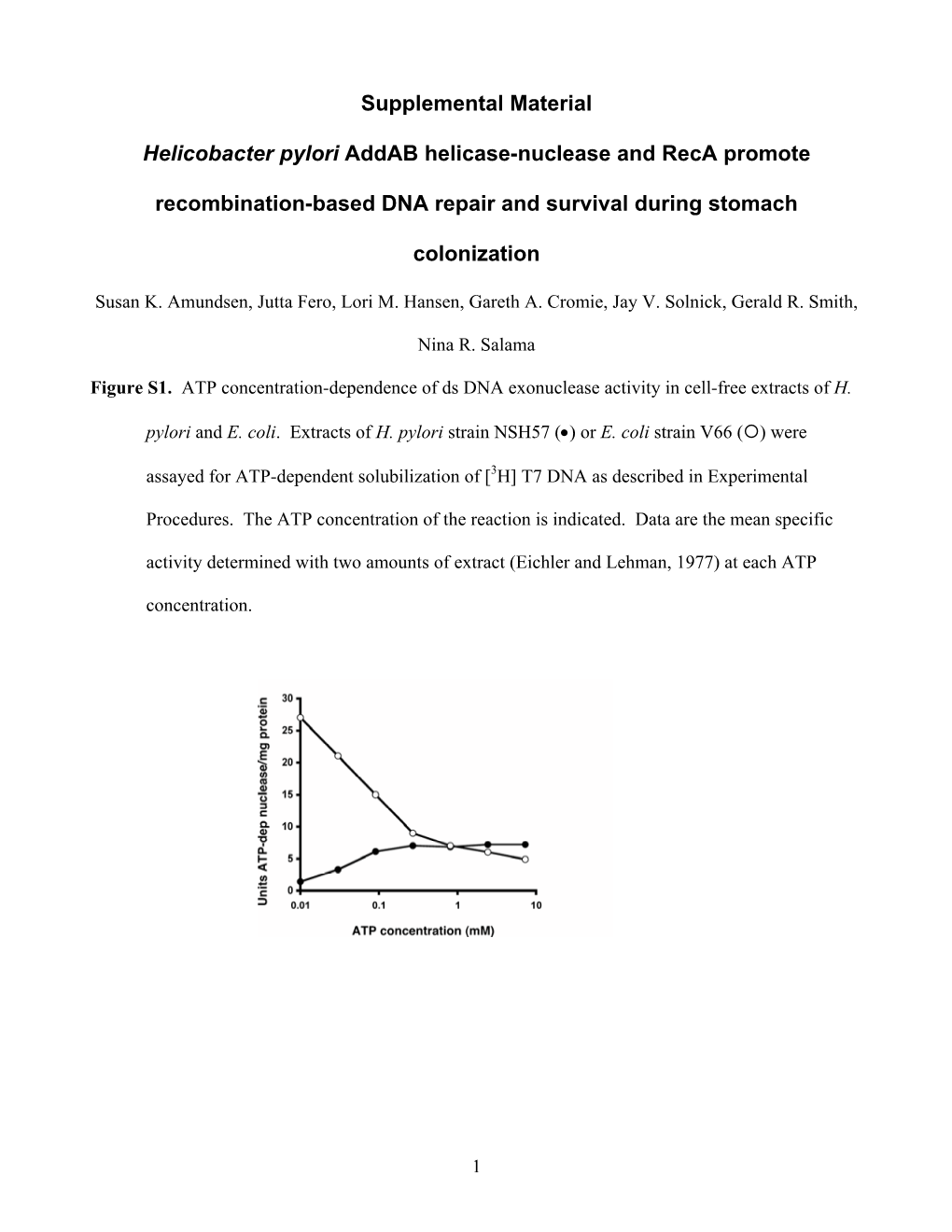
Supplemental Material Helicobacter Pylori Addab Helicase
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Evolutionary and Functional Aspects of Two-Component Signalling Systems
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Evolutionary and Functional Aspects of Two-Component Signalling Systems by Xia Sheng in the Theoretical System Biology Group Division of Molecular Biosciences February 2013 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Abstract Theoretical System Biology Group Division of Molecular Biosciences by Xia Sheng Two-component systems (TCSs) are critical for bacteria to interact with their extra- cellular environment. They define a type of signalling system that is composed of a transmembrane histidine kinase (HK) and a cytoplasmic response regulator (RR). In this thesis we have studied the evolutionary and functional aspects of these important signalling systems. By studying the distribution of the TCS orthologues of E.coli across more than 900 bacterial organisms, we have found that a pair of TCS proteins does not always coexist in one organism. The genomic localisation map of TCSs reveals a possi- ble translocation mechanism for TCS evolution. The alignments of HKs and RRs have shown that HKs are genetically more divergent, probably due to their signal recognizing role. An analysis of the steady states of TCS dynamics has shown that the outputs of the TCSs are bistable if they have positive auto-regulation feedback loops in their tran- scriptional regulation. Our analysis has also shown that the phosphorylation process of a TCS is always monostable and the factors that affect steady states have been studied. For both orthodox and non-orthodox TCSs, autophosphorylation rates of the HKs are the most important factor to affect the steady states of the TCSs' outputs. To study the phosphorelay mechanism of the non-orthodox TCS ArcB/A, we constructed plasmids carrying different copy numbers of ArcB mutants with different phosphorylation sites ablated. -

A Nanobody Targeting the Translocated Intimin Receptor Inhibits the Attachment of Enterohemorrhagic E
RESEARCH ARTICLE A nanobody targeting the translocated intimin receptor inhibits the attachment of enterohemorrhagic E. coli to human colonic mucosa 1,2 3,4 1 2 David Ruano-GallegoID , Daniel A. YaraID , Lorenza Di IanniID , Gad Frankel , 3,4 1 Stephanie SchuÈ llerID , Luis AÂ ngel FernaÂndezID * a1111111111 1 Department of Microbial Biotechnology, Centro Nacional de BiotecnologõÂa, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones CientõÂficas (CSIC), Campus UAM-Cantoblanco, Madrid, Spain, 2 MRC Centre for Molecular a1111111111 Bacteriology and Infection, Life Sciences Department, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, a1111111111 3 Norwich Medical School, University of East Anglia, Norwich Research Park, Norwich, United Kingdom, a1111111111 4 Quadram Institute Bioscience, Norwich Research Park, Norwich, United Kingdom a1111111111 * [email protected] Abstract OPEN ACCESS Citation: Ruano-Gallego D, Yara DA, Di Ianni L, Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) is a human intestinal pathogen that causes hemorrhagic Frankel G, SchuÈller S, FernaÂndez LAÂ (2019) A colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. No vaccines or specific therapies are currently avail- nanobody targeting the translocated intimin able to prevent or treat these infections. EHEC tightly attaches to the intestinal epithelium by receptor inhibits the attachment of injecting the intimin receptor Tir into the host cell via a type III secretion system (T3SS). In enterohemorrhagic E. coli to human colonic mucosa. PLoS Pathog 15(8): e1008031. https:// this project, we identified a camelid single domain antibody (nanobody), named TD4, that doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008031 recognizes a conserved Tir epitope overlapping the binding site of its natural ligand intimin Editor: Brian K. Coombes, McMaster University, with high affinity and stability. -

Recombinant Protein Expression in Escherichia Coli François Baneyx
411 Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli François Baneyx Escherichia coli is one of the most widely used hosts for the co-overexpression of additional gene products is desired, production of heterologous proteins and its genetics are far ColE1 derivatives are usually combined with compatible better characterized than those of any other microorganism. plasmids bearing a p15A replicon and maintained at Recent progress in the fundamental understanding of about 10–12 copies per cell. Under laboratory conditions, transcription, translation, and protein folding in E. coli, together such multicopy plasmids are randomly distributed dur- with serendipitous discoveries and the availability of improved ing cell division and, in the absence of selective genetic tools are making this bacterium more valuable than pressure, are lost at low frequency (10–5–10–6 per gener- ever for the expression of complex eukaryotic proteins. ation) primarily as a result of multimerization [2•]. Nevertheless, plasmid loss can increase tremendously in Addresses the case of very high copy number plasmids, when plas- Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Washington, mid-borne genes are toxic to the host or otherwise Box 351750, Seattle, WA 98195, USA; significantly reduce its growth rate, or when cells are cul- e-mail: [email protected] tivated at high density or in continuous processes. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 1999, 10:411–421 The simplest way to address this problem is to take 0958-1669/99/$ — see front matter © 1999 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. advantage of plasmid-encoded antibiotic-resistance mark- ers and supplement the growth medium with antibiotics Abbreviations to kill plasmid-free cells. -

Engineering Escherichia Coli to Sense Acidic Amino Acids by Introduction of a Chimeric Two-Component System
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 32(10), 2073-2077 (2015) pISSN: 0256-1115 DOI: 10.1007/s11814-015-0024-z eISSN: 1975-7220 INVITED REVIEW PAPER INVITED REVIEW PAPER Engineering Escherichia coli to sense acidic amino acids by introduction of a chimeric two-component system Sambandam Ravikumar*,‡, Irisappan Ganesh**,‡, Murali Kannan Maruthamuthu**, and Soon Ho Hong**,† *Department of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Catholic University of Daegu, 330, Geumrak 1-ri, Hayang-eup, Gyeongsan, Gyeongbuk 712-702, Korea **Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Ulsan, 93, Daehak-ro, Nam-gu, Ulsan 680-749, Korea (Recevied 28 September 2014 • accepted 27 January 2015) Abstract−In an attempt to create an acidic amino acid-sensing Escherichia coli, a chimeric sensor kinase (SK)-based biosensor was constructed using Pseudomonas putida AauS. AauS is a sensor kinase that ultimately controls expression of the aau gene through its cognate response regulator AauR, and is found only in P. puti d a KT2440. The AauZ chi- mera SK was constructed by integration of the sensing domain of AauS with the catalytic domain of EnvZ to control the expression of the ompC gene in response to acidic amino acids. Real-time quantitative PCR and GFP fluorescence studies showed increased ompC gene expression and GFP fluorescence as the concentration of acidic amino acids in- creased. These data suggest that AauS-based recombinant E. coli can be used as a bacterial biosensor of acidic amino acids. By employing the chimeric SK strategy, various bacteria biosensors for use in the development of biochemical- producing recombinant microorganisms can be constructed. Keywords: Acidic Amino Acids, Chimera Two-component System, Green Fluorescent Protein, Escherichia coli INTRODUCTION the transcription of related genes [6]. -

Complete Article
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Jan. 1992, p. 619-622 Vol. 174, No. 2 0021-9193/92/020619-04$02.00/0 Copyright X 1992, American Society for Microbiology NOTES Bacteriophage T7 RNA Polymerase Travels Far Ahead of Ribosomes In Vivo ISABELLE IOST, JEAN GUILLEREZ, AND MARC DREYFUS* Laboratoire de Genetique Moleculaire (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique D1302), Ecole Normale Superieure, 46 rue d'Ulm, 75230 Paris Cedex 05, France Received 2 July 1991/Accepted 24 October 1991 We show that in Escherichia coli at 32°C, the T7 RNA polymerase travels over the lacZ gene about eightfold faster than ribosomes travel over the corresponding mRNA. We discuss how the T7 phage might exploit this high rate in its growth optimization strategy and how it obviates the possible drawbacks of uncoupling transcription from translation. In Escherichia coli, transcription occurs simultaneously sequences and on the other by a terminator for T7 RNA with translation, and both processes are often tightly cou- polymerase (5). Because it is present as a single copy, the pled. Thus, the average rate of transcription matches that of lacZ gene can be transcribed constitutively from the very translation, even though it can theoretically be higher (3, active T7 promoter without affecting cell growth. For the lla). Moreover, in the absence of translation, transcription purpose of this study, we replaced the gene JO leader usually terminates prematurely (1). Based on in vitro stud- sequence by a synthetic DNA fragment encompassing the ies, it is believed that this coupling reflects the existence in lac operator (Fig. 1). Thereby, not only the transcription of most genes of specific pause sites where RNA polymerase the T7 gene I but also that of the target lacZ gene can be waits for the first translating ribosome (12). -

The Irga Homologue Adhesin Iha Is an Escherichia Coli Virulence Factor in Murine Urinary Tract Infection
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2005 The rI gA homologue adhesin Iha is an Escherichia coli virulence factor in murine urinary tract infection James R. Johnson University of Minnesota - Twin Cities Srdjan Jelacic Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, Seattle Laura M. Schoening Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, Seattle Connie Clabots University of Minnesota - Twin Cities Nurmohammad Shaikh Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis See next page for additional authors Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/open_access_pubs Recommended Citation Johnson, James R.; Jelacic, Srdjan; Schoening, Laura M.; Clabots, Connie; Shaikh, Nurmohammad; Mobley, Harry L.T.; and Tarr, Phillip I., ,"The rI gA homologue adhesin Iha is an Escherichia coli virulence factor in murine urinary tract infection." Infection and Immunology.73,2. 965-971. (2005). https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/open_access_pubs/2157 This Open Access Publication is brought to you for free and open access by Digital Commons@Becker. It has been accepted for inclusion in Open Access Publications by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons@Becker. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Authors James R. Johnson, Srdjan Jelacic, Laura M. Schoening, Connie Clabots, Nurmohammad Shaikh, Harry L.T. Mobley, and Phillip I. Tarr This open access publication is available at Digital Commons@Becker: https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/open_access_pubs/2157 The IrgA Homologue Adhesin Iha Is an Escherichia coli Virulence Factor in Murine Urinary Tract Infection James R. Johnson, Srdjan Jelacic, Laura M. Schoening, Connie Clabots, Nurmohammad Shaikh, Harry L. T. Mobley and Phillip I. -

Tuning Escherichia Coli for Membrane Protein Overexpression
Tuning Escherichia coli for membrane protein overexpression Samuel Wagner*†‡, Mirjam M. Klepsch*, Susan Schlegel*, Ansgar Appel*, Roger Draheim*, Michael Tarry*, Martin Ho¨ gbom*, Klaas J. van Wijk§, Dirk J. Slotboom¶, Jan O. Perssonʈ, and Jan-Willem de Gier*†** *Center for Biomembrane Research, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, ʈDepartment of Mathematics and Statistics, and †Xbrane Bioscience AB, Arrhenius Laboratories, Stockholm University, SE-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden; §Department of Plant Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853; and ¶Department of Biochemistry, University of Groningen, Nyenborg 4, 9747 AG Groningen, The Netherlands Edited by Douglas C. Rees, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, and approved July 30, 2008 (received for review April 28, 2008) A simple generic method for optimizing membrane protein over- produce low amounts of T7Lys, whereas pLysE hosts produce expression in Escherichia coli is still lacking. We have studied the much more enzyme and, therefore, provide a more stringent physiological response of the widely used ‘‘Walker strains’’ control (6). C41(DE3) and C43(DE3), which are derived from BL21(DE3), to Recently, we studied the physiological response of E. coli membrane protein overexpression. For unknown reasons, overex- BL21(DE3)pLysS to membrane protein overexpression (7). Our pression of many membrane proteins in these strains is hardly aim was to identify potential bottlenecks that hamper membrane toxic, often resulting in high overexpression yields. By using a protein overexpression and to use this information to engineer combination of physiological, proteomic, and genetic techniques strains with improved overexpression characteristics. We found we have shown that mutations in the lacUV5 promoter governing that membrane protein overexpression resulted in accumulation expression of T7 RNA polymerase are key to the improved mem- of cytoplasmic aggregates containing the overexpressed protein brane protein overexpression characteristics of the Walker strains. -

Tailoring the Evolution of BL21(DE3) Uncovers a Key Role for RNA Stability in Gene Expression Toxicity ✉ Sophia A
ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02493-4 OPEN Tailoring the evolution of BL21(DE3) uncovers a key role for RNA stability in gene expression toxicity ✉ Sophia A. H. Heyde1 & Morten H. H. Nørholm 1 Gene expression toxicity is an important biological phenomenon and a major bottleneck in biotechnology. Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) is the most popular choice for recombinant protein production, and various derivatives have been evolved or engineered to facilitate improved yield and tolerance to toxic genes. However, previous efforts to evolve BL21, such as the Walker strains C41 and C43, resulted only in decreased expression strength of the 1234567890():,; T7 system. This reveals little about the mechanisms at play and constitutes only marginal progress towards a generally higher producing cell factory. Here, we restrict the solution space for BL21(DE3) to evolve tolerance and isolate a mutant strain Evo21(DE3) with a truncation in the essential RNase E. This suggests that RNA stability plays a central role in gene expression toxicity. The evolved rne truncation is similar to a mutation previously engineered into the commercially available BL21Star(DE3), which challenges the existing assumption that this strain is unsuitable for expressing toxic proteins. We isolated another dominant mutation in a presumed substrate binding site of RNase E that improves protein production further when provided as an auxiliary plasmid. This makes it easy to improve other BL21 variants and points to RNases as prime targets for cell factory optimisation. -

Highly Efficient Primed Spacer Acquisition from Targets Destroyed by the Escherichia Coli Type I-E CRISPR-Cas Interfering Complex
Highly efficient primed spacer acquisition from targets destroyed by the Escherichia coli type I-E CRISPR-Cas interfering complex Ekaterina Semenovaa, Ekaterina Savitskayab,c, Olga Musharovab,d,e, Alexandra Strotskayaa,b,c,e, Daria Vorontsovaa,b,e, Kirill A. Datsenkoa,f, Maria D. Logachevag, and Konstantin Severinova,b,c,d,e,1 aWaksman Institute of Microbiology, Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey, Piscataway, NJ 08854; bSkolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Skolkovo 143025, Russia; cInstitute of Molecular Genetics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 123182, Russia; dInstitute of Gene Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119334, Russia; ePeter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg 195251, Russia; fDepartment of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907; and gM.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia Edited by Jennifer A. Doudna, University of California, Berkeley, CA, and approved May 9, 2016 (received for review February 16, 2016) Prokaryotic clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat complex alone (type II) or through recruitment of an additional (CRISPR)-CRISPR associated (Cas) immunity relies on adaptive acqui- endonuclease Cas3 (type I systems) (4). Cas1 and Cas2 are not sition of spacers—short fragments of foreign DNA. For the type I-E required for interference in vivo (2) and in vitro (15, 16). CRISPR-Cas system from Escherichia coli, efficient “primed” adapta- Point mutations in protospacer or associated PAM decrease the tion requires Cas effector proteins and a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) whose affinity of crRNA–effector complex binding to protospacer (17). spacer partially matches a segment (protospacer) in target DNA. Under pressure from CRISPR-Cas, mobile genetic elements ac- Primed adaptation leads to selective acquisition of additional spacers cumulate such mutations, which allows them to escape CRISPR from DNA molecules recognized by the effector–crRNA complex. -

A Plasmid-Encoded Papb Paralogue Modulates Autoaggregation of Escherichia Coli Transconjugants
A plasmid-encoded papB paralogue modulates autoaggregation of Escherichia coli transconjugants Ruben Monarrez Haverford College Iruka Okeke ( [email protected] ) Haverford College, University of Ibadan https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1694-7587 Research note Keywords: plasmid, PapB, PefB, mbrial regulation, autoaggregation Posted Date: December 7th, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-36006/v3 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License Version of Record: A version of this preprint was published on December 14th, 2020. See the published version at https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-020-05405-7. Page 1/17 Abstract Objective: Plasmids are key to antimicrobial resistance transmission among enteric bacteria. It is becoming increasingly clear that resistance genes alone do not account for the selective advantage of plasmids and bacterial strains that harbor them. Deletion of a 32 Kb tness-conferring region of pMB2, a conjugative resistance plasmid, produced a hyper-autoaggregation phenotype in laboratory Escherichia coli. This study sought to determine the genetic basis for hyper-autoaggregation conferred by the pMB2- derived mini-plasmid. Results: The 32 Kb fragment deleted from pMB2 included previously characterized nutrient acquisition genes as well as putative transposase and integrase genes, a 272 bp papB/ pefB-like gene, and several open-reading frames of unknown function. We cloned the papB/ pefB paralogue and found it sucient to temper the hyper-autoaggregation phenotype. Hyper-autoaggregation conferred by the mini-plasmid did not occur in a m-negative background. This study has identied and characterized a gene capable of down-regulating host adhesins and has shown that trans-acting papB/pefB paralogues can occur outside the context of an adhesin cluster. -

RNA Remodeling by Bacterial Global Regulator Csra Promotes Rho-Dependent Transcription Termination
Downloaded from genesdev.cshlp.org on October 2, 2021 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press RNA remodeling by bacterial global regulator CsrA promotes Rho-dependent transcription termination Nara Figueroa-Bossi,1 Annie Schwartz,2 Benoit Guillemardet,1 Francxois D’Heyge`re,2 Lionello Bossi,1,3 and Marc Boudvillain2,3 1CNRS UPR3404, Centre de Ge´ne´tique Mole´culaire, Gif-sur-Yvette 91198, France, affilie´ a` l’Universite´ Paris Sud XI, Orsay 91405, France; 2CNRS UPR4301, Centre de Biophysique Mole´culaire, Orle´ans 45071, France, affilie´ a` l’Universite´ d’Orle´ans, Orle´ans 45100, France RNA-binding protein CsrA is a key regulator of a variety of cellular processes in bacteria, including carbon and stationary phase metabolism, biofilm formation, quorum sensing, and virulence gene expression in pathogens. CsrA binds to bipartite sequence elements at or near the ribosome loading site in messenger RNA (mRNA), most often inhibiting translation initiation. Here we describe an alternative novel mechanism through which CsrA achieves negative regulation. We show that CsrA binding to the upstream portion of the 59 untranslated region of Escherichia coli pgaA mRNA—encoding a polysaccharide adhesin export protein—unfolds a secondary structure that sequesters an entry site for transcription termination factor Rho, resulting in the premature stop of transcription. These findings establish a new paradigm for bacterial gene regulation in which remodeling of the nascent transcript by a regulatory protein promotes Rho-dependent transcription attenuation. [Keywords: CsrA; Rho factor; transcription attenuation; bacterial gene regulation] Supplemental material is available for this article. Received February 17, 2014; revised version accepted April 18, 2014. -

Part One Expression Systems
11 Part One Expression Systems 13 1 Bacterial Systems James Samuelson 1.1 Introduction The study of membrane protein structure and function is limited by various chal- lenges. In native cells, membrane protein copy number is often very low, so the study of individual proteins is often not feasible. Alternatively, overexpression of these hydrophobic molecules in heterologous hosts is not a routine endeavor as it is for many water - soluble proteins. Most modern bacterial expression systems have been engineered for maximal output of recombinant protein. This character- istic is ideal for well - behaved soluble proteins, but less desirable when the target protein normally resides within a lipid environment. A compounding problem in the study of membrane proteins is that the isolated target protein may exhibit polydispersity, meaning that diverse oligomeric complexes can spontaneously accumulate. This latter concern may be infl uenced by the expression method, but primarily depends on the detergent/lipid and buffer used for solubilization. This chapter highlights preferred strategies for membrane protein expression in bacte- ria that will increase the likelihood of isolating adequate amounts of homogenous target protein. Many sections will also detail the features of expression strains that are relevant to the yield and quality of expressed protein. In this chapter, the term membrane protein will generally be used to represent α - helical membrane proteins that reside within a phospholipid bilayer environ- ment of either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells. Such integral membrane proteins are the most diffi cult to manipulate since each contains hydrophobic transmem- brane ( TM ) regions as well as hydrophilic extramembrane regions or domains.