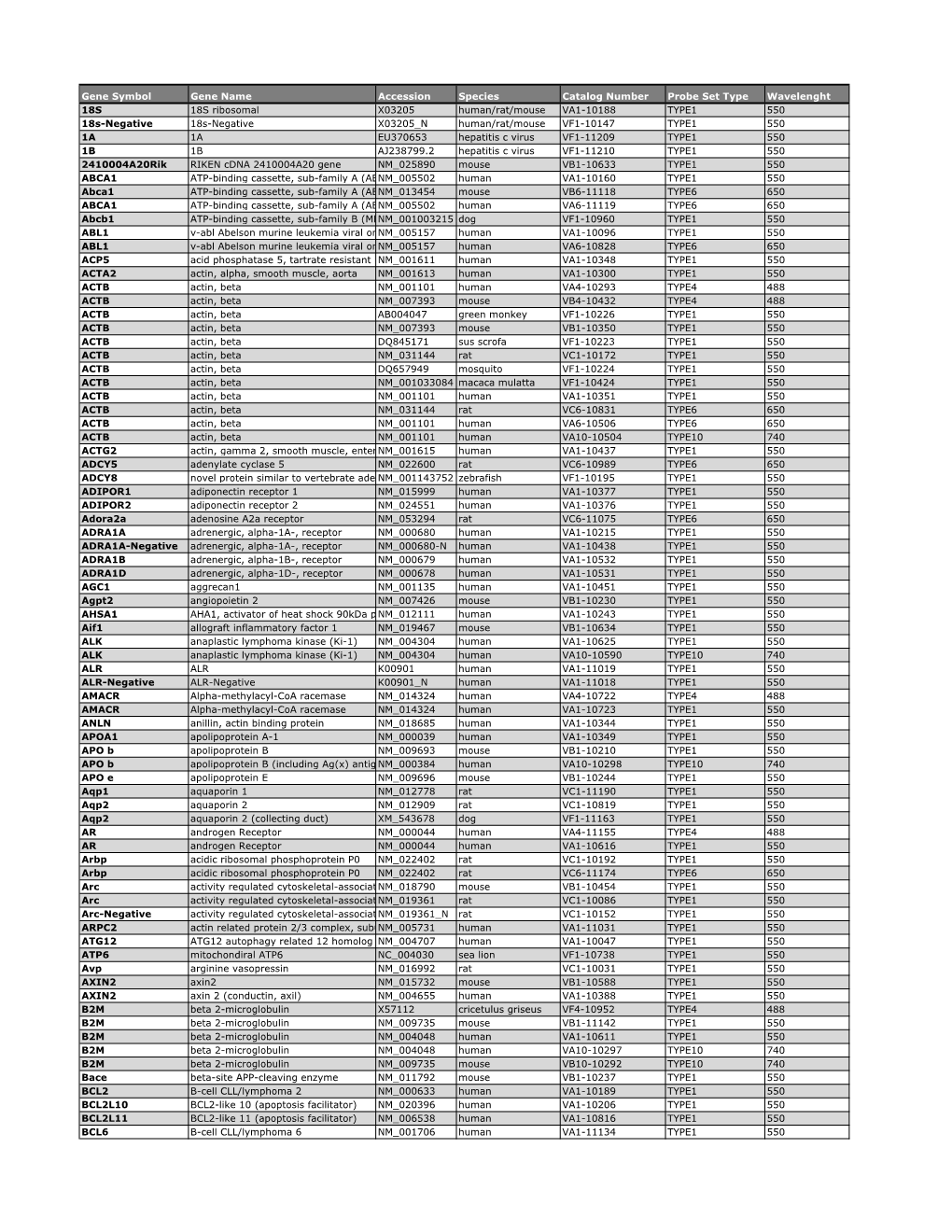
Catalog Probe Sets QG Viewrna ISH Cell Assay (2).Xlsx
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Supporting Information
Supporting Information Koyanagi et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806215105 SI Materials and Methods CNGB, NM137763; human CNGB1, NM001297; human Amino Acid Sequences. The accession numbers of amino acid CNGB3, NM 019098; box jellyfish CNG, AB435552; fruit fly sequences used for analyses are as follows: Box jellyfish opsin, CNG4, NM 167441; fruit fly CNG3, NM 137871; human AB435549; sea anemone opsin, BR000662; hydra opsin, Con- CNGA4, NM 001037329; fruit fly CNGA, NM 057768; human CNGA1, NM000087; human CNGA2, NM005140; human tig39347:487820–488855 (http://hydrazome.metazome.net); hy- drozaon jellyfish opsin, AB332435; human encephalopsin, CNGA3, NM 001298. AF140242; ragworm c-opsin, AY692353; human rhodopsin, Western Blot Analysis. The proteins extracted from half a rhopalia U49742; human blue, M13299; human red, Z68193; lamprey were separated by 12% SDS/PAGE, transferred onto a PVDF parapinopsin, AB116380; lizard parietopsin, DQ100320; am- membrane, and incubated with 1:500 diluted anti-box jellyfish phioxus peropsin, AB050610; human peropsin, AF012270; hu- opsin antiserum. Visualization was carried out by the ABC man rgr, U15790; squid retinochrome, X57143; human melan- method (Vectastain) and by staining with 3,3Ј-diaminobenzidine opsin, AF147788; amphioxus melanopsin, AB205400; squid (Sigma). rhodopsin, X70498; fruit fly Rh1, K02315; human neuropsin, AY377391; amphioxus rhodopsin, AB050606; scallop Go- In Situ Hybridization. Digoxigenin-labeled antisense and sense RNA rhodopsin, AB006455; human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor probes for the box jellyfish opsin were synthesized by using the DIG M1 (CHRM1), NM000738; human melatonin receptor 1A RNA labeling kit (Roche). Sections were pretreated with protein- (MTNR1A), NM005958; Arabidopsis AKT1, U06745; Arabi- ase K and hybridized with each RNA probe. -

The G Protein-Coupled Receptor Subset of the Dog Genome Is More Similar
BMC Genomics BioMed Central Research article Open Access The G protein-coupled receptor subset of the dog genome is more similar to that in humans than rodents Tatjana Haitina1, Robert Fredriksson1, Steven M Foord2, Helgi B Schiöth*1 and David E Gloriam*2 Address: 1Department of Neuroscience, Functional Pharmacology, Uppsala University, BMC, Box 593, 751 24, Uppsala, Sweden and 2GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, New Frontiers Science Park, 3rd Avenue, Harlow CM19 5AW, UK Email: Tatjana Haitina - [email protected]; Robert Fredriksson - [email protected]; Steven M Foord - [email protected]; Helgi B Schiöth* - [email protected]; David E Gloriam* - [email protected] * Corresponding authors Published: 15 January 2009 Received: 20 August 2008 Accepted: 15 January 2009 BMC Genomics 2009, 10:24 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-24 This article is available from: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/10/24 © 2009 Haitina et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract Background: The dog is an important model organism and it is considered to be closer to humans than rodents regarding metabolism and responses to drugs. The close relationship between humans and dogs over many centuries has lead to the diversity of the canine species, important genetic discoveries and an appreciation of the effects of old age in another species. The superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is one of the largest gene families in most mammals and the most exploited in terms of drug discovery. -

Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook Human and Mouse CD Marker Key Markers - Human Key Markers - Mouse
Welcome to More Choice CD Marker Handbook For more information, please visit: Human bdbiosciences.com/eu/go/humancdmarkers Mouse bdbiosciences.com/eu/go/mousecdmarkers Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook Human and Mouse CD Marker Key Markers - Human Key Markers - Mouse CD3 CD3 CD (cluster of differentiation) molecules are cell surface markers T Cell CD4 CD4 useful for the identification and characterization of leukocytes. The CD CD8 CD8 nomenclature was developed and is maintained through the HLDA (Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens) workshop started in 1982. CD45R/B220 CD19 CD19 The goal is to provide standardization of monoclonal antibodies to B Cell CD20 CD22 (B cell activation marker) human antigens across laboratories. To characterize or “workshop” the antibodies, multiple laboratories carry out blind analyses of antibodies. These results independently validate antibody specificity. CD11c CD11c Dendritic Cell CD123 CD123 While the CD nomenclature has been developed for use with human antigens, it is applied to corresponding mouse antigens as well as antigens from other species. However, the mouse and other species NK Cell CD56 CD335 (NKp46) antibodies are not tested by HLDA. Human CD markers were reviewed by the HLDA. New CD markers Stem Cell/ CD34 CD34 were established at the HLDA9 meeting held in Barcelona in 2010. For Precursor hematopoetic stem cell only hematopoetic stem cell only additional information and CD markers please visit www.hcdm.org. Macrophage/ CD14 CD11b/ Mac-1 Monocyte CD33 Ly-71 (F4/80) CD66b Granulocyte CD66b Gr-1/Ly6G Ly6C CD41 CD41 CD61 (Integrin b3) CD61 Platelet CD9 CD62 CD62P (activated platelets) CD235a CD235a Erythrocyte Ter-119 CD146 MECA-32 CD106 CD146 Endothelial Cell CD31 CD62E (activated endothelial cells) Epithelial Cell CD236 CD326 (EPCAM1) For Research Use Only. -

Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation And
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Review Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases Hyung Muk Choi 1, Hari Madhuri Doss 1,2 and Kyoung Soo Kim 1,2,* 1 Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul 02447, Korea; [email protected] (H.M.C.); [email protected] (H.M.D.) 2 East-West Bone & Joint Disease Research Institute, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Gandong-gu, Seoul 02447, Korea * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +82-2-961-9619 Received: 3 January 2020; Accepted: 10 February 2020; Published: 12 February 2020 Abstract: Adiponectin is the richest adipokine in human plasma, and it is mainly secreted from white adipose tissue. Adiponectin circulates in blood as high-molecular, middle-molecular, and low-molecular weight isoforms. Numerous studies have demonstrated its insulin-sensitizing, anti-atherogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, decreased serum levels of adiponectin is associated with chronic inflammation of metabolic disorders including Type 2 diabetes, obesity, and atherosclerosis. However, recent studies showed that adiponectin could have pro-inflammatory roles in patients with autoimmune diseases. In particular, its high serum level was positively associated with inflammation severity and pathological progression in rheumatoid arthritis, chronic kidney disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. Thus, adiponectin seems to have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects. This indirectly indicates that adiponectin has different physiological roles according to an isoform and effector tissue. Knowledge on the specific functions of isoforms would help develop potential anti-inflammatory therapeutics to target specific adiponectin isoforms against metabolic disorders and autoimmune diseases. -

Neurotensin Activates Gabaergic Interneurons in the Prefrontal Cortex
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 16, 2005 • 25(7):1629–1636 • 1629 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Neurotensin Activates GABAergic Interneurons in the Prefrontal Cortex Kimberly A. Petrie,1 Dennis Schmidt,1 Michael Bubser,1 Jim Fadel,1 Robert E. Carraway,2 and Ariel Y. Deutch1 1Departments of Pharmacology and Psychiatry, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee 37212, and 2Department of Physiology, University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, Massachusetts 01655 Converging data suggest a dysfunction of prefrontal cortical GABAergic interneurons in schizophrenia. Morphological and physiological studies indicate that cortical GABA cells are modulated by a variety of afferents. The peptide transmitter neurotensin may be one such modulator of interneurons. In the rat prefrontal cortex (PFC), neurotensin is exclusively localized to dopamine axons and has been suggested to be decreased in schizophrenia. However, the effects of neurotensin on cortical interneurons are poorly understood. We used in vivo microdialysis in freely moving rats to assess whether neurotensin regulates PFC GABAergic interneurons. Intra-PFC administra- tion of neurotensin concentration-dependently increased extracellular GABA levels; this effect was impulse dependent, being blocked by treatment with tetrodotoxin. The ability of neurotensin to increase GABA levels in the PFC was also blocked by pretreatment with 2-[1-(7-chloro-4-quinolinyl)-5-(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)pyrazole-3-yl)carbonylamino]tricyclo(3.3.1.1.3.7)decan-2-carboxylic acid (SR48692), a high-affinity neurotensin receptor 1 (NTR1) antagonist. This finding is consistent with our observation that NTR1 was localized to GABAergic interneurons in the PFC, particularly parvalbumin-containing interneurons. Because neurotensin is exclusively localized to dopamine axons in the PFC, we also determined whether neurotensin plays a role in the ability of dopamine agonists to increase extracellular GABA levels. -

Genetic Basis of Idiopathic Scoliosis
Research & Review: Management of Cardiovascular and Orthopedic Complications Volume 1 Issue 1 Genetic Basis of Idiopathic Scoliosis S. Sreeremya Assistant Professor, Department of Biotechnology, Sree Narayana Guru College, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India Email: [email protected] Abstract Idiopathic scoliosis (IS), the most usual spinal deformity, affects otherwise healthy children and adolescents during growth. The etiology is still not quiet understood, although genetic factors are believed to be important. This review corroborates the understanding of IS as a complex disease with a polygenic background. Presumably IS can be typically due to a spectrum of genetic risk variants, ranging from very rare or even private to very common. The most promising candidate genes are highlighted. Keywords: Idiopathic scoliosis, Genetics, Pathogenesis, Heredity INTRODUCTION marked by phenotypic complexity Idiopathic scoliosis (IS), the most general (variations in curve morphology and form of spinal deformity, affects otherwise magnitude, age of onset, rate of healthy children and adolescents during progression), and a prognosis mainly growth (Fig: 1). It usually presents as a rib ranging from increase in curve magnitude, hump visible at forward bending, together to stabilization, or to resolution with with unlevelled shoulders and an growth [5]. Genetic factors are known to asymmetrical waist [1]. According to play a pivotal role, as observed in twin Cobb, the diagnosis is specifically studies and their observation and singleton confirmed by a standing spinal radiograph multigenerational families [6]. A recent showing a lateral curvature of the spine research of monozygotic and dizygotic exceeding 10° [2]. A main concern in IS is twins from the Swedish twin registry the absence of reliable means by which to estimated that overall genetic effects predict risk of progression, leading to accounted for 39 % of the observed frequent follow-ups, radiographs, and phenotypic variance, leaving the remaining potentially unnecessary brace treatments. -

Adiporon, an Orally Active, Synthetic Agonist of Adipor1 and Adipor2 Receptors Has Gastroprotective Effect in Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Mice
molecules Article AdipoRon, an Orally Active, Synthetic Agonist of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Receptors Has Gastroprotective Effect in Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Mice Hubert Zatorski 1,2, Maciej Salaga 1 , Marta Zieli ´nska 1, Kinga Majchrzak 1, Agata Binienda 1 , Radzisław Kordek 3, Ewa Małecka-Panas 2 and Jakub Fichna 1,4,* 1 Department of Biochemistry, Medical University of Lodz, 92-215 Lodz, Poland; [email protected] (H.Z.); [email protected] (M.S.); [email protected] (M.Z.); [email protected] (K.M.); [email protected] (A.B.) 2 Department of Digestive Tract Diseases, Medical University of Lodz, 93-281 Lodz, Poland; [email protected] 3 Department of Pathology, Medical University of Lodz, 92-215 Lodz, Poland; [email protected] 4 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Medical University of Lodz, Mazowiecka 6/8, 92-215 Lodz, Poland * Correspondence: jakub.fi[email protected]; Tel.: +48-42-272-57-07 Citation: Zatorski, H.; Salaga, M.; Abstract: Introduction: Adiponectin is a hormone secreted by adipocytes, which exhibits insulin- Zieli´nska,M.; Majchrzak, K.; sensitizing and anti-inflammatory properties and acts through adiponectin receptors: AdipoR1 and Binienda, A.; Kordek, R.; AdipoR2. The aim of the study was to evaluate whether activation of adiponectin receptors AdipoR1 Małecka-Panas, E.; Fichna, J. and AdipoR2 with an orally active agonist AdipoRon has gastroprotective effect and to investigate AdipoRon, an Orally Active, the possible underlying mechanism. Methods: We used two well-established mouse models of Synthetic Agonist of AdipoR1 and gastric ulcer (GU) induced by oral administration of EtOH (80% solution in water) or diclofenac AdipoR2 Receptors Has (30 mg/kg, p.o.). -

Peptide, Peptidomimetic and Small Molecule Based Ligands Targeting Melanocortin Receptor System
PEPTIDE, PEPTIDOMIMETIC AND SMALL MOLECULE BASED LIGANDS TARGETING MELANOCORTIN RECEPTOR SYSTEM By ALEKSANDAR TODOROVIC A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA 2006 Copyright 2006 by Aleksandar Todorovic This document is dedicated to my family for everlasting support and selfless encouragement. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I would like to thank and sincerely express my appreciation to all members, former and past, of Haskell-Luevano research group. First of all, I would like to express my greatest satisfaction by working with my mentor, Dr. Carrie Haskell-Luevano, whose guidance, expertise and dedication to research helped me reaching the point where I will continue the science path. Secondly, I would like to thank Dr. Ryan Holder who has taught me the principles of solid phase synthesis and initial strategies for the compounds design. I would like to thank Mr. Jim Rocca for the help and all necessary theoretical background required to perform proton 1-D NMR. In addition, I would like to thank Dr. Zalfa Abdel-Malek from the University of Cincinnati for the collaboration on the tyrosinase study project. Also, I would like to thank the American Heart Association for the Predoctoral fellowship that supported my research from 2004-2006. The special dedication and thankfulness go to my fellow graduate students within the lab and the department. iv TABLE OF CONTENTS page ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................................................................ -

Expression of Melatonin Receptors 1A/1B, Calmodulin and Estrogen Receptor 2 in Deep Paravertebral Muscles Revisited
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 14: 5719-5724, 2016 Etiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Expression of melatonin receptors 1A/1B, calmodulin and estrogen receptor 2 in deep paravertebral muscles revisited JOSEF ZAMECNIK1*, LENKA KRSKOVA1*, JAROMIR HACEK1, IVANA STETKAROVA2 and MARTIN KRBEC3 1Department of Pathology and Molecular Medicine, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and University Hospital Motol, 15006 Prague; 2Department of Neurology, Charles University; 3Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, 3rd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and University Hospital Královské Vinohrady, 10034 Prague, Czech Republic Received October 28, 2015; Accepted October 11, 2016 DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5927 Abstract. The pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis addition, no difference in expression was detected between the (AIS), including the associated local changes in deep para- patients with AIS and the controls. With regards to MTNR1A vertebral muscles, is poorly understood. The asymmetric and MTNR1B, their expression was very weak in paravertebral expression of several molecules involved in the melatonin muscles, and in the majority of cases their expression could signaling pathway, including melatonin receptors 1A/1B not be detected by repeated RT-qPCR analysis. Therefore, (MTNR1A/MTNR1B), estrogen receptor 2 (ESR2) and these data do not support the previously suggested role of the calmodulin (CALM1), has previously been suggested to be asymmetric expression of molecules involved in the melatonin associated with AIS. However, this hypothesis is based on signaling pathway in deep paravertebral muscles in the patho- single studies in which the data were obtained by different genesis of AIS. methodological approaches. Therefore, to evaluate the symmetry of the mRNA expression levels of these molecules, Introduction 18 patients with AIS and 10 non-scoliotic controls were enrolled in the present study. -

Supporting Online Material
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Information for 8 9 Fractalkine-induced microglial vasoregulation occurs within the retina and is altered early in diabetic 10 retinopathy 11 12 *Samuel A. Mills, *Andrew I. Jobling, *Michael A. Dixon, Bang V. Bui, Kirstan A. Vessey, Joanna A. Phipps, 13 Ursula Greferath, Gene Venables, Vickie H.Y. Wong, Connie H.Y. Wong, Zheng He, Flora Hui, James C. 14 Young, Josh Tonc, Elena Ivanova, Botir T. Sagdullaev, Erica L. Fletcher 15 * Joint first authors 16 17 Corresponding author: 18 Prof. Erica L. Fletcher. Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience. The University of Melbourne, Grattan St, 19 Parkville 3010, Victoria, Australia. 20 Email: [email protected] ; Tel: +61-3-8344-3218; Fax: +61-3-9347-5219 21 22 This PDF file includes: 23 24 Supplementary text 25 Figures S1 to S10 26 Tables S1 to S7 27 Legends for Movies S1 to S2 28 SI References 29 30 Other supplementary materials for this manuscript include the following: 31 32 Movies S1 to S2 33 34 35 36 1 1 Supplementary Information Text 2 Materials and Methods 3 Microglial process movement on retinal vessels 4 Dark agouti rats were anaesthetized, injected intraperitoneally with rhodamine B (Sigma-Aldrich) to label blood 5 vessels and retinal explants established as described in the main text. Retinal microglia were labelled with Iba-1 6 and imaging performed on an inverted confocal microscope (Leica SP5). Baseline images were taken for 10 7 minutes, followed by the addition of PBS (10 minutes) and then either fractalkine or fractalkine + candesartan 8 (10 minutes) using concentrations outlined in the main text. -

Supplementary Table 3 Complete List of RNA-Sequencing Analysis of Gene Expression Changed by ≥ Tenfold Between Xenograft and Cells Cultured in 10%O2
Supplementary Table 3 Complete list of RNA-Sequencing analysis of gene expression changed by ≥ tenfold between xenograft and cells cultured in 10%O2 Expr Log2 Ratio Symbol Entrez Gene Name (culture/xenograft) -7.182 PGM5 phosphoglucomutase 5 -6.883 GPBAR1 G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 -6.683 CPVL carboxypeptidase, vitellogenic like -6.398 MTMR9LP myotubularin related protein 9-like, pseudogene -6.131 SCN7A sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 7 -6.115 POPDC2 popeye domain containing 2 -6.014 LGI1 leucine rich glioma inactivated 1 -5.86 SCN1A sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 1 -5.713 C6 complement C6 -5.365 ANGPTL1 angiopoietin like 1 -5.327 TNN tenascin N -5.228 DHRS2 dehydrogenase/reductase 2 leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain -5.115 LRFN2 containing 2 -5.076 FOXO6 forkhead box O6 -5.035 ETNPPL ethanolamine-phosphate phospho-lyase -4.993 MYO15A myosin XVA -4.972 IGF1 insulin like growth factor 1 -4.956 DLG2 discs large MAGUK scaffold protein 2 -4.86 SCML4 sex comb on midleg like 4 (Drosophila) Src homology 2 domain containing transforming -4.816 SHD protein D -4.764 PLP1 proteolipid protein 1 -4.764 TSPAN32 tetraspanin 32 -4.713 N4BP3 NEDD4 binding protein 3 -4.705 MYOC myocilin -4.646 CLEC3B C-type lectin domain family 3 member B -4.646 C7 complement C7 -4.62 TGM2 transglutaminase 2 -4.562 COL9A1 collagen type IX alpha 1 chain -4.55 SOSTDC1 sclerostin domain containing 1 -4.55 OGN osteoglycin -4.505 DAPL1 death associated protein like 1 -4.491 C10orf105 chromosome 10 open reading frame 105 -4.491 -

Structure-Based Redesigning of Pentoxifylline Analogs Against
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Structure‑based redesigning of pentoxifylline analogs against selective phosphodiesterases to modulate sperm functional competence for assisted reproductive technologies Mutyala Satish1,5, Sandhya Kumari2,5, Waghela Deeksha1, Suman Abhishek1, Kulhar Nitin1, Satish Kumar Adiga2, Padmaraj Hegde3, Jagadeesh Prasad Dasappa4, Guruprasad Kalthur2* & Eerappa Rajakumara1* Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors, such as pentoxifylline (PTX), are used as pharmacological agents to enhance sperm motility in assisted reproductive technology (ART), mainly to aid the selection of viable sperm in asthenozoospermic ejaculates and testicular spermatozoa, prior to intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). However, PTX is reported to induce premature acrosome reaction (AR) and, exert toxic efects on oocyte function and early embryo development. Additionally, in vitro binding studies as well as computational binding free energy (ΔGbind) suggest that PTX exhibits weak binding to sperm PDEs, indicating room for improvement. Aiming to reduce the adverse efects and to enhance the sperm motility, we designed and studied PTX analogues. Using structure‑guided in silico approach and by considering the physico‑chemical properties of the binding pocket of the PDEs, designed analogues of PTX. In silico assessments indicated that PTX analogues bind more tightly to PDEs and form stable complexes. Particularly, ex vivo evaluation of sperm treated with one of the PTX analogues (PTXm‑1), showed comparable benefcial efect at much lower concentration—slower