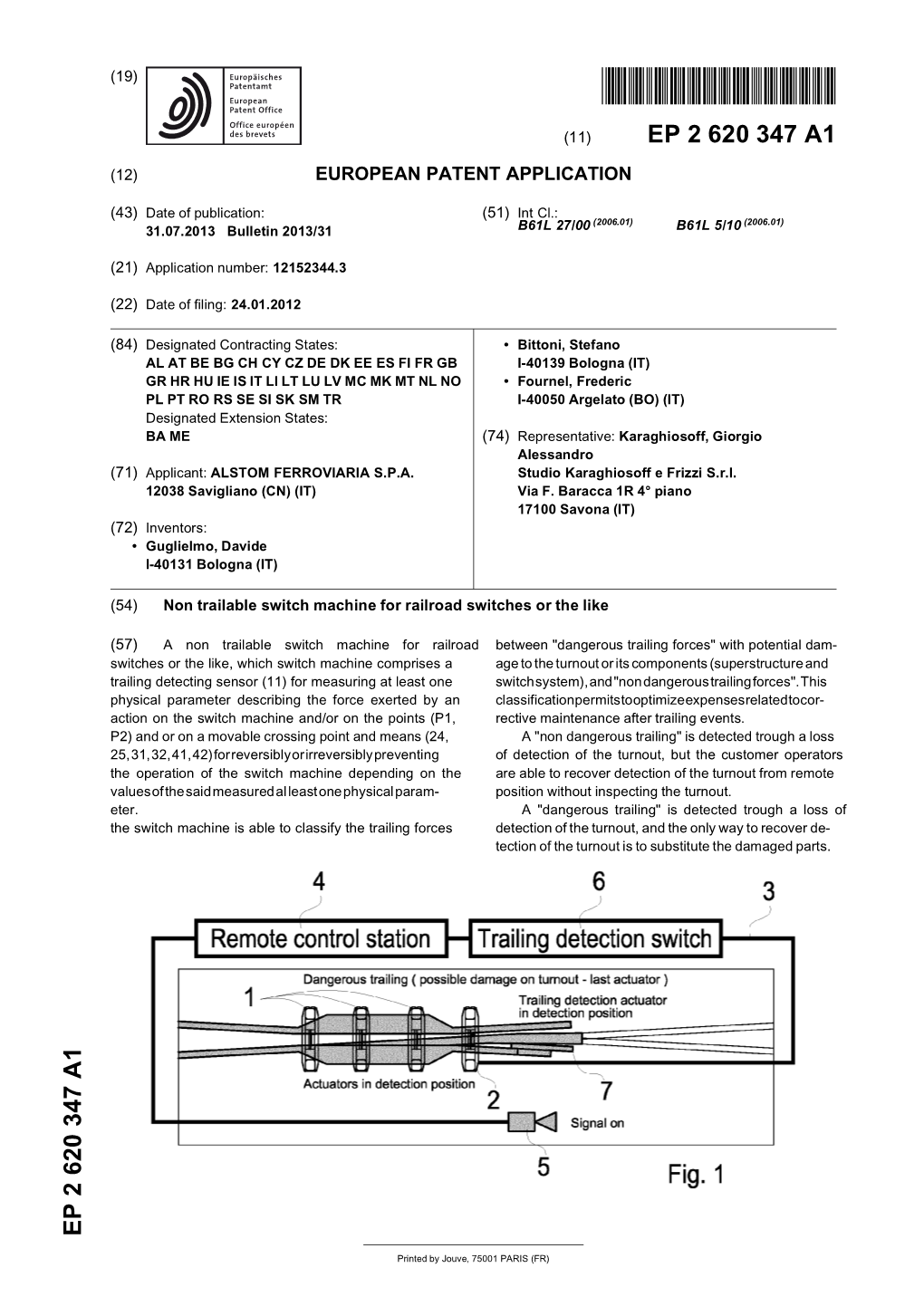
Non Trailable Switch Machine for Railroad Switches Or the Like
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Proactive Maintenance of Railway Switches
Proactive Maintenance of Railway Switches Csaba Hegedűs, Paolo Ciancarini, Attila Frankó, Aleš Kancilija, István Moldován, Gregor Papa, Špela Poklukar, Mario Riccardi, Alberto Sillitti and Pal Varga Abstract—Railway switches operate in harsh environmental conditions; still, their reliability requirements are high due to safety A. State of the Art for Railway Infrastructure Maintenance and economic factors. Once deployed, their maintenance depends Current state-of-the-art maintenance operations within the on the data collected on their status, and the decisions on due railway infrastructure are based on the concept of “preventive” or corrective actions. The more regular this data collection and “on-condition” maintenance. However, they only consist of decision cycle is, the better confidence their operator has on periodical check-ups and substitutions of parts when a failure is effective and proper service. Proactive maintenance, in general, detected. These tasks are carried out at given periodical intervals targets exactly this: rather than scheduling maintenance actions designed to mitigate risk with a considerable safety margin based on operating hours or servicing volume, actions should be involving having to send maintenance staff to the asset site on a taken when it is really needed. This requires the effective regular basis, exposing them to the usual safety risks of a running combination of data collection, analysis, presentation and decision railway [11]. making processes. Moreover, most modern railways have very low level of The MANTIS project proposes a reference architecture for capability installed as part of the signalling system. For switches, proactive maintenance, supported by the concept of cyber-physical this usually only comprises of the detection lines which verify systems. -

(202) 514-2007 Tdd (202) 514-1888
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE AT THURSDAY, OCTOBER 14, 1999 (202) 514-2007 WWW.USDOJ.GOV TDD (202) 514-1888 JUSTICE DEPARTMENT REQUIRES DIVESTITURE IN HARSCO CORPORATION’S ACQUISITION OF RAILROAD MAINTENANCE ASSETS Harsco to Divest Pandrol’s Switch and Crossing, and Transit Grinder Assets WASHINGTON, D.C. -- The Department of Justice today announced that it would require Harsco Corporation to sell machinery and services used in railroad maintenance to resolve competitive concerns over Harsco’s $89 million acquisition certain of assets of Pandrol Jackson Inc. and Pandrol Jackson Limited. The Department said the deal, as originally proposed, would have been anticompetitive, resulting in higher prices and lower quality for these products and services. The Department's antitrust lawsuit and proposed consent decree were filed today in federal court in Washington, D.C. The consent decree, if approved by the Court, would resolve the suit. According to the complaint, the proposed merger would have substantially lessened competition, since Harsco and Pandrol are the only two manufacturers of switch and crossing and transit grinding equipment and the only two providers of railroad switch and crossing grinding services in North America. Switch and crossing grinders and transit grinders are machines designed to restore the tracks of railroads and transit systems to their original shapes and are used to repair deformations caused by the rubbing of train wheels on rails used in railroad track switches, railroad track crossings, and transit systems. “Without this divestiture, railroads and transit systems would have had only one choice for this type of railroad maintenance equipment and services,” said Joel I. -

Station Sign 64” 2 14 Bennet
Boston & Maine Railroad Historical Society Inc. Hardware Collection Tag No. File No: Inventory: Size: Donor: 1 14 West Hollis – Station sign 64” 2 14 Bennett Hall – Station sign 69” Arnold Wilder 3 14 Fitchburg “Wood” Station sign 56” Arnold Wilder 4 14 Woburn “Wood” Station sign 30” Charles Smith 5 14 Danville Junction – Station Sign 96” Anonymous 6 14 West Fitchburg – Station sign 92” Arnold Wilder 7 14 West Hollis – Station sign 72” Arnold Wilder 8 14 Scheghticoke – Station sign 76” Arnold Wilder 9 14 Hubbardston – Station sign 76” Arnold Wilder 10 14 Winchester “Wood” Station sign 68” 11 14 Wedgmere “Wood” Station Sign 56” 12 14 Salem – Station sign 48” 13 14 Whately – Station sign 52”x 11” 14 14 Mt Tom – Station sign 42”x 10 ½” 15 14 Middlesex “Wood” Station sign 54” Carl Byron 16 15 Railway Express Agency - sign 72” 17 15 B&MRR Passenger Waiting Room - sign 32”x 11” 18 15 B&M Outing - sign 23”x 14” 19 15 Yard Limit – sign 16”x 14” 20 15 Notice no Deliveries “Wood” – sign 18”x 24” 21 15 Private Crossing “Plastic” – sign 18”x 6” 22 15 Free Parking “Wood” – sign 24 ½”x 8” 23 15 Railroad Crossing – Sign 36”x 36” 24 15 2 Tracks sign “White /w Black lettering (2 each) 27”x 18” 25 15 Railroad Crossbuck /w reflectors (2 each) 26 14 Lowell Station – sign reproduction Property of the Boston & Maine Railroad Historical Society Boston & Maine Railroad Historical Society Inc. Hardware Collection Tag No. File No: Inventory: Size: Donor: 27 15 Hand Held Stop – sign Donald S. -

Reliability Analysis of Switches and Crossings – a Case Study in Swedish Railway
International Journal of Railway Research, Vol. 4, No. 1, (2017), 1-12 2361 ISSN: International Journal of - Railway Research 5376 ` Reliability Analysis of Switches and Crossings – A Case Study in Swedish Railway Behzad Ghodrati1*, Alireza Ahmadi2, Diego Galar3 1,2,3Luleå University of Technology, Division of Operation and Maintenance Engineering ARTICL EINFO A B S T R A C T Article history: It is reported that switches and crossings (S&C) are one of the Received : subsystems that cause the most delays on Swedish Railways while accounting for at least 13% of maintenance costs. It is the main reason Accepted: for choosing to base this study on this subsystem. Published: Intelligent data processing allows understanding the real reliability characteristics of the assets to be maintained. The first objective of this Keywords: research is to determine the S&C reliability characteristics based on Reliability field data collection. Because field failure data are typically strongly Availability censored, an especial statistics software package is developed to Weibull model process field failure data, as commercial packages have not been found satisfactory in that respect. The resulting software, named RDAT® Switches (Reliability Data Analysis Tool) has been relied upon for this study. It RDAT is especially adapted for statistical failure data analysis. In the next step the availability of studied switches and crossings is estimated based on the reliability characteristics founded in the first step. 1. Instruction be performed near capacity limits, time between asset renewals should be long enough to balance the Railway is a complex system because it comprises maintenance and acquisition cost, and components a mix of components with different age and status should be replaced by deferred or planned that have to work together in a system. -

Magnetorheological Damping for Spring Frogs
High-Speed Rail IDEA Program Magnetorheological Damping for Spring Frogs Final Report for High-Speed Rail IDEA Project 46 Prepared by: Leslie E. Olson Texas Transportation Institute Texas A&M University System College Station, TX July 2007 INNOVATIONS DESERVING EXPLORATORY ANALYSIS (IDEA) PROGRAMS MANAGED BY THE TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD This investigation was performed as part of the High-Speed Rail IDEA program supports innovative methods and technology in support of the Federal Railroad Administration’s (FRA) next-generation high-speed rail technology development program. The High-Speed Rail IDEA program is one of four IDEA programs managed by TRB. The other IDEA programs are listed below. • NCHRP Highway IDEA focuses on advances in the design, construction, safety, and maintenance of highway systems, is part of the National Cooperative Highway Research Program. • Transit IDEA focuses on development and testing of innovative concepts and methods for improving transit practice. The Transit IDEA Program is part of the Transit Cooperative Research Program, a cooperative effort of the Federal Transit Administration (FTA), the Transportation Research Board (TRB) and the Transit Development Corporation, a nonprofit educational and research organization of the American Public Transportation Association. The program is funded by the FTA and is managed by TRB. • Safety IDEA focuses on innovative approaches to improving motor carrier, railroad, and highway safety. The program is supported by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration -

Prairie Line Terminal Section
PRAIRIE LINE TERMINAL SECTION CATALOG OF CHAR ACTER-DEFINING FEATURES This report commissioned by the University of Washington Tacoma (UWT) and performed under subcontract to THA Architects . Cover image Prairie Line linking down to the waterfront. Photograph courtesy of Jim Frederickson. II UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON TACOMA Contributors The authors of this report wish to extend our gratitude to the following entities and individuals who assisted greatly in the preparation, review and editing of this report. The authors of this report extend their deep grati- tude to the volunteers and historians associated with the Northern Pacific Railroad. In particular Jim Freder- ickson, Daniel Cozine and others, provide invaluable insight into the historic operation of the corridor and identifying the various parts of the railway. They shared wonderful images of the corridor that otherwise would have been unavailable. Their collective knowledge and enthusiasm for the subject of railroads is a tremendous regional asset. Members of the University of Washington Architectural Review Commission provided guidance. Personnel from the University of Washington including Milt Tremblay and Lanie Ralph providing overall coor- dination and site access. Reuben McKnight, Tacoma Historic Preservation Officer, Washington State Depart- ment of Archaeology and Historic Preservation, Washington Trust for Historic Preservation, Washington State Historical Society, and the Washington State Library. PRAIRIE LINE | TERMINAL SECTION III IV UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON TACOMA Contents Contributors iii Overview 1 Introduction 3 Methodology 5 1.0Catalog 7 1.1 Historical Significance 9 1.2 Chronology 11 1.3 Character-Defining Spaces 21 1.4 Character-Defining Features 25 2.0Stewardship 37 2.1 Decision Making Matrix 41 2.2 Significance Analysis 45 2.3 Treatment Recommendations 53 2.4 Photo Locations 55 3.0Supplemental 69 3.1 Maps 71 3.2 Historic Photographs 75 PRAIRIE LINE | TERMINAL SECTION V 6 UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON TACOMA Overview Tacoma waterfront to which the Prairie Line connected. -

Txdot Railroad Crossing Design Guidelines
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Railroad Crossing Design Guidelines Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS A. INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................A-1 B. ACTIVE DEVICE CONFIGURATIONS................................................................B-1 C. RAILROAD CROSSINGS ADJACENT TO TRAFFIC SIGNALS.....................C-1 D. RAILROAD CROSSING CLOSURES AND CONSOLIDATIONS....................D-1 TxDOT TOC-1 2016 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Railroad Crossing Design Guidelines Introduction A - INTRODUCTION The following design guidelines are intended to assist project designers with roadway design at railroad crossings and supplement the TxDOT Railroad Crossing Detail Standards Sheets (RCD) which contain standards for device placement distances, gate lengths, and crossing panel sizes. These guidelines are not standards, and are intended as examples for various rail-highway configurations. A diagnostic inspection team will determine the ultimate design for each railroad crossing project. The ultimate design shall be compliant with the Texas Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (TMUTCD) and American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association (AREMA) standards. The guidelines are broken down into 3 main categories: ♦ Design of Active Device Configurations ♦ Design of Railroad Crossings Adjacent to Traffic Signals ♦ Design of Railroad Crossing Closures and Consolidations Guidelines are subject to change. TxDOT A-1 2016 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Railroad Crossing Design Guidelines Active Device Configurations B - ACTIVE DEVICE CONFIGURATIONS LEGEND Cantilever Gate Assembly I-13 (9”x15”) Mast Flasher R15-1 48"X9" ACTIVE DEVICES NOTES R15-2P 1. EMERGENCY NOTIFICATION (I-13), one sign installed 27"X18" with active device on each approach to the crossing. 2. Gate distance above ground when lowered measured from bottom of gate to top of mast foundation. -
417 Part 228—Hours of Service of Railroad
Federal Railroad Administration, DOT § 228.3 Willful Section Violation violation (a) Failure to institute a training program as required ............................................................ 5,000 7,500 (b) Failure to provide training within required time frame ...................................................... 2,500 5,000 (c) Failure of program and/or training materials to include required information ................... 2,500 5,000 227.121 Recordkeeping: (a) General Requirements: (1) Failure to make record available as required ..................................................... 2,500 5,000 (3) Failure to transfer or retain records as required ................................................ 2,000 4,000 (b)–(f) Records: (1) Failure to maintain record or failure to maintain record with required informa- tion ........................................................................................................................ 2,000 4,000 (2) Failure to retain records for required time period ............................................... 2,000 4,000 1 A penalty may be assessed against an individual only for a willful violation. The Administrator reserves the right to assess a penalty of up to $100,000 for any violation where circumstances warrant. See 49 CFR part 209, appendix A. [71 FR 63123, Oct. 27, 2006, as amended at 73 FR 79703, Dec. 30, 2008] PART 228—HOURS OF SERVICE OF AUTHORITY: 49 U.S.C. 20103, 20107, 21101– 21109; Sec. 108, Div. A, Public Law 110–432, 122 RAILROAD EMPLOYEES Stat. 4860–4866; 49 U.S.C. 21301, 21303, 21304, 21311; 28 U.S.C. 2461, note; 49 CFR 1.49; and 49 Subpart A—General U.S.C. 103. Sec. SOURCE: 37 FR 12234, June 21, 1972, unless 228.1 Scope. otherwise noted. 228.3 Application. 228.5 Definitions. Subpart A—General Subpart B—Records and Reporting § 228.1 Scope. -

Rail Tie Plates Spikes & Related Equipment
Boston & Maine Railroad Historical Society Incorporated File 10 Rails, Ties, Spikes & Related Equipment Hardware Collection Maintenance of Way Foreman Job • Repair or adjust track switches, using wrenches and replacement parts. • Cut rails to specified lengths, using rail saws. • Operate track-wrench machines to tighten or loosen bolts at joints that hold ends of rail together. • Lubricate machines, change oil, or fill hydraulic reservoirs to specified levels. • Clean or make minor repairs to machines or equipment. • Drill holes through rails, tie plates, or fishplates for insertion of bolts or spikes, using power drills. • Raise rails, using hydraulic jacks, to allow for the removal and replacement. • Clean tracks or clear ice or snow from tracks or switch boxes. • Operate single – or multiple-head spike pullers to pull old spikes from ties. • Engage mechanisms that lay tracks or rails to specified gauges. • Grind ends of new or worn rails to attain smooth points, using portable grinders. • Patrol assigned track sections so that damaged or broken track can be located and reported. • Operating single or multiple-head spike driving machines to drive spikes into ties and secure rails. • Dress and reshape worn ordamaged railroad switch points or frogs, using portable power grinders. Maintenance of Way Foreman Job continues: • Ajust controls of machines that spread, shape, raise, level, or align track, according to specifications. • Observe leveling indicator arms to verify levelness and alignment of tracks. • Drive graders, tamping machines, brooms, or ballast spreading machines to redistribute gravel or ballast between rails. • Drive vehicles that automatically move and lay tracks or rails over sections of track to be constructed, repaired, or maintained. -

US272839.Pdf
(No Model.) 5 Sheets-Sheet 2. J, K, KNIGHT & W. H. BAKER, ELECTRIC INTERLOCKING RAILWAY SIGNAL AND SWITCH SYSTEM, No. 272,839. Patented Feb. 20, 1883, NVENT ORS: J.K.KNIGHT N. Peters. Photo-Lithographer, washing ct, D. C. (No Model.) 5. Sheets-Sheet 3. J. K. KNIGHT & W. H. BAKER, ELECTRIC INTERLOCKING RAILWAY SIGNAL AND SWITCH SYSTEM, No. 272,839, Patented Feb. 20, 1883, ???YATTEST, ??????? S kyyyuSSSSSSNVENTORS: (No Model.) 5 Sheets-Sheet, 4. J. K. KNIGHT & W. H. BAKER, ELECTRIC INTERLOCKING RAILWAY SIGNAL AND SWITCH SYSTEM No. 272,839, Patented Feb. 20, 1883. ? ????J LS hS S S S LL SIE LL LS RIIELL SL LLS S S LAF SLL LLS --------- s: ENETI I I ITT ?{ --- ? - - - - - - ??- 5- -? Ti—? ? ? ? ? ?– ? . ?? ?---------------- = =t| ??????? A AS ASAAAS S S S qSqqSq SSqSS S S A qqq SS SS qSLYSYL L L LS GSLLLYLL SAAA AZu SLA AuL SSSY SLLL L S - ???ü E III-916 SS SS---S_IN_II_NHLL_LL SS SS SS SS SSSS ...O.O. TSHijn:TT-BRITIEsfelt NIIT - FT T?R? ?TT?. - ????I N. ?}?? DP----- N - - - ) ^y T - 1 #4%:25-2, , 4. PETERS, Photo-Lithographer, Washington, D. C. (No Model.) 5 Sheets-Sheet 5. J. K. KNIGHT & W. H. BAKER, ELECTRIC INTERLOCKING RAILWAY SIGNAL AND SWITCH SYSTEM No. 272,839. Patented eb, 20, 1883. Imf ?ì ??? AZT NVENT FS KNIGHWHÉŠAKE (17 ?r() ?? UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE. JOHN K. KNIGHT, OF NEW YORK, AND WILLIAM. H. BAKER, OF BROOKLYN, . N. Y.; SAID KNIGHT ASSIGNOR TO SAID BAKER. ELECTRIC INTERLOCKNG RALWAY SIGNAL AND SWITCH SYSTEM, SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 272,839, dated February 20, 1888. -

On the Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Railway Switch and Crossing Systems: an Overview
applied sciences Review On the Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Railway Switch and Crossing Systems: An Overview Moussa Hamadache * , Saikat Dutta, Osama Olaby , Ramakrishnan Ambur , Edward Stewart and Roger Dixon School of Engineering, Birmingham Centre for Railway Research and Education (BCRRE), University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham B15 2TT, UK; [email protected] (S.D.); [email protected] (O.O.); [email protected] (R.A.); [email protected] (E.S.); [email protected] (R.D.) * Correspondence: [email protected] Received: 24 October 2019; Accepted: 22 November 2019; Published: 27 November 2019 Abstract: Railway switch and crossing (S&C) systems have a very complex structure that requires not only a large number of components (such as rails, check rails, switches, crossings, turnout bearers, slide chair, etc.) but also different types of components and technologies (mechanical devices to operate switches, electrical and/or electronic devices for control, etc.). This complexity of railway S&C systems makes them vulnerable to failures and malfunctions that can ultimately cause delays and even fatal accidents. Thus, it is crucial to develop suitable condition monitoring techniques to deal with fault detection and diagnosis (FDD) in railway S&C systems. The main contribution of this paper is to present a comprehensive review of the existing FDD techniques for railway S&C systems. The aim is to overview the state of the art in rail S&C and in doing so to provide a platform for researchers, railway operators, and experts to research, develop and adopt the best methods for their applications; thereby helping ensure the rapid evolution of monitoring and fault detection in the railway industry at a time of the increased interest in condition based maintenance and the use of high-speed trains on the rail network. -

Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a Railroad Switch Machine
machines Article Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a Railroad Switch Machine Dario Croccolo, Massimiliano De Agostinis, Stefano Fini * ID , Giorgio Olmi and Francesco Robusto ID Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Bologna, Viale del Risorgimento 2, 40136 Bologna, Italy; [email protected] (D.C.); [email protected] (M.D.A.); [email protected] (G.O.); [email protected] (F.R.) * Correspondence: stefano.fi[email protected]; Tel.: +39-051-2093455 Received: 15 January 2018; Accepted: 12 February 2018; Published: 17 February 2018 Abstract: This contribution deals with the numerical and experimental characterization of the structural behavior of a railroad switch machine. Railroad switch machines must meet a number of safety-related conditions such as, for instance, exhibiting the appropriate resistance against any undesired movements of the points due to the extreme forces exerted by a passing train. This occurrence can produce very high stress on the components, which has to be predicted by designers. In order to assist them in the development of new machines and in defining what the critical components are, FEA models have been built and stresses have been calculated on the internal components of the switch machine. The results have been validated by means of an ad-hoc designed experimental apparatus, now installed at the facilities of the Department of Industrial Engineering of the University of Bologna. This apparatus is particularly novel and original, as no Standards are available that provide recommendations for its design, and no previous studies have dealt with the development of similar rigs. Moreover, it has wide potential applications for lab tests aimed at assessing the safety of railroad switch machines and the fulfilment of the specifications by many railway companies.