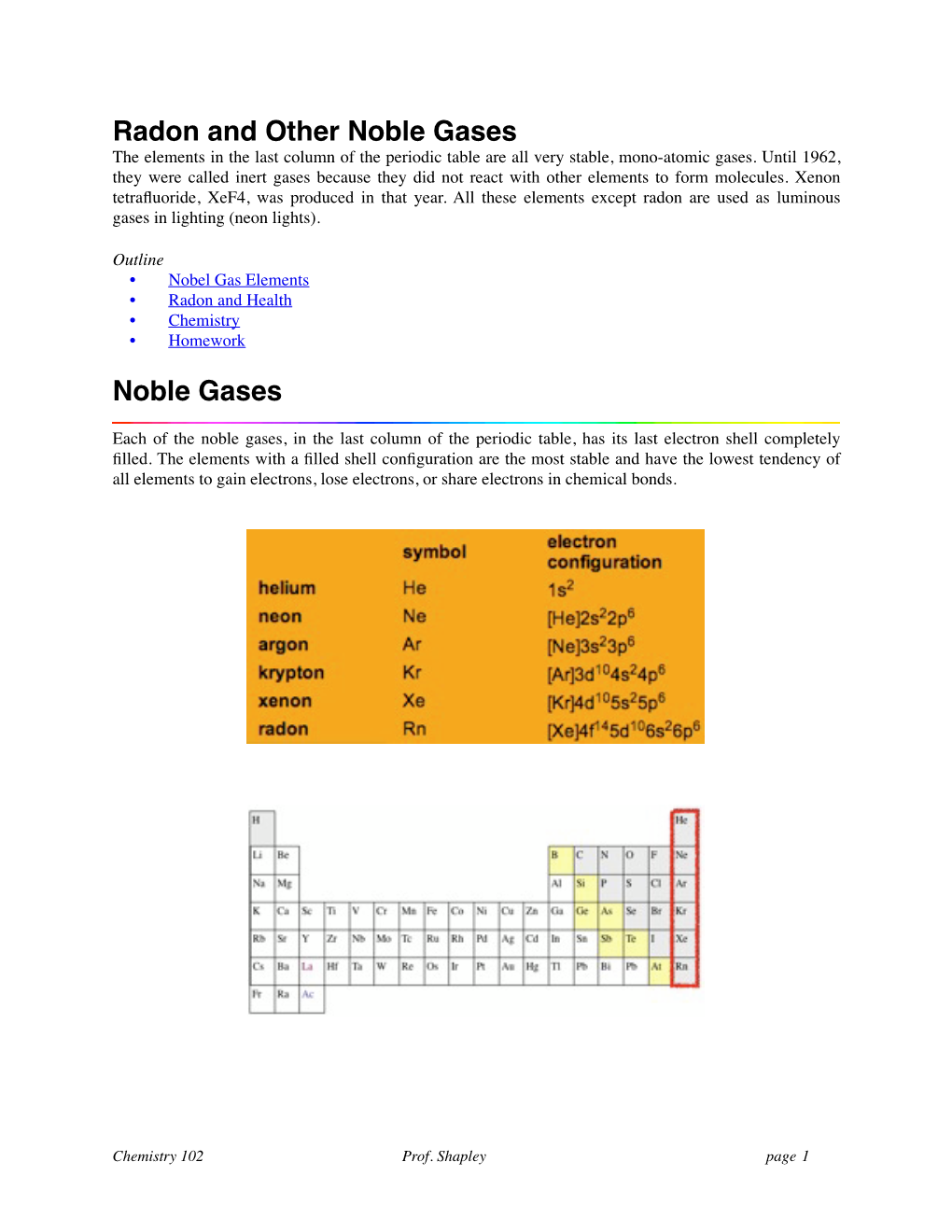
Radon and Other Noble Gases the Elements in the Last Column of the Periodic Table Are All Very Stable, Mono-Atomic Gases
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

An Alternate Graphical Representation of Periodic Table of Chemical Elements Mohd Abubakr1, Microsoft India (R&D) Pvt
An Alternate Graphical Representation of Periodic table of Chemical Elements Mohd Abubakr1, Microsoft India (R&D) Pvt. Ltd, Hyderabad, India. [email protected] Abstract Periodic table of chemical elements symbolizes an elegant graphical representation of symmetry at atomic level and provides an overview on arrangement of electrons. It started merely as tabular representation of chemical elements, later got strengthened with quantum mechanical description of atomic structure and recent studies have revealed that periodic table can be formulated using SO(4,2) SU(2) group. IUPAC, the governing body in Chemistry, doesn‟t approve any periodic table as a standard periodic table. The only specific recommendation provided by IUPAC is that the periodic table should follow the 1 to 18 group numbering. In this technical paper, we describe a new graphical representation of periodic table, referred as „Circular form of Periodic table‟. The advantages of circular form of periodic table over other representations are discussed along with a brief discussion on history of periodic tables. 1. Introduction The profoundness of inherent symmetry in nature can be seen at different depths of atomic scales. Periodic table symbolizes one such elegant symmetry existing within the atomic structure of chemical elements. This so called „symmetry‟ within the atomic structures has been widely studied from different prospects and over the last hundreds years more than 700 different graphical representations of Periodic tables have emerged [1]. Each graphical representation of chemical elements attempted to portray certain symmetries in form of columns, rows, spirals, dimensions etc. Out of all the graphical representations, the rectangular form of periodic table (also referred as Long form of periodic table or Modern periodic table) has gained wide acceptance. -

What Is Radon?
Biology Unit Radon Alert INVESTIGATION 3 WHAT IS RADON? INTRODUCTION Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas. It is formed by the radioactive breakdown of radium, and is found in soils just about everywhere. You cannot see it, taste it, or smell it. It is continuously formed in rocks and soils and escapes into the atmosphere. In some cases, it makes its way into homes, builds up to high concentrations in indoor air, and can become a health hazard. Although there are several different isotopes of radon, the one that is of greatest concern as a potential Radioactivity - the spontaneous human health threat is called radon-222. Radon-222 is emission of energy by certain (radio- formed naturally during a chain of radioactive disintegra- active) atoms, resulting in a change tion reactions (decay series). The decay series begins from one element to another or one when uranium-238 decays. Uranium is widely distrib- isotope to another. The energy can uted in rocks and soils throughout the earth’s crust. It has be in the form of alpha or beta par- a half-life of 4.5 billion years, which means a very slow ticles and gamma rays. breakdown. The decay series is shown schematically in Figure 1. There are eight different elements and 15 different isotopes in the series, beginning with uranium- 238 and ending with lead-206. New elements formed by radioactive disintegration reactions are called decay products. Thus, radium-226 is one of the decay products of uranium-238. Polonium-218 and lead-214 are decay products of radon-222. -

The Development of the Periodic Table and Its Consequences Citation: J
Firenze University Press www.fupress.com/substantia The Development of the Periodic Table and its Consequences Citation: J. Emsley (2019) The Devel- opment of the Periodic Table and its Consequences. Substantia 3(2) Suppl. 5: 15-27. doi: 10.13128/Substantia-297 John Emsley Copyright: © 2019 J. Emsley. This is Alameda Lodge, 23a Alameda Road, Ampthill, MK45 2LA, UK an open access, peer-reviewed article E-mail: [email protected] published by Firenze University Press (http://www.fupress.com/substantia) and distributed under the terms of the Abstract. Chemistry is fortunate among the sciences in having an icon that is instant- Creative Commons Attribution License, ly recognisable around the world: the periodic table. The United Nations has deemed which permits unrestricted use, distri- 2019 to be the International Year of the Periodic Table, in commemoration of the 150th bution, and reproduction in any medi- anniversary of the first paper in which it appeared. That had been written by a Russian um, provided the original author and chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev, and was published in May 1869. Since then, there have source are credited. been many versions of the table, but one format has come to be the most widely used Data Availability Statement: All rel- and is to be seen everywhere. The route to this preferred form of the table makes an evant data are within the paper and its interesting story. Supporting Information files. Keywords. Periodic table, Mendeleev, Newlands, Deming, Seaborg. Competing Interests: The Author(s) declare(s) no conflict of interest. INTRODUCTION There are hundreds of periodic tables but the one that is widely repro- duced has the approval of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is shown in Fig.1. -

Midterm Examination #3, December 11, 2015 1. (10 Point
NAME: NITROMETHANE CHEMISTRY 443, Fall, 2015(15F) Section Number: 10 Midterm Examination #3, December 11, 2015 Answer each question in the space provided; use back of page if extra space is needed. Answer questions so the grader can READILY understand your work; only work on the exam sheet will be considered. Write answers, where appropriate, with reasonable numbers of significant figures. You may use only the "Student Handbook," a calculator, and a straight edge. 1. (10 points) Argon is a noble gas. For all practical purposes it can be considered an ideal gas. DO NOT WRITE Calculate the change in molar entropy of argon when it is subjected to a process in which the molar IN THIS SPACE volume is tripled and the temperature is simultaneously changed from 300 K to 400 K. 1,2 _______/25 This is a straightforward application of thermodynamics: 3,4 _______/25 = = + = + 2 2 2 2 5 _______/20 Identifying ∆the derivative� and� doing1 � the� integrals � 1give� � �1 � � �1 3 3 400 6,7 _______/20 = + = 8.3144349 + 8.3144349 2 2 1 2 300 8 _______/10 where the∆ heat capacity � 1� at constant � 1volume� of a monatomic �ideal� gas is� . � � � 3 ============= = 9.13434 + 3.58786 = 12.722202 9 _______/5 ∆ (Extra credit) ============= TOTAL PTS 2. (15 points) Benzene ( • = 96.4 ) and toluene ( • = 28.9 ) form a nearly ideal solution over a wide range. For purposes of this question, you may assume that a solution of the two is ideal. (a) What is the total vapor pressure above a solution containing 5.00 moles of benzene and 3.25 moles of toluene? 5.00 3.25 = • + • = (96.4 ) + (28.9 ) 5.00 + 3.25 5.00 + 3.25 = 58.4 + 11.4 = 69.8 (b) What is mole fraction of benzene in the vapor above this solution? . -

The Oganesson Odyssey Kit Chapman Explores the Voyage to the Discovery of Element 118, the Pioneer Chemist It Is Named After, and False Claims Made Along the Way
in your element The oganesson odyssey Kit Chapman explores the voyage to the discovery of element 118, the pioneer chemist it is named after, and false claims made along the way. aving an element named after you Ninov had been dismissed from Berkeley for is incredibly rare. In fact, to be scientific misconduct in May5, and had filed Hhonoured in this manner during a grievance procedure6. your lifetime has only happened to Today, the discovery of the last element two scientists — Glenn Seaborg and of the periodic table as we know it is Yuri Oganessian. Yet, on meeting Oganessian undisputed, but its structure and properties it seems fitting. A colleague of his once remain a mystery. No chemistry has been told me that when he first arrived in the performed on this radioactive giant: 294Og halls of Oganessian’s programme at the has a half-life of less than a millisecond Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) before it succumbs to α -decay. in Dubna, Russia, it was unlike anything Theoretical models however suggest it he’d ever experienced. Forget the 2,000 ton may not conform to the periodic trends. As magnets, the beam lines and the brand new a noble gas, you would expect oganesson cyclotron being installed designed to hunt to have closed valence shells, ending with for elements 119 and 120, the difference a filled 7s27p6 configuration. But in 2017, a was Oganessian: “When you come to work US–New Zealand collaboration predicted for Yuri, it’s not like a lab,” he explained. that isn’t the case7. -

Helium Adsorption on Lithium Substrates
JLowTempPhys DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9516-5 Helium Adsorption on Lithium Substrates E. Van Cleve · P. Taborek · J.E. Rutledge Received: 25 July 2007 / Accepted: 13 September 2007 © Springer Science+Business Media 2007 Abstract We have developed a cryogenic pulsed laser deposition (PLD) system to deposit lithium films onto a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) at 4 K. Adsorption isotherms of 4He on lithium were measured in the temperature range between 1.42 K and 2.5 K. The isotherms are qualitatively different from isotherms on strong sub- strates such as gold and weak substrates such as cesium. There is no evidence of the formation of solid-like layers of helium, and the helium coverage is approximately linear in the pressure over a wide range. By measuring the low coverage slope of the isotherms, the binding energy of helium to lithium was found to be approxi- mately −13.6 K. For lithium substrates less than approximately 100 layers thick, the chemical potential at which the superfluid transition was observed was surprisingly sensitive to the details of lithium deposition. Keywords Helium films · Pulsed laser deposition · Superfluidity · Alkali metal 1 Introduction When helium is adsorbed onto a strong heterogenous substrate such as gold, the first 2 or 3 statistical layers are solid-like. The nature of these layers is not yet clear, but the layers are amorphous and do not participate significantly in superflow at high coverages. Superfluidity on strong substrates requires a minimum critical coverage to saturate the solid-like layers, and the superfluid phase which forms at higher cover- ages flows over these layers and does not interact directly with the strong, short range This work was supported by NSF grant DMR 0509685. -

Of the Periodic Table
of the Periodic Table teacher notes Give your students a visual introduction to the families of the periodic table! This product includes eight mini- posters, one for each of the element families on the main group of the periodic table: Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Boron/Aluminum Group (Icosagens), Carbon Group (Crystallogens), Nitrogen Group (Pnictogens), Oxygen Group (Chalcogens), Halogens, and Noble Gases. The mini-posters give overview information about the family as well as a visual of where on the periodic table the family is located and a diagram of an atom of that family highlighting the number of valence electrons. Also included is the student packet, which is broken into the eight families and asks for specific information that students will find on the mini-posters. The students are also directed to color each family with a specific color on the blank graphic organizer at the end of their packet and they go to the fantastic interactive table at www.periodictable.com to learn even more about the elements in each family. Furthermore, there is a section for students to conduct their own research on the element of hydrogen, which does not belong to a family. When I use this activity, I print two of each mini-poster in color (pages 8 through 15 of this file), laminate them, and lay them on a big table. I have students work in partners to read about each family, one at a time, and complete that section of the student packet (pages 16 through 21 of this file). When they finish, they bring the mini-poster back to the table for another group to use. -

Keeping Your Home Safe from RADON
Keeping Your Home Safe From RADON 800-662-9278 | Michigan.gov/radon 08/2019 What is Radon? Radon is a colorless and odorless gas that comes from the soil. The gas can accumulate in our home and in the air we breathe. Radon gas decays into fine particles that are radioactive. When inhaled, these fine particles can damage the lung. Exposure to radon over a long period of time can lead to lung cancer. It is estimated that 21,000 people die each year in the United States from lung cancer due to radon exposure. A radon test is the only way to know how much radon is in your home. Radon can be reduced with a mitigation system. The Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE) has created this guide to explain: • How radon accumulates in homes • The health risks of radon exposure • How to test your home for radon • What to do if your home has high radon • Radon policies C Keeping Your Home Safe From Radon Table of Contents Where Does Radon Come From? ............................................. 1 Radon in Michigan ....................................................................... 1 Percentage of Elevated Radon Test Results by County ......... 2 Is There a Safe Level of Radon? ............................................... 3 Radon Health Risks ..................................................................... 4 How Radon Enters the Home ..................................................... 6 Radon Pathways ........................................................................... 7 Radon Testing ............................................................................ -

Radionuclides (Including Radon, Radium and Uranium)
Radionuclides (including Radon, Radium and Uranium) Hazard Summary Uranium, radium, and radon are naturally occurring radionuclides found in the environment. No information is available on the acute (short-term) noncancer effects of the radionuclides in humans. Animal studies have reported inflammatory reactions in the nasal passages and kidney damage from acute inhalation exposure to uranium. Chronic (long-term) inhalation exposure to uranium and radon in humans has been linked to respiratory effects, such as chronic lung disease, while radium exposure has resulted in acute leukopenia, anemia, necrosis of the jaw, and other effects. Cancer is the major effect of concern from the radionuclides. Radium, via oral exposure, is known to cause bone, head, and nasal passage tumors in humans, and radon, via inhalation exposure, causes lung cancer in humans. Uranium may cause lung cancer and tumors of the lymphatic and hematopoietic tissues. EPA has not classified uranium, radon or radium for carcinogenicity. Please Note: The main sources of information for this fact sheet are EPA's Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) (5), which contains information on oral chronic toxicity and the RfD for uranium, and the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry's (ATSDR's) Toxicological Profiles for Uranium, Radium, and Radon. (1) Uses Uranium is used in nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons. Very small amounts are used in photography for toning, in the leather and wood industries for stains and dyes, and in the silk and wood industries. (2) Radium is used as a radiation source for treating neoplastic diseases, as a radon source, in radiography of metals, and as a neutron source for research. -

Recalling Radon's Recognition
in your element Recalling radon’s recognition Brett F. Thornton and Shawn C. Burdette look back at the discovery — and the many different names — of element 86. n 1899, Pierre and Marie Curie noted an Thoron, unlike radon, requires no such “induced radioactivity” — left behind by clarification, and 220Rn is routinely called Iradium, distinct from its own radioactivity. thoron today. Thoron is far easier to say Ernest Rutherford and Robert B. Owens also than ‘radon-two-twenty’, perhaps explaining reported that year on a radioactive substance why the annual count of scientific papers 220 ( Rn, t1/2 = 55.6 s) emitted by thorium, which mentioning thoron has increased over twenty- they called emanation. In 1900, Friedrich fold since thoron was ‘disallowed’ in 1957. Dorn realized that the Curies had observed a Distinguishing between 222Rn (the 222 220 unique substance ( Rn, t1/2 = 3.8 d), similar isotope called ‘radon’) and Rn (thoron) is to emanation. In 1904, André-Louis Debierne not of idle linguistic and historic interest. 222 found a third radioactive particle; this one © SUPERSTOCK/ALAMY Rn can persist indoors, whereas the short- 219 produced from actinium ( Rn, t1/2 = 4 s). lived thoron cannot. Not all home radon These were at first regarded as elements and actinon (An) for the three isotopes; detectors (pictured) are sensitive to thoron, and became colloquially known as thorium names suggested by Elliott Q. Adams. and thoron-sensitive detectors must be emanation, radium emanation and actinium An official statement on a name for all placed with care because thoron does not emanation, but today we recognize them three isotopes — that is, a name for the travel far from its source. -

Unit 6 the Periodic Table How to Group Elements Together? Elements of Similar Properties Would Be Group Together for Convenience
Unit 6 The periodic table How to group elements together? Elements of similar properties would be group together for convenience. The periodic table Chemists group elements with similar chemical properties together. This gives rise to the periodic table. In the periodic table, elements are arranged according to the following criteria: 1. in increasing order of atomic numbers and 2. according to the electronic arrangement The diagram below shows a simplified periodic table with the first 36 elements listed. Groups The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups . Groups are numbered from I to VII, followed by Group 0 (formerly called Group VIII). [Some groups are without group numbers.] The table below shows the electronic arrangements of some elements in some groups. Group I Group II Group VII Group 0 He (2) Li (2,1) Be (2,2) F (2,7) Ne (2,8) Na (2,8,1) Mg (2,8,2) Cl (2,8,7) Ar (2,8,8) K (2,8,8,1) Ca (2,8,8,2) Br (2,8,18,7) Kr (2,8,18,8) What is the relationship between the group numbers and the electronic arrangements of the elements? Group number = the number of outermost shell electrons in an atom of the element The chemical properties of an element depend mainly on the number of outermost shell electrons in its atoms. Therefore, elements within the same group would have similar chemical properties and would react in a similar way. However, there would be a gradual change of reactivity of the elements as we move down the group. -

Periodic Table 1 Periodic Table
Periodic table 1 Periodic table This article is about the table used in chemistry. For other uses, see Periodic table (disambiguation). The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers (numbers of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations , and recurring chemical properties. Elements are presented in order of increasing atomic number, which is typically listed with the chemical symbol in each box. The standard form of the table consists of a grid of elements laid out in 18 columns and 7 Standard 18-column form of the periodic table. For the color legend, see section Layout, rows, with a double row of elements under the larger table. below that. The table can also be deconstructed into four rectangular blocks: the s-block to the left, the p-block to the right, the d-block in the middle, and the f-block below that. The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups, with some of these having names such as halogens or noble gases. Since, by definition, a periodic table incorporates recurring trends, any such table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements and predict the properties of new, yet to be discovered or synthesized, elements. As a result, a periodic table—whether in the standard form or some other variant—provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and such tables are widely used in chemistry and other sciences. Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table.