Aircraft Instruments – Page 83 Aviation Seminars
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

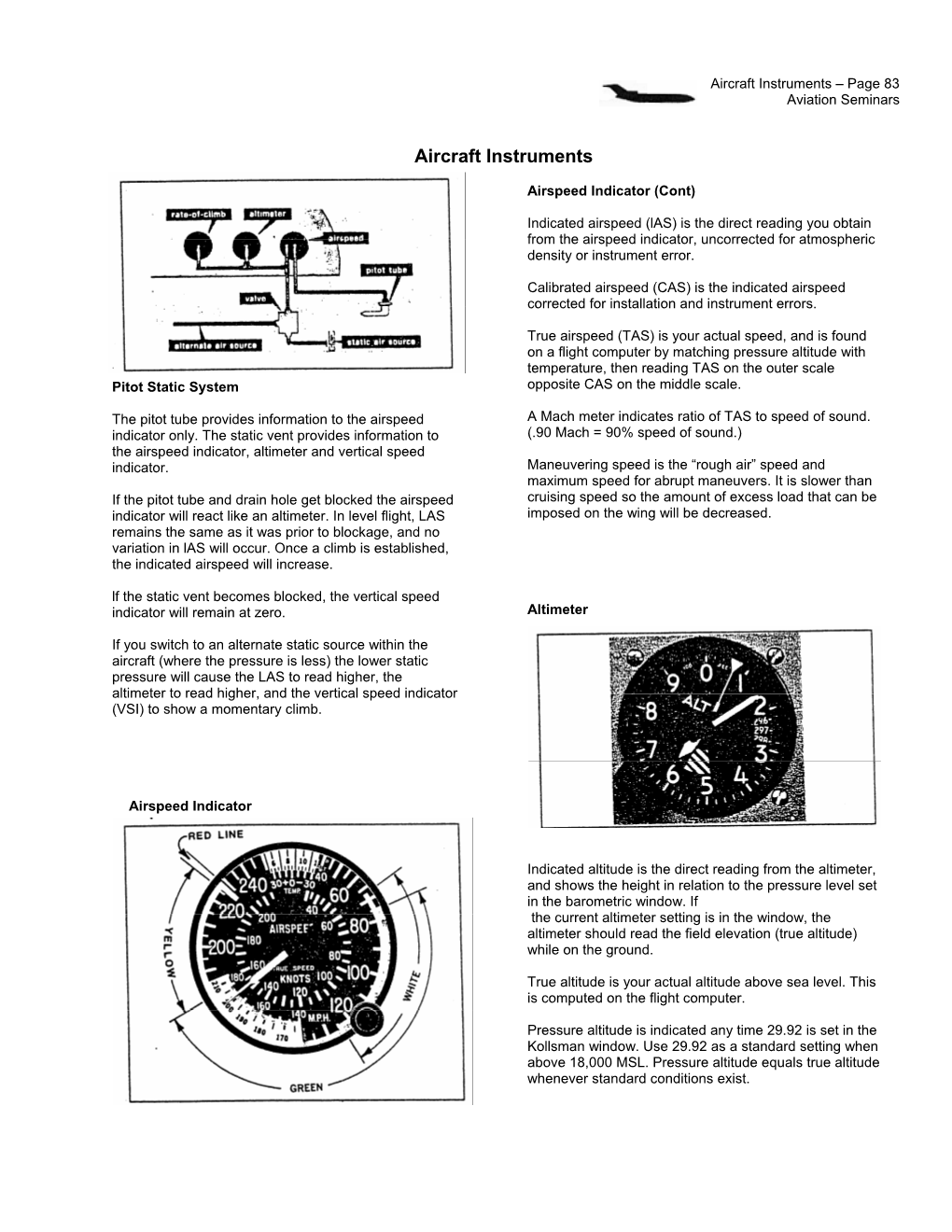
Pitot-Static System Blockage Effects on Airspeed Indicator
The Dramatic Effects of Pitot-Static System Blockages and Failures by Luiz Roberto Monteiro de Oliveira . Table of Contents I ‐ Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….1 II ‐ Pitot‐Static Instruments…………………………………………………………………………………………..3 III ‐ Blockage Scenarios – Description……………………………..…………………………………….…..…11 IV ‐ Examples of the Blockage Scenarios…………………..……………………………………………….…15 V ‐ Disclaimer………………………………………………………………………………………………………………50 VI ‐ References…………………………………………………………………………………………….…..……..……51 Please also review and understand the disclaimer found at the end of the article before applying the information contained herein. I - Introduction This article takes a comprehensive look into Pitot-static system blockages and failures. These typically affect the airspeed indicator (ASI), vertical speed indicator (VSI) and altimeter. They can also affect the autopilot auto-throttle and other equipment that relies on airspeed and altitude information. There have been several commercial flights, more recently Air France's flight 447, whose crash could have been due, in part, to Pitot-static system issues and pilot reaction. It is plausible that the pilot at the controls could have become confused with the erroneous instrument readings of the airspeed and have unknowingly flown the aircraft out of control resulting in the crash. The goal of this article is to help remove or reduce, through knowledge, the likelihood of at least this one link in the chain of problems that can lead to accidents. Table 1 below is provided to summarize -

Airspeed Indicator Calibration
TECHNICAL GUIDANCE MATERIAL AIRSPEED INDICATOR CALIBRATION This document explains the process of calibration of the airspeed indicator to generate curves to convert indicated airspeed (IAS) to calibrated airspeed (CAS) and has been compiled as reference material only. i Technical Guidance Material BushCat NOSE-WHEEL AND TAIL-DRAGGER FITTED WITH ROTAX 912UL/ULS ENGINE APPROVED QRH PART NUMBER: BCTG-NT-001-000 AIRCRAFT TYPE: CHEETAH – BUSHCAT* DATE OF ISSUE: 18th JUNE 2018 *Refer to the POH for more information on aircraft type. ii For BushCat Nose Wheel and Tail Dragger LSA Issue Number: Date Published: Notable Changes: -001 18/09/2018 Original Section intentionally left blank. iii Table of Contents 1. BACKGROUND ..................................................................................................................... 1 2. DETERMINATION OF INSTRUMENT ERROR FOR YOUR ASI ................................................ 2 3. GENERATING THE IAS-CAS RELATIONSHIP FOR YOUR AIRCRAFT....................................... 5 4. CORRECT ALIGNMENT OF THE PITOT TUBE ....................................................................... 9 APPENDIX A – ASI INSTRUMENT ERROR SHEET ....................................................................... 11 Table of Figures Figure 1 Arrangement of instrument calibration system .......................................................... 3 Figure 2 IAS instrument error sample ........................................................................................ 7 Figure 3 Sample relationship between -

Sept. 12, 1950 W
Sept. 12, 1950 W. ANGST 2,522,337 MACH METER Filed Dec. 9, 1944 2 Sheets-Sheet. INVENTOR. M/2 2.7aar alwg,57. A77OAMA). Sept. 12, 1950 W. ANGST 2,522,337 MACH METER Filed Dec. 9, 1944 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 N 2 2 %/ NYSASSESSN S2,222,W N N22N \ As I, mtRumaIII-m- III It's EARAs i RNSITIE, 2 72/ INVENTOR, M247 aeawosz. "/m2.ATTORNEY. Patented Sept. 12, 1950 2,522,337 UNITED STATES ; :PATENT OFFICE 2,522,337 MACH METER Walter Angst, Manhasset, N. Y., assignor to Square D Company, Detroit, Mich., a corpora tion of Michigan Application December 9, 1944, Serial No. 567,431 3 Claims. (Cl. 73-182). is 2 This invention relates to a Mach meter for air plurality of posts 8. Upon one of the posts 8 are craft for indicating the ratio of the true airspeed mounted a pair of serially connected aneroid cap of the craft to the speed of sound in the medium sules 9 and upon another of the posts 8 is in which the aircraft is traveling and the object mounted a diaphragm capsuler it. The aneroid of the invention is the provision of an instrument s: capsules 9 are sealed and the interior of the cas-l of this type for indicating the Mach number of an . ing is placed in communication with the static aircraft in fight. opening of a Pitot static tube through an opening The maximum safe Mach number of any air in the casing, not shown. The interior of the dia craft is the value of the ratio of true airspeed to phragm capsule is connected through the tub the speed of sound at which the laminar flow of ing 2 to the Pitot or pressure opening of the Pitot air over the wings fails and shock Waves are en static tube through the opening 3 in the back countered. -

Beforethe Runway
EDITORIAL Before the runway By Professor Sidney dekker display with fl ight information. My airspeed is leaking out of Editors Note: This time, we decided to invite some the airplane as if the hull has been punctured, slowly defl at- comments on Professor Dekker’s article from subject ing like a pricked balloon. It looks bizarre and scary and the matter experts. Their responses follow the article. split second seems to last for an eternity. Yet I have taught myself to act fi rst and question later in situations like this. e are at 2,000 feet, on approach to the airport. The big So I act. After all, there is not a whole lot of air between me W jet is on autopilot, docile, and responsively follow- and the hard ground. I switch off the autothrottle and shove ing the instructions I have put into the various computer the thrust levers forward. From behind, I hear the engines systems. It follows the heading I gave it, and stays at the screech, shrill and piercing. Airspeed picks up. I switch off altitude I wanted it at. The weather is alright, but not great. the autopilot for good measure (or good riddance) and fl y Cloud base is around 1000 feet, there is mist, a cold driz- the jet down to the runway. It feels solid in my hands and zle. We should be on the ground in the next few minutes. docile again. We land. Then everything comes to a sudden I call for fl aps, and the other pilot selects them for me. -

FAA Advisory Circular AC 91-74B
U.S. Department Advisory of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration Circular Subject: Pilot Guide: Flight in Icing Conditions Date:10/8/15 AC No: 91-74B Initiated by: AFS-800 Change: This advisory circular (AC) contains updated and additional information for the pilots of airplanes under Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) parts 91, 121, 125, and 135. The purpose of this AC is to provide pilots with a convenient reference guide on the principal factors related to flight in icing conditions and the location of additional information in related publications. As a result of these updates and consolidating of information, AC 91-74A, Pilot Guide: Flight in Icing Conditions, dated December 31, 2007, and AC 91-51A, Effect of Icing on Aircraft Control and Airplane Deice and Anti-Ice Systems, dated July 19, 1996, are cancelled. This AC does not authorize deviations from established company procedures or regulatory requirements. John Barbagallo Deputy Director, Flight Standards Service 10/8/15 AC 91-74B CONTENTS Paragraph Page CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 1-1. Purpose ..............................................................................................................................1 1-2. Cancellation ......................................................................................................................1 1-3. Definitions.........................................................................................................................1 1-4. Discussion .........................................................................................................................6 -

Aviation Glossary
AVIATION GLOSSARY 100-hour inspection – A complete inspection of an aircraft operated for hire required after every 100 hours of operation. It is identical to an annual inspection but may be performed by any certified Airframe and Powerplant mechanic. Absolute altitude – The vertical distance of an aircraft above the terrain. AD - See Airworthiness Directive. ADC – See Air Data Computer. ADF - See Automatic Direction Finder. Adverse yaw - A flight condition in which the nose of an aircraft tends to turn away from the intended direction of turn. Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) – A primary FAA publication whose purpose is to instruct airmen about operating in the National Airspace System of the U.S. A/FD – See Airport/Facility Directory. AHRS – See Attitude Heading Reference System. Ailerons – A primary flight control surface mounted on the trailing edge of an airplane wing, near the tip. AIM – See Aeronautical Information Manual. Air data computer (ADC) – The system that receives and processes pitot pressure, static pressure, and temperature to present precise information in the cockpit such as altitude, indicated airspeed, true airspeed, vertical speed, wind direction and velocity, and air temperature. Airfoil – Any surface designed to obtain a useful reaction, or lift, from air passing over it. Airmen’s Meteorological Information (AIRMET) - Issued to advise pilots of significant weather, but describes conditions with lower intensities than SIGMETs. AIRMET – See Airmen’s Meteorological Information. Airport/Facility Directory (A/FD) – An FAA publication containing information on all airports, seaplane bases and heliports open to the public as well as communications data, navigational facilities and some procedures and special notices. -

Use of the MS Flight Simulator in the Teaching of the Introduction to Avionics Course
Session 1928 Use of the MS Flight Simulator in the teaching of the Introduction to avionics course Iulian Cotoi, Ruxandra Mihaela Botez Ecole de technologie supérieure Département de génie de la production automatisée 1100 Notre Dame Ouest Montréal, Qué., Canada, H3C 1K3 Introduction The course Introduction to avionics GPA-745 is an optional course in the Aerospace program given in the Department of Automated Production Engineering at École de technologie supérieure in Montreal, Canada. The main objectif of this course is the study of electronic avionics instrumentation installed in aircraft. In this course, the following chapters are presented : History of avionics, Methods of navigation and orientation, Pilot cockpit and board instrumentation, Communication systems, Radio-navigation systems, Landing systems, Engine signalization instruments, Central alarm systems, Maintenance systems and Warning systems. The presentation of the course in the class to the students is shown on PowerPoint slides and videos on modern aircraft such as Airbus and Boeing. Also, regarding the pilot induced oscillations a video film is provided from Bombardier Aerospace. However, the presentation of the course in the class may be improved and become more efficient grace to the use of MS Flight Simulator. The main idea of this paper is to show how the participation of the students in the class will be increased by use of the MS Flight Simulator. The use of the systems and the electronic board instrumentation will be shown with the help of the new flight simulations modules realized within the MS Flight Simulator. For each instrument, one module will be created and presented in the class, which will result in a more interesting course presentation, stimulating and dynamical from pedagogical point of view, than the theory of the course by use of PowerPoint. -

Module-7 Lecture-29 Flight Experiment
Module-7 Lecture-29 Flight Experiment: Instruments used in flight experiment, pre and post flight measurement of aircraft c.g. Module Agenda • Instruments used in flight experiments. • Pre and post flight measurement of center of gravity. • Experimental procedure for the following experiments. (a) Cruise Performance: Estimation of profile Drag coefficient (CDo ) and Os- walds efficiency (e) of an aircraft from experimental data obtained during steady and level flight. (b) Climb Performance: Estimation of Rate of Climb RC and Absolute and Service Ceiling from experimental data obtained during steady climb flight (c) Estimation of stick free and fixed neutral and maneuvering point using flight data. (d) Static lateral-directional stability tests. (e) Phugoid demonstration (f) Dutch roll demonstration 1 Instruments used for experiments1 1. Airspeed Indicator: The airspeed indicator shows the aircraft's speed (usually in knots ) relative to the surrounding air. It works by measuring the ram-air pressure in the aircraft's Pitot tube. The indicated airspeed must be corrected for air density (which varies with altitude, temperature and humidity) in order to obtain the true airspeed, and for wind conditions in order to obtain the speed over the ground. 2. Attitude Indicator: The attitude indicator (also known as an artificial horizon) shows the aircraft's relation to the horizon. From this the pilot can tell whether the wings are level and if the aircraft nose is pointing above or below the horizon. This is a primary instrument for instrument flight and is also useful in conditions of poor visibility. Pilots are trained to use other instruments in combination should this instrument or its power fail. -

16.00 Introduction to Aerospace and Design Problem Set #3 AIRCRAFT
16.00 Introduction to Aerospace and Design Problem Set #3 AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE FLIGHT SIMULATION LAB Note: You may work with one partner while actually flying the flight simulator and collecting data. Your write-up must be done individually. You can do this problem set at home or using one of the simulator computers. There are only a few simulator computers in the lab area, so not leave this problem to the last minute. To save time, please read through this handout completely before coming to the lab to fly the simulator. Objectives At the end of this problem set, you should be able to: • Take off and fly basic maneuvers using the flight simulator, and describe the relationships between the control yoke and the control surface movements on the aircraft. • Describe pitch - airspeed - vertical speed relationships in gliding performance. • Explain the difference between indicated and true airspeed. • Record and plot airspeed and vertical speed data from steady-state flight conditions. • Derive lift and drag coefficients based on empirical aircraft performance data. Discussion In this lab exercise, you will use Microsoft Flight Simulator 2000/2002 to become more familiar with aircraft control and performance. Also, you will use the flight simulator to collect aircraft performance data just as it is done for a real aircraft. From your data you will be able to deduce performance parameters such as the parasite drag coefficient and L/D ratio. Aircraft performance depends on the interplay of several variables: airspeed, power setting from the engine, pitch angle, vertical speed, angle of attack, and flight path angle. -

SERVICE ALERT Avidyne Primary Flight Display {P/Ns: 700-00006-000,-001,-002,-003,-100}
SA-08-001 12 February 2008 SERVICE ALERT Avidyne Primary Flight Display {P/Ns: 700-00006-000,-001,-002,-003,-100} This SERVICE ALERT communicates important safety information concerning aircraft equipped with certain Avidyne EXP5000 Primary Flight Displays (PFDs). BACKGROUND INFORMATION Avidyne has received a limited number of field reports of PFDs displaying incorrect altitude and airspeed information. None of these occurrences led to an accident or incident. These occurrences included incorrect display of information at system startup, including one or more of the following: • Altitude significantly in error when compared to field elevation with local barometric correction setting entered on PFD. • Altitude significantly in error when compared to backup altimeter with identical barometric correction settings on both. • Non-zero airspeed (inconsistent with high winds or propwash from a nearby airplane) indicated at system startup. • Altitude or airspeed indications that vary noticeably after startup under static conditions. • Erroneous airspeed indications in combination with erroneous attitude indications. • A steady or intermittent “red X” in place of the airspeed indicator, altimeter, VSI or attitude indicator. Aircraft exhibiting any of these incorrect indications should not be flown. In any case where an erroneous indication is present at system startup (without an identifiable external cause such as surface winds or propwash) and this indication subsequently returns to normal, the PFD should nonetheless be considered unreliable and the aircraft should not be flown. As a normal practice, all pilots should be vigilant in conducting proper preflight and in- flight checks of instrument accuracy, including: • Preflight check of the accuracy of both the primary and backup altimeter against known airfield elevation and against each other. -

Radar Altimeter True Altitude
RADAR ALTIMETER TRUE ALTITUDE. TRUE SAFETY. ROBUST AND RELIABLE IN RADARDEMANDING ENVIRONMENTS. Building on systems engineering and integration know-how, FreeFlight Systems effectively implements comprehensive, high-integrity avionics solutions. We are focused on the practical application of NextGen technology to real-world operational needs — OEM, retrofit, platform or infrastructure. FreeFlight Systems is a community of respected innovators in technologies of positioning, state-sensing, air traffic management datalinks — including rule-compliant ADS-B systems, data and flight management. An international brand, FreeFlight Systems is a trusted partner as well as a direct-source provider through an established network of relationships. 3 GENERATIONS OF EXPERIENCE BEHIND NEXTGEN AVIONICS NEXTGEN LEADER. INDUSTRY EXPERT. TRUSTED PARTNER. SHAPE THE SKIES. RADAR ALTIMETERS FreeFlight Systems’ certified radar altimeters work consistently in the harshest environments including rotorcraft low altitude hover and terrain transitions. RADAROur radar altimeter systems integrate with popular compatible glass displays. AL RA-4000/4500 & FreeFlight Systems modern radar altimeters are backed by more than 50 years of experience, and FRA-5500 RADAR ALTIMETERS have a proven track record as a reliable solution in Model RA-4000 RA-4500 FRA-5500 the most challenging and critical segments of flight. The TSO and ETSO-approved systems are extensively TSO-C87 l l l deployed worldwide in helicopter fleets, including ETSO-2C87 l l l some of the largest HEMS operations worldwide. DO-160E l l l DO-178 Level B l Designed for helicopter and seaplane operations, our DO-178B Level C l l radar altimeters provide precise AGL information from 2,500 feet to ground level. -

E230 Aircraft Systems
E230 Aircraft Systems Unusual Attitude School Of 6th Presentation Engineering Artificial Horizon (AH) • Indicate aircraft pitch and roll attitudes • Do not indicate climb or descend Angle of Bank markers Pitch attitude markers Horizon Line Aircraft Symbol Quick Erection Knob School of Engineering Reading Artificial Horizon School of Engineering Air-driven AH • Utilizes a type of vertical axis displacement gyro known as Earth gyro • Earth gyro – Rotor axis is perpendicular to the earth’s surface School of Engineering Effects of movement on AH • Pitch – Outer gimbal pitches up because it is attached to casing – Horizon bar is pivoted downward – Aircraft symbol is now above horizon line, indicating pitch up attitude • Roll – Both inner and outer gimbals are stabilised – Shows aircraft bank angle • Yaw – Both inner and outer gimbals move with aircraft School of Engineering Pendulous unit • Use to keep the rotor axis vertical if it wanders away from vertical position • Vanes always hang in vertical direction due to gravity, even when rotor is tilted • Air flow into the unit from the top • Reaction force is created from the air coming out from the ports at the bottom School of Engineering How Pendulous units work • When spin axis is vertical: – Equal amount of air comes out from all 4 ports at the bottom – 4 reaction forces equal and opposite and cancel one another out School of Engineering How Pendulous unit works • If spin axis wanders away from vertical: – Port B will be fully covered by the vane – Port D will be fully opened • Unbalanced air creates a force at the base (directed into viewing plane) • This force will create another precession force that rotates the spin axis back to vertical.