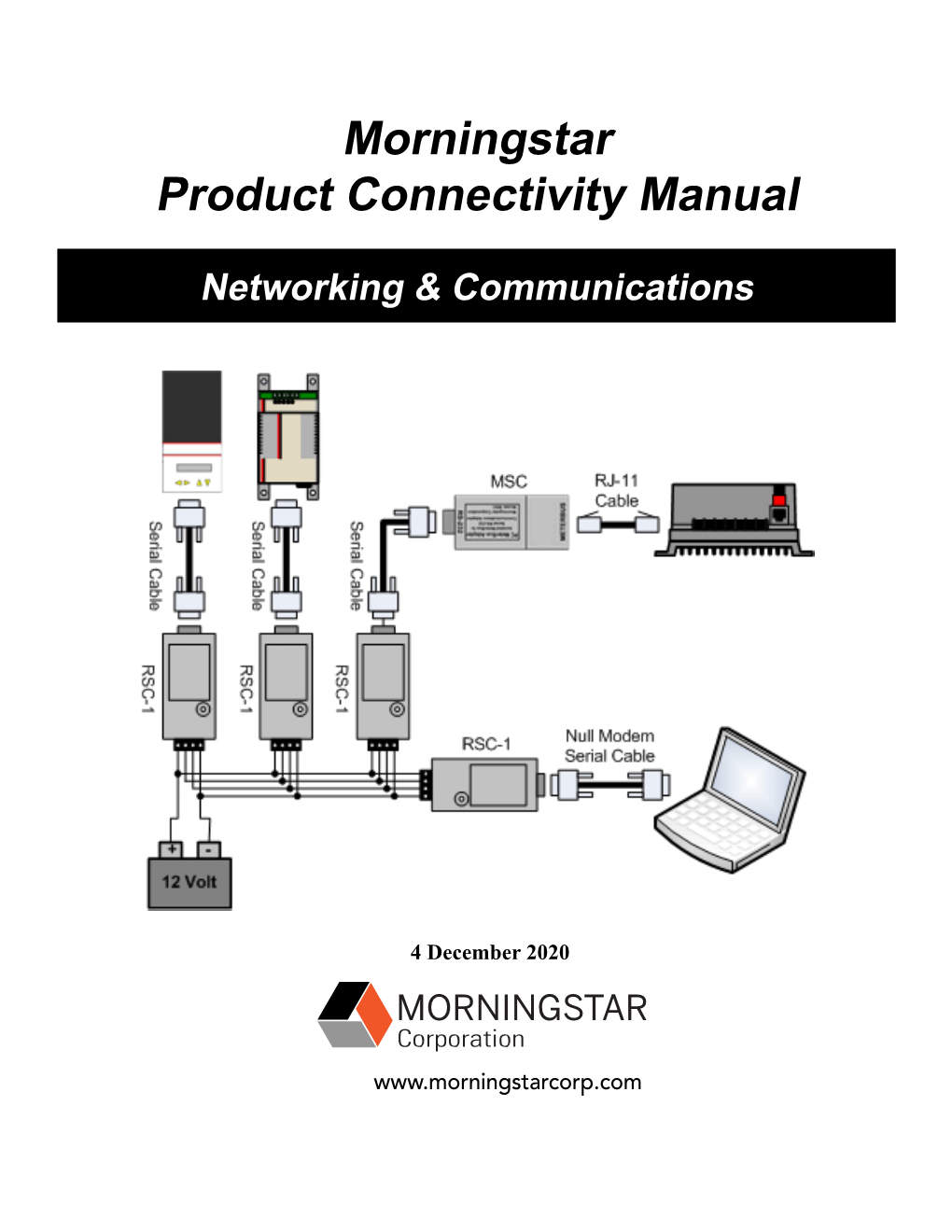
Morningstar Product Connectivity Manual
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Protect Yourself and Your Personal Information*
CYBER SAFETY Protect yourself and your personal information * Cybercrime is a growing and serious threat, making it essential that fraud prevention is part of our daily activities. Put these safeguards in place as soon as possible—if you haven’t already. Email Public Wi-Fi/hotspots Key Use separate email accounts: one each Minimize the use of unsecured, public networks CYBER SAFETY for work, personal use, user IDs, alerts Turn oF auto connect to non-preferred networks 10 notifications, other interests Tips Turn oF file sharing Choose a reputable email provider that oFers spam filtering and multi-factor authentication When public Wi-Fi cannot be avoided, use a 1 Create separate email accounts virtual private network (VPN) to help secure your for work, personal use, alert Use secure messaging tools when replying session to verified requests for financial or personal notifications and other interests information Disable ad hoc networking, which allows direct computer-to-computer transmissions Encrypt important files before emailing them 2 Be cautious of clicking on links or Never use public Wi-Fi to enter personal attachments sent to you in emails Do not open emails from unknown senders credentials on a website; hackers can capture Passwords your keystrokes 3 Use secure messaging tools when Create complex passwords that are at least 10 Home networks transmitting sensitive information characters; use a mix of numbers, upper- and Create one network for you, another for guests via email or text message lowercase letters and special characters and children -

How to Stay Safe in Today's World
REFERENCES Internet Safety http://www.aarp.org/money/scams-fraud/info-08-2011/ internet-security.html How to Stay Safe in Identify Theft Federal Trade Commission (FTC) File Complaint: https://www.ftccomplaintassistant.gov/ ID Theft Hotline: 1-877-438-4338 Today’s World Credit Bureaus: Eqiuifax: 1-888-766-0008 Experian: 1-888-397-3742 TransUnion: 1-800-680-7289 Internet Terminology Medical Fraud: Hotline: 1-800-403-0864 Internet Safety Social Security: Hotline: 1-800-269-0271 Identify/Medical Theft http://oig.ssa.gov/report-fraud-waste-or-abuse/fraud-waste- and-abuse Card Skimming http://www.ftc.gov/bcp/edu/microsites/idtheft/ Remote Controls Booklet Sponsored by: Indiana Extension Homemakers Association Education Focus Group 2015-2016 www.ieha.families.com For more information contact your County Extension Office 16 INTERNET TERMINOLOGY NOTES APPS (applications): a shortcut to information categorized by an icon Attachment: a file attached to an e-mail message. Blog: diary or personal journal posted on a web site, updated frequently. Browser: a program with a graphical user interface for displaying HTML files, used to navigate the World Wide Web (a web browser) Click: pressing and releasing a button on a mouse to select or activate the area on the screen where the cursor s pointing to. Cloud: a loosely defined term for any system providing access via processing powers. Cookies: a small piece of code that is downloaded to computers to keep track of user’s activities. Cyberstalking: a crime in which the attacker harasses a victim using electronic communication, such as -e mail, instant messaging or post- ed messages. -

32Principles and Practices to Successfully Transition To
32 PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES TO SUCCESSFULLY TRANSITION TO U.S. DOD CLOUD COMPUTING DATA CENTERS Tra·di·tion·al • Da·ta • Cen·ters (trə-dĭsh′ə-nəl • dā′tə • sĕn′tərz′). Centralized capital-intensive information technology (IT) assets, which include land, security fences, buildings, power-space-and-cooling, networks, computers, storage devices, operating systems, middleware, databases, development tools, and monitoring systems. Oftentimes, traditional IT applications were assembled one computer, server, rack elevation, or server farm at a time. That is, a computer system with a microprocessor, memory, motherboard, disk drives, network interfaces, operation systems, and input-output devices such as display screens, printers, and portable or removable tape, disk, or solid-state media. Traditional physical computer systems ranged in size from small to extremely large or monolithic. For instance, a computer system may be a laptop, desktop computer, Unix workstation, small rack elevation, small server farm with multiple racks, a building with many server farms, or even a monolithic collection of buildings with multiple data centers or high-performance computing equipment for massively parallel processing applications. About 80% to 90% of IT data centers are in the small to medium-sized range that sit underneath desks, or in conference room corners, hallway closets, or small conference rooms. Typically, small to medium-sized IT data centers were engineered to host a single information system or small ecosystem of highly interrelated applications. Rack elevations allowed engineers to assemble their computer systems one high-performance component at a time for high-performance computing needs, multitasking and multi-user systems, reliability and fault-tolerance, or fast network delivery. -

Cybersecurity Intelligence
CYBER SAFETY Cybersecurity and fraud prevention are top priorities for J.P. Morgan* In Asset & Wealth Management, our educational programs and supporting materials about cybersecurity and fraud prevention can help you understand how to better protect yourself, your family and your office against the ever-evolving threats of cyber crime. GET STARTED Cybersecurity Speak with your J.P. Morgan representative to learn more about our cyber and fraud prevention programs, for educational information Intelligence and to schedule a session with our experts. J.P. Morgan is committed to safeguarding your data, but clients remain ultimately responsible for ensuring their own cybersecurity. PROTECT yourself and your family Learn best practices that you and your family can Key topics implement to help mitigate cybersecurity risk • Email • Mobile security • Passwords • Malware Audiences: Principals, Board members, C-suite, • Wi-Fi networks • Social engineering decision makers, family members, office staff • Internet usage PROTECT your office Understand how you can help improve your Key topics family office’s, small business’s or law firm’s • Working together • Technology controls cybersecurity posture • Phishing • Operations • Social • Office security Audiences: Office staff, Board members, C-suite engineering • Third-party risk • Ransomware • Secure communications PROTECT yourself from fraud Understand the latest fraud trends and fraud Key topics prevention best practices to help strengthen • Money movement • Business email money movement controls controls compromise • Common fraud • Secure communications Audiences: Financial staff, authorized users, schemes principals, decision makers * This document is provided for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended, nor should it be relied upon, to address every aspect of the subject discussed herein. -

Trend Micro™ Scanmail™ for IBM Domino™ Administrator's Guide
Trend Micro Incorporated reserves the right to make changes to this document and to the products described herein without notice. Before installing and using the software, please review the readme files, release notes, and the latest version of the Administrator’s Guide, which are available from the Trend Micro Web site at: www.trendmicro.com/download/documentation/ NOTE: A license to the Trend Micro Software usually includes the right to product updates, pattern file updates, and basic technical support for one (1) year from the date of purchase only. Maintenance must be renewed on an annual basis at the Trend Micro then-current Maintenance fees. Trend Micro, the Trend Micro t-ball logo, and ScanMail are trademarks or registered trademarks of Trend Micro, Incorporated. All other product or company names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their owners. This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley and its contributors. All other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or organizations. Copyright© 2013 Trend Micro Incorporated. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, photocopied, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted without the express prior written consent of Trend Micro Incorporated. Document Part No. SNEM55971_130516 Release Date: September 2013 Protected by U.S. Patent Nos. 5,951,698 and 5,889,943 i Trend Micro™ ScanMail™ for IBM Domino™ Administrator’s Guide The Administrator’s Guide for ScanMail for IBM Domino introduces the main features of the software and provides installation instructions for your production environment. Read through it before installing or using the software. -

ITC 2015 DVD Files Itcconfplanner
A High Assurance Firewall in a Cloud Environment Using Hardware and Software Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Golriz, Arya; Jaber, Nur Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference Proceedings Rights Copyright © held by the author; distribution rights International Foundation for Telemetering Download date 27/09/2021 04:32:59 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/596381 A HIGH ASSURANCE FIREWALL IN A CLOUD ENVIRONMENT USING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE Dr. Arya Golriz, Nur Jaber Faculty Advisors: Dr. Richard Dean, Dr. Yacob Astatke and Dr. Farzad Moazzami Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Morgan State University ABSTRACT This paper will focus on analyzing the characteristics of firewalls and implementing them in a virtual environment as both software- and hardware-based solutions that retain the security features of a traditional firewall. INTRODUCTION With the evolution of telemetry into network environments, telemetry experts must consider the impact of cloud computing solutions in future telemetry systems. Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular and offers a wide variety of advantages over conventional networking, including the ability to centralize resources both physically and financially. While implementing a cloud infrastructure does raise security concerns, a secure cloud infrastructure similar to that of a conventional network can be achieved using tools and tactics deployed to protect the network from adversaries and various malicious attacks. One primary component in any secure network, cloud or otherwise, is a firewall that examines inbound and outbound traffic on the network to ensure that it is authentic and based on a set of rules, as well as enables the network administrator to permit safe content. -

Nortel WLAN Security Switch 2300 Series Configuration Guide (This Document)
Part No. NN47250-500 (320657-E) May 2007 4655 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 Nortel WLAN—Security Switch 2300 Series Configuration Guide Release 5.0 320657-E 2 Copyright © 2007 Nortel Networks. All rights reserved. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks. Trademarks and Service Marks *Nortel, Nortel Networks, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks. *Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. *Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated. All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Restricted rights legend Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013. Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer software, the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in the Commercial computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19. Statement of conditions In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Nortel Networks reserves the right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice. -

By SIRIN LABS, Trusted Display, IP Address Hiding and MAC Address Randomization
FINNEY™ SECURE OPEN SOURCE CONSUMER ELECTRONICS FOR THE BLOCKCHAIN ERA White Paper Prepared by: SIRIN LABS Team DISCLAIMER: This white paper represents work in progress and illustrates the intent of SIRIN LABS to develop, launch and market certain products. The implementations of these products are built on new technologies, and it is expected that significant changes will be continually required to meet the evolving requirements of the market's and customer's demands. CONTENT 1. OVERVIEW 5 2. BACKGROUND 6 2.1 About SIRIN LABS - Past, Present, Future 6 2.2 Our Vision 6 3. PROBLEM DOMAIN 7 3.1 Securing the Blockchain Ecosystem 7 3.2 Using cryptocurrencies is not trivial 7 3.3 Monetization of Secured and Trusted P2P Sharing of Resources 7 3.4 Need for Fair, Decentralized App-Store 8 4. PRODUCT 9 4.1 State-of-the Art, Secure & Blockchain Smart Devices 9 4.1.1 SOLARIN ™ Smartphone 9 4.1.2 Secure calls and massages app & services 9 4.1.3 FINNEY™ Smartphone 10 4.1.4 FINNEY™ PC 10 4.2 SIRIN OS™ 11 4.2.1 BlockShield™ 11 4.2.2 Built-in hardware "cold storage" crypto wallet 11 4.2.3 Cyber Protection 12 4.2.4 Fee-less Distributed Ledger Consensus Mechanism 12 4.2.5 Decentralized App-Store (D-App) 12 4.2.6 Peer-to-peer resource-sharing market module 12 4.2.7 SDK for Distributed Applications Development 13 5. SIRIN LABS SECURE BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY 14 5.1 Overview and Requirements 14 5.1.1 Security Requirements 14 5.1.2 Blockchain Requirements 14 5.1.3 Hardware Adaptation Requirements 15 SIRIN LABS – CROWDSALE – Whitepaper - V2.4 2 5.1.4 Resource Sharing Requirements 15 5.1.5 Development Methodology 15 5.2 Hardware Designs and Abstraction Workflows 15 5.3 Architecture 16 5.4 System Services and Core Libraries 17 5.4.1 DLC: Decentralized Ledger Component 17 5.4.2 Wallet Interface Service 17 5.4.3 DRSM: Decentralized Resource Sharing Manager 18 5.5 BlockShield™ 18 5.5.1 Application Layer 19 5.5.2 OS Layer 20 5.5.3 Hardware Layer: TrustCore™ (optional for OEMs*) 23 6. -

Nortel WLAN Security Switch
Part No. 216395-B Rev 00 April 2005 4655 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 Nortel WLAN — Security Switch (2270) Quick Installation Guide Version 2.2 *216395-B REV 00* 2 Copyright © Nortel Networks Limited 2005. All rights reserved. Copyright © Nortel Networks Limited 2005. All rights reserved. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel. Trademarks Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, the Globemark, and Unified Networks are trademarks of Nortel. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated. Airespace is a trademark of Airespace, Inc. The asterisk after a name denotes a trademarked item. Restricted rights legend Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013. Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer software, the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19. Statement of conditions In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Nortel Inc. -

Security Switch Sicherheitsschalter Commutateur De Sécurité
(19) TZZ _Z_T (11) EP 2 106 578 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention (51) Int Cl.: of the grant of the patent: G06F 21/55 (2013.01) G06F 21/70 (2013.01) 14.09.2016 Bulletin 2016/37 G06F 21/82 (2013.01) (21) Application number: 07736264.8 (86) International application number: PCT/IL2007/000524 (22) Date of filing: 29.04.2007 (87) International publication number: WO 2008/090537 (31.07.2008 Gazette 2008/31) (54) SECURITY SWITCH SICHERHEITSSCHALTER COMMUTATEUR DE SÉCURITÉ (84) Designated Contracting States: (72) Inventors: AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR •Yoffe,Simon HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE 54056 Givat Shmuel (IL) SI SK TR • Yoffe, David 54056 Givat Shmuel (IL) (30) Priority: 22.01.2007 US 881510 P (74) Representative: Modiano, Micaela Nadia et al (43) Date of publication of application: Modiano Josif Pisanty & Staub Ltd 07.10.2009 Bulletin 2009/41 Thierschstrasse 11 80538 München (DE) (73) Proprietors: •Yoffe,Simon (56) References cited: 54056 Givat Shmuel (IL) EP-A2- 1 698 990 US-A- 3 703 987 • Yoffe, David US-A- 4 945 443 US-A- 4 945 443 54056 Givat Shmuel (IL) US-A- 5 555 156 US-A1- 2003 051 162 US-A1- 2005 271 190 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. -

SWITCH-Security Report 2019 3
SWITCH-CERT report on the latest IT security and privacy trends May / June 2019 I. Brought to light: Federal Crime Office closes down the world’s second largest illegal dark web marketplace Even bad guys have business models – or at least imitate those of the good guys. Criminals on the dark web use e-commerce, encryption technologies, anonymised browsers and cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, ethereum or monero to run what are basically gigantic trad- ing platforms. Deals worth many millions are made on these platforms, involving drugs, weapons, human trafficking, illegal pornography, malware and other illegal goods and services, such as stolen login credentials, cyberattacks and botnets. For example, the Silk Road marketplace, which was shut down in 2013, turned over more than USD 1.2 billion in just two years and reportedly generated around USD 80 million in commission fees for its American founder and proprietor, Ross Ulbricht. Such lucrative prospects certainly mo- tivated many Germans to do the same. The operators of Hansa Market, which was discov- ered in 2017, are now in custody, for example. They also generated billions in turnover and made millions on commission fees. No sooner were they behind bars than the next dark web market, known as ‘Wall Street Market’, emerged – once again, in Germany. This platform also quickly became a sales powerhouse with impressive business figures: 1.1 million registered users and SWITCH Security | P.O. Box | CH-8021 Zurich | +41 44 268 15 40 | [email protected] securityblog.switch.ch | security.switch.ch | © SWITCH 2019 approximately 1,250 daily transactions with 63,000 listings, totalling 400,000 sales trans- actions, 250,000 of which were for narcotics or, in other words, drugs. -

Switchcert Report on the Latest IT Security and Privacy Trends January/February 2018
SWITCHcert report on the latest IT security and privacy trends January/February 2018 I. Meltdown and Spectre: security meltdown directly from the processor The bomb exploded right at the start of the new year. And it had absolutely nothing to do with the loud but harmless New Year Eve’s fireworks. Instead, reports of massive security flaws in INTEL, AMD and ARM processors revealed an IT security catastrophe. As early as June 2017, Jann Horn of Google Project Zero had notified the three leading processor manufacturers about severe security flaws in their products. After a long ‘grace’ period, INTEL finally informed the public of the security flaws at the beginning of 2018. Fact: millions and millions of computers, smartphones and mobile devices in which the chips are installed are so helplessly exposed to attacks from the likes of Spectre and Meltdown that the CERT team at Carnegie Mellon University could initially only recommend installing the latest operating systems as a patch or replacing the processors. Meanwhile, some patches are available, but the security problem is still so severe that we would like to provide a five-point overview here: 1) Why do Meltdown & Spectre pose such a great security risk? Computers and mobile devices have security mechanisms designed to prevent all types of programs from retrieving whatever data they want from a device's memory. Spectre and Meltdown use two different attack methods to deactivate these security mechanisms. If the security mechanisms have been hacked, programs also load and save SWITCH Security, PO Box, 8021 Zurich +41 44 268 15 40 [email protected] securityblog.switch.ch security.switch.ch 1 © SWITCH 2018 data they do not even need but which is read by malware programmed accordingly and can be ‘hijacked’.