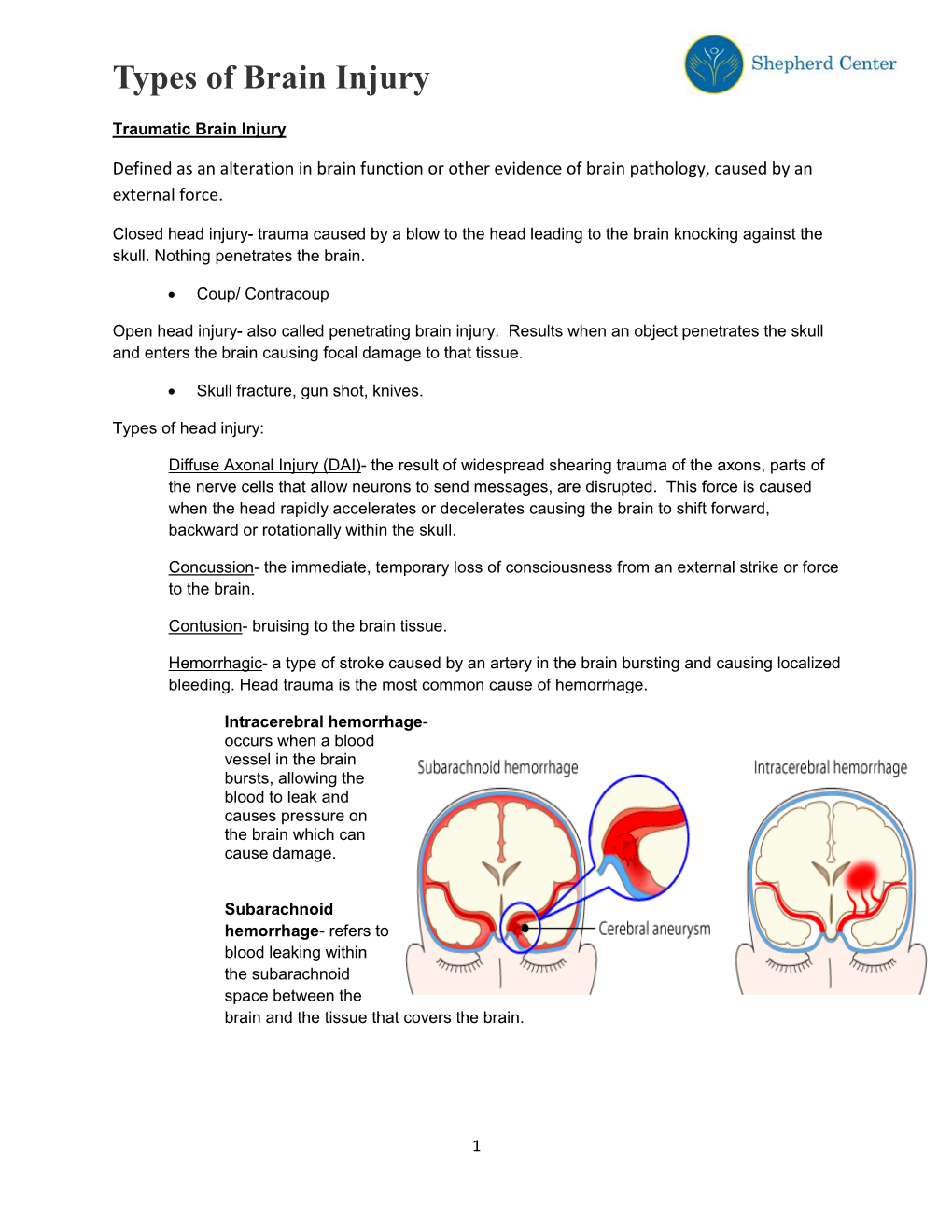
Types of Brain Injury
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Spinal Cord Injury and Traumatic Brain Injury Research Grant Program Report 2020
This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp Spinal Cord Injury and Traumatic Brain Injury Research Grant Program Report January 15, 2020 Author About the Minnesota Office of Higher Education Alaina DeSalvo The Minnesota Office of Higher Education is a Competitive Grants Administrator cabinet-level state agency providing students with Tel: 651-259-3988 financial aid programs and information to help [email protected] them gain access to postsecondary education. The agency also serves as the state’s clearinghouse for data, research and analysis on postsecondary enrollment, financial aid, finance and trends. The Minnesota State Grant Program is the largest financial aid program administered by the Office of Higher Education, awarding up to $207 million in need-based grants to Minnesota residents attending eligible colleges, universities and career schools in Minnesota. The agency oversees other state scholarship programs, tuition reciprocity programs, a student loan program, Minnesota’s 529 College Savings Plan, licensing and early college awareness programs for youth. Minnesota Office of Higher Education 1450 Energy Park Drive, Suite 350 Saint Paul, MN 55108-5227 Tel: 651.642.0567 or 800.657.3866 TTY Relay: 800.627.3529 Fax: 651.642.0675 Email: [email protected] Table of Contents Introduction 1 Spinal Cord Injury and Traumatic Brain Injury Advisory Council 1 FY 2020 Proposal Solicitation Schedule -

Why Do Bridging Veins Rupture Into the Virtual Subdural Space?
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as 10.1136/jnnp.47.2.121 on 1 February 1984. Downloaded from Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:121-127 Why do bridging veins rupture into the virtual subdural space? T YAMASHIMA, RL FRIEDE From the Department ofNeuropathology, University of Gottingen, Gottingen, Federal Republic of Germany SUMMARY Electron microscopic data on human bridging veins show thin walls of variable thick- ness, circumferential arrangement of collagen fibres and a lack of outer reinforcement by arach- noid trabecules, all contributory to the subdural portion of the vein being more fragile than its subarachnoid portion. These features explain the laceration of veins and the subdural location of resultant haematomas. Most subdural haematomas due to venous bleeding walls are delicate, lacking muscle fibres, with only a have been attributed to lacerations in bridging veins. thin fibrous wall and a thin elastic lamina adjacent to These veins form short trunks passing directly from the endothelial layer. The conclusions of these two the brain to the dura mater, almost at right angles to authors, have gained wide acceptance, although guest. Protected by copyright. both. Between these two points, bridging veins take there was little evidence concerning the fragility of a straight course with no tortuosity to allow for the the vein walls. possible displacement of brain.' Trotter2 speculated The purpose of the present communication is to that subdural haematomas are invariably due to provide electron microscopic data on tissue fixed in trauma tearing large veins, an interpretation situ, which might throw some light on to the lacera- elaborated by Krauland.3 According to Leary,4 the tion mechanism of bridging veins and its relationship common sources of subdural haematomas are rup- to the development of subdural haematoma. -

Management of the Head Injury Patient
Management of the Head Injury Patient William Schecter, MD Epidemilogy • 1.6 million head injury patients in the U.S. annually • 250,000 head injury hospital admissions annually • 60,000 deaths • 70-90,000 permanent disability • Estimated cost: $100 billion per year Causes of Brain Injury • Motor Vehicle Accidents • Falls • Anoxic Encephalopathy • Penetrating Trauma • Air Embolus after blast injury • Ischemia • Intracerebral hemorrhage from Htn/aneurysm • Infection • tumor Brain Injury • Primary Brain Injury • Secondary Brain Injury Primary Brain Injury • Focal Brain Injury – Skull Fracture – Epidural Hematoma – Subdural Hematoma – Subarachnoid Hemorrhage – Intracerebral Hematorma – Cerebral Contusion • Diffuse Axonal Injury Fracture at the Base of the Skull Battle’s Sign • Periorbital Hematoma • Battle’s Sign • CSF Rhinorhea • CSF Otorrhea • Hemotympanum • Possible cranial nerve palsy http://health.allrefer.com/pictures-images/ Fracture of maxillary sinus causing CSF Rhinorrhea battles-sign-behind-the-ear.html Skull Fractures Non-depressed vs Depressed Open vs Closed Linear vs Egg Shell Linear and Depressed Normal Depressed http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic2894.htm Temporal Bone Fracture http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/anatomy/ http://www.bartleby.com/107/illus510.html AnatomicVariants/Cardiovascular/Images0300/0386.html Epidural Hematoma http://www.chestjournal.org/cgi/content/full/122/2/699 http://www.bartleby.com/107/illus769.html Epidural Hematoma • Uncommon (<1% of all head injuries, 10% of post traumatic coma patients) • Located -

Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage Due to Autonomic Dysreflexia in a Young Man with Cervical Cord Injury
J UOEH(産業医科大学雑誌)35( 2 ): 159-164(2013) 159 [Case Report] Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage Due to Autonomic Dysreflexia in a Young Man with Cervical Cord Injury Tadashi Sumiya Department of Spinal Care Center, Division of Rehabilitation Medicine 219 Myoji, Katsuragi-cho, Ito-gun, 649-7113, Japan Abstract : The author reports the case of a 36 year old man with cervical cord injury in whom autonomic dysreflexia developed into intracerebral hemorrhage during inpatient rehabilitation. This patient showed complete quadriplegia (motor below C6 and sensory below C7) due to fracture of the 6th cervical vertebra. An indwelling urethral catheter had been inserted into the bladder for 3 months, diminishing bladder expansiveness. Bladder capacity decreased to 200 ml and the patient frequently experienced headaches whenever his bladder was full. To obtain smoother urine flow, a supra-pubic cystostomy was performed. The headaches were temporarily cured, but soon relapsed with extreme increases in blood pressure, representing typical symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia. However, no poten- tial triggers were identified or removed, and lack of blood pressure management led to left putaminal hemorrhage. Despite operative treatment, the right upper extremity showed progressive increases in muscle tonus and finally formed a frozen shoulder with elbow flexion contracture. Two factors contributed to this serious complication: first, autonomic dysreflexia triggered by minor malfunction and/or irritation from the cystostomy catheter; and second, the medical staff lacked sufficient experience in and knowledge about the management of autonomic dysreflexia. It is of the utmost importance for medical staff engaging in rehabilitation of spinal patients to share information regard- ing triggers of autonomic dysreflexia and to be thorough in ensuring proper medical management. -

Traumatic Brain Injury
REPORT TO CONGRESS Traumatic Brain Injury In the United States: Epidemiology and Rehabilitation Submitted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention The Report to Congress on Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Epidemiology and Rehabilitation is a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Debra Houry, MD, MPH Director, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Grant Baldwin, PhD, MPH Director, Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention The inclusion of individuals, programs, or organizations in this report does not constitute endorsement by the Federal government of the United States or the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). Suggested Citation: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Report to Congress on Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Epidemiology and Rehabilitation. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control; Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention. Atlanta, GA. Executive Summary . 1 Introduction. 2 Classification . 2 Public Health Impact . 2 TBI Health Effects . 3 Effectiveness of TBI Outcome Measures . 3 Contents Factors Influencing Outcomes . 4 Effectiveness of TBI Rehabilitation . 4 Cognitive Rehabilitation . 5 Physical Rehabilitation . 5 Recommendations . 6 Conclusion . 9 Background . 11 Introduction . 12 Purpose . 12 Method . 13 Section I: Epidemiology and Consequences of TBI in the United States . 15 Definition of TBI . 15 Characteristics of TBI . 16 Injury Severity Classification of TBI . 17 Health and Other Effects of TBI . -

Intracerebral Hemorrhage ICH Fact Sheet
FACT SHEET FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) What is it? An intracerebral [in-truh-suh-REE-bruh l] hemorrhage [HEM-rij], Dura mater or ICH, is bleeding inside or around the brain, which Brain Skull can put pressure on the brain. An ICH robs the brain Intracerebral of oxygen, so it must be identified and managed right hemorrhage away. Other names for ICH are cerebral hemorrhage or intracranial [in-truh-KREY-nee-uh l] hemorrhage. ICH can happen because of trauma or as a result of no known cause (spontaneous ICH), which is a type of stroke called a hemorrhagic [hem-oh-RAJ-ik] stroke. In the U.S. each year, about 1 in 10 people who have strokes do so because of an ICH. Stroke is the leading cause of disability and the 5th-leading cause of death in the U.S. What are the symptoms of spontaneous ICH? Spontaneous ICH symptoms usually develop suddenly, without warning. Key symptoms can include a SUDDEN (see BE FAST on page 2): What causes it? • Loss of balance or coordination An ICH is often caused by a blood vessel leaking or • Change in vision breaking. This can be the result of: • Weakness of the face, arm, or leg • High blood pressure that has damaged a blood vessel • Difficulty speaking • Smoking, overuse of alcohol, or use of illegal drugs Other ICH symptoms can include: such as cocaine or methamphetamine • Severe headache with no known cause (patients • Diabetes often describe it as “the worst headache of my life”) • Abnormal blood vessel proteins in the elderly • Seizures An ICH can also be caused by: • Vomiting or severe nausea, when combined with • Anticoagulant therapy (treatment with blood thinners) other symptoms from this list • Problems with vein structure • Partial or total loss of conciousness • A brain tumor that bleeds • Head injuries caused by a fall or accident 1 How is it diagnosed? What can I expect afterward? Your doctor will explain what tests will be used to Your long-term outlook depends on the location and diagnose ICH, depending on your condition. -

Early Management of Retained Hemothorax in Blunt Head and Chest Trauma
World J Surg https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4420-x ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Early Management of Retained Hemothorax in Blunt Head and Chest Trauma 1,2 1,8 1,7 1 Fong-Dee Huang • Wen-Bin Yeh • Sheng-Shih Chen • Yuan-Yuarn Liu • 1 1,3,6 4,5 I-Yin Lu • Yi-Pin Chou • Tzu-Chin Wu Ó The Author(s) 2018. This article is an open access publication Abstract Background Major blunt chest injury usually leads to the development of retained hemothorax and pneumothorax, and needs further intervention. However, since blunt chest injury may be combined with blunt head injury that typically requires patient observation for 3–4 days, other critical surgical interventions may be delayed. The purpose of this study is to analyze the outcomes of head injury patients who received early, versus delayed thoracic surgeries. Materials and methods From May 2005 to February 2012, 61 patients with major blunt injuries to the chest and head were prospectively enrolled. These patients had an intracranial hemorrhage without indications of craniotomy. All the patients received video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) due to retained hemothorax or pneumothorax. Patients were divided into two groups according to the time from trauma to operation, this being within 4 days for Group 1 and more than 4 days for Group 2. The clinical outcomes included hospital length of stay (LOS), intensive care unit (ICU) LOS, infection rates, and the time period of ventilator use and chest tube intubation. Result All demographics, including age, gender, and trauma severity between the two groups showed no statistical differences. -

A Review of Traumatic Axonal Injury
Acta Medica 2021; 52(2): 102-108 acta medica REVIEW A Review of Traumatic Axonal Injury Dicle Karakaya1, [MD] ABSTRACT ORCID: 0000-0003-1939-6802 Traumatic brain injury is a major cause of mortality and neurological Ahmet İlkay Işıkay2, [MD] disability worldwide and varies according to its cause, pathogenesis, ORCID: 0000-0001-7790-4735 severity and clinical outcome. This review summarizes a significant aspect of diffuse brain injuries – traumatic axonal injury – important cause of severe disability and vegetative state. Traumatic axonal injury is a type of traumatic brain injury caused by blunt head trauma. It is defined both clinically (immediate and prolonged unconsciousness, characteristically in the absence of space-occupying lesions) and pathologically (widespread and diffuse damage of axons). Following traumatic brain injury, progressive axonal degeneration starts with 1Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine, Department disruption of axonal transport, axonal swelling, secondary axonal of Neurosurgery, Ankara, Turkey disconnection and Wallerian degeneration, respectively. However, traumatic axonal injury is difficult to define clinically, it should be Corresponding Author: Ahmet İlkay Işıkay considered in patients with Glasgow coma score < 8 for more than six Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine, Department hours after trauma and diffuse tensor imaging and sensitivity-weighted of Neurosurgery, Sıhhiye/Ankara, Turkey imaging MRI sequences are highly sensitive in its diagnosis. Glasgow Phone: +90 312 305 17 15 coma score at the time of presentation, location and severity of axonal E-mail: [email protected] damage are prognostic factors for clinical outcome. https://doi.org/10.32552/2021.ActaMedica.467 Keywords: Diffuse, traumatic, axonal, injury. Received: 29 May 2020, Accepted: 9 March 2021, Published online: 8 June 2021 INTRODUCTION Traumatic axonal injury (TAI) is a distinct it is not diffuse but actually widespread and/or clinicopathological topic that can cause severe multifocal [3]. -

The Development of the Epidural Space in Human Embryos
Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 273–279 Copyright © 2004 Via Medica O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E ISSN 0015–5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The development of the epidural space in human embryos Magdalena Patelska-Banaszewska, Witold Woźniak Department of Anatomy, University School of Medical Sciences, Poznań, Poland [Received 25 April 2004; Accepted 25 June 2004] The epidural space is seen in embryos at stage 17 (41 days) on the periphery of the primary meninx. During stage 18 (44 days) the dura mater proper appears and the epidural space is located between this meninx and the perichondrium and contains blood vessels. During the last week of the embryonic period (stages 20–23) the epidural space is evident around the circumference of the spinal cord. On the posterior surface it is found between the dura mater and the me- soderm of the dorsal body wall. Key words: human neuroembryology, primary meninx, epidural space INTRODUCTION horizontal, frontal, and sagittal planes and stained The epidural space lies between the spinal dura according to various methods (chiefly Mallory, hae- mater and the periosteum of the vertebral canal. This matoxylin and eosin and with silver salts). In some periosteum is formed by the outer endosteal layer embryos graphic reconstructions were prepared at of the dura mater. The epidural space contains loose each of the stages investigated. connective tissue, venous plexuses and adipose tis- sue, which is particularly evident in the lumbar re- RESULTS gion [8]. There is some evidence that it is only a po- The primordium of the epidural space appears in tential space [2]. -

CHAPTER 8 Face, Scalp, Skull, Cranial Cavity, and Orbit
228 CHAPTER 8 Face, Scalp, Skull, Cranial Cavity, and Orbit MUSCLES OF FACIAL EXPRESSION Dural Venous Sinuses Not in the Subendocranial Occipitofrontalis Space More About the Epicranial Aponeurosis and the Cerebral Veins Subcutaneous Layer of the Scalp Emissary Veins Orbicularis Oculi CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF EMISSARY VEINS Zygomaticus Major CAVERNOUS SINUS THROMBOSIS Orbicularis Oris Cranial Arachnoid and Pia Mentalis Vertebral Artery Within the Cranial Cavity Buccinator Internal Carotid Artery Within the Cranial Cavity Platysma Circle of Willis The Absence of Veins Accompanying the PAROTID GLAND Intracranial Parts of the Vertebral and Internal Carotid Arteries FACIAL ARTERY THE INTRACRANIAL PORTION OF THE TRANSVERSE FACIAL ARTERY TRIGEMINAL NERVE ( C.N. V) AND FACIAL VEIN MECKEL’S CAVE (CAVUM TRIGEMINALE) FACIAL NERVE ORBITAL CAVITY AND EYE EYELIDS Bony Orbit Conjunctival Sac Extraocular Fat and Fascia Eyelashes Anulus Tendineus and Compartmentalization of The Fibrous "Skeleton" of an Eyelid -- Composed the Superior Orbital Fissure of a Tarsus and an Orbital Septum Periorbita THE SKULL Muscles of the Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Development of the Neurocranium Abducens Somitomeres Cartilaginous Portion of the Neurocranium--the The Lateral, Superior, Inferior, and Medial Recti Cranial Base of the Eye Membranous Portion of the Neurocranium--Sides Superior Oblique and Top of the Braincase Levator Palpebrae Superioris SUTURAL FUSION, BOTH NORMAL AND OTHERWISE Inferior Oblique Development of the Face Actions and Functions of Extraocular Muscles Growth of Two Special Skull Structures--the Levator Palpebrae Superioris Mastoid Process and the Tympanic Bone Movements of the Eyeball Functions of the Recti and Obliques TEETH Ophthalmic Artery Ophthalmic Veins CRANIAL CAVITY Oculomotor Nerve – C.N. III Posterior Cranial Fossa CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS Middle Cranial Fossa Trochlear Nerve – C.N. -

NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Neuropathol Exp Neurol
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 September 24. NIH-PA Author ManuscriptPublished NIH-PA Author Manuscript in final edited NIH-PA Author Manuscript form as: J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 July ; 68(7): 709±735. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181a9d503. Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in Athletes: Progressive Tauopathy following Repetitive Head Injury Ann C. McKee, MD1,2,3,4, Robert C. Cantu, MD3,5,6,7, Christopher J. Nowinski, AB3,5, E. Tessa Hedley-Whyte, MD8, Brandon E. Gavett, PhD1, Andrew E. Budson, MD1,4, Veronica E. Santini, MD1, Hyo-Soon Lee, MD1, Caroline A. Kubilus1,3, and Robert A. Stern, PhD1,3 1 Department of Neurology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 2 Department of Pathology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 3 Center for the Study of Traumatic Encephalopathy, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 4 Geriatric Research Education Clinical Center, Bedford Veterans Administration Medical Center, Bedford, Massachusetts 5 Sports Legacy Institute, Waltham, MA 6 Department of Neurosurgery, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 7 Department of Neurosurgery, Emerson Hospital, Concord, MA 8 CS Kubik Laboratory for Neuropathology, Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts Abstract Since the 1920s, it has been known that the repetitive brain trauma associated with boxing may produce a progressive neurological deterioration, originally termed “dementia pugilistica” and more recently, chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). We review the 47 cases of neuropathologically verified CTE recorded in the literature and document the detailed findings of CTE in 3 professional athletes: one football player and 2 boxers. -

Why Woodpecker Can Resist the Impact
Why woodpecker can resist the impact A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Zhe Zhang Master of Civil Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia School of Engineering College of Science, Engineering and Health RMIT University November 2019 II Declaration I certify that except where due acknowledgement has been made, the work is that of the author alone; the work has not been submitted previously, in whole or in part, to qualify for any other academic award; the content of the thesis is the result of work which has been carried out since the official commencement date of the approved research program; any editorial work, paid or unpaid, carried out by a third party is acknowledged; and ethics procedures and guidelines have been followed. Zhe Zhang 30 November 2019 III Acknowledgments The research in this thesis could not have been completed without significant support from many individuals and organisations. I would like to take this opportunity to express my deep gratitude to all of them. Firstly, I would like to express my sincere gratitude to my senior supervisor, Dr. Shiwei Zhou, for his wisdom in choosing this fascinating research topic for me and his constant encouragement and guidance. After the guidance of my Master graduation project, Dr. Zhou accepted me as one of the Ph.D. students and offered financial support for my first-year study at RMIT University. He has always been patient in providing guidance and offering supportive suggestions to me during my PhD candidature period. It is not an exaggeration to say that he has changed my life and his good characteristics have had a significant and positive impact on me which would be beneficial for the rest of my life.