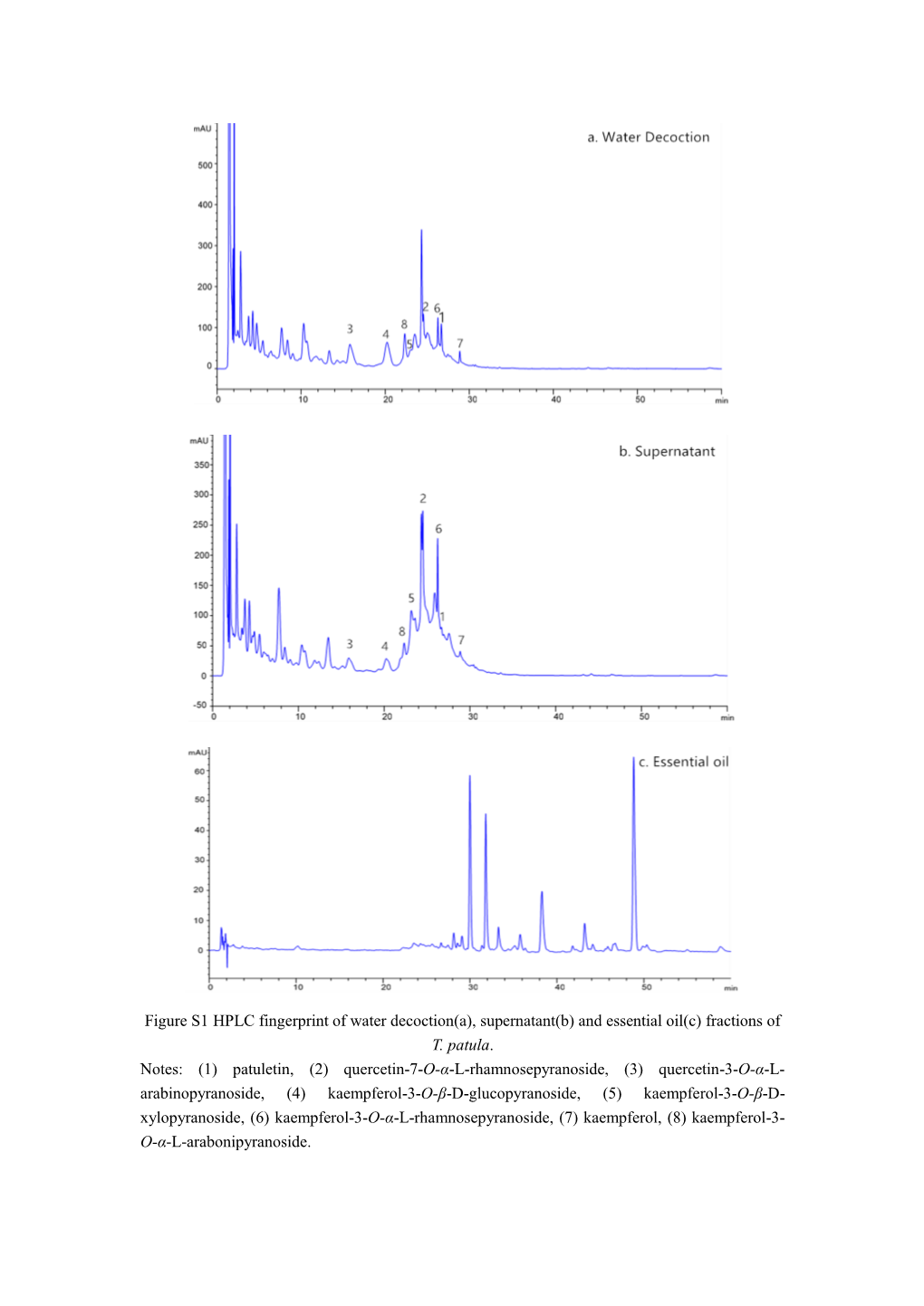
Fractions of T. Patula. Notes
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

RCAN2 Isoform 2 Recombinant Protein Cat
RCAN2 Isoform 2 Recombinant Protein Cat. No.: 95-114 RCAN2 Isoform 2 Recombinant Protein Specifications SPECIES: Mouse SOURCE SPECIES: E. coli SEQUENCE: aa 2 - 197 FUSION TAG: Fusion Partner: C-terminal His-tag TESTED APPLICATIONS: ELISA, WB APPLICATIONS: This recombinant protein can be used for WB and ELISA. For research use only. PREDICTED MOLECULAR 26 kDa (Calculated) WEIGHT: Properties PURITY: ~95% PHYSICAL STATE: Liquid 100mM sodium phosphate, 10mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 25 mM imidazole, 2mM MgCl2, 10% BUFFER: gycerol Store in working aliquots at -70˚C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. When working with proteins STORAGE CONDITIONS: care should be taken to keep recombinant protein at a cool and stable temperature. September 29, 2021 1 https://www.prosci-inc.com/rcan2-isoform-2-recombinant-protein-95-114.html Additional Info OFFICIAL SYMBOL: Rcan2 RCAN2 Antibody: Csp2, MCIP2, ZAKI-4, Dscr1l1, Zaki4, Calcipressin-2, Calcineurin inhibitory ALTERNATE NAMES: protein ZAKI-4 ACCESSION NO.: AAH62141 PROTEIN GI NO.: 38328420 GENE ID: 53901 Background and References Regulator of calcineurin 2 (RCAN2), also known as ZAKI4 and DSCR1L1, is expressed as two isoforms differing at their N-terminus. The longer of the two (isoform 1) is expressed exclusively in the brain, while isoform 2 is ubiquitously expressed, with highest expression in brain, heart, and muscle (1,2). Both isoforms bind to the catalytic subunit of calcineurin, a Ca++-dependent protein phosphatase involved in several neuronal functions, though BACKGROUND: their C-terminal region and inhibit calcineurin’s activity (3). Unlike isoform 1 of RCAN2, the expression of the second isoform is not induced by the thyroid hormone T3 (3). -

Primary Cilia Control Glucose Homeostasis Via Islet Paracrine Interactions
Primary cilia control glucose homeostasis via islet paracrine interactions Jing W. Hughesa,1, Jung Hoon Choa, Hannah E. Conwaya, Michael R. DiGrucciob, Xue Wen Ngb, Henry F. Rosemana, Damien Abreua, Fumihiko Uranoa, and David W. Pistonb aDepartment of Medicine, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO 63110; and bDepartment of Cell Biology and Physiology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO 63110 Edited by C. Ronald Kahn, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, and approved March 10, 2020 (received for review January 31, 2020) Pancreatic islets regulate glucose homeostasis through coordinated cellular synchronicity, and both intra- and intercellular signaling actions of hormone-secreting cells. What underlies the function of pathways that govern core islet functions, demonstrating that the islet as a unit is the close approximation and communication primary cilia are required for islet function as a unit and for the among heterogeneous cell populations, but the structural mediators maintenance of energy homeostasis. of islet cellular cross talk remain incompletely characterized. We generated mice specifically lacking β-cell primary cilia, a cellular or- Results ganelle that has been implicated in regulating insulin secretion, and INS1-Cre/IFT88-Flox Mice Lack β-Cell Cilia. To determine the role of found that the β-cell cilia are required for glucose sensing, calcium primary cilia in β-cell function, we generated βCKO mice by influx, insulin secretion, and cross regulation of α-andδ-cells. Pro- crossing INS1-Cre (16) with IFT88-Flox mice (17). The INS1- tein expression profiling in islets confirms perturbation in these Cre strain was chosen based on efficient and selective re- cellular processes and reveals additional targets of cilia-dependent combination in β-cells and established lack of expression in the signaling. -

Whole Exome Sequencing in ADHD Trios from Single and Multi-Incident Families Implicates New Candidate Genes and Highlights Polygenic Transmission
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020) 28:1098–1110 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0619-7 ARTICLE Whole exome sequencing in ADHD trios from single and multi-incident families implicates new candidate genes and highlights polygenic transmission 1,2 1 1,2 1,3 1 Bashayer R. Al-Mubarak ● Aisha Omar ● Batoul Baz ● Basma Al-Abdulaziz ● Amna I. Magrashi ● 1,2 2 2,4 2,4,5 6 Eman Al-Yemni ● Amjad Jabaan ● Dorota Monies ● Mohamed Abouelhoda ● Dejene Abebe ● 7 1,2 Mohammad Ghaziuddin ● Nada A. Al-Tassan Received: 26 September 2019 / Revised: 26 February 2020 / Accepted: 10 March 2020 / Published online: 1 April 2020 © The Author(s) 2020. This article is published with open access Abstract Several types of genetic alterations occurring at numerous loci have been described in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). However, the role of rare single nucleotide variants (SNVs) remains under investigated. Here, we sought to identify rare SNVs with predicted deleterious effect that may contribute to ADHD risk. We chose to study ADHD families (including multi-incident) from a population with a high rate of consanguinity in which genetic risk factors tend to 1234567890();,: 1234567890();,: accumulate and therefore increasing the chance of detecting risk alleles. We employed whole exome sequencing (WES) to interrogate the entire coding region of 16 trios with ADHD. We also performed enrichment analysis on our final list of genes to identify the overrepresented biological processes. A total of 32 rare variants with predicted damaging effect were identified in 31 genes. At least two variants were detected per proband, most of which were not exclusive to the affected individuals. -

RCAN2 Antibody Cat
RCAN2 Antibody Cat. No.: 5051 RCAN2 Antibody Immunohistochemistry of RCAN2 in mouse brain tissue Immunofluorescence of RCAN2 in mouse brain tissue with with RCAN2 antibody at 2.5 μg/mL. RCAN2 antibody at 20 μg/mL. Specifications HOST SPECIES: Rabbit SPECIES REACTIVITY: Human, Mouse, Rat HOMOLOGY: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (100%) RCAN2 antibody was raised against a 14 amino acid synthetic peptide near the center of human RCAN2. IMMUNOGEN: The immunogen is located within amino acids 70 - 120 of RCAN2. TESTED APPLICATIONS: ELISA, IF, IHC-P, WB September 26, 2021 1 https://www.prosci-inc.com/rcan2-antibody-5051.html RCAN2 antibody can be used for detection of RCAN2 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 μg/mL. APPLICATIONS: Antibody validated: Western Blot in mouse samples; Immunohistochemistry in mouse samples and Immunofluorescence in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested. POSITIVE CONTROL: 1) Cat. No. 1282 - 3T3 (NIH) Cell Lysate Properties PURIFICATION: RCAN2 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column. CLONALITY: Polyclonal ISOTYPE: IgG CONJUGATE: Unconjugated PHYSICAL STATE: Liquid BUFFER: RCAN2 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. CONCENTRATION: 1 mg/mL RCAN2 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one STORAGE CONDITIONS: year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. Additional Info OFFICIAL SYMBOL: Rcan2 RCAN2 Antibody: Csp2, MCIP2, ZAKI-4, Dscr1l1, Zaki4, Calcipressin-2, Calcineurin inhibitory ALTERNATE NAMES: protein ZAKI-4 ACCESSION NO.: AAH62141 PROTEIN GI NO.: 38328420 GENE ID: 53901 USER NOTE: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher. -

Association of the PSRC1 Rs599839 Variant with Coronary Artery Disease in a Mexican Population
medicina Communication Association of the PSRC1 rs599839 Variant with Coronary Artery Disease in a Mexican Population Martha Eunice Rodríguez-Arellano 1, Jacqueline Solares-Tlapechco 1, Paula Costa-Urrutia 1 , Helios Cárdenas-Hernández 1, Marajael Vallejo-Gómez 1, Julio Granados 2 and Sergio Salas-Padilla 3,* 1 Laboratorio de Medicina Genómica, Hospital Regional Lic. Adolfo López Mateos ISSSTE, Ciudad de Mexico 01030, Mexico; [email protected] (M.E.R.-A.); [email protected] (J.S.-T.); [email protected] (P.C.-U.); [email protected] (H.C.-H.); [email protected] (M.V.-G.) 2 División de Inmunogenética, Departamento de Trasplantes, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán, Ciudad de Mexico 14080, Mexico; [email protected] 3 Servicio de Cardiología, Hospital Regional Lic. Adolfo López Mateos ISSSTE, Ciudad de Mexico 01030, Mexico * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +52-555-322-2200 Received: 3 July 2020; Accepted: 12 August 2020; Published: 26 August 2020 Abstract: Background and Objectives: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a major health problem in México. The identification of modifiable risk factors and genetic biomarkers is crucial for an integrative and personalized CAD risk evaluation. In this work, we aimed to validate in a Mexican population a set of eight selected polymorphisms previously associated with CAD, myocardial infarction (MI), or dyslipidemia. Materials and Methods: A sample of 907 subjects (394 CAD cases and 513 controls) 40–80 years old was genotyped for eight loci: PSRC1 (rs599839), MRAS (rs9818870), BTN2A1 (rs6929846), MTHFD1L (rs6922269), CDKN2B (rs1333049), KIAA1462 (rs3739998), CXCL12 (rs501120), and HNF1A (rs2259816). The association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and CAD was evaluated by logistic regression models. -

ABCB6 Is a Porphyrin Transporter with a Novel Trafficking Signal That Is Conserved in Other ABC Transporters Yu Fukuda University of Tennessee Health Science Center
University of Tennessee Health Science Center UTHSC Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations (ETD) College of Graduate Health Sciences 12-2008 ABCB6 Is a Porphyrin Transporter with a Novel Trafficking Signal That Is Conserved in Other ABC Transporters Yu Fukuda University of Tennessee Health Science Center Follow this and additional works at: https://dc.uthsc.edu/dissertations Part of the Chemicals and Drugs Commons, and the Medical Sciences Commons Recommended Citation Fukuda, Yu , "ABCB6 Is a Porphyrin Transporter with a Novel Trafficking Signal That Is Conserved in Other ABC Transporters" (2008). Theses and Dissertations (ETD). Paper 345. http://dx.doi.org/10.21007/etd.cghs.2008.0100. This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the College of Graduate Health Sciences at UTHSC Digital Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses and Dissertations (ETD) by an authorized administrator of UTHSC Digital Commons. For more information, please contact [email protected]. ABCB6 Is a Porphyrin Transporter with a Novel Trafficking Signal That Is Conserved in Other ABC Transporters Document Type Dissertation Degree Name Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Program Interdisciplinary Program Research Advisor John D. Schuetz, Ph.D. Committee Linda Hendershot, Ph.D. James I. Morgan, Ph.D. Anjaparavanda P. Naren, Ph.D. Jie Zheng, Ph.D. DOI 10.21007/etd.cghs.2008.0100 This dissertation is available at UTHSC Digital Commons: https://dc.uthsc.edu/dissertations/345 ABCB6 IS A PORPHYRIN TRANSPORTER WITH A NOVEL TRAFFICKING SIGNAL THAT -

Functional Studies on the MRP1 Multidrug Transporter: Characterization of ABC-Signature Mutant Variants
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 24: 449-456 (2004) Functional Studies on the MRP1 Multidrug Transporter: Characterization of ABC-signature Mutant Variants ZS. SZENTPÉTERY1,2, B. SARKADI1, É. BAKOS2 and A. VÁRADI2 1National Medical Center, Institute of Haematology and Immunology, Membrane Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest; 2Institute of Enzymology, Biological Research Center, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary Abstract. Background: MRP1 is a key multidrug resistance these agents below the cell-killing threshold, thus conferring ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) transporter in tumor cells. A resistance to many structurally dissimilar anticancer drugs. functionally important signature motif is conserved within all One of the proteins causing this phenotype is the human ABC domains. Our current studies aimed to elucidate the role Multidrug Resistance Protein (MRP1), which confers of these motifs in the cooperation of MRP1 ABC domains. resistance to a wide variety of anticancer drugs (1), but has Materials and Methods: We designed human MRP1 mutants also been shown to be a high affinity primary active based on a bacterial ABC structure. Conserved leucines (Leu) transporter for glutathione (GS)-conjugates (e.g. LTC4 – see were replaced by arginines (Arg), while glycines (Gly) were 2, 3). MRP1 transports large hydrophobic drugs, playing an substituted for aspartic acids (Asp). The activity of these important role in the chemotherapy resistance of several mutants was assayed by measuring ATPase activity and types of cancer cells, and cellular GS seem to be an vesicular transport. ATP-binding and transition-state formation important modulator in these transport functions (2, 4-9). were studied by a photoreactive ATP analog. -

Inhibiting ABCG2 with Sorafenib
Published OnlineFirst May 16, 2012; DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0215 Molecular Cancer Therapeutic Discovery Therapeutics New Use for an Old Drug: Inhibiting ABCG2 with Sorafenib Yinxiang Wei1,3, Yuanfang Ma3, Qing Zhao1,4, Zhiguang Ren1,3, Yan Li1, Tingjun Hou2, and Hui Peng1 Abstract Human ABCG2, a member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter superfamily, represents a promising target for sensitizing MDR in cancer chemotherapy. Although lots of ABCG2 inhibitors were identified, none of them has been tested clinically, maybe because of several problems such as toxicity or safety and pharma- cokinetic uncertainty of compounds with novel chemical structures. One efficient solution is to rediscover new uses for existing drugs with known pharmacokinetics and safety profiles. Here, we found the new use for sorafenib, which has a dual-mode action by inducing ABCG2 degradation in lysosome in addition to inhibiting its function. Previously, we reported some novel dual-acting ABCG2 inhibitors that showed closer similarity to degradation-induced mechanism of action. On the basis of these ABCG2 inhibitors with diverse chemical structures, we developed a pharmacophore model for identifying the critical pharmacophore features necessary for dual-acting ABCG2 inhibitors. Sorafenib forms impressive alignment with the pharmacophore hypothesis, supporting the argument that sorafenib is a potential ABCG2 inhibitor. This is the first article that sorafenib may be a good candidate for chemosensitizing agent targeting ABCG2-mediated MDR. This study may facilitate the rediscovery of new functions of structurally diverse old drugs and provide a more effective and safe way of sensitizing MDR in cancer chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther; 11(8); 1693–702. -

Identification of Potential Key Genes and Pathway Linked with Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Based on Integrated Bioinformatics Analyses
medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.21.20248688; this version posted December 24, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. Identification of potential key genes and pathway linked with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on integrated bioinformatics analyses Basavaraj Vastrad1, Chanabasayya Vastrad*2 , Iranna Kotturshetti 1. Department of Biochemistry, Basaveshwar College of Pharmacy, Gadag, Karnataka 582103, India. 2. Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Chanabasava Nilaya, Bharthinagar, Dharwad 580001, Karanataka, India. 3. Department of Ayurveda, Rajiv Gandhi Education Society`s Ayurvedic Medical College, Ron, Karnataka 562209, India. * Chanabasayya Vastrad [email protected] Ph: +919480073398 Chanabasava Nilaya, Bharthinagar, Dharwad 580001 , Karanataka, India NOTE: This preprint reports new research that has not been certified by peer review and should not be used to guide clinical practice. medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.21.20248688; this version posted December 24, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. Abstract Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD) is neurodegenerative disease also called prion disease linked with poor prognosis. The aim of the current study was to illuminate the underlying molecular mechanisms of sCJD. The mRNA microarray dataset GSE124571 was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened. -

Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials Supplementary Table S1: MGNC compound library Ingredien Molecule Caco- Mol ID MW AlogP OB (%) BBB DL FASA- HL t Name Name 2 shengdi MOL012254 campesterol 400.8 7.63 37.58 1.34 0.98 0.7 0.21 20.2 shengdi MOL000519 coniferin 314.4 3.16 31.11 0.42 -0.2 0.3 0.27 74.6 beta- shengdi MOL000359 414.8 8.08 36.91 1.32 0.99 0.8 0.23 20.2 sitosterol pachymic shengdi MOL000289 528.9 6.54 33.63 0.1 -0.6 0.8 0 9.27 acid Poricoic acid shengdi MOL000291 484.7 5.64 30.52 -0.08 -0.9 0.8 0 8.67 B Chrysanthem shengdi MOL004492 585 8.24 38.72 0.51 -1 0.6 0.3 17.5 axanthin 20- shengdi MOL011455 Hexadecano 418.6 1.91 32.7 -0.24 -0.4 0.7 0.29 104 ylingenol huanglian MOL001454 berberine 336.4 3.45 36.86 1.24 0.57 0.8 0.19 6.57 huanglian MOL013352 Obacunone 454.6 2.68 43.29 0.01 -0.4 0.8 0.31 -13 huanglian MOL002894 berberrubine 322.4 3.2 35.74 1.07 0.17 0.7 0.24 6.46 huanglian MOL002897 epiberberine 336.4 3.45 43.09 1.17 0.4 0.8 0.19 6.1 huanglian MOL002903 (R)-Canadine 339.4 3.4 55.37 1.04 0.57 0.8 0.2 6.41 huanglian MOL002904 Berlambine 351.4 2.49 36.68 0.97 0.17 0.8 0.28 7.33 Corchorosid huanglian MOL002907 404.6 1.34 105 -0.91 -1.3 0.8 0.29 6.68 e A_qt Magnogrand huanglian MOL000622 266.4 1.18 63.71 0.02 -0.2 0.2 0.3 3.17 iolide huanglian MOL000762 Palmidin A 510.5 4.52 35.36 -0.38 -1.5 0.7 0.39 33.2 huanglian MOL000785 palmatine 352.4 3.65 64.6 1.33 0.37 0.7 0.13 2.25 huanglian MOL000098 quercetin 302.3 1.5 46.43 0.05 -0.8 0.3 0.38 14.4 huanglian MOL001458 coptisine 320.3 3.25 30.67 1.21 0.32 0.9 0.26 9.33 huanglian MOL002668 Worenine -

Restoration of RPGR Expression in Vivo Using CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing
Gene Therapy https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-021-00258-6 ARTICLE Restoration of RPGR expression in vivo using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing 1 1,2,3 4 5 1 5 4 Jessica D. Gumerson ● Amal Alsufyani ● Wenhan Yu ● Jingqi Lei ● Xun Sun ● Lijin Dong ● Zhijian Wu ● Tiansen Li 1 Received: 13 October 2020 / Revised: 29 March 2021 / Accepted: 1 April 2021 This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply 2021 Abstract Mutations in the gene for Retinitis Pigmentosa GTPase Regulator (RPGR) cause the X-linked form of inherited retinal degeneration, and the majority are frameshift mutations in a highly repetitive, purine-rich region of RPGR known as the OFR15 exon. Truncation of the reading frame in this terminal exon ablates the functionally important C-terminal domain. We hypothesized that targeted excision in ORF15 by CRISPR/Cas9 and the ensuing repair by non-homologous end joining could restore RPGR reading frame in a portion of mutant photoreceptors thereby correcting gene function in vivo. We tested this hypothesis in the rd9 mouse, a naturally occurring mutant line that carries a frameshift mutation in RPGRORF15, through rd9 1234567890();,: 1234567890();,: a combination of germline and somatic gene therapy approaches. In germline gene-edited mice, probing with RPGR domain-specific antibodies demonstrated expression of full length RPGRORF15 protein. Hallmark features of RPGR mutation-associated early disease phenotypes, such as mislocalization of cone opsins, were no longer present. Subretinal injections of the same guide RNA (sgRNA) carried in AAV sgRNA and SpCas9 expression vectors restored reading frame of RPGRORF15 in a subpopulation of cells with broad distribution throughout the retina, confirming successful correction of the mutation. -

The RCAN Carboxyl End Mediates Calcineurin Docking-Dependent Inhibition Via a Site That Dictates Binding to Substrates and Regulators
The RCAN carboxyl end mediates calcineurin docking-dependent inhibition via a site that dictates binding to substrates and regulators Sara Martı´nez-Martı´neza,1, Lali Genesca` b,1,2, Antonio Rodrı´gueza,c, Alicia Rayab, Eula`lia Salichsb, Felipe Werea, Marı´aDolores Lo´pez-Maderueloa, Juan Miguel Redondoa,3, and Susana de la Lunab,d,4 aDepartment of Vascular Biology and Inflammation, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares, 28029 Madrid, Spain; bGenes and Disease Program, Centre de Regulacio´Geno`mica, Universitat Pompeu Fabra and CIBER de Enfermedades Raras, 08003 Barcelona, Spain; cDepartamento de Biología Molecular, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Auto´noma de Madrid, 28049 Madrid, Spain; and dInstitucio´Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avanc¸ats, 08010 Barcelona, Spain Edited by Tony Pawson, Mt. Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada, and approved February 25, 2009 (received for review December 12, 2008) Specificity of signaling kinases and phosphatases toward their CN activity is also regulated by interaction with anchoring and targets is usually mediated by docking interactions with substrates regulatory proteins (11); however, little is known about how these and regulatory proteins. Here, we characterize the motifs involved proteins form contacts with CN. Among the regulatory proteins, in the physical and functional interaction of the phosphatase one of the most remarkable families is the recently renamed calcineurin with a group of modulators, the RCAN protein family. regulator of calcineurin (RCAN, previously known as DSCR/ Mutation of key residues within the hydrophobic docking-cleft of MCIP/calcipressin/Adapt78 in mammals) (12). RCANs bind to and the calcineurin catalytic domain impairs binding to all human RCAN inhibit CN-mediated activities in vitro (13–18).