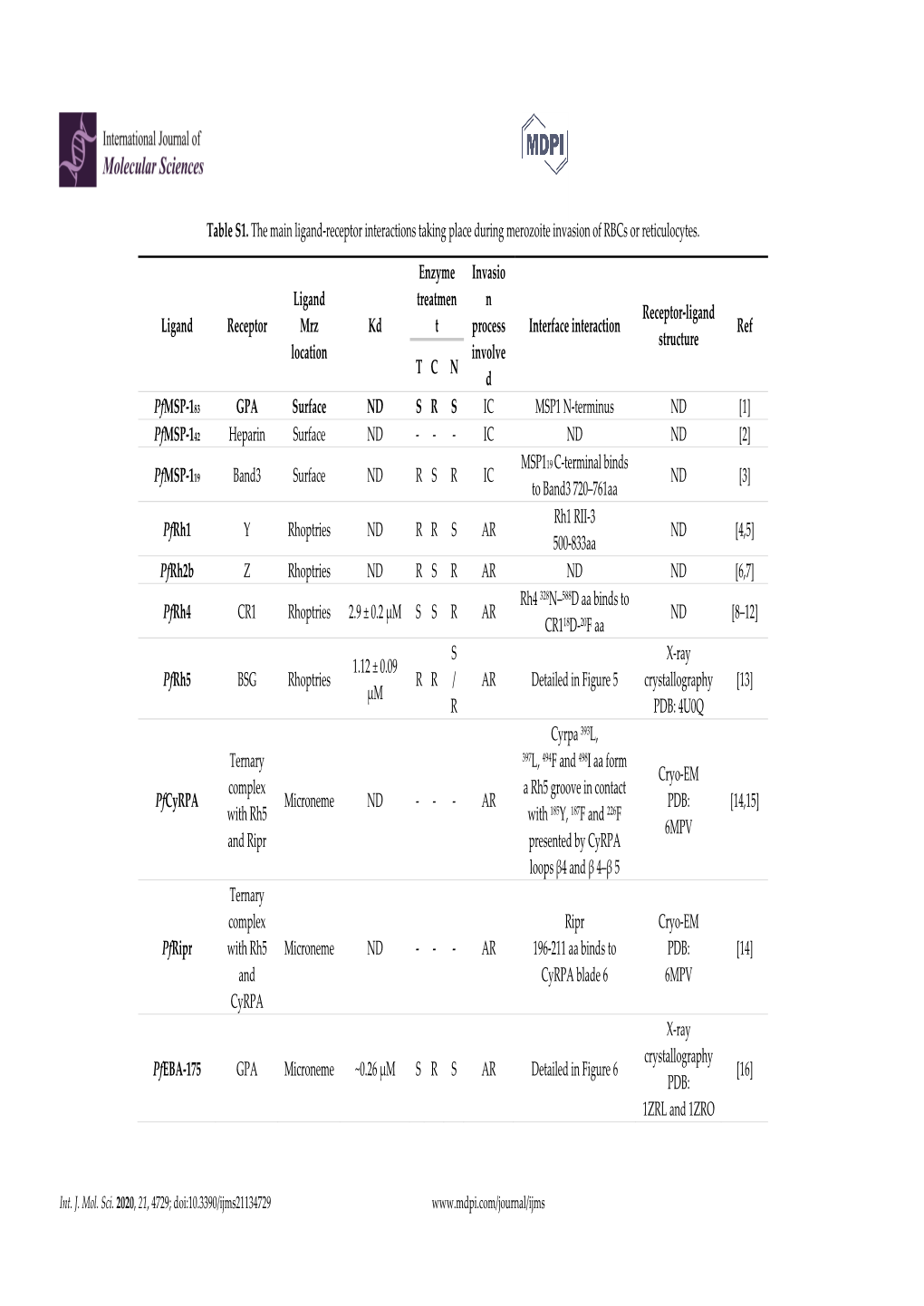
Table S1. the Main Ligand-Receptor Interactions Taking Place During Merozoite Invasion of Rbcs Or Reticulocytes
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

(CD147) Is Induced by C/Ebpβ and Is Differentially Expressed in ALK+
Laboratory Investigation (2017) 97, 1095–1102 © 2017 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0023-6837/17 EMMPRIN (CD147) is induced by C/EBPβ and is differentially expressed in ALK+ and ALK − anaplastic large-cell lymphoma Janine Schmidt1, Irina Bonzheim1, Julia Steinhilber1, Ivonne A Montes-Mojarro1, Carlos Ortiz-Hidalgo2, Wolfram Klapper3, Falko Fend1 and Leticia Quintanilla-Martínez1 Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) is characterized by expression of oncogenic ALK fusion proteins due to the translocation t(2;5)(p23;q35) or variants. Although genotypically a T-cell lymphoma, ALK+ ALCL cells frequently show loss of T-cell-specific surface antigens and expression of monocytic markers. C/EBPβ, a transcription factor constitutively overexpressed in ALK+ ALCL cells, has been shown to play an important role in the activation and differentiation of macrophages and is furthermore capable of transdifferentiating B-cell and T-cell progenitors to macrophages in vitro. To analyze the role of C/EBPβ for the unusual phenotype of ALK+ ALCL cells, C/EBPβ was knocked down by RNA interference in two ALK+ ALCL cell lines, and surface antigen expression profiles of these cell lines were generated using a Human Cell Surface Marker Screening Panel (BD Biosciences). Interesting candidate antigens were further analyzed by immunohistochemistry in primary ALCL ALK+ and ALK − cases. Antigen expression profiling revealed marked changes in the expression of the activation markers CD25, CD30, CD98, CD147, and CD227 after C/EBPβ knockdown. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed a strong, membranous CD147 (EMMPRIN) expression in ALK+ ALCL cases. In contrast, ALK − ALCL cases showed a weaker CD147 expression. -

Duffy, and Mnss Group Systems
Blood Groups – Duffy, and MNSs Group Systems Qun Lu, MD Assistant Professor Division of Transfusion Medicine Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine UCLA, School of Medicine Los Angeles, California 2009-03-12 Duffy Blood Group System History . 1950: Mrs. Duffy, a multiply transfused hemophiliac woman, developed an antibody not reacting with the known RBC antigens. Corresponding antigen was named after Mrs. Duffy . 1951: Fyb antibody was described in a woman with 3 pregnancies. 1955: Majority of blacks tested Fy(a-b-) . 1975: Fy(a-b-) RBCs were shown to resist infection by malaria organism Plasmodium vivax. Later: more Duffy antigens (Fy3, Fy4, Fy5, Fy6) were discovered . ISBT: 008 for the Duffy Blood Group Duffy Antigens . Most common: Fya and Fyb. Present at 6 weeks of gestation, well developed at birth – anti- Fy can cause hemolytic disease of newborn . Duffy antigens can be destroyed by enzymes such as ficin, papain, bromelain, chymotrypsin, ZZAP . When compared to Rh or Kell antigens, Duffy antigens are not very immunogenic. So, anti-Fya or anti-Fyb is not common. Fy (a-b-) is not Fy null, but homozygous for Fyb gene, they express Fyb antigen in other tissues, but not on RBCs → only will produce anti-Fya, not anti-Fyb. Fy (a-b-) is negative for Fy6 antigen which is the receptor for P. vivax (Fy6 is + when Fya + or Fyb+) Duffy Antigens . Phenotype Frequencies Chinese Phenotype Whites % Blacks % % Fy (a+b-) 17 9 90.8 Fy (a+b+) 49 1 8.9 Fy (a-b+) 34 22 0.3 Fy (a-b-) rare 68 0 White donor population: Fya: 66% Caucasians, 10% Blacks, 99% Asians Fya – units: 35% Fyb: 83% Caucasians, 23% Blacks, 18.5% Asians Fyb – units: 15% Fy3: 100% Caucasians, 32% Blacks, 99.9% Asians Duffy Antigens . -

Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook Human and Mouse CD Marker Key Markers - Human Key Markers - Mouse
Welcome to More Choice CD Marker Handbook For more information, please visit: Human bdbiosciences.com/eu/go/humancdmarkers Mouse bdbiosciences.com/eu/go/mousecdmarkers Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook Human and Mouse CD Marker Key Markers - Human Key Markers - Mouse CD3 CD3 CD (cluster of differentiation) molecules are cell surface markers T Cell CD4 CD4 useful for the identification and characterization of leukocytes. The CD CD8 CD8 nomenclature was developed and is maintained through the HLDA (Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens) workshop started in 1982. CD45R/B220 CD19 CD19 The goal is to provide standardization of monoclonal antibodies to B Cell CD20 CD22 (B cell activation marker) human antigens across laboratories. To characterize or “workshop” the antibodies, multiple laboratories carry out blind analyses of antibodies. These results independently validate antibody specificity. CD11c CD11c Dendritic Cell CD123 CD123 While the CD nomenclature has been developed for use with human antigens, it is applied to corresponding mouse antigens as well as antigens from other species. However, the mouse and other species NK Cell CD56 CD335 (NKp46) antibodies are not tested by HLDA. Human CD markers were reviewed by the HLDA. New CD markers Stem Cell/ CD34 CD34 were established at the HLDA9 meeting held in Barcelona in 2010. For Precursor hematopoetic stem cell only hematopoetic stem cell only additional information and CD markers please visit www.hcdm.org. Macrophage/ CD14 CD11b/ Mac-1 Monocyte CD33 Ly-71 (F4/80) CD66b Granulocyte CD66b Gr-1/Ly6G Ly6C CD41 CD41 CD61 (Integrin b3) CD61 Platelet CD9 CD62 CD62P (activated platelets) CD235a CD235a Erythrocyte Ter-119 CD146 MECA-32 CD106 CD146 Endothelial Cell CD31 CD62E (activated endothelial cells) Epithelial Cell CD236 CD326 (EPCAM1) For Research Use Only. -

Complement Recognition Pathways in Renal Transplantation
BRIEF REVIEW www.jasn.org Complement Recognition Pathways in Renal Transplantation Christopher L. Nauser, Conrad A. Farrar, and Steven H. Sacks Medical Research Council Centre for Transplantation, Division of Transplantation Immunology and Mucosal Biology, King’s College London, National Health Service Guy’s and St. Thomas’ Trust, London, United Kingdom ABSTRACT The complement system, consisting of soluble and cell membrane–bound compo- weigh its effect on organ injury and nents of the innate immune system, has defined roles in the pathophysiology of renal rejection with dampening the antimi- allograft rejection. Notably, the unavoidable ischemia-reperfusion injury inherent to crobial functions of the complement sys- transplantation is mediated through the terminal complement activation products tem, such as opsonisation, cell lysis, and C5a and C5b-9. Furthermore, biologically active fragments C3a and C5a, produced recruitment of neutrophils and other in- during complement activation, can modulate both antigen presentation and T cell flammatory cells.7 It is our belief that priming, ultimately leading to allograft rejection. Earlier work identified renal tubule therapeutic strategies can be designed cell synthesis of C3, rather than hepatic synthesis of C3, as the primary source of C3 to specificallytargetthekeyinitiators driving these effects. Recent efforts have focused on identifying the local triggers of of complement activation at the relevant complement activation. Collectin-11, a soluble C-type lectin expressed in renal tis- location, such as complement-binding sue, has been implicated as an important trigger of complement activation in renal anti-HLA antibodies in the vascular tissue. In particular, collectin-11 has been shown to engage L-fucose at sites of compartment or the initiator(s) of local ischemic stress, activating the lectin complement pathway and directing the innate complement activation in the extravas- immune response to the distressed renal tubule. -

Genetic Susceptibility to Chronic Wasting Disease in Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer: Complement Component C1q and Prnp Polymorphisms Julie A
Natural Resource Ecology and Management Natural Resource Ecology and Management Publications 12-2009 Genetic susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in free-ranging white-tailed deer: Complement component C1q and Prnp polymorphisms Julie A. Blanchong Iowa State University, [email protected] Dennis M. Heisey United States Geological Survey Kim T. Scribner Michigan State University Scot V. Libants Michigan State University Chad Johnson UFonilvloerwsit ythi of sW aiscondn asiddn - itMionadisoaln works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/nrem_pubs Part of the Animal Diseases Commons, Genetics Commons, Natural Resources Management See next page for additional authors and Policy Commons, Veterinary Infectious Diseases Commons, and the Zoology Commons The ompc lete bibliographic information for this item can be found at http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/ nrem_pubs/84. For information on how to cite this item, please visit http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/ howtocite.html. This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Natural Resource Ecology and Management at Iowa State University Digital Repository. It has been accepted for inclusion in Natural Resource Ecology and Management Publications by an authorized administrator of Iowa State University Digital Repository. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Genetic susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in free-ranging white- tailed deer: Complement component C1q and Prnp polymorphisms Abstract The eg netic basis of susceptibility to chronic wasting disease (CWD) in free-ranging cervids is of great interest. Association studies of disease susceptibility in free-ranging populations, however, face considerable challenges including: the need for large sample sizes when disease is rare, animals of unknown pedigree create a risk of spurious results due to population admixture, and the inability to control disease exposure or dose. -

Neutrophil Chemoattractant Receptors in Health and Disease: Double-Edged Swords
Cellular & Molecular Immunology www.nature.com/cmi REVIEW ARTICLE Neutrophil chemoattractant receptors in health and disease: double-edged swords Mieke Metzemaekers1, Mieke Gouwy1 and Paul Proost 1 Neutrophils are frontline cells of the innate immune system. These effector leukocytes are equipped with intriguing antimicrobial machinery and consequently display high cytotoxic potential. Accurate neutrophil recruitment is essential to combat microbes and to restore homeostasis, for inflammation modulation and resolution, wound healing and tissue repair. After fulfilling the appropriate effector functions, however, dampening neutrophil activation and infiltration is crucial to prevent damage to the host. In humans, chemoattractant molecules can be categorized into four biochemical families, i.e., chemotactic lipids, formyl peptides, complement anaphylatoxins and chemokines. They are critically involved in the tight regulation of neutrophil bone marrow storage and egress and in spatial and temporal neutrophil trafficking between organs. Chemoattractants function by activating dedicated heptahelical G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). In addition, emerging evidence suggests an important role for atypical chemoattractant receptors (ACKRs) that do not couple to G proteins in fine-tuning neutrophil migratory and functional responses. The expression levels of chemoattractant receptors are dependent on the level of neutrophil maturation and state of activation, with a pivotal modulatory role for the (inflammatory) environment. Here, we provide an overview -

An Anticomplement Agent That Homes to the Damaged Brain and Promotes Recovery After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice
An anticomplement agent that homes to the damaged brain and promotes recovery after traumatic brain injury in mice Marieta M. Rusevaa,1,2, Valeria Ramagliab,1, B. Paul Morgana, and Claire L. Harrisa,3 aInstitute of Infection and Immunity, School of Medicine, Cardiff University, Cardiff CF14 4XN, United Kingdom; and bDepartment of Genome Analysis, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam 1105 AZ, The Netherlands Edited by Douglas T. Fearon, Cornell University, Cambridge, United Kingdom, and approved September 29, 2015 (received for review July 15, 2015) Activation of complement is a key determinant of neuropathology to rapidly and specifically inhibit MAC at sites of complement and disability after traumatic brain injury (TBI), and inhibition is activation, and test its therapeutic potential in experimental TBI. neuroprotective. However, systemic complement is essential to The construct, termed CD59-2a-CRIg, comprises CD59a linked fight infections, a critical complication of TBI. We describe a to CRIg via the murine IgG2a hinge. CD59a prevents assembly targeted complement inhibitor, comprising complement receptor of MAC in cell membranes (16), whereas CRIg binds C3b/iC3b of the Ig superfamily (CRIg) fused with complement regulator CD59a, deposited at sites of complement activation (17). The IgG2a designed to inhibit membrane attack complex (MAC) assembly at hinge promotes dimerization to increase ligand avidity. CD59- sites of C3b/iC3b deposition. CRIg and CD59a were linked via the 2a-CRIg protected in the TBI model, demonstrating that site- IgG2a hinge, yielding CD59-2a-CRIg dimer with increased iC3b/C3b targeted anti-MAC therapeutics may be effective in prevention binding avidity and MAC inhibitory activity. CD59-2a-CRIg inhibited of secondary neuropathology and improve neurologic recovery MAC formation and prevented complement-mediated lysis in vitro. -

The Gerbich Blood Group System: a Review
Review The Gerbich blood group system: a review P.S. Walker and M.E. Reid Antigens in the Gerbich blood group system are expressed on glycoproteins are also known as CD236R, and they attach glycophorin C (GPC) and glycophorin D (GPD), which are both to the RBC membrane through an interaction with protein encoded by a single gene, GYPC. The GYPC gene is located on 4.1R and p55. GPC and GPD contain three domains: an ex- the long arm of chromosome 2, and Gerbich antigens are in- tracellular NH2 domain, a transmembrane domain, and an herited as autosomal dominant traits. There are 11 antigens in intracellular or cytoplasmic COOH domain (Figure 1). GPC the Gerbich blood group system, six of high prevalence (Ge2, Ge3, Ge4, GEPL [Ge10*], GEAT [Ge11*], GETI [Ge12*]) and and GPD are encoded by the same gene, GYPC. When the five of low prevalence (Wb [Ge5], Lsa [Ge6], Ana [Ge7], Dha fi rst AUG initiation codon is used, GPC is encoded, whereas [Ge8], GEIS [Ge9]). GPC and GPD interact with protein 4.1R, when the second AUG is used, GPD is encoded. Thus, GPD contributing stability to the RBC membrane. Reduced lev- is a shorter version of GPC, and the amino acids in GPD els of GPC and GPD are associated with hereditary elliptocy- are identical to those found in GPC but lacking the fi rst 21 tosis, and Gerbich antigens act as receptors for the malarial amino acids at the N-terminal of GPC.9,10 parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Anti-Ge2 and anti-Ge3 have caused hemolytic transfusion reactions, and anti-Ge3 has pro- duced hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). -

Flow Reagents Single Color Antibodies CD Chart
CD CHART CD N° Alternative Name CD N° Alternative Name CD N° Alternative Name Beckman Coulter Clone Beckman Coulter Clone Beckman Coulter Clone T Cells B Cells Granulocytes NK Cells Macrophages/Monocytes Platelets Erythrocytes Stem Cells Dendritic Cells Endothelial Cells Epithelial Cells T Cells B Cells Granulocytes NK Cells Macrophages/Monocytes Platelets Erythrocytes Stem Cells Dendritic Cells Endothelial Cells Epithelial Cells T Cells B Cells Granulocytes NK Cells Macrophages/Monocytes Platelets Erythrocytes Stem Cells Dendritic Cells Endothelial Cells Epithelial Cells CD1a T6, R4, HTA1 Act p n n p n n S l CD99 MIC2 gene product, E2 p p p CD223 LAG-3 (Lymphocyte activation gene 3) Act n Act p n CD1b R1 Act p n n p n n S CD99R restricted CD99 p p CD224 GGT (γ-glutamyl transferase) p p p p p p CD1c R7, M241 Act S n n p n n S l CD100 SEMA4D (semaphorin 4D) p Low p p p n n CD225 Leu13, interferon induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1). p p p p p CD1d R3 Act S n n Low n n S Intest CD101 V7, P126 Act n p n p n n p CD226 DNAM-1, PTA-1 Act n Act Act Act n p n CD1e R2 n n n n S CD102 ICAM-2 (intercellular adhesion molecule-2) p p n p Folli p CD227 MUC1, mucin 1, episialin, PUM, PEM, EMA, DF3, H23 Act p CD2 T11; Tp50; sheep red blood cell (SRBC) receptor; LFA-2 p S n p n n l CD103 HML-1 (human mucosal lymphocytes antigen 1), integrin aE chain S n n n n n n n l CD228 Melanotransferrin (MT), p97 p p CD3 T3, CD3 complex p n n n n n n n n n l CD104 integrin b4 chain; TSP-1180 n n n n n n n p p CD229 Ly9, T-lymphocyte surface antigen p p n p n -

Analysis of RNA Expression Profiles Identifies Dysregulated Vesicle Trafficking Pathways in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2019) 56:5009–5024 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1421-1 Analysis of RNA Expression Profiles Identifies Dysregulated Vesicle Trafficking Pathways in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Anna Bartoletti-Stella1 & Patrizia Corrado2 & Nicola Mometto2 & Simone Baiardi2 & Pascal F. Durrenberger3 & Thomas Arzberger4,5 & Richard Reynolds6 & Hans Kretzschmar5 & Sabina Capellari1,2 & Piero Parchi1,7 Received: 18 July 2018 /Accepted: 1 November 2018 /Published online: 16 November 2018 # Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2018 Abstract Functional genomics applied to the study of RNA expression profiles identified several abnormal molecular processes in experimental prion disease. However, only a few similar studies have been carried out to date in a naturally occurring human prion disease. To better characterize the transcriptional cascades associated with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD), the most common human prion disease, we investigated the global gene expression profile in samples from the frontal cortex of 10 patients with sCJD and 10 non-neurological controls by microarray analysis. The comparison identified 333 highly differentially expressed genes (hDEGs) in sCJD. Functional enrichment Gene Ontology analysis revealed that hDEGs were mainly associated with synaptic transmission, including GABA (q value = 0.049) and glutamate (q value = 0.005) signaling, and the immune/ inflammatory response. Furthermore, the analysis of cellular components performed on hDEGs showed a compromised regu- lation of vesicle-mediated transport with mainly up-regulated genes related to the endosome (q value = 0.01), lysosome (q value = 0.04), and extracellular exosome (q value < 0.01). A targeted analysis of the retromer core component VPS35 (vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35) showed a down-regulation of gene expression (p value= 0.006) and reduced brain protein levels (p value= 0.002). -

Quantitation of the Number of Molecules of Glycophorins C and D on Normal Red Blood Cells Using Radioiodinatedfab Fragments of Monoclonal Antibodies
Quantitation of the Number of Molecules of Glycophorins C and D on Normal Red Blood Cells Using RadioiodinatedFab Fragments of Monoclonal Antibodies By Jon Smythe, Brigitte Gardner, andDavid J. Anstee Two rat monoclonal antibodies (BRAC 1 and BRAC 1 1 ) cytes. Fabfragments of BRAC 1 1 and ERIC 10 gave values have been produced. BRAC 1 recognizes an epitope com- of 143,000 molecules GPC per red blood cell (RBC). Fab mon to the human erythrocyte membrane glycoproteins fragments of BRAC1 gave 225,000 molecules of GPC and glycophorin C (GPC) and glycophorin D (GPD). BRAC 11 GPD per RBC. These results indicate that GPC and GPD is specific for GPC. Fabfragments of these antibodies and together are sufficiently abundantto provide membrane at- BRlC 10, a murine monoclonal anti-GPC,were radioiodin- tachment sites for all ofthe protein 4.1 in normal RBCs. ated and used in quantitative binding assays to measure 0 1994 by The American Societyof Hematology. the number of GPC and GPD molecules on normal erythro- HE SHAPE AND deformability of the mature human (200,000)" and those reported for GPC (50,000).7 This nu- Downloaded from http://ashpublications.org/blood/article-pdf/83/6/1668/612763/1668.pdf by guest on 24 September 2021 T erythrocyte is controlled by a flexible two-dimensional merical differencehas led to the suggestion that a significant lattice of proteins, which together comprise the membrane proportion of protein 4.1 in normal erythrocyte membranes skeleton.' The major components of the skeleton are spec- must be bound to sites other than GPC and GPD.3 The trin, actin, ankyrin, and protein 4.1. -

Immuno 2014 No. 1
Journal of Blood Group Serology and Molecular Genetics VOLUME 30, N UMBER 1, 2014 Immunohematology Journal of Blood Group Serology and Molecular Genetics Volume 30, Number 1, 2014 CONTENTS R EPORT 1 Indirect antiglobulin test-crossmatch using low-ionic-strength saline–albumin enhancement medium and reduced incubation time: effectiveness in the detection of most clinically significant antibodies and impact on blood utilization C.L. Dinardo, S.L. Bonifácio, and A. Mendrone, Jr. R EV I EW 6 Raph blood group system M. Hayes R EPORT 11 I-int phenotype among three individuals of a Parsi community from Mumbai, India S.R. Joshi C A SE R EPORT 14 Evans syndrome in a pediatric liver transplant recipient with an autoantibody with apparent specificity for the KEL4 (Kpb) antigen S.A. Koepsell, K. Burright-Hittner, and J.D. Landmark R EV I EW 18 JMH blood group system: a review S.T. Johnson R EPORT 24 Demonstration of IgG subclass (IgG1 and IgG3) in patients with positive direct antiglobulin tests A. Singh, A. Solanki, and R. Chaudhary I N M EMOR ia M 28 George Garratty, 1935–2014 Patricia A. Arndt and Regina M. Leger 30 A NNOUNCEMENTS 34 A DVERT I SEMENTS 39 I NSTRUCT I ONS FOR A UTHORS E D I TOR - I N -C H I EF E D I TOR ia L B OA RD Sandra Nance, MS, MT(ASCP)SBB Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Patricia Arndt, MT(ASCP)SBB Paul M. Ness, MD Pomona, California Baltimore, Maryland M A N AG I NG E D I TOR James P.