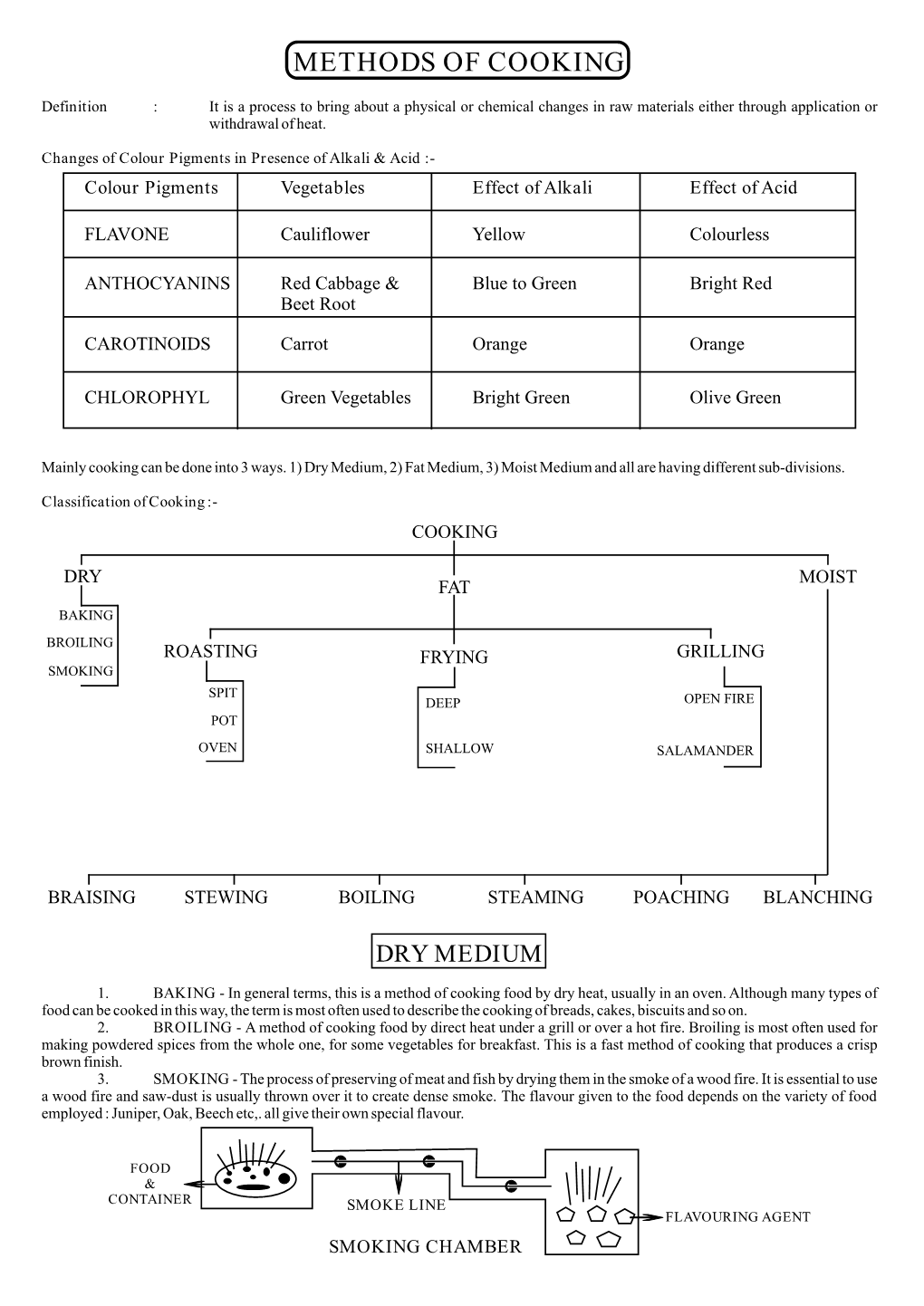
Methods of Cooking
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cooking-Principles, Methods & Its Effects
COOKING-PRINCIPLES, METHODS & ITS EFFECTS COOKING INTRODUCTION Most of the food products which we eat are cooked before consumption. Cooking makes the food tasty, attractive, colourful, easily digestable & also ass variety to texture. Cooking also kills many micro-organisms & make the food safe to be consumed. Several raw food have antinutritional factors which are destroyed by cooking. However, if proper care is not taken while cooking, several important nutrients rae destroyed. So, it is very important to employ proper method of cooking to avoid nutrient loss. Some methods employed before cooking 1. Peeling: It is a method of removing the outer firm skin before cooking or eating fruit or vegetable. Some of vegetables & fruits are eaten with the peel. 2. Chopping It involves cutting of fruits & vegetables. Food is cut into several sizes to create variety in the cooked food 3. Grinding & pounding In grinding, the food is reduced to very fine form like spices. Sometimes cereals are also ground to powder. Pounding is also like crushing food to reduce thickness for easier cooking. 4. Soaking Pulses & legumes are soaked for few hours before cooking to make cooking easier. 5. Sprouting or germinating This method is used for pulses, legumes & grains. This method not only add variety to food, but also increases the content of vitamin C & vitamin B complex in the food. Cooking methods Methods employed for cooking of food can be categorized under two heads: 1. Moist heat methods 2. Dry heat methods 3. Other methods COOKING METHODS Moist heat dry heat other methods Boiling roasting sautering Simmering grilling frying Pressure cooking toasting - deep frying Steaming baking - shallow frying Poaching Stewing Blanching Moist heat methods It is defined as those methods of cooking, in which water is used as medium for transferring heat for ccokingg. -

COOKERY PROCESSES (COOKING METHODS) a Lot of Cooking
COOKERY PROCESSES (COOKING METHODS) A lot of cooking methods are used in catering and hotel industry. Each is specific and has its advantages and disadvantages. The cookery processes or cooking methods are: a) Boiling b) Poaching c) Stewing d) Braising e) Steaming f) Baking g) Roasting h) Pot roasting i) Grilling j) Shallow Frying k) Deep Frying l) Microwaving 1. Boiling www.astro.su.se/.../small_500/Boiling_water.jpg 1.1 Definition Boiling is cooking prepared foods in a liquid (water, bouillon, stock, milk) at boiling point. 1.2 Methods Food is boiled in two ways: a) food is placed into boiling liquid, reboiled, then the heat is reduced, so that the liquid boils gently – simmering; b) food is covered with cold liquid, brought to the boil, then the heat is reduced, so that the food simmers. 1.3 Advantages a) older, tougher joints of meat can be made palatable and digestible b) appropriate for large-scale cookery - 2 - c) economic on fuel d) nutritious, well flavoured stock is produced e) labor saving, requires little attention f) safe and simple g) maximum colour and nutritive value are retained with green vegetables – but the boiling time must be kept to the minimum 1.4 Disadvantages a) foods can look unattractive b) it can be slow c) loss of soluble vitamins in the water 1.5 Examples of foods which might be cooked by boiling - stocks (beef, mutton, chicken, fish) - sauces (brown, white, curry) - glazes (fish, meat) - soup (tomato, lentil) - farinaceous (pasta) - fish (cod, salmon) - meat (beef, leg of mutton) - vegetables (carrots, cabbage, potatoes). -

The Thermal Pro™ Stainless
the Thermal Pro™ Stainless Instruction Book - BEF560 IMPORTANT Contents SAFEGUARDS READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS 2 Breville Recommends Safety First BEFORE USE AND SAVE 5 Components FOR FUTURE REFERENCE 6 Functions 8 Care & Cleaning • Do not place frypan near the 9 Hints & Tips edge of a bench or table during operation. Ensure the surface is level, clean and free of water. BREVILLE • Remove any promotional stickers before using the frypan RECOMMENDS for the first time. SAFETY FIRST • Do not place the frypan on At Breville we are very safety or near a hot gas or electric conscious. We design and burner, or where it could touch manufacture consumer a heated oven. Place frypan at products with the safety of you, least 20cm away from walls our valued customer, foremost and curtains. in mind. In addition we ask • Do not use on metal surfaces, that you exercise a degree of for example, a sink drain board. care when using any electrical • Always insert Temperature appliance and adhere to the Control Probe into probe following precautions. socket and ensure is fully inserted, before inserting power plug into power outlet and switching on appliance. Ensure the probe socket is completely dry before inserting the Temperature Control Probe. • Ensure the cord is not touching the hot pan. 2 • To protect against electric • Always turn the Temperature shock, do not immerse cord or Control Probe to the Temperature Control Probe in MINIMUM position, then water or any other liquid. switch off at the power outlet • Ensure the Temperature and allow probe to cool, then Control Probe has cooled remove probe and unplug, before removing from the if appliance is to be left appliance. -

01 Methods of Cooking
Food Production Foundation -II BHM -201T UNIT: 01 METHODS OF COOKING Structure 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Heat and Cooking 1.3.1 What is heat? 1.3.2 Effect of Heat on food 1.3.3 Method of heat transfer 1.4 Methods of cooking 1.5 Moist heat Methods of Cooking 1.5.1 Boiling 1.5.2 Poaching 1.5.3 Steaming 1.5.4 Stewing 1.5.5 Braising 1.6 Dry heat Methods of Cooking 1.6.1 Baking 1.6.2 Roasting 1.6.3 Grilling 1.7 Frying 1.8 Modern Methods of cooking 1.8.1 Paper Bag (en papillotte) 1.8.2 Microwave Cooking 1.8.3 Infra-red Cooking 1.9 HACCP Standards and Professional Kitchens 1.9.1 Introduction 1.9.2 What is HACCP? 1.9.3 Food Preparation Hazard and Control Rules 1.10 Summary 1.11 Key Terms 1.12 References and Bibliography 1.13 Review Questions 1.1 Introduction This chapter deals with basic principles. You will learn about what happens to food when it is heated, about how food is cooked by different methods, and about rules of seasoning and flavouring. It is important to understand the science of food and cooking so you can successfully use these principles in the kitchen. 1.2 Objectives After reading this unit the learner will be able to understand: • Methods of heat transfer Uttarakhand Open University 1 Food Production Foundation -II BHM -201T • Effect of heat on food • Moist heat Methods of Cooking • Dry heat Methods of Cooking • Frying • Modern Methods of cooking 1.3 Heat and Cooking To cook food means to heat it in order to make certain changes in it. -

Why Olive Oil Is the Best Oil for Frying
Why olive oil is the best oil for frying October 14, 2016 Tweet Share Contrary to popular belief, olive oil is one of the best oils for frying. The medium-high smoke point of olive oil exceeds the temperatures needed for frying. Furthermore, olive oil contains oleic acid and minor compounds that protect the oil from breaking down, even after reuse. Frying is one of the most common and most delicious ways to prepare food. Throughout the Mediterranean, traditional foods like pescadillo, calamari, keftedes, patatas a la pobre, carcio alla giudea, and falafel are all fried in olive oil. Mediterraneans know that olive oil is the best oil for cooking and frying. So why do Americans believe that olive oil should only be used raw? The science Olive oil is one of the most stable oils for cooking. Unlike other common cooking oils, olive oil contains compounds and antioxidants that prevent the oil from breaking down under moderate heat. Additionally, olive oil is mostly composed of oleic acid (Omega-9), a monounsaturated fatty acid that is naturally resistant to oxidation. Multiple peer-reviewed studies have shown that olive oil is the best oil for frying. Olive oil outperformed vegetable, peanut, corn, soybean, sunower and canola oils. Olive oil can be heated to high temperatures - In 2013, Food Chemistry published a report comparing free radical formation and oxidation (rancidity) when heating peanut oil and extra virgin olive oil. The researchers found that more heat was needed to start the oxidation process in the extra virgin olive oil than in the peanut oil. -

Cooking Methods
Cooking Methods Method Definition Details Sautéing works best for flat and To cook food in a thin film of relatively thin foods such as steaks Sauté hot oil in a skillet on a hot and chops. Also small items such as burner vegetables, shrimp and scallops Roasting works with large cuts of To cook foods in a pan in a hot meat and whole birds, even sliced Roast oven potatoes Food can be partially immersed in oil, To cook in a larger amount of shallow frying or pan frying. Foods Fry hot oil in a skillet or pot set on that are completely submerged in hot a hot burner oil is called deep frying. At sea level water boils at 212 To cook foods in boiling liquid degrees. The boiling point drops 2 Boil with a pot set on a hot burner degrees for every 1,000 foot increase in elevation. Temperature of the liquid is 180 – 205 To cook foods in liquid that is degrees. When a liquid simmers, just below the boiling point in small bubbles gently break the Simmer a pot set on a hot burner surface of the liquid slowly, whereas boiling is a fast bubbling action. Poaching is related to simmering, but To cook foods in a liquid that is the temperature of the liquid is lower well below the boiling point in than 180 and there are no bubbles Poach a covered pot set on a stove breaking the surface. The pot is top generally covered to create a gentle cooking environment. To cook food that are Steaming is an especially gentle suspended in a basket over cooking method. -

Open Methods of Cookery
METHODS OF COOKERY Teacher’s Guide METHODS OF COOKERY Support resources for Hospitality training. As a precursor to undertaking Hospitality training, Fliplets eLearning resources introduce students to the operations and terminology used in kitchens in the hospitality industry. Fliplets were initially developed for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students in remote locations but will also have value for students in other contexts. This resource will be valuable both for students undertaking specific vocational learning and those interested in the food preparation and hospitality aspects of Technologies and Work Studies subjects of the Australian Curriculum. RECOMMENDATION It is recommended that students examine the ‘Fliplet’ several times prior to commencement of training, this gives the student basic underpinning knowledge of the subject being taught by the teacher / trainer. Once this has been done it is time for you to begin facilitation of the students learning. It is suggested that you use the recommended activities, questions or group discussions outlined at the end of each topic to develop and test the students understanding of the information in the ‘Fliplet’. ICT for Learning Teachers Guide for Methods of Cookery Fliplet Version 3 September 2016 Author: S Neale OVERVIEW 1 This resource is designed to assist students in gaining an understanding of the different methods of cooking. Understanding the methods helps the student to choose the appropriate method for different food types. Specifically, it focuses on the following topics: 1. Heat transfer 2. Dry Heat Cooking Methods Shallow and Stir Frying Methods Deep Frying Grilling Roasting Baking 3. Moist Cooking Methods Poaching Boiling Steaming 4. -

Toughened Non-Stick Shallow Frying Pan – Care & Instruction Guide
Toughened Non-Stick Shallow Frying Pan – Care & Instruction Guide Toughened Non-Stick Cooking with Toughened Non-Stick Le Creuset Toughened Non-Stick pans are manufactured from premium materials that will provide the best in durability and cooking performance. Each pan is made from heavy gauge, forged aluminium that has been specially treated to provide a strong, toughened finish that will withstand the demands of everyday use. Each pan spreads heat evenly and efficiently, so there are no hot spots in your cooking. The specially constructed base incorporates a magnetic, stainless steel disc that provides extra strength and stability to the pan and makes it suitable for use on ALL HEAT SOURCES including the latest induction hobs. Both the interior and exterior of each pan are finished with one of the most modern, PFOA-free, toughened non-stick finishes available providing superb release of food and easy cleaning – every day. It is an ideal surface for healthier cooking with very little oil or fat.. Optional heat-resistant glass lids are available to buy separately. Handles are secured with stainless steel rivets. Before first use Remove all packaging and labels, wash pans in hot soapy water, rinse and dry thoroughly. Condition the interior non-stick cooking surface. DO NOT condition the black exterior sidewall. Rub a film of vegetable or corn oil over the entire surface using a pad of kitchen paper towels. Rinse the pan with hot water, dry thoroughly. The pan is now ready for use. Occasional re-conditioning after this will help protect the surface and promote longer life. -

Historically, Cast Iron Has Been the Prime Material Chosen
www.lecreuset.co.za 1 Le Creuset is consistently chosen by leading chefs, restauranteurs, and those who just enjoy cooking; all of whom appreciate its performance, cooking advantages and style. 1 istorically, cast iron has been the prime material chosen The many enamel colours of Le Creuset cast iron cookware are as for cooking vessels. Evidence of this can be seen in durable as the cookware itself. From the most classic to the most Hheritage centres all over the world. Durability is the most contemporary, we have a wide range of colours to match your lifestyle. obvious benefit of cast iron, but durability is not its only strength. Many The initial coat of colourless enamel provides a perfect base on which Le Creuset pieces are handed down from one generation to the next, the colour-rich second coat is applied. No matter which colour you which mimics their lifetime guarantee. choose, you can be sure that the colour won’t fade, the finish is durable and hygienic and your cookware will stay looking good for a lifetime. Cast iron cooks very evenly, distributing heat throughout the piece so that each corner or curve achieves the same temperature. Every single Flame piece of Le Creuset cast iron can be used on the stove, in the oven or under the grill - and then served directly to the table. Cast iron is a highly efficient material that absorbs heat from the hob Cherry very well. This is why medium and low hob settings should be used at all times in order to achieve the best cooking results. -

Turning up the Heat- Dry Cooking Teacher Notes
Video Education Australasia Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Secondary - Tafe Turning Up the Heat! 28mins Basic Dry Cooking Methods Teacher Notes by Yvonne Ashton BAppSci(Con Sci) BAppSci(Food Sci)(Hons) BT(Prim and Sec) Produced by Video Education Australasia Commissioning Editor Christine Henderson B.Sc. Ph.D. Dip.Ed. Executive Producer Mark McAuliffe Dip.Art (Film & TV) Dip.Ed. B.Ed. Ph.D. © Video Education Australasia Pty. Ltd. Suitable for: Hospitality Home Economics To order or inquire please contact VEA: WARNING The Copyright proprietor has licensed the Australia New Zealand E-mail motion picture contained on this video cassette for non-theatrical use only and prohibits any 111A, Mitchell Street, PO BOX 4390, [email protected] other use, copying, reproduction or performance Bendigo, Victoria 3550 Shortland St., Auckland in public, in whole or part. The penalties for unauthorised copying of this program include a FREECALL: 1800 034 282 FREECALL: 0800 486 688 Website $50,000 fine for individuals and a $250,000 fine Phone: (03) 5442 2433 Facsimile: 0800 488 668 www.vea.com.au for institutions. These notes can be freely copied for Facsimile: (03) 5441 1148 classroom use only. Turning Up the Heat! Basic Dry Cooking Methods For Teachers: Brief Summary In recent years the practice and art of cooking has been on the decline. This may be due to ready-to-eat meals and takeaway options becoming more readily available, but has been fuelled in part by the lack of cooking knowledge and skills displayed by the average consumer. This program is an informative and in-depth look at the basic dry cooking methods, the first of two productions centred on the methods of cooking food. -

02 Heat Transfer and Materials in Cooking 1Lahu P
JOURNAL OF INFORMATION, KNOWLEDGE AND RESEARCH IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ISSN 0975 – 668X| NOV 16 TO OCT 17 , VOLUME –04, ISSUE – 02 HEAT TRANSFER AND MATERIALS IN COOKING 1LAHU P. MASKEPATIL, 2PREETI .R. BHALCHAKRA 3RAHUL R. BIRADAR 1, 2, 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rajgad Dnyanpeeth’s, Shri chhatrapati Shivajiraje College of engineering, Bhor, Pune, Maharashtra, India. ABSTRACT: Heat transfer is a very important aspect in the cooking process. Heating food destroys potentially harmful bacteria and other microorganisms, which makes food safe to eat and easier to digest. When food or liquids become hot, their molecules absorb energy, begin vibrating rapidly, and start to bounce off of each other. As they collide, heat energy is produced and transferred, which warms and cooks our food. Heat transfer is the process of an item or substance coming into contact with a heat source and becoming hot. In more scientific terms, heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. There are three methods of heat transfer namely conduction, convention and radiation. All these methods are being used in cooking methods. Taste and healthiness of the food is our prime requirement. Does mode of heat transfer affect the test and Vitamins and other contents in the food? Various cooking method and their corresponding mode of heat transfer has been discussed and investigated all aspects concerned with the topic . KEY WORDS: Cookware, Cooking methods, heat transfer in cooking I. Introduction: Human prime requirement of life to survive is food and water. Without food human can’t survive. From the ancient period, human has been changing his food from hunger”. -

To Read the Meal Kit Instructions
THE SOUR COCKTAILS The sours could not be easier to serve. Each bottle contains two cocktails. Fill two short glasses to the top with ice. Pour a little of the cocktail into each glass to leave enough room in the bottle to shake. Give it your best bartender impression and shake for about 10 seconds. Pour over the top of the ice and get creative with your garnish! CHICK ‘N’ CLUB #3 Gin, crème de mure, raspberry shrub, black currant leaf THE MEXINESE Tequila, pandan leaf, ginger & lime CHICKEN HOT WINGS THE MENU KUNG PAO WINGS (CONTAINS NUTS) CHICKEN TENDERS & SEAWEED CRACK K-POP &/OR THE GENERAL FRIED CHICKEN SANDWICH SIDES FREE VIBES WATERMELON SALAD (CONTAINS NUTS) TAG US IN YOUR PICS GINGER MISO GREEN ‘SLAW (VG) (VG) BANG BANG CUCUMBERS (CONTAINS NUTS) 24 HOURS OF PURE TUNES AND EACH MONTH WE’LL Are you ready for maximum deliciousness with as PICK A WINNER TO WIN minimal effort (& washing up) as possible? Well, here goes. A FREE MEAL KIT Please put everything in the fridge, except the bread, as soon as it arrives. All of the food should be consumed on the day you receive it, or the following day. You’ll be pleased to know all our packaging is recyclable, just give it a rinse first. All in all cooking the whole meal should take no more than 30/45 minutes to prepare and serve. CHECK US OUT To complete your experience, scan the QR code on the back for our playlist crammed full of 24 hours of awesome tunes.