The Comet's Tale
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

On the Origin and Evolution of the Material in 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko
On the Origin and Evolution of the Material in 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Martin Rubin, Cécile Engrand, Colin Snodgrass, Paul Weissman, Kathrin Altwegg, Henner Busemann, Alessandro Morbidelli, Michael Mumma To cite this version: Martin Rubin, Cécile Engrand, Colin Snodgrass, Paul Weissman, Kathrin Altwegg, et al.. On the Origin and Evolution of the Material in 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Space Sci.Rev., 2020, 216 (5), pp.102. 10.1007/s11214-020-00718-2. hal-02911974 HAL Id: hal-02911974 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02911974 Submitted on 9 Dec 2020 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Space Sci Rev (2020) 216:102 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-020-00718-2 On the Origin and Evolution of the Material in 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Martin Rubin1 · Cécile Engrand2 · Colin Snodgrass3 · Paul Weissman4 · Kathrin Altwegg1 · Henner Busemann5 · Alessandro Morbidelli6 · Michael Mumma7 Received: 9 September 2019 / Accepted: 3 July 2020 / Published online: 30 July 2020 © The Author(s) 2020 Abstract Primitive objects like comets hold important information on the material that formed our solar system. Several comets have been visited by spacecraft and many more have been observed through Earth- and space-based telescopes. -

ABCD the 4Th Quarter 2013 Catalog
ABCD springer.com The 4th quarter 2013 catalog Medicine springer.com Dentistry 2 T. Eliades, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; G. Eliades, Dentistry University of Athens, Athens, Greece (Eds.) Medicine Plastics in Dentistry and K. Rötzscher (Ed.) Estrogenicity J. Sadek, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada Forensic and Legal Dentistry A Guide to Safe Practice A Clinician’s Guide to ADHD This book provides a timely and comprehensive This book both explains in detail diverse aspects of review of our current knowledge of BPA release from The Clinician’s Guide to ADHD combines the use- the law as it relates to dentistry and examines key dental polymers and the potential endocrinologi- ful diagnostic and treatment approaches advocated issues in forensic odontostomatology. A central aim cal consequences. After a review of the history and in different guidelines with insights from other is to enable the dentist to achieve a realistic assess- evolution of the issue within the broader biomedical sources, including recent literature reviews and web ment of the legal situation and to reduce uncer- context, the estrogenicity of BPA is explained. The resources. The aim is to provide clinicians with clear, tainties and liability risk. To this end, experts from basic chemistry of the polymers used in dentistry is concise, and reliable advice on how to approach this across the world discuss the dental law in their own then presented in a simplified and clinically relevant complex disorder. The guidelines referred to in com- countries, covering both civil and criminal law and manner. Key chapters in the book carefully evaluate piling the book derive from authoritative sources in highlighting key aspects such as patient rights, insur- the release of BPA from polycarbonate products and different regions of the world, including the United ance, and compensation. -

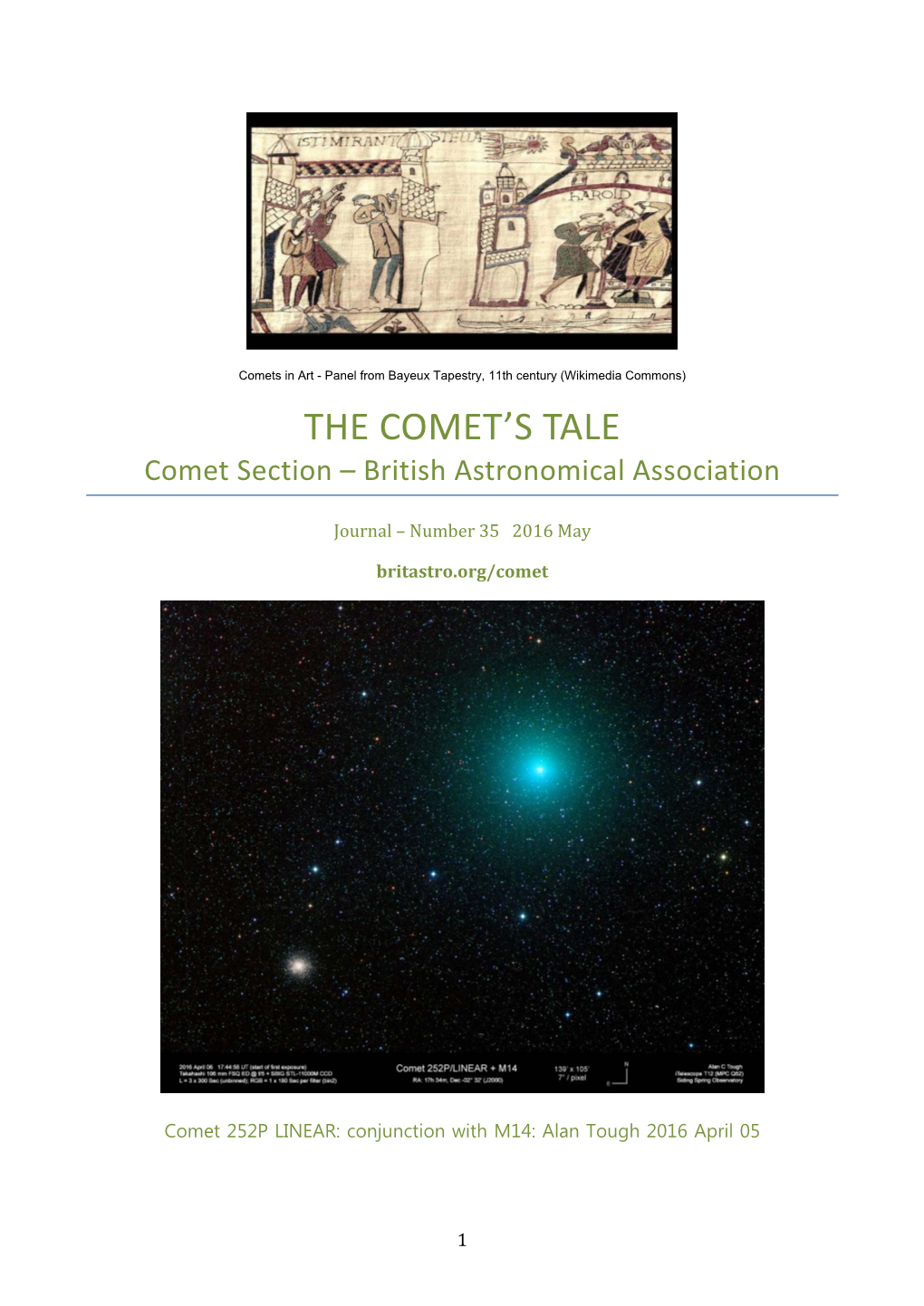
The Comet's Tale, and Therefore the Object As a Whole Would the Section Director Nick James Highlighted Have a Low Surface Brightness
1 Diebold Schilling, Disaster in connection with two comets sighted in 1456, Lucerne Chronicle, 1513 (Wikimedia Commons) THE COMET’S TALE Comet Section – British Astronomical Association Journal – Number 38 2019 June britastro.org/comet Evolution of the comet C/2016 R2 (PANSTARRS) along a total of ten days on January 2018. Composition of pictures taken with a zoom lens from Teide Observatory in Canary Islands. J.J Chambó Bris 2 Table of Contents Contents Author Page 1 Director’s Welcome Nick James 3 Section Director 2 Melvyn Taylor’s Alex Pratt 6 Observations of Comet C/1995 01 (Hale-Bopp) 3 The Enigma of Neil Norman 9 Comet Encke 4 Setting up the David Swan 14 C*Hyperstar for Imaging Comets 5 Comet Software Owen Brazell 19 6 Pro-Am José Joaquín Chambó Bris 25 Astrophotography of Comets 7 Elizabeth Roemer: A Denis Buczynski 28 Consummate Comet Section Secretary Observer 8 Historical Cometary Amar A Sharma 37 Observations in India: Part 2 – Mughal Empire 16th and 17th Century 9 Dr Reginald Denis Buczynski 42 Waterfield and His Section Secretary Medals 10 Contacts 45 Picture Gallery Please note that copyright 46 of all images belongs with the Observer 3 1 From the Director – Nick James I hope you enjoy reading this issue of the We have had a couple of relatively bright Comet’s Tale. Many thanks to Janice but diffuse comets through the winter and McClean for editing this issue and to Denis there are plenty of images of Buczynski for soliciting contributions. 46P/Wirtanen and C/2018 Y1 (Iwamoto) Thanks also to the section committee for in our archive. -

October 2017 BRAS Newsletter
October 2017 Issue Next Meeting: Monday, October 9th at 7PM at HRPO nd (2 Mondays, Highland Road Park Observatory) October Program: BRAS President John Nagle will. reveal how he researches and puts together his Observing Notes column for our newsletter each. month. What's In This Issue? HRPO’s Great American Eclipse Event Summary (Page 2) President’s Message Secretary's Summary Outreach Report - FAE Light Pollution Committee Report Recent Forum Entries 20/20 Vision Campaign Messages from the HRPO Spooky Spectrum Observe The Moon Night Natural Sky Conference HRPO 20th Anniversary Observing Notes – Phoenix & Mythology Like this newsletter? See past issues back to 2009 at http://brastro.org/newsletters.html Newsletter of the Baton Rouge Astronomical Society October 2017 President’s Message The first Sidewalk Astronomy of the season was a success. We had a good time, and About 100 people (adult and children) attended. Ben Toman live streamed on the BRAS Facebook page. See his description in this newsletter. A copy of the proposed, revised By-Laws should be in your mail soon. Read through them, and any proposed changes need to be communicated to me before the November meeting. Wally Pursell (who wrote the original and changed by-laws) and I worked last year on getting the By-Laws updated to the current BRAS policies, and we hope the revised By-Laws will need no revisions for a long time. We need more Globe at Night observations – we are behind in the observations compared to last year at this time. We also need observations of variable stars to help in a school project by a new BRAS member, Shreya. -

How We Found About COMETS
How we found about COMETS Isaac Asimov Isaac Asimov is a master storyteller, one of the world’s greatest writers of science fiction. He is also a noted expert on the history of scientific development, with a gift for explaining the wonders of science to non- experts, both young and old. These stories are science-facts, but just as readable as science fiction.Before we found out about comets, the superstitious thought they were signs of bad times ahead. The ancient Greeks called comets “aster kometes” meaning hairy stars. Even to the modern day astronomer, these nomads of the solar system remain a puzzle. Isaac Asimov makes a difficult subject understandable and enjoyable to read. 1. The hairy stars Human beings have been watching the sky at night for many thousands of years because it is so beautiful. For one thing, there are thousands of stars scattered over the sky, some brighter than others. These stars make a pattern that is the same night after night and that slowly turns in a smooth and regular way. There is the Moon, which does not seem a mere dot of light like the stars, but a larger body. Sometimes it is a perfect circle of light but at other times it is a different shape—a half circle or a curved crescent. It moves against the stars from night to night. One midnight, it could be near a particular star, and the next midnight, quite far away from that star. There are also visible 5 star-like objects that are brighter than the stars. -

Comet Section Observing Guide
Comet Section Observing Guide 1 The British Astronomical Association Comet Section www.britastro.org/comet BAA Comet Section Observing Guide Front cover image: C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp) by Geoffrey Johnstone on 1997 April 10. Back cover image: C/2011 W3 (Lovejoy) by Lester Barnes on 2011 December 23. © The British Astronomical Association 2018 2018 December (rev 4) 2 CONTENTS 1 Foreword .................................................................................................................................. 6 2 An introduction to comets ......................................................................................................... 7 2.1 Anatomy and origins ............................................................................................................................ 7 2.2 Naming .............................................................................................................................................. 12 2.3 Comet orbits ...................................................................................................................................... 13 2.4 Orbit evolution .................................................................................................................................... 15 2.5 Magnitudes ........................................................................................................................................ 18 3 Basic visual observation ........................................................................................................ -

Michael Kühn Detlev Auvermann RARE BOOKS
ANTIQUARIAT 55Michael Kühn Detlev Auvermann RARE BOOKS 1 Rolfinck’s copy ALESSANDRINI, Giulio. De medicina et medico dialogus, libris quinque distinctus. Zurich, Andreas Gessner, 1557. 4to, ff. [6], pp. AUTOLYKOS (AUTOLYCUS OF PYTANE). 356, ff. [8], with printer’s device on title and 7 woodcut initials; a few annotations in ink to the text; a very good copy in a strictly contemporary binding of blind-stamped pigskin, the upper cover stamped ‘1557’, red Autolyci De vario ortu et occasu astrorum inerrantium libri dvo nunc primum de graeca lingua in latinam edges, ties lacking; front-fly almost detached; contemporary ownership inscription of Werner Rolfinck on conuersi … de Vaticana Bibliotheca deprompti. Josepho Avria, neapolitano, interprete. Rome, Vincenzo title (see above), as well as a stamp and duplicate stamp of Breslau University library. Accolti, 1588. 4to, ff. [6], pp. 70, [2]; with large woodcut device on title, and several woodcut diagrams in the text; title a little browned, else a fine copy in 19th-century vellum-backed boards, new endpapers. EUR 3.800.- EUR 4.200.- First edition of Alessandrini’s medical dialogues, his most famous publication and a work of rare erudition. Very rare Latin edition, translated from a Greek manuscript at the Autolycus was a Greek mathematician and astronomer, who probably Giulio Alessandrini (or Julius Alexandrinus de Neustein) (1506–1590) was an Italian physician and author Vatican library, of Autolycus’ work on the rising and setting of the fixed flourished in the second half of the 4th century B.C., since he is said to of Trento who studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Padua, then mathematical science, stars. -

Initial Characterization of Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov
Initial characterization of interstellar comet 2I/Borisov Piotr Guzik1*, Michał Drahus1*, Krzysztof Rusek2, Wacław Waniak1, Giacomo Cannizzaro3,4, Inés Pastor-Marazuela5,6 1 Astronomical Observatory, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland 2 AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland 3 SRON, Netherlands Institute for Space Research, Utrecht, the Netherlands 4 Department of Astrophysics/IMAPP, Radboud University, Nijmegen, the Netherlands 5 Anton Pannekoek Institute for Astronomy, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands 6 ASTRON, Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy, Dwingeloo, the Netherlands * These authors contributed equally to this work; email: [email protected], [email protected] Interstellar comets penetrating through the Solar System had been anticipated for decades1,2. The discovery of asteroidal-looking ‘Oumuamua3,4 was thus a huge surprise and a puzzle. Furthermore, the physical properties of the ‘first scout’ turned out to be impossible to reconcile with Solar System objects4–6, challenging our view of interstellar minor bodies7,8. Here, we report the identification and early characterization of a new interstellar object, which has an evidently cometary appearance. The body was discovered by Gennady Borisov on 30 August 2019 UT and subsequently identified as hyperbolic by our data mining code in publicly available astrometric data. The initial orbital solution implies a very high hyperbolic excess speed of ~32 km s−1, consistent with ‘Oumuamua9 and theoretical predictions2,7. Images taken on 10 and 13 September 2019 UT with the William Herschel Telescope and Gemini North Telescope show an extended coma and a faint, broad tail. We measure a slightly reddish colour with a g′–r′ colour index of 0.66 ± 0.01 mag, compatible with Solar System comets. -

The April 2017
The Volume 126 No. 4 April 2017 Bullen Monthly newsleer of the Astronomical Society of South Australia Inc In this issue: ♦ Vera Rubin - the “mother” of dark maer dies ♦ Astronomical discoveries during ASSA’s second decade ♦ Trappist-1 - 7 Earth-sized planets orbit this dim star ♦ Observing Copeland’s Septet in Leo ♦ Registered by Australia Post Visit us on the web: Bullen of the ASSA Inc 1 April 2017 Print Post Approved PP 100000605 www.assa.org.au In this issue: ASSA Acvies 3-4 Details of general meengs, viewing nights etc History of Astronomy 5-6 ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY of Astronomical discoveries in ASSA’s second decade SOUTH AUSTRALIA Inc Saying Goodbye 7-8 GPO Box 199, Adelaide SA 5001 Vera Rubin, mother of dark maer dies The Society (ASSA) can be contacted by post to the Astro News 9-10 address above, or by e-mail to [email protected]. Latest astronomical discoveries and reports Membership of the Society is open to all, with the only prerequisite being an interest in Astronomy. The Sky this month 11-14 Solar System, Comets, Variable Stars, Deep Sky Membership fees are: Full Member $75 ASSA Contact Informaon 15 Concessional Member $60 Subscribe e-Bullen only; discount $20 Members’ Image Gallery 16 Concession informaon and membership brochures can A gallery of members’ astrophotos be obtained from the ASSA web site at: hp://www.assa.org.au or by contacng The Secretary (see contacts page). Member Submissions Sister Society relaonships with: Submissions for inclusion in The Bullen are welcome Orange County Astronomers from all members; submissions may be held over for later edions. -

The Comet's Tale
THE COMET’S TALE Journal of the Comet Section of the British Astronomical Association Number 33, 2014 January Not the Comet of the Century 2013 R1 (Lovejoy) imaged by Damian Peach on 2013 December 24 using 106mm F5. STL-11k. LRGB. L: 7x2mins. RGB: 1x2mins. Today’s images of bright binocular comets rival drawings of Great Comets of the nineteenth century. Rather predictably the expected comet of the century Contents failed to materialise, however several of the other comets mentioned in the last issue, together with the Comet Section contacts 2 additional surprise shown above, put on good From the Director 2 appearances. 2011 L4 (PanSTARRS), 2012 F6 From the Secretary 3 (Lemmon), 2012 S1 (ISON) and 2013 R1 (Lovejoy) all Tales from the past 5 th became brighter than 6 magnitude and 2P/Encke, 2012 RAS meeting report 6 K5 (LINEAR), 2012 L2 (LINEAR), 2012 T5 (Bressi), Comet Section meeting report 9 2012 V2 (LINEAR), 2012 X1 (LINEAR), and 2013 V3 SPA meeting - Rob McNaught 13 (Nevski) were all binocular objects. Whether 2014 will Professional tales 14 bring such riches remains to be seen, but three comets The Legacy of Comet Hunters 16 are predicted to come within binocular range and we Project Alcock update 21 can hope for some new discoveries. We should get Review of observations 23 some spectacular close-up images of 67P/Churyumov- Prospects for 2014 44 Gerasimenko from the Rosetta spacecraft. BAA COMET SECTION NEWSLETTER 2 THE COMET’S TALE Comet Section contacts Director: Jonathan Shanklin, 11 City Road, CAMBRIDGE. CB1 1DP England. Phone: (+44) (0)1223 571250 (H) or (+44) (0)1223 221482 (W) Fax: (+44) (0)1223 221279 (W) E-Mail: [email protected] or [email protected] WWW page : http://www.ast.cam.ac.uk/~jds/ Assistant Director (Observations): Guy Hurst, 16 Westminster Close, Kempshott Rise, BASINGSTOKE, Hampshire. -

Comet Prospects for 2017
Comet Prospects for 2017 February could be a busy month with the possibility of three periodic comets visible in binoculars. Three comets in parabolic orbits may also become visible in binoculars. These predictions focus on comets that are likely to be within range of visual observers, though comets often do not behave as expected and can spring surprises. Members are encouraged to make visual magnitude estimates, particularly of periodic comets, as long term monitoring over many returns helps understand their evolution. Please submit your magnitude estimates in ICQ format. Guidance on visual observation and how to submit estimates is given in the BAA Observing Guide to Comets. Drawings are also useful, as the human eye can sometimes discern features that initially elude electronic devices. Theories on the structure of comets suggest that any comet could fragment at any time, so it is worth keeping an eye on some of the fainter comets, which are often ignored. They would make useful targets for those making electronic observations, especially those with time on instruments such as the Faulkes telescopes. Such observers are encouraged to report electronic visual equivalent magnitude estimates via COBS. When possible use a waveband approximating to Visual or V magnitudes. These estimates can be used to extend the visual light curves, and hence derive more accurate absolute magnitudes. Such observations of periodic comets are particularly valuable as observations over many returns allow investigation into the evolution of comets. In addition to the information in the BAA Handbook and on the Section web pages, ephemerides for the brighter observable comets are published in the Circulars, and ephemerides for new and currently observable comets are on the JPL, CBAT and Seiichi Yoshida's web pages. -

Detecting the Yarkovsky Effect Among Near-Earth Asteroids From
Detecting the Yarkovsky effect among near-Earth asteroids from astrometric data Alessio Del Vignaa,b, Laura Faggiolid, Andrea Milania, Federica Spotoc, Davide Farnocchiae, Benoit Carryf aDipartimento di Matematica, Universit`adi Pisa, Largo Bruno Pontecorvo 5, Pisa, Italy bSpace Dynamics Services s.r.l., via Mario Giuntini, Navacchio di Cascina, Pisa, Italy cIMCCE, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS, Sorbonne Universits, UPMC Univ. Paris 06, Univ. Lille, 77 av. Denfert-Rochereau F-75014 Paris, France dESA SSA-NEO Coordination Centre, Largo Galileo Galilei, 1, 00044 Frascati (RM), Italy eJet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology, 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, 91109 CA, USA fUniversit´eCˆote d’Azur, Observatoire de la Cˆote d’Azur, CNRS, Laboratoire Lagrange, Boulevard de l’Observatoire, Nice, France Abstract We present an updated set of near-Earth asteroids with a Yarkovsky-related semi- major axis drift detected from the orbital fit to the astrometry. We find 87 reliable detections after filtering for the signal-to-noise ratio of the Yarkovsky drift esti- mate and making sure the estimate is compatible with the physical properties of the analyzed object. Furthermore, we find a list of 24 marginally significant detec- tions, for which future astrometry could result in a Yarkovsky detection. A further outcome of the filtering procedure is a list of detections that we consider spurious because unrealistic or not explicable with the Yarkovsky effect. Among the smallest asteroids of our sample, we determined four detections of solar radiation pressure, in addition to the Yarkovsky effect. As the data volume increases in the near fu- ture, our goal is to develop methods to generate very long lists of asteroids with reliably detected Yarkovsky effect, with limited amounts of case by case specific adjustments.