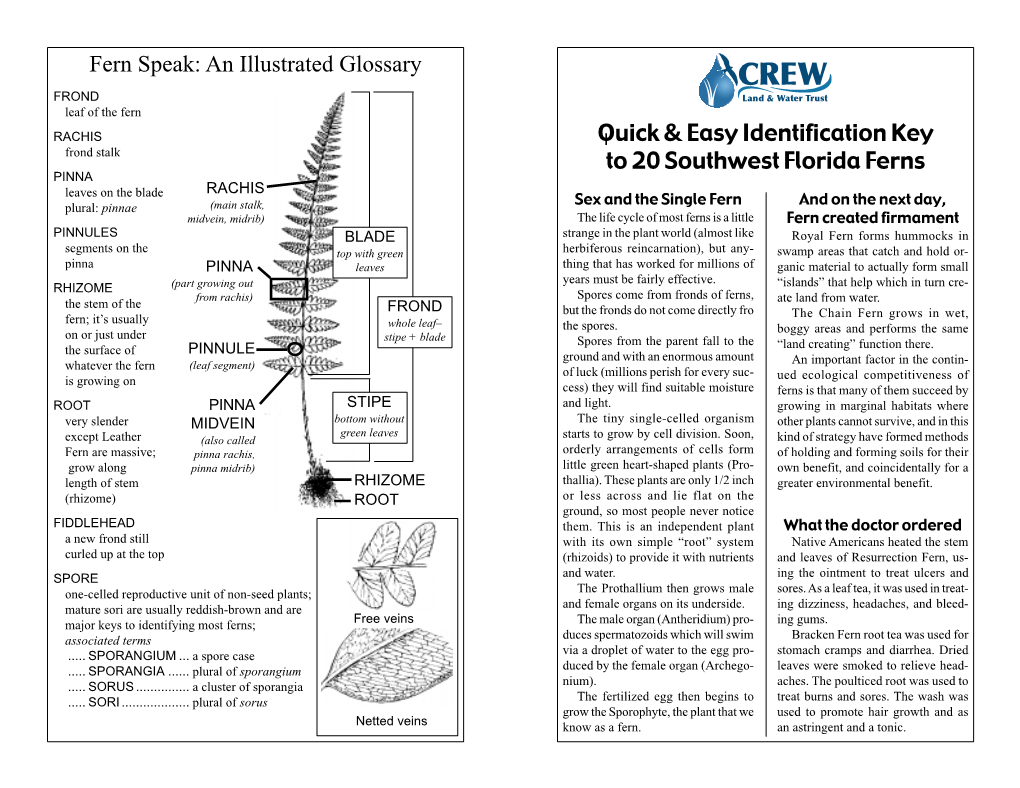
Quick Fern Guide
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Spores of Serpocaulon (Polypodiaceae): Morphometric and Phylogenetic Analyses
Grana, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00173134.2016.1184307 Spores of Serpocaulon (Polypodiaceae): morphometric and phylogenetic analyses VALENTINA RAMÍREZ-VALENCIA1,2 & DAVID SANÍN 3 1Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, Center of Tropical Paleocology and Arqueology, Grupo de Investigación en Agroecosistemas y Conservación de Bosques Amazonicos-GAIA, Ancón Panamá, Republic of Panama, 2Laboratorio de Palinología y Paleoecología Tropical, Departamento de Ciencias Biológicas, Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia, 3Facultad de Ciencias Básicas, Universidad de la Amazonia, Florencia Caquetá, Colombia Abstract The morphometry and sculpture pattern of Serpocaulon spores was studied in a phylogenetic context. The species studied were those used in a published phylogenetic analysis based on chloroplast DNA regions. Four additional Polypodiaceae species were examined for comparative purposes. We used scanning electron microscopy to image 580 specimens of spores from 29 species of the 48 recognised taxa. Four discrete and ten continuous characters were scored for each species and optimised on to the previously published molecular tree. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) showed that verrucae width/verrucae length and verrucae width/spore length index and outline were the most important morphological characters. The first two axes explain, respectively, 56.3% and 20.5% of the total variance. Regular depressed and irregular prominent verrucae were present in derived species. However, the morphology does not support any molecular clades. According to our analyses, the evolutionary pathway of the ornamentation of the spores is represented by depressed irregularly verrucae to folded perispore to depressed regular verrucae to irregularly prominent verrucae. Keywords: character evolution, ferns, eupolypods I, canonical correspondence analysis useful in phylogenetic analyses of several other Serpocaulon is a fern genus restricted to the tropics groups of ferns (Wagner 1974; Pryer et al. -
Ferns of the National Forests in Alaska
Ferns of the National Forests in Alaska United States Forest Service R10-RG-182 Department of Alaska Region June 2010 Agriculture Ferns abound in Alaska’s two national forests, the Chugach and the Tongass, which are situated on the southcentral and southeastern coast respectively. These forests contain myriad habitats where ferns thrive. Most showy are the ferns occupying the forest floor of temperate rainforest habitats. However, ferns grow in nearly all non-forested habitats such as beach meadows, wet meadows, alpine meadows, high alpine, and talus slopes. The cool, wet climate highly influenced by the Pacific Ocean creates ideal growing conditions for ferns. In the past, ferns had been loosely grouped with other spore-bearing vascular plants, often called “fern allies.” Recent genetic studies reveal surprises about the relationships among ferns and fern allies. First, ferns appear to be closely related to horsetails; in fact these plants are now grouped as ferns. Second, plants commonly called fern allies (club-mosses, spike-mosses and quillworts) are not at all related to the ferns. General relationships among members of the plant kingdom are shown in the diagram below. Ferns & Horsetails Flowering Plants Conifers Club-mosses, Spike-mosses & Quillworts Mosses & Liverworts Thirty of the fifty-four ferns and horsetails known to grow in Alaska’s national forests are described and pictured in this brochure. They are arranged in the same order as listed in the fern checklist presented on pages 26 and 27. 2 Midrib Blade Pinnule(s) Frond (leaf) Pinna Petiole (leaf stalk) Parts of a fern frond, northern wood fern (p. -

Quercus ×Coutinhoi Samp. Discovered in Australia Charlie Buttigieg
XXX International Oaks The Journal of the International Oak Society …the hybrid oak that time forgot, oak-rod baskets, pros and cons of grafting… Issue No. 25/ 2014 / ISSN 1941-2061 1 International Oaks The Journal of the International Oak Society … the hybrid oak that time forgot, oak-rod baskets, pros and cons of grafting… Issue No. 25/ 2014 / ISSN 1941-2061 International Oak Society Officers and Board of Directors 2012-2015 Officers President Béatrice Chassé (France) Vice-President Charles Snyers d’Attenhoven (Belgium) Secretary Gert Fortgens (The Netherlands) Treasurer James E. Hitz (USA) Board of Directors Editorial Committee Membership Director Chairman Emily Griswold (USA) Béatrice Chassé Tour Director Members Shaun Haddock (France) Roderick Cameron International Oaks Allen Coombes Editor Béatrice Chassé Shaun Haddock Co-Editor Allen Coombes (Mexico) Eike Jablonski (Luxemburg) Oak News & Notes Ryan Russell Editor Ryan Russell (USA) Charles Snyers d’Attenhoven International Editor Roderick Cameron (Uruguay) Website Administrator Charles Snyers d’Attenhoven For contributions to International Oaks contact Béatrice Chassé [email protected] or [email protected] 0033553621353 Les Pouyouleix 24800 St.-Jory-de-Chalais France Author’s guidelines for submissions can be found at http://www.internationaloaksociety.org/content/author-guidelines-journal-ios © 2014 International Oak Society Text, figures, and photographs © of individual authors and photographers. Graphic design: Marie-Paule Thuaud / www.lecentrecreatifducoin.com Photos. Cover: Charles Snyers d’Attenhoven (Quercus macrocalyx Hickel & A. Camus); p. 6: Charles Snyers d’Attenhoven (Q. oxyodon Miq.); p. 7: Béatrice Chassé (Q. acerifolia (E.J. Palmer) Stoynoff & W. J. Hess); p. 9: Eike Jablonski (Q. ithaburensis subsp. -

Pleopeltis ×Cerro-Altoensis (Polypodiaceae), a New Fern Hybrid from Robinson Crusoe Island (Juan Fernandez Archipelago, Chile)
FERN GAZ. 20(2):65-78. 2015 65 PLEOPELTIS ×CERRO-ALTOENSIS (POLYPODIACEAE), A NEW FERN HYBRID FROM ROBINSON CRUSOE ISLAND (JUAN FERNANDEZ ARCHIPELAGO, CHILE) P. DANTON 1*, M. BOUDRIE 2, A. BIZOT 3 & R.L.L. VIANE 4 15, rue Galilée, F-38000 Grenoble, France. E-Mail: 216, rue des Arènes, F-87000 Limoges, France. E-mail: 3 1, rue de la Faye, F-08160 Hannogne-Saint-Martin, France . E-mail: [email protected] 4 Universiteit Ghent, Vakgroep Biologie, Pteridologie, K.L. Ledeganckstraat 35, Bm-9ic0h0e0l bGohuednrt,i eB@elogriuamng. e.fr E-mail: * Auathronra ufodr. bciozroret@spwonadneandcoe o.fr Keywords : Pleopeltis , hybrid, Polypodiaceae, Juan Fernández, Chile [email protected] ABSTRACT A fern hybrid of the genus Pleopeltis was discovered on Robinson Crusoe Island in the Juan Fernández Archipelago, off the coast of Chile, and is described as P. ×cerro-altoensis . Its putative parents are P. macrocarpa and P. masafuerae , two species present in the archipelago. Mots-clés : Pleopeltis , hybride, Polypodiaceae, Juan Fernández, Chili RÉSUMÉ Un hybride de fougère appartenant au genre Pleopeltis a été découvert sur l’île Robinson Crusoë, dans l’archipel Juan Fernández, au large du Chili, et est décrit sous le nom de P. × cerro-altoensis . Ses parents probables sont P. macrocarpa et P. masafuerae , deux espèces présentes dans l’archipel. Palabras clavas : Pleopeltis , híbrido, Polypodiaceae, Juan Fernández, Chile RESUMEN Un híbrido de helecho que pertenece al género Pleopeltis ha sido descubierto en la isla Robinson Crusoe, en el archipiélago Juan Fernández, a la altura de Chile, y es descrito con el nombre de P. -

Sequencing of Small Rnas of the Fern Pleopeltis Minima (Polypodiaceae) Offers Insight Into the Evolution of the Microrna Repertoire in Land Plants
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/078907; this version posted October 4, 2016. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license. Sequencing of small RNAs of the fern Pleopeltis minima (Polypodiaceae) offers insight into the evolution of the microRNA repertoire in land plants Florencia Berruezo1, Flávio S. J. de Souza3,4, Pablo I. Picca5, Sergio I. Nemirovsky6, Leandro Martínez-Tosar1,2, Mercedes Rivero7, Alejandro N. Mentaberry1,2, Alicia M. Zelada1,2* 1Laboratorio de Agrobiotecnología, Departamento de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Celular, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina 2Instituto de Biodiversidad y Biología Experimental y Aplicada, Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas-Universidad de Buenos Aires (IBBEA, CONICET-UBA), Buenos Aires, Argentina 3Instituto de Investigaciones en Ingeniería Genética y Biología Molecular "Dr Héctor N. Torres" (INGEBI- CONICET), Buenos Aires, Argentina 4Departamento de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Celular, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina 5Departamento de Biodiversidad y Biología Experimental, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina 6Instituto de Química Biológica de la Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales (IQUIBICEN, CONICET- UBA), Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina 7Instituto de Agrobiotecnología de Rosario (INDEAR), Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina. *Author for correspondence: [email protected] bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/078907; this version posted October 4, 2016. -

The Ferns and Their Relatives (Lycophytes)
N M D R maidenhair fern Adiantum pedatum sensitive fern Onoclea sensibilis N D N N D D Christmas fern Polystichum acrostichoides bracken fern Pteridium aquilinum N D P P rattlesnake fern (top) Botrychium virginianum ebony spleenwort Asplenium platyneuron walking fern Asplenium rhizophyllum bronze grapefern (bottom) B. dissectum v. obliquum N N D D N N N R D D broad beech fern Phegopteris hexagonoptera royal fern Osmunda regalis N D N D common woodsia Woodsia obtusa scouring rush Equisetum hyemale adder’s tongue fern Ophioglossum vulgatum P P P P N D M R spinulose wood fern (left & inset) Dryopteris carthusiana marginal shield fern (right & inset) Dryopteris marginalis narrow-leaved glade fern Diplazium pycnocarpon M R N N D D purple cliff brake Pellaea atropurpurea shining fir moss Huperzia lucidula cinnamon fern Osmunda cinnamomea M R N M D R Appalachian filmy fern Trichomanes boschianum rock polypody Polypodium virginianum T N J D eastern marsh fern Thelypteris palustris silvery glade fern Deparia acrostichoides southern running pine Diphasiastrum digitatum T N J D T T black-footed quillwort Isoëtes melanopoda J Mexican mosquito fern Azolla mexicana J M R N N P P D D northern lady fern Athyrium felix-femina slender lip fern Cheilanthes feei net-veined chain fern Woodwardia areolata meadow spike moss Selaginella apoda water clover Marsilea quadrifolia Polypodiaceae Polypodium virginanum Dryopteris carthusiana he ferns and their relatives (lycophytes) living today give us a is tree shows a current concept of the Dryopteridaceae Dryopteris marginalis is poster made possible by: { Polystichum acrostichoides T evolutionary relationships among Onocleaceae Onoclea sensibilis glimpse of what the earth’s vegetation looked like hundreds of Blechnaceae Woodwardia areolata Illinois fern ( green ) and lycophyte Thelypteridaceae Phegopteris hexagonoptera millions of years ago when they were the dominant plants. -

100 Years of Change in the Flora of the Carolinas
Flora of the Carolinas, Virginia, Georgia, and surrounding areas Working Draft of 11 January 2007 by Alan S. Weakley University of North Carolina Herbarium (NCU) North Carolina Botanical Garden University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Campus Box 3280 Chapel Hill NC 27599-3280 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents THE FLORA .................................................................................................................................................................................................................6 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................................................................................................................................................................9 FERNS AND “FERN ALLIES”............................................................................................................................................................................10 ASPLENIACEAE Frank 1877 (Spleenwort Family) ........................................................................................................................................17 AZOLLACEAE Wettstein 1903 (Mosquito Fern Family) .................................................................................................................................20 BLECHNACEAE (C. Presl) Copeland 1947 (Deer Fern Family) ...................................................................................................................21 DENNSTAEDTIACEAE Pichi Sermolli 1970 (Bracken Family) ....................................................................................................................22 -

Transformative Paleobotany
Chapter 6 Lower Permian Flora of the Sanzenbacher Ranch, Clay County, Texas William A. DiMichele1, Robert W. Hook2, Hans Kerp3, Carol L. Hotton1,4, Cindy V. Looy5 and Dan S. Chaney1 1NMNH Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, United States; 2The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, United States; 3Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Münster, Germany; 4National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States; 5University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States 1. INTRODUCTION 1985; Broutin, 1986; Popa, 1999; Steyer et al., 2000; Wagner and Mayoral, 2007; Bercovici and Broutin, 2008; Since 1989, field parties supported by the U.S. National Barthel, 2009; Wagner and Álvarez-Vázquez, 2010; Museum of Natural History have obtained large collections Barthel and Brauner, 2015). Furthermore, because this of mainly Permian plant fossils from north central Texas. locality was collected on three occasions over a time period This work was undertaken to study known localities and to of 50 years and by different parties, comparative analysis of find new fossiliferous deposits that would contribute to a the Sanzenbacher collections provides a basis for assessing better understanding of floral and paleoenvironmental sites that have comparable histories. changes within the region during the early Permian. From the outset, the effort was interdisciplinary and grew, through the contributions of nearly 20 paleobotanists, 2. GEOLOGY palynologists, invertebrate and vertebrate paleontologists, Clay County is the only county in the Permo-Carboniferous and sedimentary geologists of several subdisciplines, to be outcrop belt of north central Texas that lacks marine rocks. quite comprehensive. Our reporting of results, however, has These alluvial sediments accumulated east of a broad been influenced by unexpected developments, including the coastal plain that bordered the Eastern Shelf of the Midland discovery of new plant-fossil assemblages in areas once Basin. -

Polypodiaceae-Polypodiidae)
Núm. 46: 179-191 Julio 2018 ISSN electrónico: 2395-9525 Polibotánica ISSN electrónico: 2395-9525 [email protected] Instituto Politécnico Nacional México http:www.polibotanica.mx DESCRIPCIÓN MORFOGÉNICA DE GAMETÓFITOS Y ESPORÓFITOS JÓVENES DE Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE). MORPHOGENIC DESCRIPTION OF GAMETOPHYTE AND SPOROPHYTE OF Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE). Herrera-Soriano, A.; M.L. Arreguín-Sánchez, J.L. Meza-Padilla, L.Á. Lepe-Becerra, y R. Fernández-Nava. DESCRIPCIÓN MORFOGÉNICA DE GAMETÓFITOS Y ESPORÓFITOS JÓVENES DE Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE). MORPHOGENIC DESCRIPTION OF GAMETOPHYTE AND SPOROPHYTE OF Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE). Núm. 46: 179-191 México. Julio 2018 Instituto Politécnico Nacional DOI: 10.18387/polibotanica.46.11 179 Núm. 46: 179-191 Julio 2018 ISSN electrónico: 2395-9525 DESCRIPCIÓN MORFOGÉNICA DE GAMETÓFITOS Y ESPORÓFITOS JÓVENES DE Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE)* MORPHOGENIC DESCRIPTION OF GAMETOPHYTE AND SPOROPHYTE OF Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER (POLYPODIACEAE-POLYPODIIDAE)* A. Herrera-Soriano Instituto Politécnico Nacional, CECYT 11 “Wilfrido Massieu” Herrera–Soriano, A.; Av. de los Maestros Núm. 217, Col. Santo Tomas CP 11340, M.L. Arreguín–Sánchez, J.L. Meza-Padilla, Ciudad de México, México. L.Á. Lepe- Becerra, y R. Fernández-Nava M. L. Arreguín-Sánchez/ [email protected] Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Escuela Nacional de Ciencias Biológicas, DESCRIPCIÓN Plan de Ayala y Carpio, Col. Santo Tomas CP 11340, Ciudad de México, México. MORFOGÉNICA DE GAMETÓFITOS Y J. L. Meza-Padilla ESPORÓFITOS JÓVENES L. Á. Lepe- Becerra DE Pleopeltis astrolepis (LIEBM.) FOURNIER Instituto Politécnico Nacional, CECYT 5 “Benito Juárez García” (POLYPODIACEAE- Emilio Dondé Núm. 1, Col. -

A Comparative Study of Lady Ferns and Japanese Painted Ferns (Athyrium Spp.)
Plant Evaluation Notes Issue 39, 2015 A Comparative Study of Lady Ferns and Japanese Painted Ferns (Athyrium spp.) Richard G. Hawke, Plant Evaluation Manager and Associate Scientist Photo by Richard Hawke Athyrium filix-femina Lady ferns and Japanese painted ferns of the wood fern family (Dryopteridaceae) Japanese painted ferns has spawned an (Athyrium spp.) are among the most elegant and just a few of the nearly 200 species array of new colorful cultivars as well as a yet utilitarian plants for the shade garden. native to temperate and tropical regions few exceptional hybrids with the common Their lacy fronds arch and twist in a graceful worldwide. The common lady fern lady fern. manner, being both structural and ethereal (A. filix-femina) is a circumglobal species at the same time. Ferns stand on their found in moist woodlands, meadows, While common botanical terms such as foliar merits alone, having no flowers to and ravines throughout North America, leaf, stem, and midrib can be used to overshadow their feathery foliage. The lush Europe, and Asia, and is represented in describe fern foliage, specialized terminology green fronds of lady ferns are in marked gardens by a plethora of cultivars—many of further defines fern morphology. The fern contrast to the sage green, silver, and the oldest forms originated in England leaf or frond is composed of the stipe burgundy tones of the colorful Japanese during the Victorian era. Eared lady fern (stem), blade (leaf), rachis (midrib), and painted ferns. The delicate quality of their (A. otophorum) and Japanese lady fern pinna (leaflet). Crosier or fiddlehead fronds belies their stoutness—they are (A. -

Fern Classification
16 Fern classification ALAN R. SMITH, KATHLEEN M. PRYER, ERIC SCHUETTPELZ, PETRA KORALL, HARALD SCHNEIDER, AND PAUL G. WOLF 16.1 Introduction and historical summary / Over the past 70 years, many fern classifications, nearly all based on morphology, most explicitly or implicitly phylogenetic, have been proposed. The most complete and commonly used classifications, some intended primar• ily as herbarium (filing) schemes, are summarized in Table 16.1, and include: Christensen (1938), Copeland (1947), Holttum (1947, 1949), Nayar (1970), Bierhorst (1971), Crabbe et al. (1975), Pichi Sermolli (1977), Ching (1978), Tryon and Tryon (1982), Kramer (in Kubitzki, 1990), Hennipman (1996), and Stevenson and Loconte (1996). Other classifications or trees implying relationships, some with a regional focus, include Bower (1926), Ching (1940), Dickason (1946), Wagner (1969), Tagawa and Iwatsuki (1972), Holttum (1973), and Mickel (1974). Tryon (1952) and Pichi Sermolli (1973) reviewed and reproduced many of these and still earlier classifica• tions, and Pichi Sermolli (1970, 1981, 1982, 1986) also summarized information on family names of ferns. Smith (1996) provided a summary and discussion of recent classifications. With the advent of cladistic methods and molecular sequencing techniques, there has been an increased interest in classifications reflecting evolutionary relationships. Phylogenetic studies robustly support a basal dichotomy within vascular plants, separating the lycophytes (less than 1 % of extant vascular plants) from the euphyllophytes (Figure 16.l; Raubeson and Jansen, 1992, Kenrick and Crane, 1997; Pryer et al., 2001a, 2004a, 2004b; Qiu et al., 2006). Living euphyl• lophytes, in turn, comprise two major clades: spermatophytes (seed plants), which are in excess of 260 000 species (Thorne, 2002; Scotland and Wortley, Biology and Evolution of Ferns and Lycopliytes, ed. -

Ferns: the Final Frond-Tier in Plant Model Systems
Ferns: The Final Frond-tier in Plant Model Systems Authors: Alaina R. Petlewski, and Fay-Wei Li Source: American Fern Journal, 109(3) : 192-211 Published By: The American Fern Society URL: https://doi.org/10.1640/0002-8444-109.3.192 BioOne Complete (complete.BioOne.org) is a full-text database of 200 subscribed and open-access titles in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences published by nonprofit societies, associations, museums, institutions, and presses. Your use of this PDF, the BioOne Complete website, and all posted and associated content indicates your acceptance of BioOne’s Terms of Use, available at www.bioone.org/terms-of-use. Usage of BioOne Complete content is strictly limited to personal, educational, and non-commercial use. Commercial inquiries or rights and permissions requests should be directed to the individual publisher as copyright holder. BioOne sees sustainable scholarly publishing as an inherently collaborative enterprise connecting authors, nonprofit publishers, academic institutions, research libraries, and research funders in the common goal of maximizing access to critical research. Downloaded From: https://bioone.org/journals/American-Fern-Journal on 15 Oct 2019 Terms of Use: https://bioone.org/terms-of-use Access provided by Cornell University American Fern Journal 109(3):192–211 (2019) Published on 16 September 2019 Ferns: The Final Frond-tier in Plant Model Systems 1,2 1,2 ALAINA R. PETLEWSKI AND FAY-WEI LI * 1 Boyce Thompson Institute, Ithaca, New York, USA 14853 ORCID: 0000-0003-4516-1214, 0000-0002-0076-0152 2 Plant Biology Section, Cornell University, New York, USA 14853 Email: 1 [email protected], 2 fl[email protected] ABSTRACT.—Ferns are one of the most speciose lineages of land plants, and occupy an important phylogenetic position sister to seed plants.