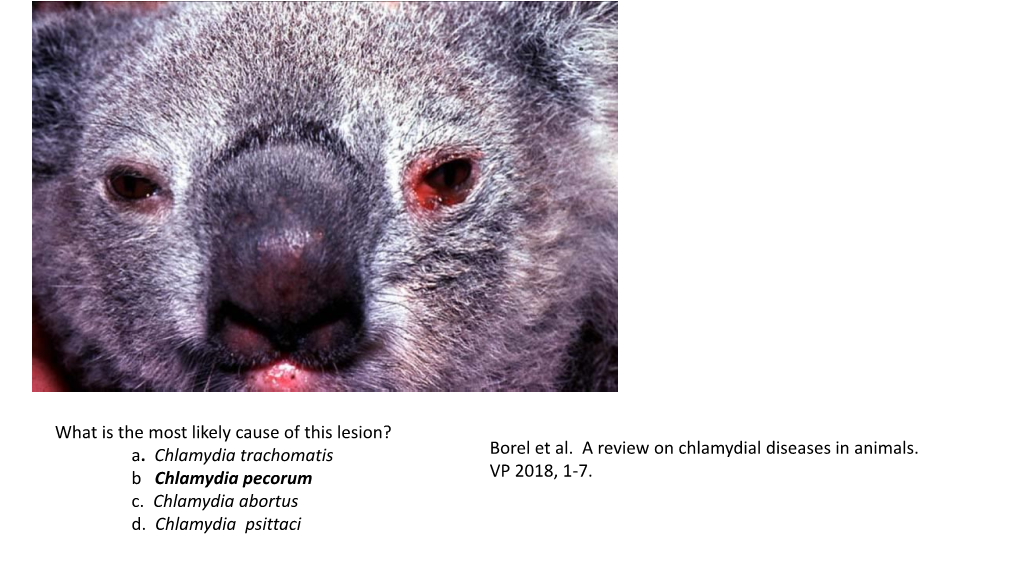
What Is the Most Likely Cause of This Lesion? A
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Are You Suprised ?
B DAMB 721 Microbiology Final Exam B 100 points December 11, 2006 Your name (Print Clearly): _____________________________________________ I. Matching: The questions below consist of headings followed by a list of phrases. For each phrase select the heading that best describes that phrase. The headings may be used once, more than once or not at all. Mark the answer in Part 2 of your answer sheet. 1. capsid 7. CD4 2. Chlamydia pneumoniae 8. Enterococcus faecalis 3. oncogenic 9. hyaluronidase 4. pyruvate 10. interferon 5. Koplik’s spot 11. hydrophilic viruses 6. congenital Treponema pallidum 12. Streptococcus pyogenes 1. “spreading factor” produced by members of the staphylococci, streptococci and clostridia 2. viral protein coat 3. central intermediate in bacterial fermentation 4. persistant endodontic infections 5. a cause of atypical pneumonia 6. nonspecific defense against viral infection 7. has a rudimentary life cycle 8. HIV receptor 9. Hutchinson’s Triad 10. measles 11. resistant to disinfection 12. β-hemolytic, bacitracin sensitive, cause of suppurative pharyngitis 2 Matching (Continued): The questions below consist of diseases followed by a list of etiologic agents. Match each disease with the etiologic agent. Continue using Part 2 of your answer sheet. 1. dysentery 6. Legionnaire’s 2. botulism 7. gas gangrene 3. cholera 8. tuberculosis 4. diphtheria 9. necrotizing fascitis 5. enteric fever 10. pneumoniae/meningitis 13. Clostridium botulinum 14. Vibrio cholera 15. Mycobacterium bovis 16. Shigella species 17. Streptococcus pneumoniae 18. Clostridium perfringens 19. Salmonella typhi 20. Streptococcus pyogenes 3 II. Multiple Choice: Choose the ONE BEST answer. Mark the correct answer on Part 1 of the answer sheet. -

Compendium of Measures to Control Chlamydia Psittaci Infection Among
Compendium of Measures to Control Chlamydia psittaci Infection Among Humans (Psittacosis) and Pet Birds (Avian Chlamydiosis), 2017 Author(s): Gary Balsamo, DVM, MPH&TMCo-chair Angela M. Maxted, DVM, MS, PhD, Dipl ACVPM Joanne W. Midla, VMD, MPH, Dipl ACVPM Julia M. Murphy, DVM, MS, Dipl ACVPMCo-chair Ron Wohrle, DVM Thomas M. Edling, DVM, MSpVM, MPH (Pet Industry Joint Advisory Council) Pilar H. Fish, DVM (American Association of Zoo Veterinarians) Keven Flammer, DVM, Dipl ABVP (Avian) (Association of Avian Veterinarians) Denise Hyde, PharmD, RP Preeta K. Kutty, MD, MPH Miwako Kobayashi, MD, MPH Bettina Helm, DVM, MPH Brit Oiulfstad, DVM, MPH (Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists) Branson W. Ritchie, DVM, MS, PhD, Dipl ABVP, Dipl ECZM (Avian) Mary Grace Stobierski, DVM, MPH, Dipl ACVPM (American Veterinary Medical Association Council on Public Health and Regulatory Veterinary Medicine) Karen Ehnert, and DVM, MPVM, Dipl ACVPM (American Veterinary Medical Association Council on Public Health and Regulatory Veterinary Medicine) Thomas N. Tully JrDVM, MS, Dipl ABVP (Avian), Dipl ECZM (Avian) (Association of Avian Veterinarians) Source: Journal of Avian Medicine and Surgery, 31(3):262-282. Published By: Association of Avian Veterinarians https://doi.org/10.1647/217-265 URL: http://www.bioone.org/doi/full/10.1647/217-265 BioOne (www.bioone.org) is a nonprofit, online aggregation of core research in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences. BioOne provides a sustainable online platform for over 170 journals and books published by nonprofit societies, associations, museums, institutions, and presses. Your use of this PDF, the BioOne Web site, and all posted and associated content indicates your acceptance of BioOne’s Terms of Use, available at www.bioone.org/page/terms_of_use. -

Abstract Betaproteobacteria Alphaproteobacteria
Abstract N-210 Contact Information The majority of the soil’s biosphere containins biodiveristy that remains yet to be discovered. The occurrence of novel bacterial phyla in soil, as well as the phylogenetic diversity within bacterial phyla with few cultured representatives (e.g. Acidobacteria, Anne Spain Dr. Mostafa S.Elshahed Verrucomicrobia, and Gemmatimonadetes) have been previously well documented. However, few studies have focused on the Composition, Diversity, and Novelty within Soil Proteobacteria Department of Botany and Microbiology Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics novel phylogenetic diversity within phyla containing numerous cultured representatives. Here, we present a detailed University of Oklahoma Oklahoma State University phylogenetic analysis of the Proteobacteria-affiliated clones identified in a 13,001 nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene clones 770 Van Vleet Oval 307 LSE derived from Oklahoma tall grass prairie soil. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum in the community, and comprised Norman, OK 73019 Stillwater, OK 74078 25% of total clones. The most abundant and diverse class within the Proteobacteria was Alphaproteobacteria, which comprised 405 325 5255 405 744 6790 39% of Proteobacteria clones, followed by the Deltaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, and Gammaproteobacteria, which made Anne M. Spain (1), Lee R. Krumholz (1), Mostafa S. Elshahed (2) up 37, 16, and 8% of Proteobacteria clones, respectively. Members of the Epsilonproteobacteria were not detected in the dataset. [email protected] [email protected] Detailed phylogenetic analysis indicated that 14% of the Proteobacteria clones belonged to 15 novel orders and 50% belonged (1) Dept. of Botany and Microbiology, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK to orders with no described cultivated representatives or were unclassified. -

Anaplasmosis: an Emerging Tick-Borne Disease of Importance in Canada
IDCases 14 (2018) xxx–xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect IDCases journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/idcr Case report Anaplasmosis: An emerging tick-borne disease of importance in Canada a, b,c d,e e,f Kelsey Uminski *, Kamran Kadkhoda , Brett L. Houston , Alison Lopez , g,h i c c Lauren J. MacKenzie , Robbin Lindsay , Andrew Walkty , John Embil , d,e Ryan Zarychanski a Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada b Cadham Provincial Laboratory, Government of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada c Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada d Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Medical Oncology and Hematology, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada e CancerCare Manitoba, Department of Medical Oncology and Hematology, Winnipeg, MB, Canada f Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Section of Infectious Diseases, Winnipeg, MB, Canada g Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada h Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Max Rady College of Medicine, Department of Community Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada i Public Health Agency of Canada, National Microbiology Laboratory, Zoonotic Diseases and Special Pathogens, Winnipeg, MB, Canada A R T I C L E I N F O A B S T R A C T Article history: Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA) is an infection caused by the intracellular bacterium Received 11 September 2018 Anaplasma phagocytophilum. -

2012 Case Definitions Infectious Disease
Arizona Department of Health Services Case Definitions for Reportable Communicable Morbidities 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition of Terms Used in Case Classification .......................................................................................................... 6 Definition of Bi-national Case ............................................................................................................................................. 7 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ............................................... 7 AMEBIASIS ............................................................................................................................................................................. 8 ANTHRAX (β) ......................................................................................................................................................................... 9 ASEPTIC MENINGITIS (viral) ......................................................................................................................................... 11 BASIDIOBOLOMYCOSIS ................................................................................................................................................. 12 BOTULISM, FOODBORNE (β) ....................................................................................................................................... 13 BOTULISM, INFANT (β) ................................................................................................................................................... -

Evolutionary Origin of Insect–Wolbachia Nutritional Mutualism
Evolutionary origin of insect–Wolbachia nutritional mutualism Naruo Nikoha,1, Takahiro Hosokawab,1, Minoru Moriyamab,1, Kenshiro Oshimac, Masahira Hattoric, and Takema Fukatsub,2 aDepartment of Liberal Arts, The Open University of Japan, Chiba 261-8586, Japan; bBioproduction Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Tsukuba 305-8566, Japan; and cCenter for Omics and Bioinformatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa 277-8561, Japan Edited by Nancy A. Moran, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, and approved June 3, 2014 (received for review May 20, 2014) Obligate insect–bacterium nutritional mutualism is among the insects, generally conferring negative fitness consequences to most sophisticated forms of symbiosis, wherein the host and the their hosts and often causing hosts’ reproductive aberrations to symbiont are integrated into a coherent biological entity and un- enhance their own transmission in a selfish manner (7, 8). Re- able to survive without the partnership. Originally, however, such cently, however, a Wolbachia strain associated with the bedbug obligate symbiotic bacteria must have been derived from free-living Cimex lectularius,designatedaswCle, was shown to be es- bacteria. How highly specialized obligate mutualisms have arisen sential for normal growth and reproduction of the blood- from less specialized associations is of interest. Here we address this sucking insect host via provisioning of B vitamins (9). Hence, it –Wolbachia evolutionary -

Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis Are Tick-Borne Diseases Caused by Obligate Anaplasmosis: Intracellular Bacteria in the Genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma
Ehrlichiosis and Importance Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases caused by obligate Anaplasmosis: intracellular bacteria in the genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These organisms are widespread in nature; the reservoir hosts include numerous wild animals, as well as Zoonotic Species some domesticated species. For many years, Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species have been known to cause illness in pets and livestock. The consequences of exposure vary Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, from asymptomatic infections to severe, potentially fatal illness. Some organisms Canine Hemorrhagic Fever, have also been recognized as human pathogens since the 1980s and 1990s. Tropical Canine Pancytopenia, Etiology Tracker Dog Disease, Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are caused by members of the genera Ehrlichia Canine Tick Typhus, and Anaplasma, respectively. Both genera contain small, pleomorphic, Gram negative, Nairobi Bleeding Disorder, obligate intracellular organisms, and belong to the family Anaplasmataceae, order Canine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, Rickettsiales. They are classified as α-proteobacteria. A number of Ehrlichia and Canine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Anaplasma species affect animals. A limited number of these organisms have also Equine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, been identified in people. Equine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Recent changes in taxonomy can make the nomenclature of the Anaplasmataceae Tick-borne Fever, and their diseases somewhat confusing. At one time, ehrlichiosis was a group of Pasture Fever, diseases caused by organisms that mostly replicated in membrane-bound cytoplasmic Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, vacuoles of leukocytes, and belonged to the genus Ehrlichia, tribe Ehrlichieae and Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, family Rickettsiaceae. The names of the diseases were often based on the host Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, species, together with type of leukocyte most often infected. -

Acidification Increases Abundances of Vibrionales And
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Sapientia Acidification increases abundances of Vibrionales and Planctomycetia associated to a seaweed-grazer system: potential consequences for disease and prey digestion efficiency Tania Aires1,*, Alexandra Serebryakova1,2,*, Frédérique Viard2,3, Ester A. Serrão1 and Aschwin H. Engelen1 1 Center for Marine Sciences (CCMAR), CIMAR, University of Algarve, Campus de Gambelas, Faro, Portugal 2 Sorbonne Université, CNRS, Lab Adaptation and Diversity in Marine Environments (UMR 7144 CNRS SU), Station Biologique de Roscoff, Roscoff, France 3 CNRS, UMR 7144, Divco Team, Station Biologique de Roscoff, Roscoff, France * These authors contributed equally to this work. ABSTRACT Ocean acidification significantly affects marine organisms in several ways, with complex interactions. Seaweeds might benefit from rising CO2 through increased photosynthesis and carbon acquisition, with subsequent higher growth rates. However, changes in seaweed chemistry due to increased CO2 may change the nutritional quality of tissue for grazers. In addition, organisms live in close association with a diverse microbiota, which can also be influenced by environmental changes, with feedback effects. As gut microbiomes are often linked to diet, changes in seaweed characteristics and associated microbiome can affect the gut microbiome of the grazer, with possible fitness consequences. In this study, we experimentally investigated the effects of acidification on the microbiome of the invasive brown seaweed Sargassum muticum and a native isopod consumer Synisoma nadejda. Both were exposed to ambient CO2 conditions Submitted 13 September 2017 (380 ppm, pH 8.16) and an acidification treatment (1,000 ppm, pH 7.86) for three Accepted 26 January 2018 weeks. -

Ultrastructure and Localization of Neorickettsia in Adult Digenean
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2017 Ultrastructure and localization of Neorickettsia in adult digenean trematodes provides novel insights into helminth-endobacteria interaction Kerstin Fischer Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Vasyl V. Tkach University of North Dakota Kurt C. Curtis Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Peter U. Fischer Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/open_access_pubs Recommended Citation Fischer, Kerstin; Tkach, Vasyl V.; Curtis, Kurt C.; and Fischer, Peter U., ,"Ultrastructure and localization of Neorickettsia in adult digenean trematodes provides novel insights into helminth-endobacteria interaction." Parasites & Vectors.10,. 177. (2017). https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/open_access_pubs/5789 This Open Access Publication is brought to you for free and open access by Digital Commons@Becker. It has been accepted for inclusion in Open Access Publications by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons@Becker. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Fischer et al. Parasites & Vectors (2017) 10:177 DOI 10.1186/s13071-017-2123-7 RESEARCH Open Access Ultrastructure and localization of Neorickettsia in adult digenean trematodes provides novel insights into helminth- endobacteria interaction Kerstin Fischer1, Vasyl V. Tkach2, Kurt C. Curtis1 and Peter U. Fischer1* Abstract Background: Neorickettsia are a group of intracellular α proteobacteria transmitted by digeneans (Platyhelminthes, Trematoda). These endobacteria can also infect vertebrate hosts of the helminths and cause serious diseases in animals and humans. Neorickettsia have been isolated from infected animals and maintained in cell cultures, and their morphology in mammalian cells has been described. -

Zoonotic Diseases Birds
Zoonotic Diseases Birds Zoonotic diseases Psittacosis (Ornithosis, Chlamydiosis): Psittacosis is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia psittaci. C. psittaci is common in wild birds and can occur in laboratory bird colonies. Infected birds are highly contagious to other birds and to humans. The organism is spread to humans by aerosolization of respiratory secretions or feces from the infected birds. Typical symptoms in the bird are diarrhea, ocular discharge, and nasal discharge. The infection in humans by C.psittaci, can cause fever, headache, myalgia chills, and upper and lower respiratory disease. Serious complications can occur and include pneumonia, hepatitis, myocarditis, thrombophlebitis and encephalitis. It is responsive to antibiotic therapy but relapses can occur in untreated infections. Prevention: Only disease-free flocks should be allowed into the research facility. Wild-caught birds or birds of unknown status should be treated prophylactically for 45 days with chlortetracycline. Animal Biosafety Level 2 practices are recommended for personnel working with naturally infected birds or experimentally infected birds. Wearing NIOSH certified dust masks should be considered in rooms housing birds of unknown health status. Newcastle Disease: Newcastle disease is caused by a paramyxovirus and can be seen in birds both wild and domestic. Transmission is mainly by aerosol but contaminated food, water and equipment can also transmit the infection within bird colonies. Pathogenic strains produce anorexia and respiratory disease in adult birds.Young birds often show neurologic signs. In humans the disease is characterized by conjunctivitis, fever, and respiratory symptoms. Prevention: The disease can be prevented by immunizing susceptible birds and obtaining birds from flocks free of infection. -

Ehrlichiosis in Brazil
Review Article Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet., Jaboticabal, v. 20, n. 1, p. 1-12, jan.-mar. 2011 ISSN 0103-846X (impresso) / ISSN 1984-2961 (eletrônico) Ehrlichiosis in Brazil Erliquiose no Brasil Rafael Felipe da Costa Vieira1; Alexander Welker Biondo2,3; Ana Marcia Sá Guimarães4; Andrea Pires dos Santos4; Rodrigo Pires dos Santos5; Leonardo Hermes Dutra1; Pedro Paulo Vissotto de Paiva Diniz6; Helio Autran de Morais7; Joanne Belle Messick4; Marcelo Bahia Labruna8; Odilon Vidotto1* 1Departamento de Medicina Veterinária Preventiva, Universidade Estadual de Londrina – UEL 2Departamento de Medicina Veterinária, Universidade Federal do Paraná – UFPR 3Department of Veterinary Pathobiology, University of Illinois 4Department of Veterinary Comparative Pathobiology, Purdue University, Lafayette 5Seção de Doenças Infecciosas, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul – UFRGS 6College of Veterinary Medicine, Western University of Health Sciences 7Department of Clinical Sciences, Oregon State University 8Departamento de Medicina Veterinária Preventiva e Saúde Animal, Universidade de São Paulo – USP Received June 21, 2010 Accepted November 3, 2010 Abstract Ehrlichiosis is a disease caused by rickettsial organisms belonging to the genus Ehrlichia. In Brazil, molecular and serological studies have evaluated the occurrence of Ehrlichia species in dogs, cats, wild animals and humans. Ehrlichia canis is the main species found in dogs in Brazil, although E. ewingii infection has been recently suspected in five dogs. Ehrlichia chaffeensis DNA has been detected and characterized in mash deer, whereas E. muris and E. ruminantium have not yet been identified in Brazil. Canine monocytic ehrlichiosis caused by E. canis appears to be highly endemic in several regions of Brazil, however prevalence data are not available for several regions. -

Successful Treatment of Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis in Children Using Rifampin
Successful Treatment of Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis in Children Using Rifampin Peter J. Krause, MD*; Cathy L. Corrow, MD*; and Johan S. Bakken, MD‡ ABSTRACT. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (HGE) is the removal of a small brown tick attached behind her left ear 7 an emerging tick-borne infectious disease caused by days earlier. The physical examination was unremarkable other Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Clinical features include a than a temperature of 39.8°C. The hemogram showed a white ϫ 9 flu-like illness that usually resolves within 1 week. More blood cell count (WBC) of 10.9 10 /L with 61% segmented neutrophils, 24% band neutrophils, 10% lymphocytes, and 5% serious infection may occur that requires hospital admis- monocytes, and a platelet count of 238 ϫ 109/L. Microscopic sion or culminates in death. Doxycycline is the treatment examination of 800 leukocytes on a Wright-stained peripheral of choice for HGE but may cause permanent staining of blood smear failed to reveal diagnostic inclusions (morulae) in teeth in children younger than 8 years of age. We report neutrophils. The patient was thought to have a viral syndrome, successful treatment of HGE with rifampin in 2 children, and she was asked to return for follow-up examination in 48 4 and 6 years old. A course of rifampin for 5 to 7 days hours. Her fever exceeded 39°C and her other symptoms per- should be considered in children younger than 8 years of sisted. age who experience non–life-threatening A phagocyto- At a follow-up visit 2 days later on June 19, 1998, the total WBC ϫ 9 ϫ 9 philum infection.