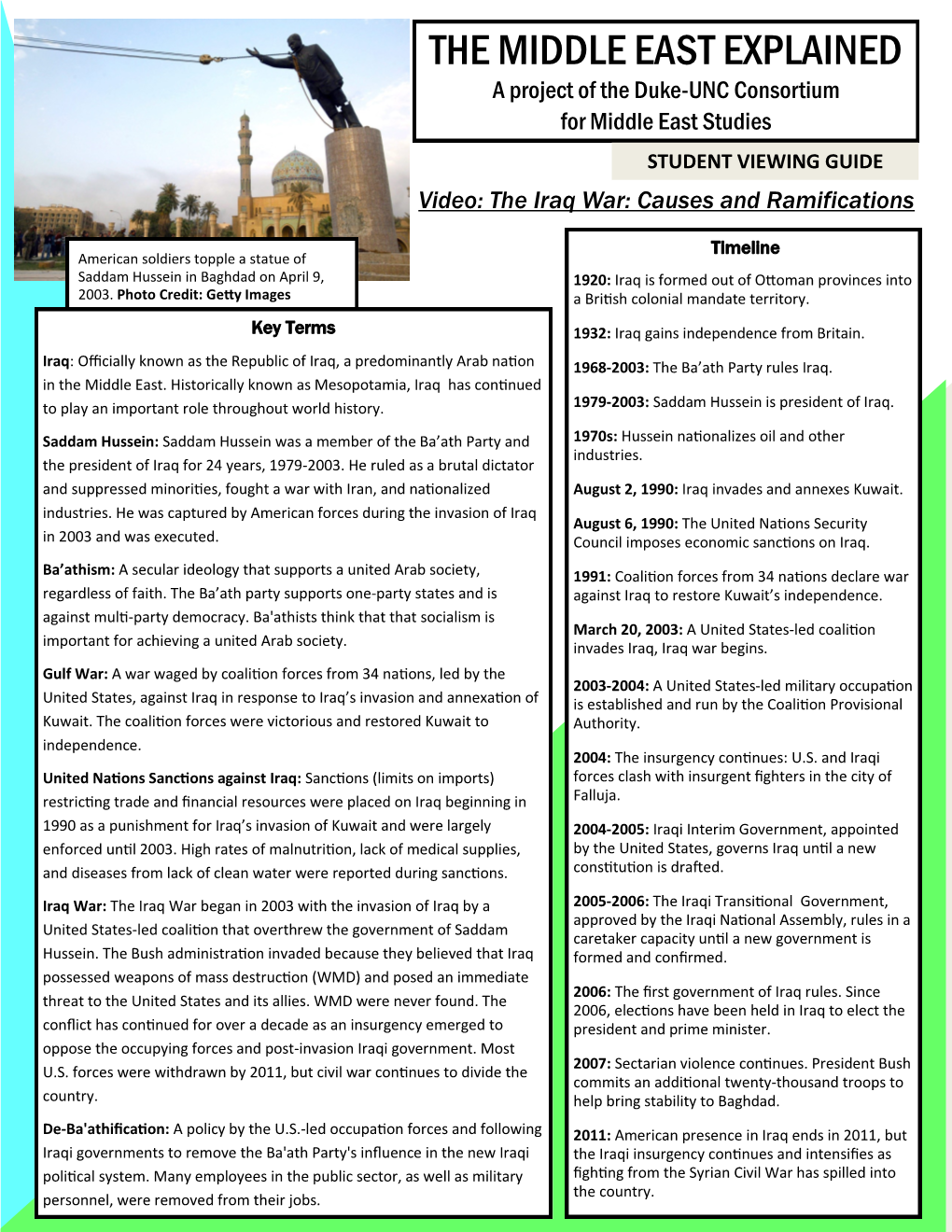
STUDENT VIEWING GUIDE Video: the Iraq War: Causes and Ramifications
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Yazidi Survivors in Germany and Iraq's Reparation Pro- Gramme
IOM IRAQ YAZIDI SURVIVORS IN GERMANY AND IRAQ’S REPARATION PRO- GRAMME: “I WANT FOR US TO HAVE A SHARE IN IRAQ” YAZIDI SURVIVORS IN GERMANY AND IRAQ’S REPARATION PROGRAMME: “I WANT FOR US TO HAVE A SHARE IN IRAQ” The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is committed to the principle that humane and orderly migration benefits migrants and society. As an intergovernmental organization, IOM acts with its partners in the international community to: assist in meeting the operational challenges of migration; advance understanding of migration issues; encourage social and economic development through migration; and uphold the human dignity and well-being of migrants. The opinions expressed in the report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the International Organization for Migration (IOM). The information contained in this report is for general information purposes only. Names and boundaries do not imply official endorsement or acceptance by the International Organization for Migration (IOM). IOM Iraq endeavours to keep this information as accurate as possible but makes no claim – expressed or implied – on the completeness, accuracy and suitability of the information provided through this report. International Organization for Migration Address: UNAMI Compound (Diwan 2), International Zone, Baghdad/Iraq Email: [email protected] Website: iraq.iom.int This report is authored by Güley Bor © 2021 International Organization for Migration (IOM) All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise without the prior written permission of the publisher. -

Iraqi Invasion of Kuwait-International Response Iraq Invaded and Overran Kuwait on Aug
Keesing's Record of World Events (formerly Keesing's Contemporary Archives), Volume 36, August, 1990 International, Page 37631 © 1931-2006 Keesing's Worldwide, LLC - All Rights Reserved. Iraqi invasion of Kuwait-International Response Iraq invaded and overran Kuwait on Aug. 2 and by the end of August had completely absorbed Kuwait into its administrative structure, despite the international condemnation of the invasion. Shortly after the invasion United States troops, backed up by forces from various European, Arab and Asian countries, were quickly dispatched to Saudi Arabia in an attempt to shield the kingdom from Iraqi assault and to impress upon President Saddam Hussein of Iraq that he should withdraw his troops from Kuwait. The invasion, and the subsequent entry of US forces into Saudi Arabia, had a massive impact on Arab regional politics, causing alliances and antagonisms to shift and crumble. The Iraqi move was the culmination of several months of incident in the Middle East which appeared to be aimed at building up Saddam Hussein's anti- Western and anti-Israeli credentials whilst at the same time confirming Iraq's regional ascendency [see pp. 37332; 37390; 37471]. For many Arabs the invasion of Kuwait confirmed Saddam as the foremost pan- Arab nationalist leader and the first Arab ruler since Egypt's Abdel Gamal Nasser who was fully prepared to stand up to the USA. Tension between Iraq and OPEC over-producers Tension between Iraq and Kuwait came to the world's attention in mid-July when Saddam Hussein launched a fierce attack on the policy of those Gulf states, principally Kuwait and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), whose over-production of oil he blamed for a corresponding slump in world oil prices. -

Montana Model UN High School Conference
Montana Model UN High School Conference Security Council Topic Background Guide Topic 1: The Situation in Iraq1 19 August 2014 According to the UN Charter, the Security Council has primary responsibility for maintaining international peace and security. For decades, the situation in Iraq has presented complex and changing challenges to the Council, ranging from concerns about Iraq’s relations with its neighbors (during the Iran-Iraq war of the 1980s and the 1990 Iraqi invasion of Kuwait); to Iraq’s development of weapons of mass destruction and attacks on Iraqi civilians (during the 1980s and 1990s); the 2003 invasion and occupation of Iraq by the US and UK, which resulted in an Iraqi insurgency and civil war; and the conflict between domestic political opponents, specifically the more recent actions by Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS) against the Iraqi government. The situation in Iraq is far from stable. Unresolved ethnic tensions among Iraq’s main ethnic groups — the Shiites, Sunni, and Kurds — could exacerbate the present crisis or lead to further conflicts in the future. Finally, there are concerns about regional stability. The situation within Iraq is also far from resolved from the point of view of Iraqi civilians, who suffered both under the authoritarian government of Saddam Hussein, in the eight years of war that began with the US invasion, and under the attacks by insurgents that followed the US’s withdrawal. Because the US and Iraqi governments refused for many years to release data on civilian casualties, the number of civilian deaths can only be estimated. The most reliable estimates are considered to be those of the Iraq Body Count (IBC), which bases its estimates on media reports. -

Chapter 5: the United Nations and the Sanctions Against Iraq
5 7KH8QLWHG1DWLRQVDQGWKH6DQFWLRQV $JDLQVW,UDT 5.1 The historical involvement of the international community, the League of Nations and the United Nations (UN) in the wider Middle East region was outlined in Chapter 2 of this report. As discussed in that Chapter, the Middle East became a focus for international rivalry with the demise of the Ottoman (Turkish) Empire, the period of the French and British Mandates, the UN partition plan for Palestine of 1947 and the post-war creation of the State of Israel in 1948. 5.2 Chapter 2 also outlined developments in the wider Arab-Israeli conflict after World War 2, the path of the multilateral tracks of the Oslo peace process from 1991 onwards and the 'shuttle diplomacy' efforts of the major powers, particularly the United States (US), until the present time. The UN in the Middle East 5.3 The UN officially came into existence in October 1945. Australia was one of the original 51 member states. In the post World War 2 environment, one of the earliest UN involvements in the Middle East region involved the former British-mandate Palestine. 5.4 By 1947, Britain had found the Palestine Mandate unworkable and, accordingly, submitted the problem to the UN. The UN General Assembly (UNGA) adopted Resolution 181 in November 1947, which provided for a 'Plan of Partition with Economic Union'. This laid down steps for bringing both Arab and Jewish peoples to independence, with special provisions for Jerusalem. No progress had been made towards implementing the plan before Britain relinquished the Mandate on 14 May 94 1948 and the Jewish leadership proclaimed the State of Israel. -

The UN Security Council and Iraq1
United Nations University Working Paper Series Number 01 – November 2013 The UN Security Council and Iraq1 Poorvi Chitalkar and David M. Malone2 Overview The UN Security Council, largely handicapped by the Cold War until the late 1980s, has become considerably more proactive over the last twenty-five years. The results are mixed. One constant for the Council since 1980 is that it has been at grips with conflicts involving Iraq – conflicts with Iraq’s neighbours and also internal strife prior to and particularly since 2003. Every instrument at the Council’s disposal, in- cluding all the coercive ones, have been invoked at one time or another against authorities in Iraq or to assist them. After a promising beginning in helping to end the Iran-Iraq war (1980-88), and in mandating the expulsion of Iraqi forces from Kuwait, which Baghdad had sought to annex in 1990, the Council’s silent tolerance of intrusive interna- tional humanitarian activities in Iraq’s Kurdish provinces as of 1991 was ground-breaking. Nevertheless, the Council’s post-war strategy for Iraq outlined in Resolution 687 of 1991 wound up over-reaching, involved serious unintended consequences arising from an overzealous sanctions regime (and a related humanitar- ian program the UN did not possess the administrative machinery to oversee effectively), and eventually sundered relations among the Permanent Five (P-5) members of the Council through a series of fractious episodes from 1988 to 2003. This working paper outlines a three-decade span of Security Council resolutions, actions and impasses on Iraq, investigating closely the period of diplomatic confrontation in 2002-2003 culminating in unilateral military action to remove Saddam Hussein from power by the US, the UK and a very few others without a mandate from the Council to do so. -

Iraq: Politics and Governance
Iraq: Politics and Governance Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Carla E. Humud Analyst in Middle Eastern and African Affairs March 9, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RS21968 Iraq: Politics and Governance Summary Iraq’s sectarian and ethnic divisions—muted toward the end of the 2003-2011 U.S. military intervention in Iraq—are fueling a major challenge to Iraq’s stability and to U.S. policy in Iraq and the broader Middle East region. The resentment of Iraq’s Sunni Arabs toward the Shiite- dominated central government facilitated the capture in 2014 of nearly one-third of Iraqi territory by the Sunni Islamist extremist group called the Islamic State (IS, also known as ISIL, ISIS, or the Arabic acronym Da'esh). Iraq’s Kurds are separately embroiled in political, territorial, and economic disputes with Baghdad, but those differences have been at least temporarily subordinated to the common struggle against the Islamic State. U.S. officials assert that the Iraqi government must work to gain the loyalty of more of Iraq’s Sunnis—and to resolve differences with the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG)—if an eventual defeat of the Islamic State is to result in long-term stability. Prospects for greater inter- communal unity appeared to increase in 2014 with the replacement of former Prime Minister Nuri al-Maliki with the current Prime Minister, Haydar al-Abbadi. Although both men are from the Shiite Islamist Da’wa Party, Abbadi has taken some steps to try to compromise with Sunnis and with the KRG. However, a significant point of contention with the KRG remains the KRG’s marketing of crude oil exports separately from Baghdad. -

ISIS Success in Iraq: a Movement 40 Years in the Making Lindsay Church a Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirem
ISIS Success in Iraq: A Movement 40 Years in the Making Lindsay Church A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF ARTS IN INTERNATIONAL STUDIES: MIDDLE EAST University of Washington 2016 Committee: Terri DeYoung Arbella Bet-Shlimon Program Authorized to Offer Degree: Jackson School of International Studies !1 ©Copyright 2016 Lindsay Church !2 University of Washington Abstract ISIS Success in Iraq: A Movement 40 Years in the Making Lindsay Church Chair of the Supervisory Committee: Terri DeYoung, Near Eastern Language and Civilization In June 2014, the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS)1 took the world by surprise when they began forcibly taking control of large swaths of territory in Iraq and Syria. Since then, policy makers, intelligence agencies, media, and academics have been scrambling to find ways to combat the momentum that ISIS has gained in their quest to establish an Islamic State in the Middle East. This paper will examine ISIS and its ability to build an army and enlist the support of native Iraqis who have joined their fight, or at the very least, refrained from resisting their occupation in many Iraqi cities and provinces. In order to understand ISIS, it is imperative that the history of Iraq be examined to show that the rise of the militant group is not solely a result of contemporary problems; rather, it is a movement that is nearly 40 years in the making. This thesis examines Iraqi history from 1968 to present to find the historical cleavages that ISIS exploited to succeed in taking and maintaining control of territory in Iraq. -

Is the Continues Use of Sanctions As Implemented Against Iraq a Violation of International Human Rights
Denver Journal of International Law & Policy Volume 28 Number 4 Fall Article 4 May 2020 Is the Continues Use of Sanctions as Implemented against Iraq a Violation of International Human Rights Peggy Kozal Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.du.edu/djilp Recommended Citation Peggy Kozal, Is the Continues Use of Sanctions as Implemented against Iraq a Violation of International Human Rights, 28 Denv. J. Int'l L. & Pol'y 383 (2000). This Article is brought to you for free and open access by Digital Commons @ DU. It has been accepted for inclusion in Denver Journal of International Law & Policy by an authorized editor of Digital Commons @ DU. For more information, please contact [email protected],[email protected]. IS THE CONTINUED USE OF SANCTIONS AS IMPLEMENTED AGAINST IRAQ A VIOLATION OF INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS? PEGGY KOZAL" I. INTRODUCTION Since 1990, the fate of the Iraqi population has constantly been threatened by the most extensive sanctions in the history of the United Nations (UN). These sanctions were imposed on Iraq to influence its government to change its nuclear warfare policies and comply with UN inspections of its chemical, nuclear and biological weapons. The impact of the sanctions, however, has not coerced the Iraqi government to alter its policies, but has instead led to a humanitarian crisis among the innocent civilian population.' Saddam Hussein still remains in power and the Iraqi government suffers a small portion of what the economy and people do.2 The international community employs sanctions, inter alia, as a method of policing human rights policies in other countries.3 But when the enforcement of the sanctions worsens the humanitarian situation or violates human rights, the efficacy of the method employed must be examined. -

1 the Human Cost of US Interventions in Iraq
The Human Cost of U.S. Interventions in Iraq: A History From the 1960s Through the Post-9/11 Wars Zainab Saleh1 October 13, 2020 The United States government has justified decades of intervention in Iraq in a variety of ways, the most recent of which is the current “war on terrorism.” All of these interventions have had devastating costs and consequences for Iraqis. Since the 1960s, the U.S. has treated Iraq as essential to its own economic and geopolitical interests; Iraqi arms purchases have bolstered the American military-industrial complex and stable access to Middle East oil has secured U.S. dominance in the global economy. As the U.S. has pursued these interests in Iraq, U.S. interventions have reshaped the Iraqi social, political, and cultural landscape. While the role the United States has played in Iraq since the 1960s is beginning to receive some scholarly attention, it remains widely unknown to the American public. Iraqis have lived in the shadow of U.S. interventions for decades, whereby the United States has attempted to control events and resources in the Gulf region. In 1958, the fall of the Iraqi monarchy brought an end to British influence in Iraq and the emergence of the United States as a major player in Iraqi affairs. In 1963, under the pretext of protecting the region from a communist threat, the Central Intelligence Agency backed the Ba‘th coup, an Arab nationalist party, after Iraq nationalized most of its oil fields. During the 1980s, the United States supported Saddam Hussein’s regime and prolonged the Iran-Iraq War in order to safeguard its national interests in the region, which entailed weakening Iran after the Islamic Revolution in 1979 to prevent it from posing a threat to U.S. -

The President of the United States
106th Congress, 1st Session ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± House Document 106±34 IRAQ'S COMPLIANCE WITH THE U.N. SECURITY COUNCIL COMMUNICATION FROM THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES TRANSMITTING A REPORT ON THE STATUS OF EFFORTS TO OBTAIN IRAQ'S COM- PLIANCE WITH THE RESOLUTIONS ADOPTED BY THE U.N. SECU- RITY COUNCIL, PURSUANT TO PUB. L. 102±1, SEC. 3 (105 STAT. 4) MARCH 4, 1999.ÐReferred to the Committee on International Relations and ordered to be printed U.S. GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE 69±011 WASHINGTON : 1999 THE WHITE HOUSE, Washington, March 3, 1999. Hon. J. DENNIS HASTERT, Speaker of the House of Representatives, Washington, DC. DEAR MR. SPEAKER: Consistent with the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq Resolution (Public Law 102±1) and as part of my effort to keep the Congress fully informed, I am report- ing on the status of efforts to obtain Iraq's compliance with the res- olutions adopted by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). My last report, consistent with Public Law 102±1, was transmitted on December 18, 1998. OVERVIEW As stated in my December 18 report, on December 16, United States and British forces launched military strikes on Iraq (Oper- ation Desert Fox) to degrade Iraq's capacity to develop and deliver weapons of mass destruction (WMD) and to degrade its ability to threaten its neighbors. The decision to use force was made after U.N. Special Commission (UNSCOM) Executive Chairman Richard Butler reported to the U.N. Secretary General on December 14, that Iraq was not cooperating fully with the Commission and that it was ``not able to conduct the substantive disarmament work mandated to it by the Security Council.'' The build-up to the current crisis began on August 5 when the Iraqi government suspended cooperation with UNSCOM and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), except on a limited- range of monitoring activities. -

Iraq: a Geography. INSTITUTION Military Academy, West Point, NY
DOCUMENT RESUME ED 476 013 SO 034 831 AUTHOR Malinowski, Jon C., Ed. TITLE Iraq: A Geography. INSTITUTION Military Academy, West Point, NY. Dept. of Geography and Environmental Engineering. PUB DATE 2002-00-00 NOTE 120p.; Introduction by Wendell C. King and Eugene J. Palka. AVAILABLE FROM United States Military Academy, West Point Department of Geography & Environmental Engineering, Building 600, West Point, New York 10996. Tel: 845-938-3128; Fax: 845-938-3339; Web site: http://www.dean.usma.edu/geo/gene.htm. PUB TYPE Guides Non-Classroom (055) Reports Descriptive (141) EDRS PRICE EDRS Price MF01/PC05 Plus Postage. DESCRIPTORS Area Studies; *Educational Resources; Foreign Countries; Geographic Concepts; Geographic Location; Higher Education; Secondary Education; Social Studies; *World Geography; *World Problems IDENTIFIERS *Iraq; Mesopotamia ABSTRACT Accused of harboring and supporting terrorists, Saddam Hussein's country of Iraq sits at the top of a short list of targets in United States war on terrorism. Iraq is a country about twice the size of the state of Idaho with a population of over 22 million. The country relies on oil for its economic well-being and controls what some estimate to be the second largest reserve in the world. The 5000-year history of the land between the rivers (Mesopotamia), has shown that armies conquer, are conquered, governments rise and fall, and there is no reason to predict that the future will not follow the same script. This collection of articles, written by the geography faculty of the U.S. Military Academy (West Point, New York), is meant to educate military and governmental leaders as they consider diplomatic and military solutions to deal with Iraq's threat to the region and to the world. -

Refugees from Iraq Their History, Cultures, and Background Experiences
COR Center Enhanced Refugee Backgrounder No. 1 October 2008 Refugees fromIraq COR Center Enhanced Refugee Backgrounder No. 1 October 2008 Refugees from Iraq Their History, Cultures, and Background Experiences Writers: Edmund Ghareeb, Donald Ranard, and Jenab Tutunji Editor: Donald A. Ranard Published by the Center for Applied Linguistics Cultural Orientation Resource Center Center for Applied Linguistics 4646 40th Street, NW Washington, DC 20016-1859 Tel. (202) 362-0700 Fax (202) 363-7204 http://www.culturalorientation.net http://www.cal.org The contents of this Backgrounder were developed with funding from the Bureau of Population, Refugees, and Migration, United States Department of State, but do not necessarily represent the policy of that agency and the reader should not assume endorsement by the federal government. The Backgrounder was published by the Center for Applied Linquistics (CAL), but the opinions expressed herein do not necessarily reflect positions or policies of CAL. Production supervision: Sanja Bebic Writers: Edmund Ghareeb, Donald Ranard, and Jenab Tutunji Editor: Donald A. Ranard Copyediting: Jeannie Rennie Proofreading: Craig Packard Cover: Ellipse Design Design, illustration, production: Ellipse Design ©2008 by the Center for Applied Linguistics The U.S. Department of State reserves a royalty-free, nonexclusive, and irrevocable right to reproduce, publish, or otherwise use, and to authorize others to use, the work for Government purposes. All other rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. All inquiries should be addressed to the Cultural Orientation Resource Center, Center for Applied Linguistics, 4646 40th Street, N.W., Washington, D.C.