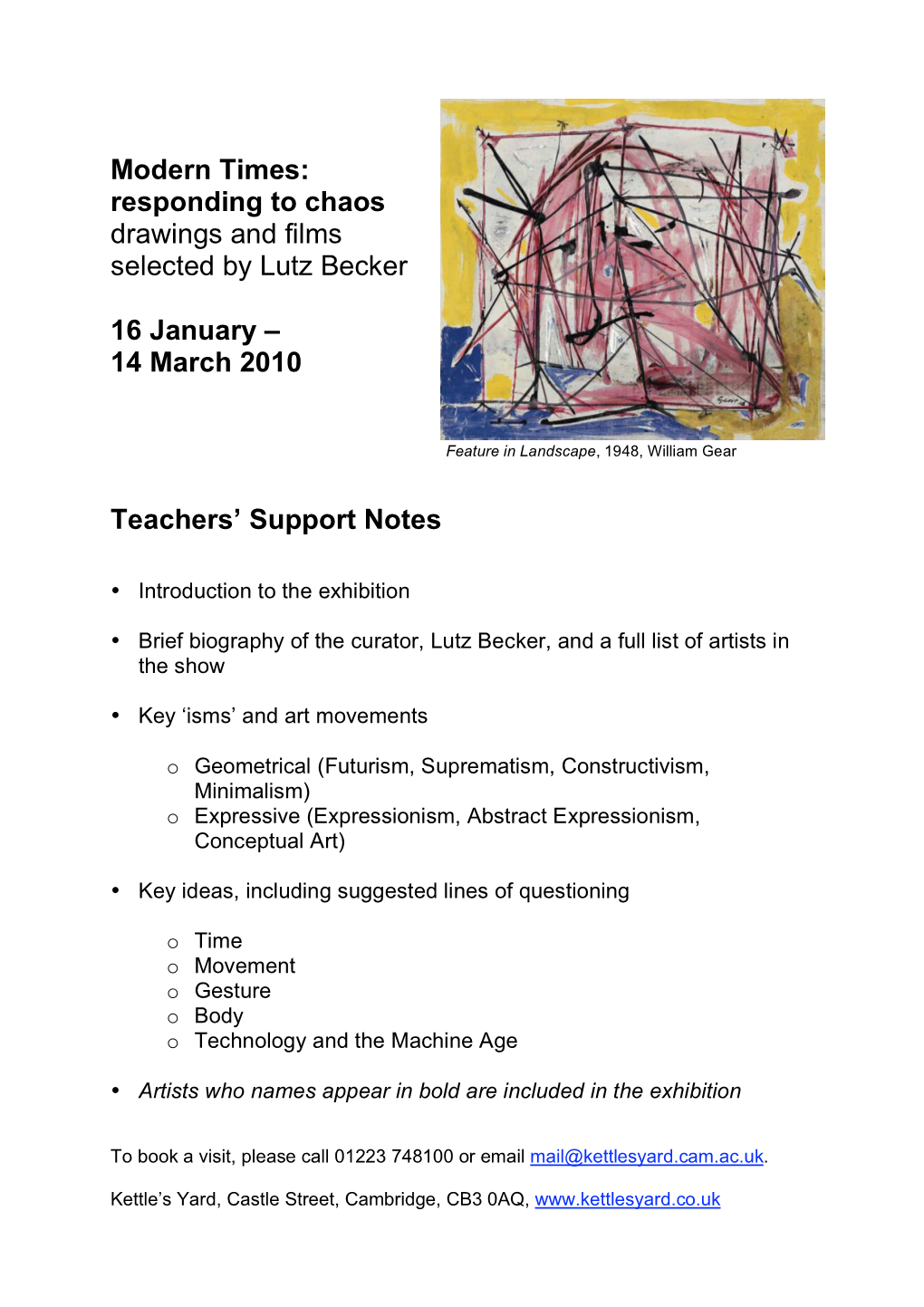
Modern Times: Responding to Chaos Drawings and Films Selected by Lutz Becker
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

A Legacy Regained: Niko and the Russian Avant-Garde
A LEGACY REGAINED: NIKO AND THE RUSSIAN AVANT-GARDE PALACE EDITIONS Contents 8 Foreword Evgeniia Petrova 9 Preface Job de Ruiter 10 Acknowledgements and Notes to the Reader John E. Bowlt and Mark Konecny 13 Introduction John E. Bowlt and Mark Konecny Part I. Nikolai Khardzhiev and the Russian Avant Garde Remembering Nikolai Khardzhiev 21 Nikolai Khardzhiev RudolfDuganov 24 The Future is Now! lra Vrubel-Golubkina 36 Nikolai Khardzhiev and the Suprematists Nina Suetina 43 Nikolai Khardzhiev and the Maiakovsky Museum, Moscow Gennadii Aigi 50 My Memoir of Nikolai Khardzhiev Vyacheslav Ivanov 53 Nikolai Khardzhiev and My Family Zoya Ender-Masetti 57 My Meetings with Nikolai Khardzhiev Galina Demosfenova 59 Nikolai Khardzhiev, Knight of the Avant-garde Jean-C1aude Marcade 63 A Sole Encounter Szymon Bojko 65 The Guardian of the Temple Andrei Nakov 69 A Prophet in the Wilderness John E. Bowlt 71 The Great Commentator, or Notes About the Mole of History Vasilii Rakitin Writings by Nikolai Khardzhiev Essays 75 Autobiography 76 Poetry and Painting:The Early Maiakovsky 81 Cubo-Futurism 83 Maiakovsky as Partisan 92 Painting and Poetry Profiles ofArtists and Writers 99 Elena Guro 101 Boris Ender 103 In Memory of Natalia Goncharova and Mikhail Larionov 109 Vladimir Maiakovsky 122 Velimir Khlebnikov 131 Alexei Kruchenykh 135 VladimirTatlin 137 Alexander Rodchenko 139 EI Lissitzky Contents Texts Edited and Annotated by Nikolai Khardzhiev 147 Nikolai Khardzhiev Introductions to Kazimir Malevich's Autobiography (Parts 1 and 2) 157 Kazimir Malevieh Autobiography 172 Nikolai Khardzhiev Introduction to Mikhail Matiushin's The Russian Cubo-Futurists 173 Mikhail Matiushin The Russian Cubo-Futurists 183 Alexei Morgunov A Memoir 186 Nikolai Khardzhiev Introduction to Khlebnikov Is Everywhere! 187 Khlebnikov is Everywhere! Memoirs by Oavid Burliuk, Nadezhda Udaltsova, Amfian Reshetov, and on Osip Mandelshtam 190 Nikolai Khardzhiev Introduction to Lev Zhegin's Remembering Vasilii Chekrygin 192 Lev Zhegin Remembering Vasilii Chekrygin Part 11. -

Eduardo Paolozzi Born Edinburgh, Scotland. 1924 Resident London
Eduardo Paolozzi Born Edinburgh, Scotland. 1924 ResidentLondon Eduardo Paolozziwas visited in London by MT in Octo- really preparedto offer him the kind of freedom or the ber, 1968. When A & T was describedto Paolozzion degreeof accessto their personneland hardwarethat he that occasion,he respondedby expressinginterest in required--thoughthe corporation was equipped techni- working with computers. His work at that time was cally to deal with whatever demandsthe artist might involved in computer-generatedimagery, and thus it was make in the areaof computer graphics.On the evening natural that he should wish to developthese ideas. In after this encounter,Paolozzi telephoned Jane Living- Paolozzi'sletter to us of October 30, he spoke about the ston from his hotel and explainedto her that he saw no areashe visualizedpursuing: point in touring the San Josefacility or bothering It is my intention of bringing a portfolio of schemes further with lBM. Paolozzithen visited Wyle Laborator- in connection with the Los Angelesshow. These ies.He was interviewedby the company's president, schemesare an extension of work concerningimages Frank Wyle [1] ; Gail Scott wrote the following memo and words (ref: the Berkeleycatalogue; Christopher recountingthis event and later discussion: Finch's book Art and Objectsl. You may realizethat I did a certain amount of com- puter researchwhile at Berkeley,but the Art Depart- ment there was unable to extend any of these ideas- which certainly could be realizedwithin the frame- work that we discussedin London during your visit. At the moment, I have an assistantworking on colour mosaicsand endlesspermutations on the grid pattern. This is accordingto my interpretation of current computer literature and can be used in connection with sound experiments.Also the reverse,I under- stand, is possible;which is, soundscan be usedto create patterns. -

Politics and History of 20Th Century Europe Shifted Radically, Swinging Like a Pendulum in a Dramatic Cause and Effect Relationship
Politics and history of 20th Century Europe shifted radically, swinging like a pendulum in a dramatic cause and effect relationship. I explored the correlation between art movements and revolutions, focusing specifically on Russian Constructivism and the Russian Revolution in the 1920s, as well as the Punk movement in East Germany that instigated the Fall of the Berlin Wall. I am fascinated by the structural similarities of these movements, and their shared desire of egalitarianism, which progressed with the support of opposing political ideologies. I chose fashion design because it was at the forefront of both Constructivism and Punk, and because it is what I hope to pursue as a career. After designing a full collection in 2D, I wanted to challenge myself by bringing one of my garments to life. The top is a plaster cast cut in half and shaped with epoxy and a lace up mechanism so that it can be worn. A paste made of plaster and paper pulp serves to attach the pieces of metal and create a rough texture that produces the illusion of a concrete wall. For the skirt, I created 11 spheres of various sizes by layering and stitching together different shades of white, cream, off-white, grey, and beige colored fabrics, with barbed wire and hardware cloth, that I then stuffed with Polyfil. The piece is wearable, and meant to constrict one’s freedom of movement - just like the German Democratic Party constricted freedom of speech in East Germany. The bottom portion is meant to suffocate the body in a different approach, with huge, outlandish, forms like the ones admired by the Constructivists. -

The Conceptual Art Game a Coloring Game Inspired by the Ideas of Postmodern Artist Sol Lewitt
Copyright © 2020 Blick Art Materials All rights reserved 800-447-8192 DickBlick.com The Conceptual Art Game A coloring game inspired by the ideas of postmodern artist Sol LeWitt. Solomon (Sol) LeWitt (1928-2007), one of the key pioneers of conceptual art, noted that, “Each person draws a line differently and each person understands words differently.” When he was working for architect I.M. Pei, LeWitt noted that an architect Materials (required) doesn't build his own design, yet he is still Graph or Grid paper, recommend considered an artist. A composer requires choice of: musicians to make his creation a reality. Koala Sketchbook, Circular Grid, He deduced that art happens before it 8.5" x 8.5", 30 sheets (13848- becomes something viewable, when it is 1085); share two across class conceived in the mind of the artist. Canson Foundation Graph Pad, 8" x 8" grid, 8.5" x 11" pad, 40 He said, “When an artist uses a conceptual sheets, (10636-2885); share two form of art, it means that all of the planning across class and decisions are made beforehand and Choice of color materials, the execution is a perfunctory affair. The recommend: idea becomes a machine that makes the Blick Studio Artists' Colored art.” Pencils, set of 12 (22063-0129); Over the course of his career, LeWitt share one set between two students produced approximately 1,350 designs known as “Wall Drawings” to be completed at specific sites. Faber-Castell DuoTip Washable Markers, set of 12 (22314-0129); The unusual thing is that he rarely painted one share one set between two himself. -

Bideford Bay (1946) David Bomberg
Chapter 5: Compositional Effects of Color Color (hue, chroma and value) effect the perception of space… …both 2D… (shapes can be made to seem larger or smaller by altering color) …and 3D (advancing and receding). The size of colored regions also effects the perceived color (larger areas seem brighter). Aerial Perspective or Atmospheric Perspective • (both phrases refer to the same phenomena – they are interchangeable terms) • Several color effects can be described in terms of Aerial perspective. • — Colors tend to be lighter and lower in chroma in the distance. (color moves closer to sky color) • — Contrast in value diminishes in the distance. (value range diminishes in distance) • — Sharp contrasting edge tends to bring (at least) one surface forward. (sharp detail or edges advance forms; blurred forms recede) The Space Between • The physical cause of atmospheric perspective in nature is dust and moisture in the air. • These scattered particles diffuse light, thereby softening the appearance of distant objects and causing their color to move closer to the prevailing sky color. • The Moisture-filled Space Between • Fog is an atmosphere densely filled with moisture – atmospheric perspective can be apparent at a very short distance. • Albert Bierstadt’s 19th c. paintings of the American West were composed to express the vast space open to expansion. • Aerial Perspective • Lighter values, reduced contrast, lower chroma all tend to establish a sense receding (distant) space. • Limited structure and detail are present — there are David Bomberg no linear perspective clues to structure, location, size or distance. Yet there is a definite sense of space— near regions and far regions. -

The Leeds Arts Club and the New Age: Art and Ideas in a Time of War by Tom Steele Thank You Very Much Nigel, That's a Very Generous Introduction
TRANSCRIPT Into the Vortex: The Leeds Arts Club and the New Age: Art and Ideas in a Time of War by Tom Steele Thank you very much Nigel, that's a very generous introduction. Thank you for inviting me back to the Leeds Art Gallery where I spent so many happy hours. As Nigel said, the book was actually published in 1990, but it was a process of about 5 or 6 year work, in fact it's turned into a PHD. I've not done a lot of other work on it since, I have to say some very very good work has been done on Tom Perry and other peoples in the meantime, and it's grievously in danger of being the new edition, which I might or might not get around to, but maybe somebody else will. Anyway, what I'm going to do is to read a text. I'm not very good at talking extensively, and it should take about 40 minutes, 45 minutes. This should leave us some time for a discussion afterwards, I hope. Right, I wish I'd thought about the title and raw text before I offered the loan up to the gallery, because it makes more sense, and you'll see why as we go along. I want to take the liberty of extending the idea of war to cover the entire decade 1910-1920, one of the most rebellious and innovative periods in the history of British art. By contrast, in cultural terms, we now live in a comparatively quiet period. -

All These Post-1965 Movements Under the “Conceptual Art” Umbrella
All these post-1965 movements under the “conceptual art” umbrella- Postminimalism or process art, Site Specific works, Conceptual art movement proper, Performance art, Body Art and all combinations thereof- move the practice of art away from art-as-autonomous object, and art-as-commodification, and towards art-as-experience, where subject becomes object, hierarchy between subject and object is critiqued and intersubjectivity of artist, viewer and artwork abounds! Bruce Nauman, Live-Taped Video Corridor, 1970, Conceptual Body art, Postmodern beginning “As opposed to being viewers of the work, once again they are viewers in it.” (“Subject as Object,” p. 199) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9IrqXiqgQBo A Postmodern beginning: Body art and Performance art as critique of art-as-object recap: -Bruce Nauman -Vito Acconci focus on: -Chris Burden -Richard Serra -Carolee Schneemann - Hannah Wilke Chapter 3, pp. 114-132 (Carolee Schneemann and Hannah Wilke, First Generation Feminism) Bruce Nauman, Bouncing Two Balls Between the Floor and Ceiling with Changing Rhythms, 1967-1968. 16mm film transferred to video (black and white, sound), 10 min. Body art/Performance art, Postmodern beginning- performed elementary gestures in the privacy of his studio and documented them in a variety of media Vito Acconci, Following Piece, 1969, Body art, Performance art- outside the studio, Postmodern beginning Video documentation of the event Print made from bite mark Vito Acconci, Trademarks, 1970, Body art, Performance art, Postmodern beginning Video and Print documentation -

Feininger Klee Bauhaus Feininger Klee Bauhaus
feininger klee bauhaus feininger klee bauhaus 01.05.2019 — 18.01.2020 New York Dortmund Wien Inhalt contents 06 Lyonel Feininger – vom Karikaturisten zum Bauhausmeister Wolfgang Büche 07 Lyonel Feininger —from Caricaturist to Bauhaus Master Wolfgang Büche 22 werke Lyonel Feininger 22 works by Lyonel Feininger 60 lyonel feininger über paul klee 61 lyonel feininger on paul klee 70 werke Paul Klee 70 works by paul klee 84 biografien 84 biographies 92 ausgestellte werke 92 exhibited works 104 impressum Die Bauhausmeister auf dem Dach des Bauhauses in Dessau anlässlich der Eröffnung am 4. und 5. Dezember 1926 The Bauhaus Masters on the roof of the Bauhaus in Dessau at its opening on December 4 & 5, 1926 104 imprint Lyonel Feininger 04 05 Lyonel Feininger Lyonel Feininger – vom Karikaturisten —from Caricaturist zum Bauhausmeister to Bauhaus Master Wolfgang Büche Wolfgang Büche Als Lyonel Feininger im Mai 1919 als der erstberufene Bau- When Lyonel Feininger was sitting on the train to Weimar hausmeister im Zug nach Weimar saß, gehörte er in Deutsch- in May 1919 on his way to become one of the first Bauhaus land bereits zu den arrivierten Malern. Es gab Sammler masters appointed to teach at the school, he was already seiner Werke und Museen begannen sich für sein Schaffen a well-established painter in Germany. There were already zu interessieren. Mit seiner ersten Einzelausstellung 1917 in a few collectors of his work, and museums were starting to der Galerie Der Sturm in Berlin war er endgültig als einer der take an interest in him. His first solo exhibition at the Galerie Protagonisten der Moderne in Deutschland eingeführt. -

Intangible Heritage(S): an Interplay of Design, Social and Cultural Critiques of the Built Environment
TANGIBLE - INTANGIBLE HERITAGE(S): AN INTERPLAY OF DESIGN, SOCIAL AND CULTURAL CRITIQUES OF THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT • Paper / Proposal Title: ‘ARCHITECTS – WHERE IS YOUR VORTEX? VORTICISM, THE CITY AND URBAN EXPERIENCE • Author(s) Name: Dr. JONATHAN BLACK FRSA • University or Company Affiliation: KINGSTON SCHOOL OF ART, KINGSTON UNIVERSITY • Presentation Method. I would like to: i. present in person (with/without a written paper)* • Abstract (300 words): From its conception in the spring of 1914 the British avant garde art movement known as Vorticism was obsessed with the city and urban existence as central to the forward march of technologically innovative modernity. Indeed, the movement largely owed its very name to the American poet Ezra Pound having already identified London as the ‘great modern vortex’, the end point for all the energies of modern life and of British/Imperial power. My paper is rooted in many years of research into Vorticism and British Art before, during and after the First World War. It will focus on some of the many images that evoked the strikingly positive Vorticist vision of the city – one that as much looked to the example of vertically vertiginous New York as that by experimental thinkers on the European continent – by leading adherents of the movement such as: Wyndham Lewis, Edward Wadsworth, Frederick Etchells, Jessica Dismorr and Helen Saunders. Living in London much of their imagery was indebted to that city. However, examples will be discussed alongside a group of woodcut prints produced c. 1914-18 by Wadsworth inspired by the cities and industrial towns of his native Yorkshire such as Leeds, Bradford, Halifax and Huddersfield. -

International Journal of Education & the Arts
International Journal of Education & the Arts Editors Terry Barrett Peter Webster The Ohio State University University of Southern California Eeva Anttila Brad Haseman Theatre Academy Helsinki Queensland University of Technology http://www.ijea.org/ ISSN: 1529-8094 Volume 17 Number 21 July 23, 2016 Land Art In Preschools. An Art Practice Ingunn Solberg Queen Maud University College of Early Childhood Education, Norway Citation: Solberg, I. (2016). Land art in preschools. An art practice. International Journal of Education & the Arts, 17(21). Retrieved from http://www.ijea.org/v17n21/. Abstract The basis for my article is how, and if, a collaborative land art project can provide opportunities for such co-creating as suggested in the national framework plan for preschools, which explicitly states the child as a co-creator of a shared expressive culture. I further wish to propose land art as a meaningful cultural practice, closely connected to children’s physical awareness and sense of place. In doing so, I use the concepts of sensation, making and knowledge, exploring them as mutually beneficial. The way I worked to explore these matters, was to initiate and conduct a land art project in an open air preschool. I was with a group of children for several days. Adults and children worked together to make a shape, in a landscape well known to the children. While initiating, suggesting and participating, I experienced and observed the children’s interaction with the land, with forms of knowledge and with each other. IJEA Vol. 17 No. 21 - http://www.ijea.org/v17n21/ 2 My experiences and observations, that constitute my data from this project, are composed into a story. -

Futurism's Photography
Futurism’s Photography: From fotodinamismo to fotomontaggio Sarah Carey University of California, Los Angeles The critical discourse on photography and Italian Futurism has proven to be very limited in its scope. Giovanni Lista, one of the few critics to adequately analyze the topic, has produced several works of note: Futurismo e fotografia (1979), I futuristi e la fotografia (1985), Cinema e foto- grafia futurista (2001), Futurism & Photography (2001), and most recently Il futurismo nella fotografia (2009).1 What is striking about these titles, however, is that only one actually refers to “Futurist photography” — or “fotografia futurista.” In fact, given the other (though few) scholarly studies of Futurism and photography, there seems to have been some hesitancy to qualify it as such (with some exceptions).2 So, why has there been this sense of distacco? And why only now might we only really be able to conceive of it as its own genre? This unusual trend in scholarly discourse, it seems, mimics closely Futurism’s own rocky relationship with photography, which ranged from an initial outright distrust to a later, rather cautious acceptance that only came about on account of one critical stipulation: that Futurist photography was neither an art nor a formal and autonomous aesthetic category — it was, instead, an ideological weapon. The Futurists were only able to utilize photography towards this end, and only with the further qualification that only certain photographic forms would be acceptable for this purpose: the portrait and photo-montage. It is, in fact, the very legacy of Futurism’s appropriation of these sub-genres that allows us to begin to think critically about Futurist photography per se. -

The Joan and Lester Avnet Collection in the Museum of Modern Art : Exhibited, Apr
A Treasury of modern drawing : the Joan and Lester Avnet Collection in the Museum of Modern Art : exhibited, Apr. 27-July 4, 1978 William S. Lieberman Date 1978 Publisher The Museum of Modern Art ISBN 08707060980 Exhibition URL www.moma.org/calendar/exhibitions/2355 The Museum of Modern Art's exhibition history—from our founding in 1929 to the present—is available online. It includes exhibition catalogues, primary documents, installation views, and an index of participating artists. MoMA © 2017 The Museum of Modern Art A TREASURY OF MODERN I DRAWING THE JOANAND LESTER AVNET COLLECTION Archive MoMA 1210 ft TREASURY OF MODERN DRAWING A TREASURY OF MODERN DRAWING THE JOANAND LESTER AVNET COLLECTION IN THE MUSEUMOF MODERNART WILLIAMS.LIEBERMAN THE MUSEUM OFMODERN ART, NEW YORK 4«-CH'«C lAOrf/) 12-10 MUSEUM OF MODERNART LIBRARY Copyright © 1978 by The Museum of Modern Art All rights reserved The Museum of Modern Art 11 West 53 Street New York, N.Y. 10019 Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 78-50658 ISBN: 0-87070-609-8 Designed by Steven Schoenfelder Printed by Meriden Gravure Co., Meriden, Conn. Bound by Sendor Bindery, Inc., New York, N.Y. Printed in the United States of America cover Matisse: The Necklace. 1950. Brush and ink, ioVz x i6Vi" frontispiece Feininger: The Town ofLegefeld. 1916. Pen and ink, charcoal, 9 Vi x 12V2" INTRODUCTION 7 ILLUSTRATIONS 35 CA TALOG OF THE COLLECTION 108 Lester Avnet was a devoted son, brother, husband, and father. His life was dedicated to his family; indeed he thought more often of them, always with pride, than he did of himself.