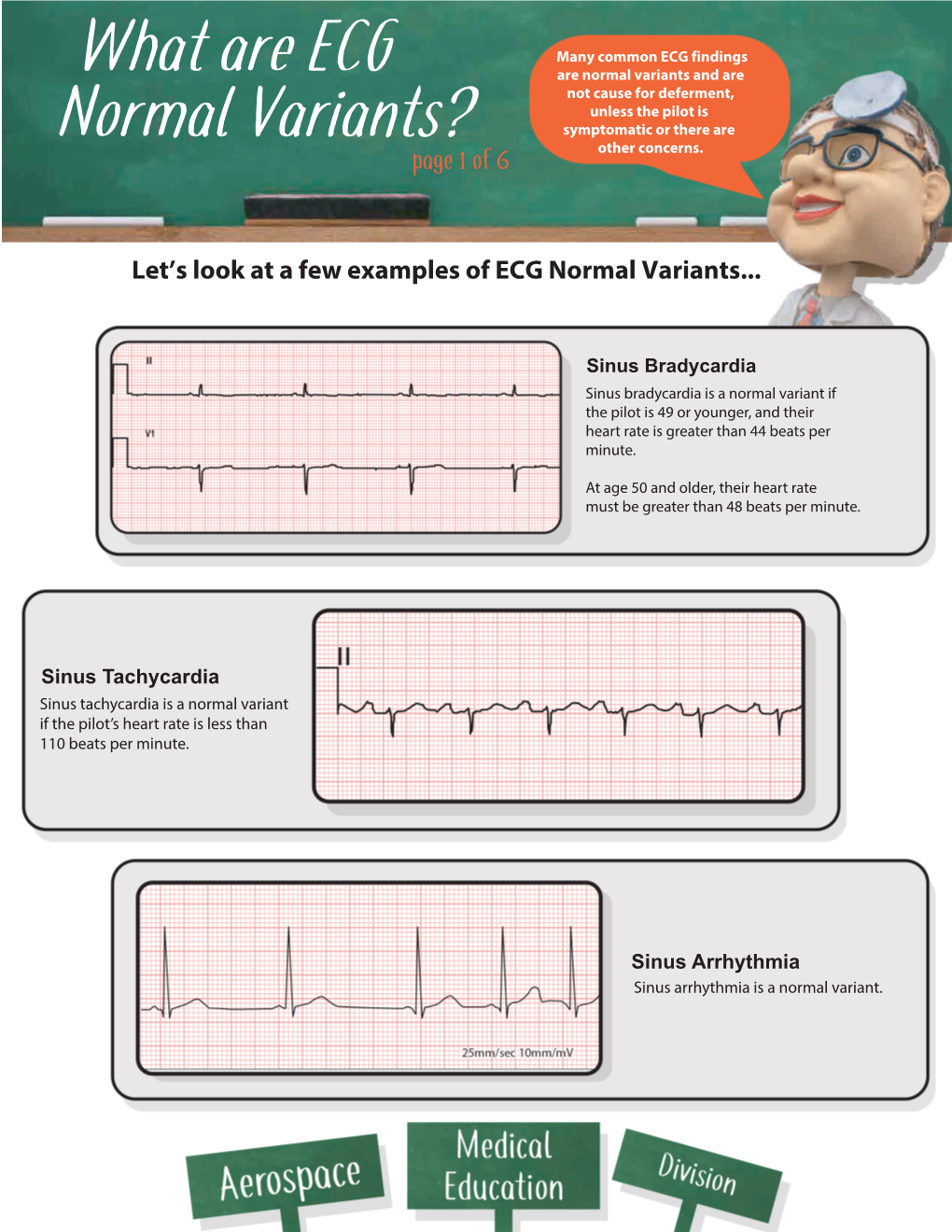
What Are ECG Normal Variants?
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

WPW: WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE Syndrome
WPW: WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE Syndrome What is Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome? Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, or WPW, is named for three physicians who described a syndrome in 1930 in young people with episodes of heart racing and an abnormal pattern on their electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Over the next few decades, it was discovered that this ECG pattern and the heart racing was due to an extra electrical pathway in the heart. Thus, WPW is a syndrome associated with an abnormal heart rhythm, or “arrhythmia”. Most people with WPW do not have any other problems with their heart. Normally, the electrical impulses in the heart originate in the atria or top chambers of the heart and spread across the atria. The electrical impulses are then conducted to the ventricles (the pumping/bottom chambers of the heart) through a group of specialized cells called the atrioventricular node or AV node. This is usually the only electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles. In WPW, there is an additional pathway made up of a few extra cells left over from when the heart formed. The conduction of electricity through the heart causes the contractions which are the “heartbeat”. What is WPW Syndrome as opposed to a WPW ECG? A person has WPW Syndrome if they experience symptoms from abnormal conduction through the heart by the WPW pathway. Most commonly, the symptom is heart racing, or “palpitations”. The particular type of arrhythmia in WPW is called “supraventricular tachycardia” or SVT. “Tachycardia” means fast heart rate; “supraventricular” means the arrhythmia requires the cells above the ventricles to be part of the abnormal circuit. -

Cardiology-EKG Michael Bradley
Cardiology/EKG Board Review Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine Residency Objectives • Review general method for EKG interpretation • Review specific points of “data gathering” and “diagnoses” on EKG • Review treatment considerations • Review clinical cases/EKG’s • Board exam considerations EKG EKG – 12 Leads • Anterior Leads - V1, V2, V3, V4 • Inferior Leads – II, III, aVF • Left Lateral Leads – I, aVL, V5, V6 • Right Leads – aVR, V1 11 Step Method for Reading EKG’s • “Data Gathering” – steps 1-4 – 1. Standardization – make sure paper and paper speed is standardized – 2. Heart Rate – 3. Intervals – PR, QT, QRS width – 4. Axis – normal vs. deviation 11 Step Method for Reading EKG’s • “Diagnoses” – 5. Rhythm – 6. Atrioventricular (AV) Block Disturbances – 7. Bundle Branch Block or Hemiblock of – 8. Preexcitation Conduction – 9. Enlargement and Hypertrophy – 10. Coronary Artery Disease – 11. Utter Confusion • The Only EKG Book You’ll Ever Need Malcolm S. Thaler, MD Heart Rate • Regular Rhythms Heart Rate • Irregular Rhythms Intervals • Measure length of PR interval, QT interval, width of P wave, QRS complex QTc • QTc = QT interval corrected for heart rate – Uses Bazett’s Formula or Fridericia’s Formula • Long QT syndrome – inherited or acquired (>75 meds); torsades de ponites/VF; syncope, seizures, sudden death Axis Rhythm • 4 Questions – 1. Are normal P waves present? – 2. Are QRS complexes narrow or wide (≤ or ≥ 0.12)? – 3. What is relationship between P waves and QRS complexes? – 4. Is rhythm regular or irregular? -

Idiopathic Isolated Right Ventricular Apical Hypertrophy
Acta Cardiol Sin 2018;34:288-290 Letter to the Editor doi: 10.6515/ACS.201805_34(3).20180122A Idiopathic Isolated Right Ventricular Apical Hypertrophy Debika Chatterjee1 and Pradeep Narayan2 INTRODUCTION creased RV compliance or RV dysfunction. Isolated right ventricular hypertrophy is extremely rare and reports in the literature are very sparse. We re- DISCUSSION port a case of focal apical right ventricular hypertrophy without involvement of the left ventricular cavity or the RV hypertrophy is usually reported in association inter-ventricular septum. with left ventricular hypertrophy which in turn could be secondary to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), hy- pertensive left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) or other CASE infiltrative conditions.1 However, isolated involvement of right ventricle is extremely rare in these conditions. The A 50 year old male, asymptomatic, normotensive only situation where isolated RV hypertrophy is seen is in patient on routine medical evaluation was found to have presence of idiopathic pulmonary artery hypertension. inverted T-waves on the electrocardiogram (Figure 1). However, the hypertrophy in these cases is rarely focal. He had no history of angina or any other symptoms. Isolated apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is an However, despite complete lack of symptoms, because extremely unusual nonobstructive hypertrophy that is of the abnormality on the electrocardiography (ECG) an localized to the cardiac apex.2 Even in these cases spar- echocardiography was carried out for further evaluation. ing of the left ventricular apex with involvement of only Echocardiography revealed focal hypertrophy of the the right ventricular apex is even more uncommon. The right ventricular (RV) apex almost obliterating the apex most common presenting symptom in patients with api- (Figure 2A) but sparing the inter-ventricular septum. -

Evidence of Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation Due to Atrial Fibrillation Reversal with Arrhythmia Control
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 58, No. 14, 2011 © 2011 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.032 Heart Rhythm Disorders Evidence of Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation Due to Atrial Fibrillation Reversal With Arrhythmia Control Zachary M. Gertz, MD,* Amresh Raina, MD,* Laszlo Saghy, MD,† Erica S. Zado, PA-C,* David J. Callans, MD,* Francis E. Marchlinski, MD,* Martin G. Keane, MD,* Frank E. Silvestry, MD* Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; and Szeged, Hungary Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine whether atrial fibrillation (AF) might cause significant mitral regurgi- tation (MR), and to see whether this MR improves with restoration of sinus rhythm. Background MR can be classified by leaflet pathology (organic/primary and functional/secondary) and by leaflet motion (nor- mal, excessive, restrictive). The existence of secondary, normal leaflet motion MR remains controversial. Methods We performed a retrospective cohort study. Patients undergoing first AF ablation at our institution (n ϭ 828) were screened. Included patients had echocardiograms at the time of ablation and at 1-year clinical follow-up. The MR cohort (n ϭ 53) had at least moderate MR. A reference cohort (n ϭ 53) was randomly selected from those patients (n ϭ 660) with mild or less MR. Baseline echocardiographic and clinical characteristics were compared, and the effect of restoration of sinus rhythm was assessed by follow-up echocardiograms. Results MR patients were older than controls and more often had persistent AF (62% vs. 23%, p Ͻ 0.0001). -

Mitral Valve Prolapse, Arrhythmias, and Sudden Cardiac Death: the Role of Multimodality Imaging to Detect High-Risk Features
diagnostics Review Mitral Valve Prolapse, Arrhythmias, and Sudden Cardiac Death: The Role of Multimodality Imaging to Detect High-Risk Features Anna Giulia Pavon 1,2,*, Pierre Monney 1,2,3 and Juerg Schwitter 1,2,3 1 Cardiac MR Center (CRMC), Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV), 1100 Lausanne, Switzerland; [email protected] (P.M.); [email protected] (J.S.) 2 Cardiovascular Department, Division of Cardiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV), 1100 Lausanne, Switzerland 3 Faculty of Biology and Medicine, University of Lausanne (UniL), 1100 Lausanne, Switzerland * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +41-775-566-983 Abstract: Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) was first described in the 1960s, and it is usually a benign condition. However, a subtype of patients are known to have a higher incidence of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death, the so called “arrhythmic MVP.” In recent years, several studies have been published to identify the most important clinical features to distinguish the benign form from the potentially lethal one in order to personalize patient’s treatment and follow-up. In this review, we specifically focused on red flags for increased arrhythmic risk to whom the cardiologist must be aware of while performing a cardiovascular imaging evaluation in patients with MVP. Keywords: mitral valve prolapse; arrhythmias; cardiovascular magnetic resonance Citation: Pavon, A.G.; Monney, P.; Schwitter, J. Mitral Valve Prolapse, Arrhythmias, and Sudden Cardiac Death: The Role of Multimodality 1. Mitral Valve and Arrhythmias: A Long Story Short Imaging to Detect High-Risk Features. In the recent years, the scientific community has begun to pay increasing attention Diagnostics 2021, 11, 683. -

The Syndrome of Alternating Bradycardia and Tachycardia by D
Br Heart J: first published as 10.1136/hrt.16.2.208 on 1 April 1954. Downloaded from THE SYNDROME OF ALTERNATING BRADYCARDIA AND TACHYCARDIA BY D. S. SHORT From the National Heart Hospita. Received September 15, 1953 Among the large number of patients suffering from syncopal attacks who attended the National Heart Hospital during a four-year period, there were four in whom examination revealed sinus bradycardia alternating with prolonged phases of auricular tachycardia. These patients presented a difficult problem in treatment. Each required at least one admission to hospital and in one case the symptoms were so intractable as to necessitate six admissions in five years. Two patients had mitral valve disease, one of them with left bundle branch block. One had aortic valve sclerosis while the fourth had no evidence of heart disease. THE HEART RATE The sinus rate usually lay between 30 and 50 a minute, a rate as slow as 22 a minute being observed in one patient (Table I). Sinus arrhythmia was noted in all four patients, wandering of TABLE I http://heart.bmj.com/ RATE IN SINus RHYTHM AND IN AURICULAR TACHYCARDIA Rate in Case Age Sex Associated Rate in auricular tachycardia heart disease sinus rhythm Auricular Venliicular 1 65 M Aortic valve sclerosis 28-48 220-250 60-120 2 47 F Mitral valve disease 35-75 180-130 90-180 on September 26, 2021 by guest. Protected copyright. 3 38 F Mitral valve disease 22-43 260 50-65 4 41 F None 35-45 270 110 the pacemaker in three, and periods of sinus standstill in two (Fig. -

Parasystole in a Mahaim Accessory Pathway
223 Case Report Parasystole in a Mahaim Accessory Pathway Chandramohan Ramasamy MD, Senthil Kumar MD, Raja J Selvaraj MD, DNB Department of Cardiology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India Address for Correspondence: Dr. Raja J Selvaraj, Assistant Professor of Cardiology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry - 605006, India. E-Mail: [email protected] Abstract Automaticity has been described in Mahaim pathways, both spontaneously and during radiofrequency ablation. We describe an unusual case of automatic rhythm from a Mahaim pathway presenting as parasystole. The parasystolic beats were also found to initiate tachycardia, resulting in initial presentation with incessant tachycardia and tachycardia induced cardiomyopathy. Key words: Mahaim tachycardia, Parasystole, Automaticity Introduction Mahaim pathways are atriofascicular accessory pathways with decremental, anterograde only conduction. The most common clinical manifestation related to these pathways is antidromic reentrant tachycardia. Less commonly, the pathway may be a bystander with atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia or atrial tachycardia. Rarely, automaticity has been reported from the pathway, manifesting as ectopic beats during sinus rhythm or as an automatic tachycardia [1,2]. Parasystole is a condition where an ectopic focus is unaffected by the underlying rhythm due to entrance block. Parasystole has been reported from atrial musculature, ventricular musculature -

Clinical Manifestation and Survival of Patients with I Diopathic Bilateral
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Manifestation and Survival of Patients with Mizuhiro Arima, TatsujiI diopathicKanoh, Shinya BilateralOkazaki, YoshitakaAtrialIwama,DilatationAkira Yamasaki and Sigeru Matsuda Westudied the histories of eight patients who lacked clear evidence of cardiac abnormalities other than marked bilateral atrial dilatation and atrial fibrillation, which have rarely been dis- cussed in the literature. From the time of their first visit to our hospital, the patients' chest radio- graphs and electrocardiograms showed markedly enlarged cardiac silhouettes and atrial fibrilla- tion, respectively. Each patient's echocardiogram showed a marked bilateral atrial dilatation with almost normal wall motion of both ventricles. In one patient, inflammatory change was demonstrated by cardiac catheterization and endomyocardial biopsy from the right ventricle. Seven of our eight cases were elderly women.Over a long period after the diagnosis of cardiome- galy or arrhythmia, diuretics or digitalis offered good results in the treatment of edema and congestion in these patients. In view of the clinical courses included in the present study, we conclude that this disorder has a good prognosis. (Internal Medicine 38: 112-118, 1999) Key words: cardiomegaly, atrial fibrillation, elder women,good prognosis Introduction echocardiography. The severity of mitral and tricuspid regur- gitation was globally assessed by dividing into three equal parts Idiopathic enlargement of the right atrium was discussed by the distance from the valve orifice. The regurgitant jet was de- Bailey in 1955(1). This disorder may be an unusual congenital tected on color Doppler recording in the four-chamber view malformation. A review of the international literature disclosed and classified into one of the three regions (-: none, +: mild, that although several cases have been discussed since Bailey's ++:moderate, +++: severe). -

Brugada Syndrome Associated to Myocardial Ischemia Sindrome De Brugada Associado a Isquemia Miocárdica
Brugada syndrome associated to Myocardial ischemia Sindrome de Brugada associado a isquemia miocárdica Case of Dr Raimundo Barbosa Barros From Fortaleza - Ceará - Brazil Caro amigo Dr. Andrés Gostaria de ouvir a opinião dos colegas do foro sobre este paciente masculino 56anos internado na emergência do nosso hospital dia 03 de Novembro de 2010. Relata que em abril deste ano foi internado por quadro clínico compatível com angina instável (ECG1). Na ocasião foi submetido à coronariografia que revelou lesão crítica proximal da arteria descendente anterior e lesão de 90% na porção distal da artéria coronária direita. Nesta ocasião realizou angioplastia com colocação de stent apenas na artéria descendente anterior ( ECG2 pós ATC) A artéria coronaria direita não foi abordada. O paciente evoluiu assintomático(ECG3). Em 20/09/2010 realizou cintilografia miocárdica de rotina que resultou normal. No dia 03 de novembro de 2010 procura emergência refirindo ter sofrido episódio de sincope precedido de palpitações rápidas e desconforto torácico atípico.(ECGs 4 e 5). Adicionalmente, informa que 4 horas antes da sua admissão havia apresentado febre (não documentada). Não há relato de episódio prévio semelhante ou história familiar positiva para Morte súbita em familiar jovem de primeiro grau. Dosagem seriada de CK-MB e troponina normais. Qual os diagnósticos ECGs e qual a conduta? Um abraço para todos Raimundo Barbosa Barros Fortaleza Ceará Brasil Dear friend, Dr. Andrés, I would like to know the opinion from the colleagues of the forum about this patient (male, 56 years old), admitted in the ER of our hospital, on November 3rd, 2010. He claims that in April of this year he was admitted with symptoms of unstable angina (ECG1). -

Cardiac Hypertrophy, Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, and Hyperparathyroidism-An Association
Br Heart J: first published as 10.1136/hrt.54.5.539 on 1 November 1985. Downloaded from Br HeartJ 1985; 54: 539-42 Cardiac hypertrophy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and hyperparathyroidism-an association C SYMONS, F FORTUNE, R A GREENBAUM, P DANDONA From the Departments of Cardiology and Human Metabolism, the Royal Free Hospital, London SUMMARY Left ventricular hypertrophy (symmetric, asymmetric, or hypertrophic cardio- myopathy) is an almost invariable accompaniment of primary hyperparathyroidism. Five of 18 patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy had raised serum concentrations of parathyroid hor- mone with normal serum calcium concentrations. Left ventricular hypertrophy did not occur in any of the six patients with hypercalcaemia alone. These relations suggest that parathyroid hormone rather than a rise in the extracellular calcium concentration is associated with a spectrum of left ventricular hypertrophy. All patients with increased circulating parathyroid hormone concentrations should have echo- cardiographic examination of the left ventricle. Conversely, parathyroid hormone concentrations should be measured in all patients with left ventricular hypertrophy from an unknown cause, especially those with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. copyright. Calcium has powerful positive inotropic and chro- included.) Sixteen of these patients were found to notropic effects on cardiac muscle.' Any factor that have primary hyperparathyroidism and six of these promotes transmembrane calcium flux could be had had operations to remove either a parathyroid -

Basic Arrhythmia Review Guide-Advanced
BASIC ARRHYTHMIA REVIEW GUIDE ADVANCED The following study guide provides a review of information covered in the basic arrhythmia competency. Preparation with this guide will help to achieve success on the exam. Sample questions and websites are provided at the end of this guide. DESCRIPTION OF THE HEART The adult heart is a muscular organ weighing less than a pound and about the size of a clenched fist. It lies between the right and Left left lung in an area called the mediastinal cavity behind the sternum of the breast bone. Approximately two-thirds of the heart Atrium lies to the left of the sternum and one-third to the right of the sternum. Right HEART MUSCLES Atrium The heart is composed of three layers each with its own special function. The outermost layer is called the pericardium, essentially a sac around the heart. The middle and thickest layer of the heart is called the Left myocardium. This layer contains all the atrial and ventricular Ventricle muscle fibers needed for contraction as well as the blood supply Right and electrical conduction system. Ventricle The innermost layer of the heart is the endocardium and is composed of endothelium and connective tissue. Any disruption or injury to this endothelium can lead to infection, which in turn can cause valve damage, sepsis, or death. CHAMBERS A normal human heart contains four separate chambers: right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The right and left sides of the heart are divided by a septum. The right atrium (RA) receives oxygen-poor (venous) blood from the body’s organs via the superior and inferior vena cava (SVC and IVC). -

Young Adults. Look for ST Elevation, Tall QRS Voltage, "Fishhook" Deformity at the J Point, and Prominent T Waves
EKG Abnormalities I. Early repolarization abnormality: A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity at the J point, and prominent T waves. ST segment elevation is maximal in leads with tallest R waves. Note high take off of the ST segment in leads V4-6; the ST elevation in V2-3 is generally seen in most normal ECG's; the ST elevation in V2- 6 is concave upwards, another characteristic of this normal variant. Characteristics’ of early repolarization • notching or slurring of the terminal portion of the QRS wave • symmetric concordant T waves of large amplitude • relative temporal stability • most commonly presents in the precordial leads but often associated with it is less pronounced ST segment elevation in the limb leads To differentiate from anterior MI • the initial part of the ST segment is usually flat or convex upward in AMI • reciprocal ST depression may be present in AMI but not in early repolarization • ST segments in early repolarization are usually <2 mm (but have been reported up to 4 mm) To differentiate from pericarditis • the ST changes are more widespread in pericarditis • the T wave is normal in pericarditis • the ratio of the degree of ST elevation (measured using the PR segment as the baseline) to the height of the T wave is greater than 0.25 in V6 in pericarditis. 1 II. Acute Pericarditis: Stage 1 Pericarditis Changes A. Timing 1. Onset: Day 2-3 2. Duration: Up to 2 weeks B. Findings 1.