CHAMELEON Your First
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
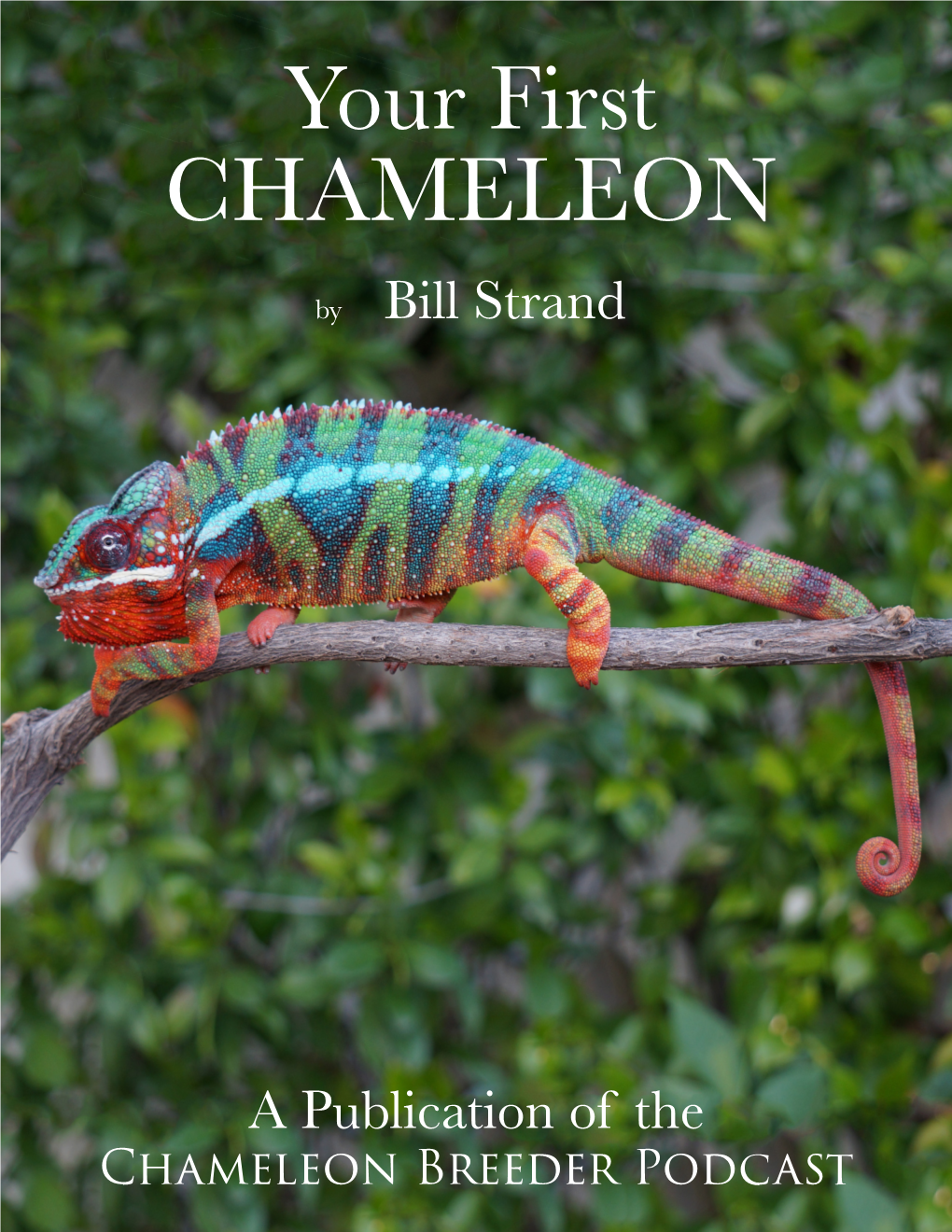
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Veiled Chameleon Care Sheet Because We Care !!!
Veiled Chameleon Care Sheet Because we care !!! 1250 Upper Front Street, Binghamton, NY 13901 607-723-2666 Congratulations on your new pet. The popularity of the veiled chameleon is due to a number of factors: veiled chameleons are relatively hardy, large, beautiful, and prolific. Veiled chameleons are native to Yemen and southern Saudi Arabia, they are quite tolerant of tem- perature and humidity extremes, which contributes to its hardiness as a captive. Veiled chameleons are among the easiest chameleons to care for, but they still require careful attention. They range in size from 6-12 inches and will live up to five years with the proper care. Males tend to be larger and more colorful than females. With their ability to change colors, prehensile tails, independently moving eyes and stuttering walk make them fascinating to watch. They become stressed very easily so regular handling is not recommended. HOUSING A full-screen enclosure is a must for veiled chameleons. Zoomed’s ReptiBreeze is an ideal habitat. Glass aquariums can lead to respiratory diseases due to the stagnant air not being circulated, and they will be stressed if they can see their reflection. These Chameleons also need a large enclosure to climb around in because smaller enclosures will stress them. A 3’x3’x3’ or 2’x2’x4’ habitat is best, but larger is bet- ter. Chameleons should be house separately to avoid fighting. The interior of the enclosure should be furnished with medium sized vines and foliage for the chameleons to hide in. The medium sized vines provide important horizontal perches for the chameleon to rest and bask. -

Addo Elephant National Park Reptiles Species List
Addo Elephant National Park Reptiles Species List Common Name Scientific Name Status Snakes Cape cobra Naja nivea Puffadder Bitis arietans Albany adder Bitis albanica very rare Night adder Causes rhombeatus Bergadder Bitis atropos Horned adder Bitis cornuta Boomslang Dispholidus typus Rinkhals Hemachatus hemachatus Herald/Red-lipped snake Crotaphopeltis hotamboeia Olive house snake Lamprophis inornatus Night snake Lamprophis aurora Brown house snake Lamprophis fuliginosus fuliginosus Speckled house snake Homoroselaps lacteus Wolf snake Lycophidion capense Spotted harlequin snake Philothamnus semivariegatus Speckled bush snake Bitis atropos Green water snake Philothamnus hoplogaster Natal green watersnake Philothamnus natalensis occidentalis Shovel-nosed snake Prosymna sundevalli Mole snake Pseudapsis cana Slugeater Duberria lutrix lutrix Common eggeater Dasypeltis scabra scabra Dappled sandsnake Psammophis notosticus Crossmarked sandsnake Psammophis crucifer Black-bellied watersnake Lycodonomorphus laevissimus Common/Red-bellied watersnake Lycodonomorphus rufulus Tortoises/terrapins Angulate tortoise Chersina angulata Leopard tortoise Geochelone pardalis Green parrot-beaked tortoise Homopus areolatus Marsh/Helmeted terrapin Pelomedusa subrufa Tent tortoise Psammobates tentorius Lizards/geckoes/skinks Rock Monitor Lizard/Leguaan Varanus niloticus niloticus Water Monitor Lizard/Leguaan Varanus exanthematicus albigularis Tasman's Girdled Lizard Cordylus tasmani Cape Girdled Lizard Cordylus cordylus Southern Rock Agama Agama atra Burrowing -

Changes to CITES Species Listings
NOTICE TO THE WILDLIFE IMPORT/EXPORT COMMUNITY December 21, 2016 Subject: Changes to CITES Species Listings Background: Party countries of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) meet approximately every two years for a Conference of the Parties. During these meetings, countries review and vote on amendments to the listings of protected species in CITES Appendix I and Appendix II. Such amendments become effective 90 days after the last day of the meeting unless Party countries agree to delay implementation. The most recent Conference of the Parties (CoP 17) was held in Johannesburg, South Africa, September 24 – October 4, 2016. Action: Except as noted below, the amendments to CITES Appendices I and II that were adopted at CoP 17, will be effective on January 2, 2017. Any specimens of these species imported into, or exported from, the United States on or after January 2, 2017 will require CITES documentation as specified under the amended listings. The import, export, or re-export of shipments of these species that are accompanied by CITES documents reflecting a pre-January 2 listing status or that lack CITES documents because no listing was previously in effect must be completed by midnight (local time at the point of import/export) on January 1, 2017. Importers and exporters can find the official revised CITES appendices on the CITES website. Species Added to Appendix I . Abronia anzuetoi (Alligator lizard) . Abronia campbelli (Alligator lizard) . Abronia fimbriata (Alligator lizard) . Abronia frosti (Alligator lizard) . Abronia meledona (Alligator lizard) . Cnemaspis psychedelica (Psychedelic rock gecko) . Lygodactylus williamsi (Turquoise dwarf gecko) . Telmatobius coleus (Titicaca water frog) . -

1 the Multiscale Hierarchical Structure of Heloderma Suspectum
The multiscale hierarchical structure of Heloderma suspectum osteoderms and their mechanical properties. Francesco Iacoviello a, Alexander C. Kirby b, Yousef Javanmardi c, Emad Moeendarbary c, d, Murad Shabanli c, Elena Tsolaki b, Alana C. Sharp e, Matthew J. Hayes f, Kerda Keevend g, Jian-Hao Li g, Daniel J.L. Brett a, Paul R. Shearing a, Alessandro Olivo b, Inge K. Herrmann g, Susan E. Evans e, Mehran Moazen c, Sergio Bertazzo b,* a Electrochemical Innovation Lab, Department of Chemical Engineering University College London, London WC1E 7JE, UK. b Department of Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK. c Department of Mechanical Engineering University College London, London WC1E 7JE, UK. d Department of Biological Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 02139, USA. e Department of Cell & Developmental Biology University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK. f Department of Ophthalmology University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK. g Department of Materials Meet Life Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) Lerchenfeldstrasse 5, CH-9014, St. Gallen, Switzerland. * Correspondence: Sergio Bertazzo [email protected] Tel: +44 (0) 2076790444 1 Abstract Osteoderms are hard tissues embedded in the dermis of vertebrates and have been suggested to be formed from several different mineralized regions. However, their nano architecture and micro mechanical properties had not been fully characterized. Here, using electron microscopy, µ-CT, atomic force microscopy and finite element simulation, an in-depth characterization of osteoderms from the lizard Heloderma suspectum, is presented. Results show that osteoderms are made of three different mineralized regions: a dense apex, a fibre-enforced region comprising the majority of the osteoderm, and a bone-like region surrounding the vasculature. -

A Revision of the Chameleon Species Chamaeleo Pfeili Schleich
A revision of the chameleon species Chamaeleo pfeili Schleich (Squamata; Chamaeleonidae) with description of a new material of chamaeleonids from the Miocene deposits of southern Germany ANDREJ ÈERÒANSKÝ A revision of Chamaeleo pfeili Schleich is presented. The comparisons of the holotypic incomplete right maxilla with those of new specimens described here from the locality Langenau (MN 4b) and of the Recent species of Chamaeleo, Furcifer and Calumma is carried out. It is shown that the type material of C. pfeili and the material described here lack autapomorphic features. Schleich based his new species on the weak radial striations on the apical parts of bigger teeth. However, this character is seen in many species of extant chameleons, e.g. Calumma globifer, Furcifer pardalis and C. chamaeleon. For this reason, the name C. pfeili is considered a nomen dubium. This paper provides detailed descrip- tions and taxonomy of unpublished material from Petersbuch 2 (MN 4a) and Wannenwaldtobel (MN 5/6) in Germany. The material is only fragmentary and includes jaw bits. The morphology of the Petersbuch 2 material is very similar to that of the chameleons described from the Czech Republic. • Key words: Chamaeleo pfeili, nomen dubium, morphology, Wannenwaldtobel, Petersbuch 2, Langenau, Neogene. ČERŇANSKÝ, A. 2011. A revision of the chameleon species Chamaeleo pfeili Schleich (Squamata; Chamaeleonidae) with description of a new material of chamaeleonids from the Miocene deposits of southern Germany. Bulletin of Geosciences 86(2), 275–282 (6 figures). Czech Geological Survey, Prague. ISSN 1214-1119. Manuscript received Feb- ruary 11, 2011; accepted in revised form March 21, 2011; published online April 20, 2011; issued June 20, 2011. -

Literature Cited in Lizards Natural History Database
Literature Cited in Lizards Natural History database Abdala, C. S., A. S. Quinteros, and R. E. Espinoza. 2008. Two new species of Liolaemus (Iguania: Liolaemidae) from the puna of northwestern Argentina. Herpetologica 64:458-471. Abdala, C. S., D. Baldo, R. A. Juárez, and R. E. Espinoza. 2016. The first parthenogenetic pleurodont Iguanian: a new all-female Liolaemus (Squamata: Liolaemidae) from western Argentina. Copeia 104:487-497. Abdala, C. S., J. C. Acosta, M. R. Cabrera, H. J. Villaviciencio, and J. Marinero. 2009. A new Andean Liolaemus of the L. montanus series (Squamata: Iguania: Liolaemidae) from western Argentina. South American Journal of Herpetology 4:91-102. Abdala, C. S., J. L. Acosta, J. C. Acosta, B. B. Alvarez, F. Arias, L. J. Avila, . S. M. Zalba. 2012. Categorización del estado de conservación de las lagartijas y anfisbenas de la República Argentina. Cuadernos de Herpetologia 26 (Suppl. 1):215-248. Abell, A. J. 1999. Male-female spacing patterns in the lizard, Sceloporus virgatus. Amphibia-Reptilia 20:185-194. Abts, M. L. 1987. Environment and variation in life history traits of the Chuckwalla, Sauromalus obesus. Ecological Monographs 57:215-232. Achaval, F., and A. Olmos. 2003. Anfibios y reptiles del Uruguay. Montevideo, Uruguay: Facultad de Ciencias. Achaval, F., and A. Olmos. 2007. Anfibio y reptiles del Uruguay, 3rd edn. Montevideo, Uruguay: Serie Fauna 1. Ackermann, T. 2006. Schreibers Glatkopfleguan Leiocephalus schreibersii. Munich, Germany: Natur und Tier. Ackley, J. W., P. J. Muelleman, R. E. Carter, R. W. Henderson, and R. Powell. 2009. A rapid assessment of herpetofaunal diversity in variously altered habitats on Dominica. -

A New Species of Chameleon Dragon Chelosania Gray, 1845 from the Northern Territory, Australia
20 Australasian Journal of Herpetology Australasian Journal of Herpetology 39:20-22. Published 12 June 2019. ISSN 1836-5698 (Print) ISSN 1836-5779 (Online) A new species of Chameleon Dragon Chelosania Gray, 1845 from the Northern Territory, Australia. LSID urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9D8A0752-C290-4FB8-BEDE-C60FB5819C65 RAYMOND T. HOSER 488 Park Road, Park Orchards, Victoria, 3134, Australia. Phone: +61 3 9812 3322 Fax: 9812 3355 E-mail: snakeman (at) snakeman.com.au Received 21 December 2018, Accepted 6 January 2019, Published 12 June 2019. ABSTRACT The Chameleon Dragon, genus Chelosania Gray, 1845 has until now been treated as a single species throughout its known range across the dry tropics of Northern Australia. As part of an audit of the taxonomy and nomenclature of Australian agamids, it emerged that those specimens from the eastern sector of the Northern Territory (NT) are significantly different to the type race of Chelosania brunnea Gray, 1845, from Western Australia (WA) and separated by a well defined distribution gap in the western side of the Northern Territory. Other putative species also split across the same biogeographcal barrier, approximating the Daly River, have recently on the basis of morphological and molecular evidence been found to consist of multiple species. These include Odatria glauerti (Mertens, 1957) from WA, and O. hoserae Hoser, 2013 from the NT, or Cannia weigeli Wells and Wellington, 1987 from WA and Cannia burgessi (Hoser, 2001) from the NT). Therefore I have no hesitation at all in formally describing the eastern NT population of Chelosania as a new species, namely Chelosania neilsonnemanni sp. -

Varanus Doreanus) in Australia
BIAWAK Journal of Varanid Biology and Husbandry Volume 11 Number 1 ISSN: 1936-296X On the Cover: Varanus douarrha The individuals depicted on the cover and inset of this issue represent a recently redescribed species of monitor lizard, Varanus douarrha (Lesson, 1830), which origi- nates from New Ireland, in the Bismark Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. Although originally discovered and described by René Lesson in 1830, the holotype was lost on its way to France when the ship it was traveling on became shipwrecked at the Cape of Good Hope. Since then, without a holotype for comparitive studies, it has been assumed that the monitors on New Ireland repre- sented V. indicus or V. finschi. Recent field investiga- tions by Valter Weijola in New Ireland and the Bismark Archipelago and phylogenetic analyses of recently col- lected specimens have reaffirmed Lesson’s original clas- sification of this animal as a distinct species. The V. douarrha depicted here were photographed by Valter Weijola on 17 July and 9 August 2012 near Fis- soa on the northern coast of New Ireland. Both individu- als were found basking in coconut groves close to the beach. Reference: Weijola, V., F. Kraus, V. Vahtera, C. Lindqvist & S.C. Donnellan. 2017. Reinstatement of Varanus douarrha Lesson, 1830 as a valid species with comments on the zoogeography of monitor lizards (Squamata: Varanidae) in the Bismarck Archipelago, Papua New Guinea. Australian Journal of Zoology 64(6): 434–451. BIAWAK Journal of Varanid Biology and Husbandry Editor Editorial Review ROBERT W. MENDYK BERND EIDENMÜLLER Department of Herpetology Frankfurt, DE Smithsonian National Zoological Park [email protected] 3001 Connecticut Avenue NW Washington, DC 20008, US RUSTON W. -

Extending the Known Distribution of Nicosia's Chameleon
Herpetology Notes, volume 14: 455-460 (2021) (published online on 26 February 2021) Extending the known distribution of Nicosia’s chameleon, Furcifer nicosiai Jesu, Mattioli & Schimmenti, 1999 (Squamata: Chamaeleonidae) Francesco Belluardo1,*, Gonçalo M. Rosa2,3, Franco Andreone4, Elodie A. Courtois5, Javier Lobón-Rovira1, Ronald A. Nussbaum6, Miary Raselimanana7, Malalatiana Rasoazanany7, Christopher J. Raxworthy8, and Angelica Crottini1 The genus Furcifer Fitzinger, 1843 includes 24 region (Fig. 1, white circles; Table 1) (Randrianantoandro species of chameleons, most of which are endemic to et al., 2008; Raselimanana, 2008; Bora et al., 2010; Madagascar (Glaw and Vences, 2007; Uetz et al., 2020). Randriamoria, 2011; Brown et al., 2014; Goodman et Furcifer nicosiai Jesu, Mattioli & Schimmenti, 1999 al., 2018). Furcifer nicosiai habitat encompasses dense is a medium-sized species belonging to the Furcifer sub-humid and dry forests of low elevation, between verrucosus (Cuvier, 1829) phenetic group (Glaw and 57–571 m above sea level ~ a.s.l. (Bora et al., 2010). Vences, 2007). Although slightly smaller, F. nicosiai is Several records within the Menabe region (within the morphologically similar to Furcifer oustaleti (Mocquard, Paysage Harmonieux Protégé de Menabe Antimena, 1894), whose subadults can be mistaken with adults of about 60 km south of Tsingy de Bemaraha) refer to this species (Glaw and Vences, 2007). a population of F. nicosiai that appears to have some With Tsingy de Bemaraha as the type locality of F. morphological differences to the population from the nicosiai (Jesu et al., 1999), the species was thought to type locality. A molecular characterisation is needed have a distribution limited to western Madagascar, with, to assess the taxonomic identity of these populations, until now, only a few additional records in the Melaky but for consistency we here continue to assign them to this species (Raselimanana, 2008; Randrianantoandro et al., 2010; Eckhardt et al., 2019) (Fig. -

Panther Chameleon Furcifer Pardalis Adult Size: Males up to 20 Inches
Care and information sheet Panther Chameleon Furcifer pardalis Adult Size: Males up to 20 inches. Females much smaller, almost half the size of males. Life Span: Up to ten years in captivity, with an average lifespan of five. Breeding females tend only to live a couple of years. Male/Female Differences: Males are almost twice the size of females and are much more brightly coloured Compatibility: Panther Chameleons are solitary creatures and should be kept as such. Females may be introduced to a male's cage during breeding season, but should be removed as soon as possible. Origin: Panther Chameleons are exclusively found on the island of Madagascar Climate: Warm temperate, high humidity but not excessively hot. Day Cycle: Diurnal (awake during the day) Temperature: A gradient of heat from 75 – 85°F should be provided during the day with a basking point. Temp should drop 10 – 15° at night, but not below 65. Lighting: Chameleons need a source of UVB light to properly metabolize calcium. This should be provided in the form of a reptile fluorescent or mercury vapor bulb in a normal day cycle (10 – 12 hours/day). Humidity: High humidity is essential to a Panther's well being. 65-80%. Accomplish this by misting the cage several times daily or with the addition of moisture retaining decorations, such as live plants or water features. Wilmette Pet – 625 Green Bay Road – Wilmette, IL 60091 www.wilmettepet.com – 847.251.6750 Page 1 Habitat/Territory: Jungle/Rain forest. Chameleons from different geographical areas in Madagascar can be identified by different colour markings. -

Effects of Artificial Ultraviolet Light Exposure on Reproductive Success of the Female Panther Chameleon (Furcifer Pardalis) In
Zoo Biology 21:525–537 (2002) Effects of Artificial Ultraviolet Light Exposure on Reproductive Success of the Female Panther Chameleon (Furcifer pardalis) in Captivity Gary W. Ferguson,1n W.H. Gehrmann,1 T.C. Chen,2 E.S. Dierenfeld,3 and M.F. Holick2 1Department of Biology, Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, Texas 2Vitamin D, Skin, and Bone Laboratory, Boston University Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts 3Department of Wildlife Nutrition, Wildlife Conservation Society, Bronx, New York Having previously documented experimentally the need for ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation (290–315 nm) in the light environment of captive female panther chameleons (Furcifer pardalis) to ensure hatching success of their eggs, we investigated optimal UVB irradiation levels. From 1996–1998 28 hatchling female panther chameleons were raised to maturity and bred (using vitamin and mineral- fortified insect diets low in vitamin D) in nine different artificial UVB light environments. Seven of the environments included long (12 hr/day) low irradia- tion exposures ranging from 1.7 to 22 mW/cm2 UVB, with a corresponding conversion of provitamin D3 to photoproducts in in vitro models of 0.18 to 1.52% in 2 hr. Two environments included short (0.5 and 1.0 hr/day), high irradiation exposures of 55 and 49 mW/cm2 UVB, respectively, with a corres- ponding conversion of provitamin D3 to photoproducts in in vitro models of 8.3% to 14.6% in the respective 0.5- and 1.0-hr time periods. Females raised with the mid-level long/low exposures (5–15 mW/cm2 UVB; 0.52–1.32% conversion to photoproducts in in vitro models) produced viable eggs with a significantly higher percentage of hatching compared to those with the extreme (highest or lowest) long/low exposures. -

Lizards & Snakes: Alive!
LIZARDSLIZARDS && SNAKES:SNAKES: ALIVE!ALIVE! EDUCATOR’SEDUCATOR’S GUIDEGUIDE www.sdnhm.org/exhibits/lizardsandsnakeswww.sdnhm.org/exhibits/lizardsandsnakes Inside: • Suggestions to Help You Come Prepared • Must-Read Key Concepts and Background Information • Strategies for Teaching in the Exhibition • Activities to Extend Learning Back in the Classroom • Map of the Exhibition to Guide Your Visit • Correlations to California State Standards Special thanks to the Ellen Browning Scripps Foundation and the Nordson Corporation Foundation for providing underwriting support of the Teacher’s Guide KEYKEY CONCEPTSCONCEPTS Squamates—legged and legless lizards, including snakes—are among the most successful vertebrates on Earth. Found everywhere but the coldest and highest places on the planet, 8,000 species make squamates more diverse than mammals. Remarkable adaptations in behavior, shape, movement, and feeding contribute to the success of this huge and ancient group. BEHAVIOR Over 45O species of snakes (yet only two species of lizards) An animal’s ability to sense and respond to its environment is are considered to be dangerously venomous. Snake venom is a crucial for survival. Some squamates, like iguanas, rely heavily poisonous “soup” of enzymes with harmful effects—including on vision to locate food, and use their pliable tongues to grab nervous system failure and tissue damage—that subdue prey. it. Other squamates, like snakes, evolved effective chemore- The venom also begins to break down the prey from the inside ception and use their smooth hard tongues to transfer before the snake starts to eat it. Venom is delivered through a molecular clues from the environment to sensory organs in wide array of teeth.