Second Midterm Answer
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Often an Acidic Proton)
314 Arrow Pushing practice/Beauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) Nucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair donor = Lewis base, (often donated to an acidic proton) Problems - In the following reactions each step has been written without the formal charge or lone pairs of electrons and curved arrows. Assume each atom follows the normal octet rule, except hydrogen (duet rule). Supply the lone pairs, formal charge and the curved arrows to show how the electrons move for each step of the reaction mechanism. Identify any obvious nucleophiles and electrophiles in each of the steps of the reactions below (on the left side of each reaction arrow). A separate answer file will be created, as I get to it. Let me know when you find errors. RX reactions Examples of important patterns to know from our starting points (plus a few extras). methyl and primary secondary tertiary special H3C X very good very poor SN2 patterns SN2,E2,SN1,E1 X X X X X vinyl allylic X X X X X X X benzylic X phenyl X X There are many X variations. X 1o neopentyl 1. SN2 and SN2 a b I Br Br N C I I C I N 2. SN2 and E2 a b H Br H O HC C H I HC C Br OH I 3. SN2 and SN2 a Na b Na Na Br S HC C Br Br O O S Na Br R R Z:\classes\315\315 Handouts\arrow pushing mechs, probs.doc 314 Arrow Pushing practice/Beauchamp 2 4. -

Arrow Pushing: Mechanisms
Arrow Pushing: Mechanisms A few rules to follow: X H H 1) Arrows show the movement of ELECTRONS! HO HO They go from site of high electron density, usually a lone pair or alkene, to sites of low electron density, Correct OTs Incorrect OTs usually a cation, hydrogen, or unfilled orbital. H H H H 2) Balance the equation. Be sure to conserve mass and charge. If you start with an over charge of +1, +1 Incorrect 0 you need to end with an overall charge of +1. +1 Correct +1 Br Br CN Br CN Br H H 3) Draw out all intermediates. Include hydrogens, lone CN NC pairs, and charges. Be sure there are no carbons with X Incorrect H 5 bonds or other chemical errors in the intermediates. Correct 5 bonds to C OH Cl Cl HCl 4) The mechanism should give the observed product. + Do not forget about stereochemistry and regiochemistry. This mechanism HAS to go via a SN1 Let's try an example: HO cat. TsOH Given this reaction scheme we can determine that this will be an elimination type mechanism, specifically E1. CH HO CH3 2 The reaction scheme may not show all by products! CH CH3 cat. TsOH 3 + H2O Let's draw all hydrogens and balance the equation. H The lone pair on oxygen would be a site of high electron HO CH3 O CH3 O H O density and an acidic hydrogen (TsOH) is a site of low OH + OH CH3 H S CH3 S electron density. Note: TsOH is catalytic so it needs to O O O O be regenerated in our mechanism! H Now that we have made a charged species we want to CH H O CH3 3 find a way to stabalize or neutralize the charge. -

Property Relationships Acid-Base Chemistry W
109, Structure & Properties, Acid-Base CHEM 109, Lecture 1 Structure – Property Relationships Acid-Base Chemistry McMurry & Begley (M&B) Chapter 1.1-1.2 (posted on CHEM 109 website) CONCEPT MAP: CHEMICAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTY RELATIONSHIPS WHAT DO WE KNOW WELL & WHAT COULD WE KNOW BETTER? The intention of this exercise is to figure out your current knowledge of the relationship between chemical structures and properties. Perhaps more importantly, we want to identify misconceptions or gaps in knowledge. Learning that you don’t understand something as well as you thought is actually a good thing! This will be based on your knowledge and, eventually, that of your peers. No outside resources such as cell phones, notebooks, textbooks, etc. are necessary. Before Class: Cut out each term on page E1-3 to create a set of cards. Begin to categorize and relate the fundamental general chemistry terms to each other by moving the term cards around. Brainstorm your current understanding of each term on a separate sheet of paper. Draw structures and/or figures to exemplify the term where appropriate (this is appropriate for most terms). Create a concept map (example on next page) with these terms – use the cards, write the terms by hand, or use a digital format such as ThinkSpace or Mindmeister. Add terms and links as necessary to complete your map. There are many, many ways to organize and describe these terms. Do what make sense to you! I can’t stop you from looking up terms on your own, but I’d recommend avoiding this as much as possible. -

CH4103 Organic and Biological Chemistry LCM Lecture 5
CH4103 Organic and Biological Chemistry LCM Lecture 5 Dr Louis C. Morrill School of Chemistry, Cardiff University Main Building, Rm 1.47B [email protected] Autumn Semester For further information see Learning Central: CH4103/Learning Materials/LCM 1 Lecture 5 Preparation To best prepare yourself for the contents of this lecture, please refresh • Atomic and molecular orbitals (Unit 1, Lecture 2) • Molecular shape and hybridisation (Unit 1, Lecture 2) • Sigma and pi bonds (Unit 1, Lecture 2) • Electronegativity and bond polarisation (Unit 1, Lecture 3) • Stereochemistry (Unit 1, Lecture 4-7) • Reactive intermediates – carbocations (Unit 1, Lecture 8) • Acids and bases – pKa (Unit 1, Lecture 9) • Reaction thermodynamics (Unit 2, Lecture 1) and kinetics (Unit 2, Lecture 2) • Curly arrow pushing mechanisms (Unit 2, Lecture 3) and SN2 (Unit 2, Lecture 4) For further information see Learning Central: CH4103/Learning Materials/LCM 2 Lecture 5: Introduction to Substitution Reaction – SN1 Key learning objectives: • Know the difference between the possible mechanisms for nucleophilic substitution at saturated carbon – SN2 and SN1 • The rate law for a SN1 reaction • The free energy diagram for a SN1 reaction • The curly arrow pushing mechanism, molecular orbital analysis, intermediate and stereochemical outcome of a SN1 reaction • The factors that favour a SN1 mechanism including the nature of the substrate, nucleophile, solvent and leaving group • Synthetic Analysis – How to favour one substitution mechanism over the other? For further information -

2014 Purple Book Answers Week 4.Pdf
Chem S-20ab Purple Book Solutions Week 4 - Page 1 of 38 Aromaticity 1. Given the following structures, circle any that are aromatic. Explain why the other species are not aromatic. 4n electrons not a continuous antiaromatic cyclic system. NH not a continuous 4n electrons cyclic system. antiaromatic 2. In the following molecule, which nitrogen atom is more basic (i.e. more willing to accept a proton)? Why? The other one has its lone pair as part of CH3 the 6 electron aromatic system. Protonating that lone pair would destroy the aromaticity, N which would be bad: H CH3 this one is more basic N N not a continuous cyclic system. N 3. When the following molecule is oxidized, the expected ketone is not formed, but phenol is formed instead. Describe what is going on here, and explain this unusual behavior. OH O OH CrO3 oxidation phenol Tautomerizes in order to achieve aromaticity. Chem S-20ab Purple Book Solutions Week 4 - Page 2 of 38 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Mechanisms 1. Provide a curved-arrow mechanism for the following transformation. Show resonance structures for the cationic intermediate which make it clear why the substitution goes where it does. O O Cl HN CH3 HN CH3 AlCl3 catalyst Cl AlCl3 Cl AlCl3 O O O O HN CH3 HN CH3 HN CH3 HN CH3 H H H want to put + charge next to :Solvent electron-donating nitrogen 2. Provide a curved-arrow mechanism for the following transformation. H+ + O: H2SO4 catalyst H OH :Sol :Solvent OH2 H OH H+ OH OH Chem S-20ab Purple Book Solutions Week 4 - Page 3 of 38 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Direction 1. -

Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (Ears) - Halides - Heteroatoms - Carbons (Alkylation & Acylation)
8B, UCSC Chapter 16, Part 1 CHEM 8B, Lecture 1 - Mini-8A Overview - CH 16.1-16.3 – Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EArS) - Halides - Heteroatoms - Carbons (Alkylation & Acylation) Functional Groups = Organizing ochem by specific bonding patterns - Be able to identify & draw a simple example of each from Table 3.1 including… OH O O O H NH2 O O O O OH CN OCH3 Cl NH2 Skill Check: Arrow Pushing ** Arrows start at Electron Rich (Nucleophile) and end at Electron Poor (Electrophile)** Add arrows with a note – which bonds are broken and/or formed according to that arrow? B: H + O O O H+ O O H OH + C H H H O O :B O Step 1 Step 2 Bonds broken Bonds formed Bonds broken Bonds formed Reflect on mistakes: did you have different arrows? Copy your mistakes below and/or your neighbor’s mistakes. Discuss what those incorrect arrows mean and why it’s incorrect. L1-1 8B, UCSC Chapter 16, Part 1 Acid-Base Chemistry B: H A pKa’s to memorize in Study Expectations & Learning Advice (also in 8B Lecture 3) Add those standards and pKa’s here on your own time: Direction of equilibrium: Who wants that proton (H+) more?? Compare acid (left) to conjugate acid (right)…weaker acid (lower pKa) favored O H CH3NH2 O Reaction Mechanisms Any mechanisms from 8A that you need to know will be reviewed in 8B, starting with… Chapter 8 – Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes H Br Chapter 11 – E1 = unimolecular elimination weak base LG ex. CH OH 3 L1-2 8B, UCSC Chapter 16, Part 1 CHAPTER 16, PART 1 ! Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EArS) of Benzene Template EArS Mechanism Halides (Cl, Br, I…not covering F) - Know the identity of E+ to start the mechanism; always OK to use “:B” for base Representative chlorination mechanism Heteroatoms (N & S) Nitration Sulfonation L1-3 8B, UCSC Chapter 16, Part 1 Friedel-Crafts (FC) Reactions (Rxns) ***Add C’s to Benzene*** FC Acylation - No C+ RRGTs FC Alkylation - Start Simple… - Is there a more substituted carbon on the alkyl halide? Alkyl C+ rearranges to more substituted C L1-4 8B, UCSC Chapter 16, Part 1 Hydride Shifts in FC Alkylations How to handle this… 1. -

Mechanisms of Organic Chemistry Prof. Nandita Madhavan Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology – Bombay
Mechanisms of Organic Chemistry Prof. Nandita Madhavan Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology – Bombay Lecture – 40 Course Summary So welcome to the last lecture in this course and in today's lecture what will be doing is I would just be summarizing whatever you have studied from week one. So the overall picture that I had given you in the very first class is, when you think of reaction mechanisms, reaction mechanism tell you the pathway of a particular reaction and this is there in the introductory video as well. So what we have been doing over the past 8 weeks is, we have been looking at ways to propose a reasonable mechanism. (Refer Slide Time: 00:47) Once you propose the mechanism check the hypothesis using experiments. If the experiments are matching then you can say yes this is the correct mechanism. If not you need to go back rewrite your mechanism and again check it. So it is a cycle; a loop which will be useful in determining what is the probable mechanism. So I have show you examples from Chemistry and Biology where people have use these kind of experiments to confirm the most probable mechanism. (Refer Slide Time: 01:22) So initially in week 1 we have started with a broad classification of reactions so we had classify them as reactions that have a polar mechanism. So in polar mechanism you have charged intermediates or with intermediates with partial charge that is developed and you can think of electrophilic and nucleophilic species coming together to form this new bond. -

Kinetic Isotope Effects - Theory
Chemistry 202 - Organic Reaction Mechanisms II Some Common Mechanistic Tools David Van Vranken University of California, Irvine Crossover Experiment ■ Crossover experiments allow one to distinguish intramolecular processes from those that involve dissociation and recombination. Stevens "1,2-shift" + N CO Et + KOt-Bu N CO Et Bn 2 2 Bn intramolecular, concerted + N - CO2Et Bn .. or dissociative + stepwise N - CO Et +.N - CO Et N CO Et Bn .. 2 2 .. 2 . .. Bn Bn. ■ Formation of mixed products rules out an intramolecular mechanism. t-BuOK + N CO2Me + N CO2Et N CO2Me N CO2Me N CO2Et N CO2Et + + + Ph Tol Ph Tol Ph Tol ∴Can’t be intramolecular Stevens, T.S.; et al. J. Chem. Soc. 1928, 3193 Primary Kinetic Isotope Effects - Theory ■ Isotopes (e.g., H vs. D) exhibit the same chemical reactivity. ■ Bonds to lighter isotopes vibrate more quickly. ■ Biggest difference for 1H vs 2H as opposed to 12C vs 13C. ■ C-H reacts faster than C-D. Using linear stretch frequencies, you can estimate the maximum ratio of rates for a primary kinetic isotope effect to be a factor of 7. Planck from IR spectra h (νH - νD) k H = 2kT = kD e 6.9 Boltzmann ■ Primary K.I.E.: If H transfer is the rate-determining step, then the D analog will be up to 7x slower. primary R R K.I.E. R C H X R C D X transition states: R faster R slower ■ Theoretically, rates of H transfer can be up to 15 times faster than D transfer due to bending contributions in the T.S., but in practice, they aren’t higher than a factor of 8. -

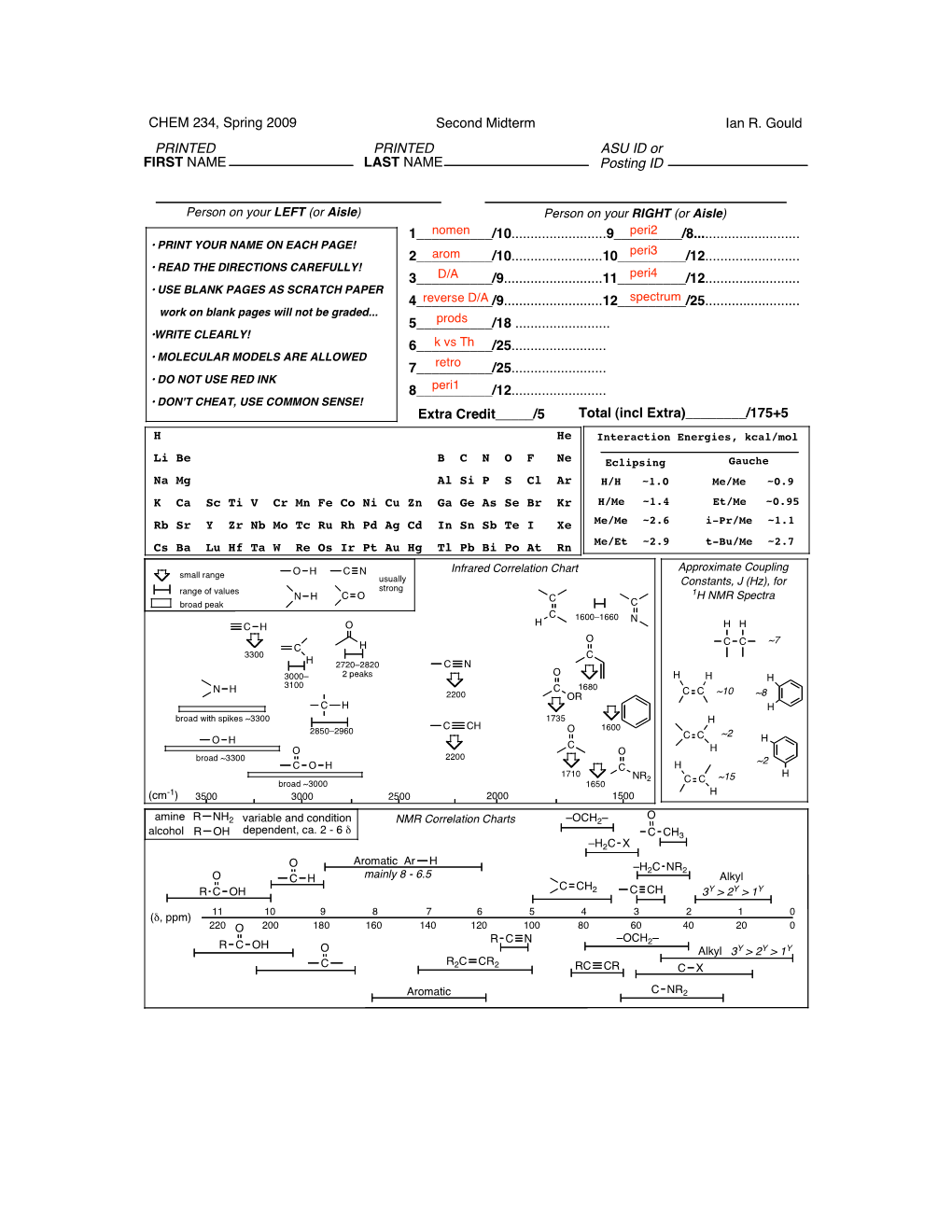
Second Midterm Ian R. Gould PRINTED FIRST NAME CHEM 234
CHEM 234, Spring 2009 Second Midterm Ian R. Gould PRINTED PRINTED ASU ID or FIRST NAME LAST NAME Posting ID Person on your LEFT (or Aisle) Person on your RIGHT (or Aisle) 1__________/10.........................9_________/8............................ •!PRINT YOUR NAME ON EACH PAGE! 2__________/10........................10_________/12......................... • READ THE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY! 3__________/9..........................11_________/12......................... • USE BLANK PAGES AS SCRATCH PAPER 4__________/9..........................12_________/25......................... work on blank pages will not be graded... 5__________/18 ......................... •WRITE CLEARLY! 6__________/25......................... • MOLECULAR MODELS ARE ALLOWED 7__________/25......................... • DO NOT USE RED INK 8__________/12......................... • DON'T CHEAT, USE COMMON SENSE! Extra Credit_____/5 Total (incl Extra)________/175+5 H He Interaction Energies, kcal/mol Li Be B C N O F Ne Eclipsing Gauche Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar H/H ~1.0 Me/Me ~0.9 K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr H/Me ~1.4 Et/Me ~0.95 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Me/Me ~2.6 i-Pr/Me ~1.1 Cs Ba Lu Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Me/Et ~2.9 t-Bu/Me ~2.7 Infrared Correlation Chart Approximate Coupling small range O H C N usually Constants, J (Hz), for range of values strong 1 N H C O C H NMR Spectra broad peak C C 1600–1660 N C H O H H H O C C ~7 C H 3300 C H 2720–2820 C N O 3000– 2 peaks H H H 3100 N H C 1680 C C ~10 2200 OR ~8 C H H broad with spikes ~3300 1735 H C CH 2850–2960 O 1600 C C ~2 H O H C O O H broad ~3300 2200 ~2 C O H C H 1710 H NR2 ~15 broad ~3000 1650 C C (cm-1) 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 H O amine R NH2 variable and condition NMR Correlation Charts –OCH2– alcohol R OH dependent, ca. -

108B Exam 2A SS15
UCSC, Binder Name______________________________________ CHEM 108B Organic Chemistry II EXAM 2, Version A (300 points) In each of the following problems, use your knowledge of organic chemistry conventions to answer the questions in the proper manner. Be sure to read each question carefully. You will have the entire class period to complete this exam (approximately 2 hours), but hopefully you won’t need it! You are welcome to use pre-built models. Keep your eyes on your own paper. Electronic devices of any kind are not allowed, including cell phones and calculators. Any student found using any of said devices, or found examining another student’s exam, will be promptly removed from the exam room and at minimum will receive a zero on this exam. Such an incident may also be considered a form of academic dishonesty and reported to the UCSC Judiciary Affairs Committee. 1 (50) 2 (40) 3 (40) 4 (45) 5 (40) 6 (45) 7 (45) 8 (40) Total Functional Group Suffix Acid chloride -oyl chloride Acid Anhydride -oic anhyride Carboxylic Acid -oic acid Esters -oate Amides -amide CHEM 108B, Exam 2A Last Name, First Initial ______________________ 1. Nomenclature – suffixes for acyl derivatives on the cover page (a) (20 points) Provide IUPAC names for any three of the following compounds. “X” out the ones to skip. O O ______________________________________________________________ O O _______________________________________________________________ O Cl _______________________________________________________________ O O O ___________________________________________________________ O N(CH3)2 _____________________________________________________________ (b) (20 points) Draw structures corresponding to the following names. Diisopropylamine N-Methylaniline Pyridine N-Methyl-N-Propylcyclohexylamine (c) (10 points) Name the following compound. -
![Arxiv:1805.10970V2 [Physics.Chem-Ph] 20 Mar 2019](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/8866/arxiv-1805-10970v2-physics-chem-ph-20-mar-2019-3348866.webp)
Arxiv:1805.10970V2 [Physics.Chem-Ph] 20 Mar 2019
Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2019 AGENERATIVE MODEL FOR ELECTRON PATHS John Bradshaw Matt J. Kusner Brooks Paige University of Cambridge University of Oxford The Alan Turing Institute Max Planck Institute, Tübingen The Alan Turing Institute University of Cambridge [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Marwin H. S. Segler José Miguel Hernández-Lobato BenevolentAI University of Cambridge [email protected] Microsoft Research Cambridge The Alan Turing Institute [email protected] ABSTRACT Chemical reactions can be described as the stepwise redistribution of electrons in molecules. As such, reactions are often depicted using “arrow-pushing” diagrams which show this movement as a sequence of arrows. We propose an electron path prediction model (ELECTRO) to learn these sequences directly from raw reaction data. Instead of predicting product molecules directly from reactant molecules in one shot, learning a model of electron movement has the benefits of (a) being easy for chemists to interpret, (b) incorporating constraints of chemistry, such as balanced atom counts before and after the reaction, and (c) naturally encoding the sparsity of chemical reactions, which usually involve changes in only a small number of atoms in the reactants. We design a method to extract approximate reaction paths from any dataset of atom-mapped reaction SMILES strings. Our model achieves excellent performance on an important subset of the USPTO reaction dataset, comparing favorably to the strongest baselines. Furthermore, we show that our model recovers a basic knowledge of chemistry without being explicitly trained to do so. 1 INTRODUCTION The ability to reliably predict the products of chemical reactions is of central importance to the manufacture of medicines and materials, and to understand many processes in molecular biology. -

Cocaine Esterase” That Is Produced in Bacteria That Live at the Base of the Coca Plant
Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Name Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. 1. There is a real enzyme called “cocaine esterase” that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme employs nucleophilic catalysis to hydrolyze cocaine. Download and open the file, esterase.pse, and examine the active site of the enzyme. a. To start, draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the hydrolysis of a benzoic acid ester (you don’t need to draw the entire cocaine molecule) assuming a nucleophilic serine residue activated by a general base. b. The PyMOL model contains phenyl boronic acid (right) covalently OH bound to a serine residue in the active site. The boron is electron deficient and B therefore a great electrophile. ID the residues of the catalytic triad found in cocaine esterase and sketch the geometry, with distances here. OH c. Identify the two groups that comprise the oxyanion hole in cocaine esterase and give relevant distances between H-bonding groups (no sketch necessary). Note that only one of the two hydroxyls on boron occupy the hole. The other is pointed to where the leaving group would be. b. Note that Asp 259 H-bonds to His287, which in turn H-bonds to the sidechain oxygen of Ser117. That’s the triad, with the serine caught flagrantly attacking an electrophile. c. The amide NH of Tyr118 and the side chain hydroxyl of Tyr44 are doing the oxyanion hole thing. d. Why wouldn’t a phosphonate transition state analog (such as the one used in generating a catalytic antibody) work as an inhibitor for this enzyme? The phosphonate is a tetrahedral species that does not include the active site serine, so that’s not going to work.