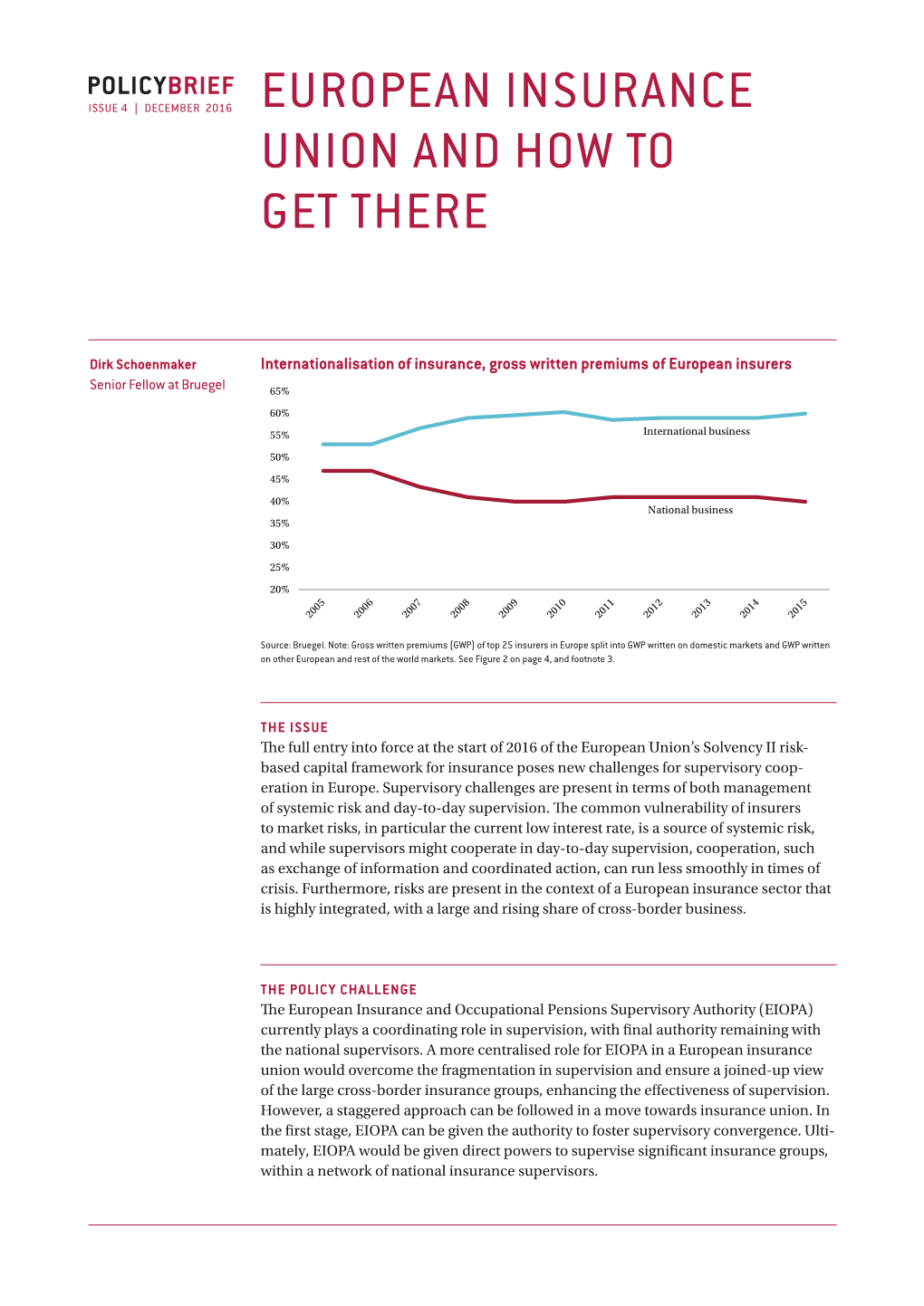
European Insurance Union and How to Get There
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

OSB Representative Participant List by Industry
OSB Representative Participant List by Industry Aerospace • KAWASAKI • VOLVO • CATERPILLAR • ADVANCED COATING • KEDDEG COMPANY • XI'AN AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY • CHINA FAW GROUP TECHNOLOGIES GROUP • KOREAN AIRLINES • CHINA INTERNATIONAL Agriculture • AIRBUS MARINE CONTAINERS • L3 COMMUNICATIONS • AIRCELLE • AGRICOLA FORNACE • CHRYSLER • LOCKHEED MARTIN • ALLIANT TECHSYSTEMS • CARGILL • COMMERCIAL VEHICLE • M7 AEROSPACE GROUP • AVICHINA • E. RITTER & COMPANY • • MESSIER-BUGATTI- CONTINENTAL AIRLINES • BAE SYSTEMS • EXOPLAST DOWTY • CONTINENTAL • BE AEROSPACE • MITSUBISHI HEAVY • JOHN DEERE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRIES • • BELL HELICOPTER • MAUI PINEAPPLE CONTINENTAL • NASA COMPANY AUTOMOTIVE SYSTEMS • BOMBARDIER • • NGC INTEGRATED • USDA COOPER-STANDARD • CAE SYSTEMS AUTOMOTIVE Automotive • • CORNING • CESSNA AIRCRAFT NORTHROP GRUMMAN • AGCO • COMPANY • PRECISION CASTPARTS COSMA INDUSTRIAL DO • COBHAM CORP. • ALLIED SPECIALTY BRASIL • VEHICLES • CRP INDUSTRIES • COMAC RAYTHEON • AMSTED INDUSTRIES • • CUMMINS • DANAHER RAYTHEON E-SYSTEMS • ANHUI JIANGHUAI • • DAF TRUCKS • DASSAULT AVIATION RAYTHEON MISSLE AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS COMPANY • • ARVINMERITOR DAIHATSU MOTOR • EATON • RAYTHEON NCS • • ASHOK LEYLAND DAIMLER • EMBRAER • RAYTHEON RMS • • ATC LOGISTICS & DALPHI METAL ESPANA • EUROPEAN AERONAUTIC • ROLLS-ROYCE DEFENCE AND SPACE ELECTRONICS • DANA HOLDING COMPANY • ROTORCRAFT • AUDI CORPORATION • FINMECCANICA ENTERPRISES • • AUTOZONE DANA INDÚSTRIAS • SAAB • FLIR SYSTEMS • • BAE SYSTEMS DELPHI • SMITH'S DETECTION • FUJI • • BECK/ARNLEY DENSO CORPORATION -

Aegon N.V. Aegon N.V
Insurance Life Insurance Netherlands Ratings Aegon N.V. Aegon N.V. Long-Term IDR A- And Core Subsidiaries Short-Term IDR F2 Scottish Equitable Plc Insurer Financial Strength Rating A+ Transamerica Financial Life Insurance Company Key Rating Drivers Insurer Financial Strength Rating A+ Short-Term Insurer Financial WD Very Strong Business Profile: Fitch Ratings ranks Aegon N.V.’s business profile as ‘favourable’ Strength Rating compared to other Dutch insurance companies. Geographic diversification is broad; non- Transamerica Life Insurance Company Dutch assets account for about 80% of the group’s assets. Aegon has a substantial life Insurer Financial Strength Rating A+ insurance franchise in the Netherlands focusing on retirement services and savings, where it Short-Term Insurer Financial F1+ has top three market positions. It also has significant life and pension operations in the US and Strength Rating the UK. Transamerica Premier Life Insurance ‘Very Strong’ Capitalisation and Leverage: Aegon’s end-2019 Prism Factor-Based Capital Company Model (Prism FBM) score was unchanged at ‘Very Strong’ and the group’s Solvency II (S2) ratio Insurer Financial Strength Rating A+ was 201%. The S2 ratio improved to 208% in 1Q20 due to the increase of the S2 volatility Short-Term Insurer Financial WD adjuster (VA), although this was partly offset by adverse market movements in the US. The Strength Rating financial leverage ratio (FLR) decreased to 25% in 2019 on the successful issuance of Note: See additional ratings on page 8. restricted Tier 1 (RT1) notes during the year. Good Financial Performance: Aegon’s underlying earnings could weaken in 2020 due to the Outlooks impact of the coronavirus pandemic on US operations, while earnings in Europe are expected Negative to remain more resilient. -

Cross-Border Financial Institutions in the EU: Analysis of Total Assets and Ultimate Ownership
Directorate-General for Internal Policies Directorate A - Economic and Scientific Policy Policy Department A.: Economic and Scientific Policy and Quality of Life Unit Cross-Border Financial Institutions in the EU: Analysis of Total Assets and Ultimate Ownership Briefing Note IP/A/ECON/NT/2008-10 PE 408.550 Only published in English. Author: Josina KAMERLING Policy Department Economy and Science DG Internal Policies European Parliament Rue Wiertz 60 - ATR 00L046 B-1047 Brussels Tel: +32 (0)2 283 27 86 Fax: +32(0)2 284 69 29 E-mail: [email protected] Arttu MAKIPAA Policy Department Economy and Science DG Internal Policies European Parliament Rue Wiertz 60 - ATR 00L042 B-1047 Brussels Tel: +32 (0)2 283 26 20 Fax: +32(0)2 284 69 29 E-mail: [email protected] Manuscript completed in August 2008. The opinions expressed in this document do not necessarily represent the official position of the European Parliament. Reproduction and translation for non-commercial purposes are authorised provided the source is acknowledged and the publisher is given prior notice and receives a copy. Rue Wiertz – B-1047 Bruxelles - 32/2.284.43.74 Fax: 32/2.284.68.05 Palais de l‘Europe – F-67000 Strasbourg - 33/3.88.17.25.56 Fax: 33/3.88.36.92.14 E-mail: [email protected] IP/A/ECON/NT/2008-10 PE 408.550 Table of Contents 1. The Data on Financial Institutions in EU27 ......................................................................1 2. Largest Financial Institutions in Europe (Tables 1-5) .......................................................2 -

Achmea Bank N.V. Reports a Positive Result of Eur 37 Million Limited Impact Covid-19 Crisis on Achmea Bank’S Financial Position
ACHMEA BANK N.V. PRESS RELEASE 2020 ACHMEA BANK N.V. REPORTS A POSITIVE RESULT OF EUR 37 MILLION LIMITED IMPACT COVID-19 CRISIS ON ACHMEA BANK’S FINANCIAL POSITION Tilburg, 15 March 2021 • Achmea Bank N.V. reported for 2020 an operating profit of EUR 37 million, EUR 28 million after tax (2019: EUR 50 million, after tax EUR 37 million) • The Common Equity Tier 1 Capital Ratio remains strong at 20.4% (2019: 19.2%) • Achmea Bank further executed its ambition to grow in mortgages, through the acquisition of a portfolio of Dutch residential mortgages from BinckBank of EUR 0.5 billion • Achmea Bank combined its mortgage activities with Syntrus Achmea Real Estate & Finance to focus on growth in mortgages • The Bank positions itself to become a data driven connected bank optimizing its asset base to support the Achmea strategy Achmea Bank reported a profit before tax of EUR 37 million in 2020 (2019 EUR 50 million). The 2019 result included an one-off accounting result of EUR 18 million related to the a.s.r. transaction. The operating result for 2020, excluding one-off results and fair value result, increased from EUR 34 million in 2019 to EUR 42 million in 2020. The increase in operating result is mainly due to a higher interest margin of EUR 16 million. Impairment charges amounted EUR 3 million (2019 EUR +4 million). 2020 was dominated by the Covid-19 crisis. This crisis affects the social and economic living environment and thereby also our customers. Since March 2020, Achmea Bank offered the possibility of a payment holiday to mortgage customers with payment difficulties directly related to the Covid-19 crisis. -

In Deze Lijst Wordt Aangegeven Van Welke Landen We Staatsobligaties Bezitten Die Direct Op Naam Staan Van Het Pensioenfonds TNO
Overzicht Stewardship beleid 2e kwartaal 2021 In deze lijst wordt aangegeven van welke landen we staatsobligaties bezitten die direct op naam staan van het Pensioenfonds TNO. Vervolgens worden daarnaast de beleggingsfondsen genoemd waar we op 30 juni 2021 in beleggen. Tot slot staat in dit overzicht een lange lijst van instellingen en bedrijven waarvan de obligaties direct op naam van het Pensioenfonds TNO staan. Het overzicht is vanaf het vierde kwartaal van 2016 ook aangevuld met de namen van de bedrijven bij waarvan de aandelen direct op naam staan van Pensioenfonds TNO. (Quasi) staatsobligaties Fixed Income Beleggingsfondsen direct op naam van Pensioenfonds (30 juni 2021) TNO (30 juni 2021) Arcmont -Direct Lending België Fund Duitsland BlackRock Emerging Market Finland debt (hard currency) Frankrijk Neuberger Berman Emerging Nederland Market debt (local currency) Nieuw-Zeeland Permira Credit Solutions Oostenrijk Fund SSA (Supranational, sub-sovereign and agency)-obligaties (30 juni 2021) Aandelenbeleggingsfondsen (30 juni 2021) Bank Nederlandse BlackRock Japan Equity index ESG Gemeenten (BNG) screened fund De Europese BlackRock Pacific ex Japan Equity Investeringsbank (EIB) index ESG screened fund Europese financiële Northern Trust Emerging Markets stabiliteitsfaciliteit (EFS) custom ESG equity index fund Vanguard Institutional US-equity Europees Index Fund stabiliteitsmechanisme Vanguard SRI European Stock Index (ESM) Fund Vanguard Emerging Markets Equity Kreditanstalt für Fund Wiederaufbau (KFW) Europese Unie (EU) Pagina 1 van 22 -

The Changing Composition of the Supervisory Boards of the Eight Largest Banks and Insurers During 2008-2014 And
No. 502 / February 2016 The changing composition of the supervisory boards of the eight largest banks and insurers during 2008-2014 and the impact of the “4+4 suitability screenings” Mijntje Lückerath-Rovers and Margriet Stavast-Groothuis The changing composition of the supervisory boards of the eight largest banks and insurers during 2008-2014 and the impact of the “4+4 suitability screenings” Mijntje Lückerath-Rovers and Margriet Stavast-Groothuis * * Views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect official positions of De Nederlandsche Bank. De Nederlandsche Bank NV Working Paper No. 502 P.O. Box 98 1000 AB AMSTERDAM February 2016 The Netherlands The changing composition of the supervisory boards of the eight largest banks and insurers during 2008-2014 and the impact of the “4+4 suitability screenings”* Mijntje Lückerath-Roversa and Margriet Stavast-Groothuisb a Tilburg University/TIAS, the Netherlands b De Nederlandsche Bank, the Netherlands 15 February 2016 Abstract In this article we describe the changes in the composition of management boards and supervisory boards that have taken place in the Dutch financial sector since 2008. In particular, we consider the effects of the introduction of suitability screening for executive directors and supervisory directors at the four largest banks and the four largest insurers in the Netherlands (the “4+4 screenings”). In the summer of 2012, the supervisory directors of these eight institutions were the first group to undergo suitability screening, enabling the impact of screening on the composition of the board to be examined in isolation. This article demonstrates that the composition of the management boards and supervisory boards of these Dutch financial institutions has changed substantially since 2008. -

Second Update to the 2014 Registration Document and Half Year Financial Report Filed with the Amf on August 3, 2015
SECOND UPDATE TO THE 2014 REGISTRATION DOCUMENT AND HALF YEAR FINANCIAL REPORT FILED WITH THE AMF ON AUGUST 3, 2015 Registration document and annual financial report filed with the AMF (Autorité des Marchés Financiers) on March 6, 2015 under No. D.15-0107 First update filed with the AMF (’Autorité des Marchés Financiers) on April 30, 2015 under No. D.15-0107 sous le numéro D.15-0107-A01 The English language version of this report is a free translation from the original, which was prepared in French. All possible care has been taken to ensure that the translation is accurate presentation of the original. However, in all matters of interpretation, views or opinion expressed in the original language version of the document in French take precedence over the translation. Société Anonyme (Public Limited Company) with capital of 2,492,372,484 euros Head office : 16 boulevard des Italiens, 75009 PARIS R.C.S.: PARIS 662 042 449 BNP PARIBAS – SECOND UPDATE TO THE REGISTRATION DOCUMENT 1. HALF YEAR MANAGEMENT REPORT .................................................................................................... 3 2. GOVERNANCE ......................................................................................................................................... 67 3. FINANCIAL INFORMATION AS AT 30 JUNE 2015 ................................................................................ 68 4. RISKS AND CAPITAL ADEQUACY (UNAUDITED) ............................................................................. 152 5. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ............................................................................................................... -

Achmea Interim Results 2021 12 August 2021 General Overview Bianca Tetteroo, Chair of the Executive Board Well on the Way to Realising Our Strategy ‘The Sum of Us’
Bianca Tetteroo Chair of the Executive Board Michel Lamie Chief Financial Officer and Vice-Chair of the Executive Board Achmea Interim Results 2021 12 August 2021 General overview Bianca Tetteroo, Chair of the Executive Board Well on the way to realising our strategy ‘The Sum of Us’ Operational result increased to €363 million in the first half year of 2021 . Strong growth in result supported by: . Increased operational result and premium growth Non-Life, driven by strong brands, increased number of customers and high customer ratings; combined ratio 95.8% . Higher result Pension & Life due to higher investment income and further reduction in operational expenses . Higher result Health due to lower expenses for elective care and additional Covid-19-related contributions from the statutory catastrophe scheme . New asset management and pension administration mandates; AuM €225 billion . Further premium growth International; distribution power in Slovakia strengthened with completion of acquisition Poštová poisťovňa . Robust solvency of 211% and sound liquidity position . First estimates of water damage in Limburg are up to €50 million and are part of the result for the second half of 2021 3 Operational result increased to €363 million . Increased result at both Health and Non-Health activities Operational result Net result Gross written premiums (€ million) Health (€ million) (€ million) . Non-Health results driven by higher Non-Health result Pension & Life and contribution 17,675 17,402 Non-Life 363 306 . Higher result on Health activities 147 thanks to lower costs for elective care and additional Covid-19-related 127 108 contributions from the statutory 7 216 120 catastrophe scheme . -

Eurekoannualreport2010 1.Pdf
EUREKO HAS A CLEAR AMBITION: TO BE THE MOST TRUSTED CONTACT DETAILS INSURER It may be ambitious but the foundations are already in place. We started in a small village called Achlum 200 years ago, 1811, as a cooperative. The clear ambition at that time was to provide mutual insurance at a reasonable premium. After 200 years, we still have the same principles. OPERATING COMPANIES We are still a community of committed people in Eureko Achmea Eureko Sigorta Interamerican Bulgaria which the customer is and feels well insured. That Mailing address Mailing address Büyükdere Caddesi 55 Alexander is our higher goal because we form an integral part P.O.Box 866 P.O.Box 866 Nurol Plaza No:71 Stambolyiski Blvd of, and have a responsibility to, the communities in 3700 AW Zeist 3700 AW Zeist 34398 Maslak, Istanbul Sofi a 1301, Bulgaria which we operate. The Netherlands The Netherlands Turkey T +359 2 801 3700 T +90 212 304 1000 We still work to a stakeholder model – customers, Offi ce address Offi ce address www.interamerican.bg employees, shareholders and business partners, with Handelsweg 2 Handelsweg 2 www.eurekosigorta.com.tr customers first among equals. 3707 NH Zeist 3707 NH Zeist Eureko Romania The Netherlands The Netherlands Friends First Ireland 25-29 Decebal Blvd So we strive always to create innovative, transparent T +31 30 69370 00 T +31 30 69370 00 Cherrywood Business Park 030964 Bucharest 3, solutions that customers understand and that meet Loughlinstown Romania their needs. To do that, we must reduce the complexity www.eureko.com www.achmea.nl Dublin 18, Ireland T +40 21 202 6700 of our business processes and make our products T +353 1 661 06 00 accessible and simple. -

Delta Lloyd Levensverzekering NV Dated Subordinated Notes - Investor Presentation, August 2012 Table of Contents I
Delta Lloyd Levensverzekering NV Dated Subordinated Notes - Investor Presentation, August 2012 Table of contents I. Delta Lloyd Group II. Delta Lloyd Levensverzekering NV III. Transaction information IV. Appendix 2 Delta Lloyd Group reliable partner since 1807 FY 2011 GWP by Geography1 • A strong Group secured on 200 years Belgium of reliability and trust 15% • An insurance company and financial services provider – Life & Pension insurance, General Insurance, Asset Management and Netherlands 85% Banking Total: € 5,529m • Distribution mainly through three FY 2011 GWP by Segment1 brands: Delta Lloyd, OHRA and ABN General Insurance AMRO 28% • Approx. 6,000 FTE, focus on the Netherlands and Belgium Life & Pensions 72% Total: € 5,529m 1. GWP excluding Germany. 3 Overview of Delta Lloyd Group Simplified Group Structure 1 Free Float 19.8%79.3% Aviva Delta Lloyd NV Issuer DL Levens – DL Schade – Other Subs.2 Verzekering NV Verzekering NV Key Financials H1 (IFRS) €m, Delta Lloyd Group 2012 2011 €m, Levensverzekering3 2012 2011 Net operational profit 218 227 Net operational profit 144 127 Net profit (942) (342) Net profit (773) (218) Total assets 76.8bn 71.4bn Total assets 38.1bn 35.5n⁴ Shareholders’ funds 2,860 4,021 Shareholders’ funds 2,033 2,859⁴ FTE 5,963 6,034 FTE 756 782 GWP 2,877 2,818 GWP 1,402 1,408 Current rating (S&P) BBB+ (stable) Current rating (S&P) A (stable) IGD Group solvency 194% 203% Regulatory solvency 275% 200%⁴ 1. 0.9% of shares are owned by Delta Lloyd. See appendix for further details. 2. Includes, amongst others, Delta Lloyd Bank and Delta Lloyd Asset Management. -

Achmea B.V. (Incorporated with Limited Liability in the Netherlands with Its Statutory Seat in Zeist) €5,000,000,000 Programme for the Issuance of Debt Instruments
Achmea B.V. (incorporated with limited liability in the Netherlands with its statutory seat in Zeist) €5,000,000,000 Programme for the Issuance of Debt Instruments Under the Programme described in this Base Prospectus (the “Programme”), Achmea B.V. (the “Issuer”), subject to compliance with all relevant laws, regulations and directives, may from time to time issue notes (the “Notes”) and capital securities (the “Capital Securities” and, together with the Notes, the “Instruments”). The Notes may be issued as subordinated notes (the “Subordinated Notes”) or senior notes (the “Senior Notes”). The aggregate nominal amount of Instruments outstanding will not at any time exceed €5,000,000,000 (or the equivalent in other currencies). Application has been made to the Irish Stock Exchange for the Instruments issued under the Programme to be admitted to the Official List and trading on its regulated market. References in this Base Prospectus to Instruments being “listed” (and all related references) shall mean that such Instruments have been listed and admitted to trading on the regulated market of the Irish Stock Exchange (or any other stock exchange). The regulated market of the Irish Stock Exchange is a regulated market for the purposes of the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive 2004/39/EC. However, unlisted Instruments may be issued as well pursuant to the Programme. The relevant Final Terms in respect of the issue of any Instruments will specify whether or not such Instruments will be listed and admitted to trading on the regulated market of the Irish Stock Exchange (or any other stock exchange). This Base Prospectus has been approved by the Central Bank of Ireland, as competent authority under Directive 2003/71/EC, as amended and implemented (the “Prospectus Directive”). -

CRO Forum – October 2013 1
Environmental, Social and Governance factors in Country Risk Management – a new horizon October 2013 Full Members: Aegon, Allianz, Aviva, AXA, Achmea, Ageas, Generali, Groupama, Hannover Re, ING, Munich Re, Prudential, Swiss Re, Zurich Financial Services Associate Members: Lloyds Banking Group, Manulife Financial, Old Mutual, RSA, Unipol, ACE, Legal and General, Chartis Table of Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Why ESG country risk management? 3 3 UN Global Compact - ESG on the international stage 6 4 ESG country risk management using ESG factors 7 5 Approaches to ESG country risk management 10 6 ESG country risk management – case studies 12 6.1 A comprehensive ESG risk framework 12 6.2 ESG integration for investing in sovereign bonds 12 7 Conclusion: a common position 14 8 Annex 15 8.1 Selected events worldwide related to ESG factors 15 8.2 Key socio-economic indicators Egypt 2005 - 2011 23 8.3 Principles for Responsible Investments (PRI) 24 8.4 Principles for Responsible Insurance (PSI) 24 8.5 External sources of information 25 9 Glossary of abbreviations 26 10 References 27 CRO Forum – October 2013 1 1 Introduction This paper is the fourth1 blueprint in our series on managing environmental, social and governance (ESG) challenges in business transactions, focusing on the core functions of the insurance industry – risk transfer and investments. Environmental, socio-economic and geopolitical developments shaping country risk profiles have become a focal point for the insurance industry in the past few years. This is because they address one business-critical issue, namely the stability of countries. Stability is a foundation for any business undertaking worldwide.