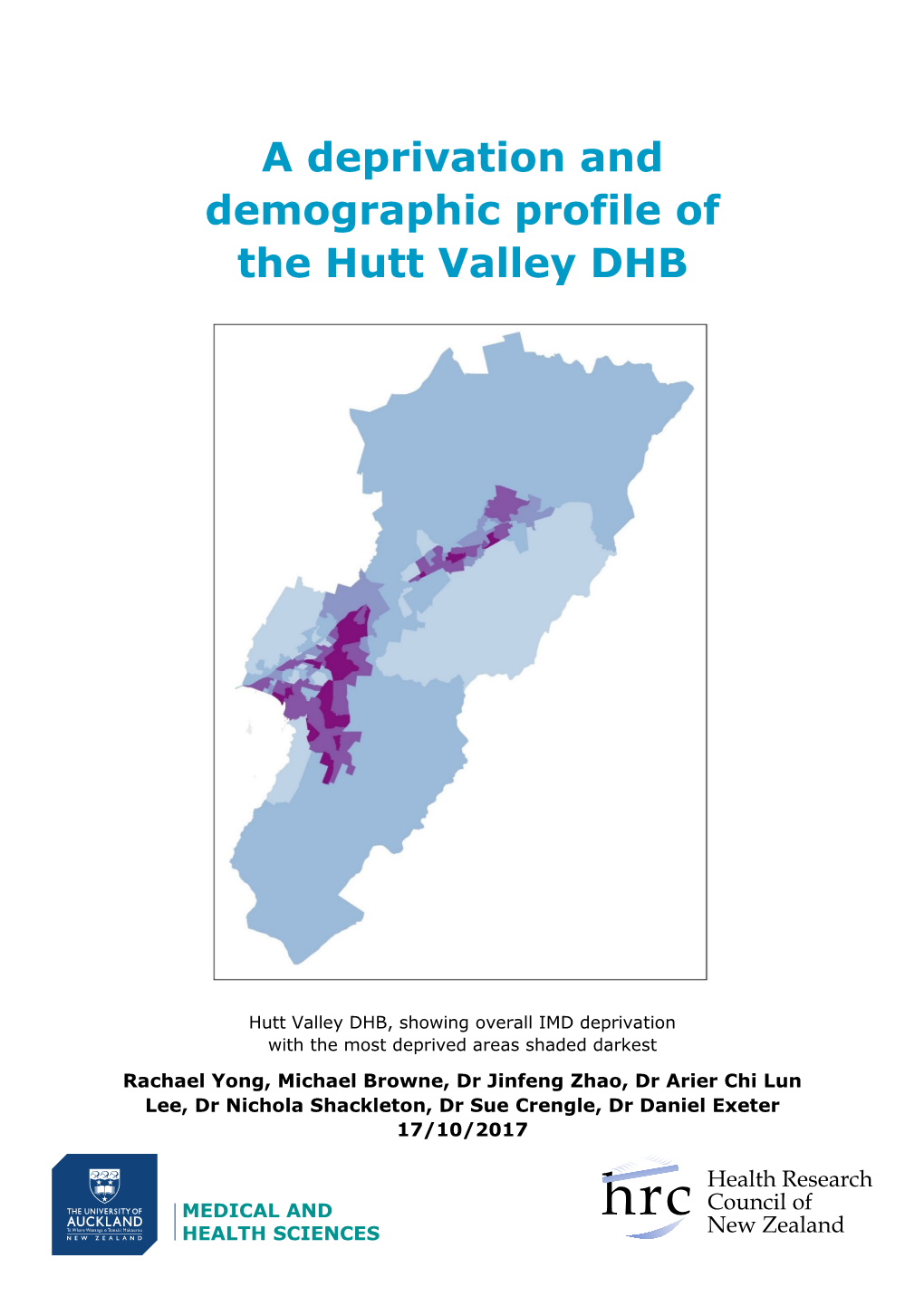
Hutt Valley DHB
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Level 3 Chamber of Commerce House 15 Daly Street Lower Hutt Wellington 5010 New Zealand 30 April 2021 Hon Michael Wood Minister
Level 3 Chamber of Commerce House 15 Daly Street Lower Hutt Wellington 5010 New Zealand 30 April 2021 Hon Michael Wood Minister of Transport By email; [email protected] Dear Minister, NZ Upgrade Programme – Melling Interchange The Board and membership of the Hutt Valley Chamber of Commerce and Industry is alarmed and deeply disappointed to read recent media articles regarding the inclusion of Melling Interchange in the Government’s reassessment of infrastructure development projects. As you may be aware the Hutt Valley Chamber has been calling for the re-development of the Melling Interchange with SH2 for many years. As a national roading project the current Melling/SH2 intersection is completely inadequate, causing traffic bottlenecks daily and regular accidents. It is a crucial piece of local infrastructure that is a constant chokepoint for all our businesses trying to move people, materials and products around the valley, the region, and nationally. It is an economic drain on our local Hutt Valley economy as well as the wider Wellington region and continues to get worse every year. However, it is not a stand alone transport project. The redevelopment of the SH2/Melling interchange underpins the greater RiverLink project which completely transforms the Lower Hutt city centre. RiverLink is regarded as a shining example of how Waka Kotahi, the Greater Wellington Regional Council and the Hutt City Council can work collaboratively, leveraging combined budgets to deliver a single project in a cohesive manner. It includes improving public transport to the city centre with upgraded railway infrastructure, new active transport modes with cycling and walking, as well as enabling new housing options for city centre residents. -

Main Ridge Hill to Ferry Road, Days Bay — NZ Walking Access Commission Ara Hīkoi Aotearoa
10/1/2021 Main Ridge Hill to Ferry Road, Days Bay — NZ Walking Access Commission Ara Hīkoi Aotearoa Main Ridge Hill to Ferry Road, Days Bay Walking Dog Friendly Length 5.2 km Journey Time 2 hours 30 mins Region Wellington Sub-Region Lower Hutt Part of Collections Greater Wellington , East Harbour Regional Park Track maintained by Greater Wellington Regional Council https://www.walkingaccess.govt.nz/track/main-ridge-hill-to-ferry-road-days-bay/pdfPreview 1/4 10/1/2021 Main Ridge Hill to Ferry Road, Days Bay — NZ Walking Access Commission Ara Hīkoi Aotearoa This track provides a route through the heart of the northern area, from where you can access the eastern bays of Wellington Harbour or the Wainuiomata Valley. The track passes through regenerating bush and impressive stands of mature beech/rata forest. Times are one way. Conditions: Dogs are welcome in the northern block. Keep them under control and remove droppings. Dogs must be on a leash on the Pencarrow Coast Road to protect wildlife habitat. Do not take them south of the steep foot track to the historic lighthouse. No dogs are permitted at Baring Head as livestock graze the area. Pack in and pack out. Take your rubbish home and recycle it where possible. Do not remove, disturb or damage native plants and animals. Light no res. Portable stoves are permitted. Mountain biking is permitted on designated tracks in the northern forest (Main Ridge from Wainuiomata to Rata Ridge), in the Parangarahu (Pencarrow) Lakes Area and at Baring Head. The park has moderately steep hills and is exposed in places. -

2. Hutt Valley Line
2. Hutt Valley Line TDW | Transdev Train Replacement Booklet 4 SUMMARY OF HUTT VALLEY LINE TRAIN REPLACEMENT SERVICES OUTBOUND FROM WELLINGTON: When two buses depart for one service: • Bus 1: (Waterloo Loop) Depart Wellington to Ngauranga, drop of Woburn and connect to all stopper at Waterloo • Bus 2: Depart Wellington express to Petone, all stops to Waterloo, connect with Waterloo Loop and all stops to Upper Hutt • Manor Park is serviced by a shuttle operating between Manor Park and Silverstream INBOUND FROM UPPER-HUTT: When two buses are operating one service: • Bus 1: (Waterloo Loop) Departs Waterloo and then all stops to Wellington • Bus 2: Depart Upper Hutt all stops to Waterloo then express to Wellington • Manor Park is serviced by a shuttle operating between Manor Park and Silverstream HVL LINE HVL TDW | Transdev Train Replacement Booklet 5 TDW | Transdev Train Replacement Booklet 6 HUTT VALLEY LINE BUSES REPLACING TRAIN STOPS Ngauranga Inbound: On Hutt Road, after the underbridge Outbound: On Hutt Road, after the intersection HVL LINEHVL Petone Inbound: On Hutt Road, opposite the station Outbound: Bus stop B on Hutt Road, on the East side of the station TDW | Transdev Train Replacement Booklet 7 Ava Inbound: On Wakefield Street near the pedestrian over bridge access Outbound: On Wakefield Street, just before Cuba Street HVL LINE HVL Woburn Inbound: On Cambridge Terrace, opposite the station car park Outbound: The Cambridge Terrace bus shelter in front of the station car park TDW | Transdev Train Replacement Booklet 8 Waterloo -

Our Outcomes Journey
TE WHĀNAU O WAIPAREIRA l ANNUAL REPORT 2015 -2016 2 #FUTUREMAKERS OUR OUTCOMES JOURNEY - TE WHĀ NAU O WAIPAREIRA #FUTUREMAKERS PERFORMANCE SUMMARY - l Annual Report 2015 – 2016 l Te Rārangi Upoko CONTENTS HE MIHI 2 NGĀ HUA O MATAORA OUR MATAORA OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK 2 OUTCOMES MEASUREMENT PILOT PĒPI AND TAMARIKI SERVICES 3 OUR WHĀNAU 5 6 OUR TAMARIKI 5 7 KORURE WHĀNAU – WHĀNAU TRANSFORMATION 8 REPORTING ON OUTCOMES 10 RANGATAHI OUTCOMES 11 OUR TAITAMARIKI SPEAK UP 12 SUPPORTING KORURE WHĀNAU - LIST OF SERVICES 14 HĀPORI MOMOHO - THRIVING COMMUNITIES 16 TE KĀHUI ORA O TĀMAKI COLLECTIVE IMPACT ACROSS THE TĀMAKI REGION 17 CRITICAL PARTNERSHIPS 20 SOCIAL VALUE AOTEAROA 20 HĀPAI TE HAUORA 21 WAITEMATA DISTRICT HEALTH BOARD 22 #FUTUREMAKERS MANA MĀORI 22 URBAN MAORI ADVANCEMENT NUMA 23 TE POU MATAKANA 25 WHĀNAU TAHI 27 DIRECTORY 28 OUR OUTCOMES JOURNEY - l Annual Report 2015 – 2016 l 1 He Mihi GREETINGS OUR MATAORA noho ana au ki te tara Waiatarua Ka hoki ngā whakaaro ki te wā o mua OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK EKi wana ki te wehi o ngā iwi Māori Ūhia ngā kanohi kei raro te whenua o te awa e are accountable to those that have papaku come before us, our communities and our Te waitohitohia rangatira ka roaka te ingoa Wwhānau. In 2013 we acknowledged this Waipareira! responsibility and laid out our vision for whānau in the “Whānau Future Makers, A 25 Year Outlook Ko te wehi ki a Ihowa ora o ngā mano. Kia Strategic Plan” māturuturu te tōmairangi o tōnā nui o tōnā atawhai ki runga i a tātau katoa. -

Annual Report for the Year Ended 31 December 2019
MAUNGARAKI SCHOOL ANNUAL REPORT FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2019 School Directory Ministry Number: 2968 Principal: Shane Robinson School Address: 137 Dowse Drive, Maungaraki, Lower Hutt School Postal Address: 137 Dowse Drive, Maungaraki, LOWER HUTT, 5010 School Phone: 04 569 7205 School Email: [email protected] Members of the Board of Trustees How Term Position Expires/ Name Position Gained Occupation Expired Paul Matthews Chairperson Elected CEO IT Professionals Jun 2022 Shane Robinson Principal ex Officio Kaylee Gibbs Parent Rep Elected Cafe Assistant Jun 2022 Megan Hurley Parent Rep Elected Business Development Manager Jun 2022 Wayne Church Parent Rep Elected Governance Advisor Jun 2022 Elizabeth Briscoe Parent Rep Elected Stay at home mum Jun 2022 Julie McDonald Parent Rep Co-opted Secondary school Teacher Jun 2022 Chris Cowman Staff Rep Elected Teacher Jun 2022 Accountant / Service Provider: Education Services Ltd MAUNGARAKI SCHOOL Annual Report - For the year ended 31 December 2019 Index Page Statement Financial Statements 1 Statement of Responsibility 2 Statement of Comprehensive Revenue and Expense 3 Statement of Changes in Net Assets/Equity 4 Statement of Financial Position 5 Statement of Cash Flows 6 - 12 Statement of Accounting Policies 13 - 21 Notes to the Financial Statements Other Information Analysis of Variance Kiwisport Maungaraki School Statement of Comprehensive Revenue and Expense For the year ended 31 December 2019 2019 2019 2018 Budget Notes Actual (Unaudited) Actual $ $ $ Revenue Government Grants 2 -

Newsletter January 2015
Friends of Baring Head Newsletter Visit us on line at http://www.baringhead.org.nz/ or follow us on Facebook January 2015 Number 9 Message from the Chair The regional park at Baring Head provides visitors with all sorts of recreation activities as well as opportunities for volunteer workers to protect and enhance the environment. For some time now the Friends have been thinking how to allow visitors and volunteers to combine their involvement in both of these interests and the first trip we’ve arranged for summer 2014/15 showed us this approach has real possibilities. The Friends arranged with a four-wheel drive group, the Cross Country Group, to transport people over to the Fitzroy Bay beach from the bridge car-park for a small charge. Available seats were in great demand, with some people having to be asked to wait for trips later in the summer. Many of those lucky enough to claim a seat hadn’t previously been to Baring Head and some weren’t even sure where it was! The first part of the trip was to the coast where, after an introductory talk and a chance to look at a new beachcombing booklet (see below in Finding out about what your beachcombing turns up) visitors were able to walk along the beach, finding treasures, removing horned poppy and picking up rubbish. The much- reduced horned poppy density is obvious along the sections of the beach that have been tackled – good work previous visitors and volunteers! On this occasion, more of the weed was cleared, particularly further south and near the climbing rocks. -

2015 Sunday Festival Report and Survey Results
2015 Sunday Festival Report and Survey Results CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................... 3 2.0 BACKGROUND ....................................................................................................................... 3 3.0 PURPOSE ................................................................................................................................ 3 4.0 FESTIVAL PROFILE .................................................................................................................. 4 5.0 SURVEY METHODOLOGY ..................................................................................................... 11 6.0 FINDINGS ............................................................................................................................. 12 Who came to Te Rā? ...................................................................................................... 12 Where did people at Te Rā festival come from? ............................................................ 13 How did people hear about Te Rā? ................................................................................ 14 What the Te Rā festival means for those who came...................................................... 14 What did people think of Te Rā 2015? ........................................................................... 16 Entertainment, hauora and mātauranga tents and the youth zone .............................. 17 Stalls food -

28927-Article Text-66259-1-10-20171212
Governed by Contracts: The Development of Indigenous Primary Health Services in Canada, Australia and New Zealand Josée G. Lavoie, PhD Candidate London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Health Policy Unit Abstract This paper is concerned with the emergence of Indigenous primary health care organizations in Canada, Australia and New Zealand. In Canada, the adoption of the 1989 Health Transfer Policy promoted the transfer of on-reserve health services from the federal government to First Nations. In Australia, Aboriginal Community-Controlled Health Services first appeared in the 1970s because of community mobilization. It aims to provide some access to free health care to Aboriginal People. A more recent model, the Primary Health Care Access Program, aims at guaranteeing Aboriginal access to comprehensive primary health care services under the authority of Regional Aboriginal Health Boards. In New Zealand, Maori providers emerged because of the market-like conditions implemented in the 1990s. This study compares the policy and contractual environment put in place to support Indigenous health providers in Canada, Australia and New Zealand, using a case study approach. Results show that the contractual environment does not necessarily match declared policy objectives, especially where competitive models for accessing funding have been implemented. Key Words Primary health care, policy, self-determination, Indigenous People, health care financing, fourth sector INTRODUCTION needs of that group; and to promote their political as- This paper is concerned with the emergence of a pirations involving a renegotiation of their relation- fourth sector in Canada’s, Australia’s and New ship with the nation-state. Key features include in- Zealand’s health care systems. -

Ministry of Health Contracted Adolescent Dental Providers
Ministry of Health Contracted Adolescent Dental Providers The Dental Studio Verve@Connolly Bdg, Wellington Newtown Dental Level 1, 2 Connolly Street Surgery 568 4006 Joanna 100 Riddiford Street 389 3808 I Care Dental Level 2 Mackay House Hodgkinson Level 1, 90 The Terrace 472 3510 560 3637 920 Queens Drive Capital Dental Ben Catherwood Newtown 1st Level 90 The Terrace Newtown 125-129 Riddiford Street ne 472 3510 Eastbourne Dental Cnr Marine Parade and 389 8880 Centre Capital Dental The bour Rimu Street, Eastbourne Ground Floor, Montreaux 562 7506 Terrace Adrian Tong Raine Street Dental Building, 164 The Terrace East 499 9360 476 7295 4 Raine Street Raymond Joe Capital Dental Karori Dental Dental Reflections 155 The Terrace Petone 272 Jackson Street, Petone Centre 146 Karori Road 472 5377 Petone 920 0880 Karori Karori 476 6451 Ferry Dental 155 The Terrace Singleton Dental Whai Oranga 472 5377 338 Karori Road 476 6252 Dental - Cuc Dang 7 The Strand, Wainuiomata Angela McKeefry Level 3, The Dominion Wainui 564 6966 473 7802 Bldg, 78 Victoria Street Khandallah Dental Irina Kvatch Central Dental Surgery, Centre 2 Ganges Road Lumino Dental 180 Stokes Valley Road, Wellington CityWellington 472 6306 139 Featherston Street 479 2294 alley Khandallah V 939 1818 Stokes Valley Navin Vithal Tennyson Dental Centre, S 32 Lorne Street, Te Aro CODE Dental 220 Main Road 801 6228 Ashwin Magan Victoria St Dental 232 8001 Tawa Level 3, 84-90 Main Street Level 6, 86 Victoria Street Tawa 527 7914 555 1001 The Dental Centre Art of Dentistry 10 Royal Street David -

Modeling Site Effects in the Lower Hutt Valley, New Zealand
2694 MODELING SITE EFFECTS IN THE LOWER HUTT VALLEY, NEW ZEALAND Brian M ADAMS1, John B BERRILL2, Rob O DAVIS3 And John J TABER4 SUMMARY Lower Hutt City lies atop a wedge of Quaternary sediments forming a long alluvial valley. On its western edge the sediments butt up against the near vertical wall of the potentially active Wellington Fault, capable of an earthquake of moment magnitude 7.6. A two-dimensional linear finite-element method has been used to model the propagation of antiplane SH waves within the soft sediments and surrounding bedrock. The technique has proved to be an efficient and accurate means of modeling fine geological detail. Two detailed geological cross-sections through the Lower Hutt were modeled to gain an overall impression of the valley's seismic behaviour. It was found that horizontally propagating surface waves, generated at the valley edges, are the cause of significant amplification. The aptly named basin-edge effect – speculated to be the cause of a belt of severe shaking during the 1995 Kobe earthquake – is observed in the simulation results, occuring some 70-200 metres out from the fault. Fourier spectral ratios across the valley indicate a behaviour dominated by two-dimensional resonance, and compare favourably in magnitude with previously collected weak motion data. Certain resonant frequencies within the range 0.3-2.5 hertz are amplified up to 14 times that for nearby outcropping bedrock. Results are likely to be conservative due to the linear modeling, yet exclude fault-rupture effects due to the teleseismic nature of the input scheme. INTRODUCTION In this paper we describe our use of a two-dimensional finite-element numerical scheme to simulate ground motions from earthquake shaking in the soft sediments in-filling the Lower Hutt Valley. -

Mahere-Ā-Tau 2020/21 Annual Plan 2020/21
Mahere-ā-Tau 2020/21 Annual Plan 2020/21 WHAT GREATER WELLINGTON DOES IN OUR REGION Greater Wellington has a role as an environmental protection organisation for our region. Greater Wellington has another role as the owner of Metlink, the organisation that delivers public transport across the region. Now, these might seem like incompatible roles but that’s not necessarily the case. More people using public transport, means fewer cars on the road, means less pollution and a cleaner environment. Further down, you’ll find more information about what Greater Wellington does across the region. WHAT GREATER WELLINGTON IS DOING IN THE HUTT VALLEY We’re continuing to work on We’re upgrading the Hutt Restoring the lower the RiverLink project Valley Line through the Future Kilmister block in Rail project Belmont Regional Park RiverLink is one of Greater Wellington’s major projects. It’s being delivered in We know how frustrating it can be when Located in the hills between Porirua collaboration by Greater Wellington, there are delays on the Hutt Valley and Hutt Valley, Belmont Regional Park Hutt City Council and the New Zealand railway line during peak times. contains much of the headwaters of the Transport Agency to achieve some big western side of the valley. improvements for Lower Hutt. To reduce these delays and allow more people to travel on the trains in the The Kilmister block within Belmont RiverLink will make Hutt City safer from future, KiwiRail and Greater Wellington Regional Park has been grazed under severe floods, help the city develop are working together to upgrade the licence for many years. -

Conjunctive Water Management Recommendations for the Hutt Valley Conjunctive Water Management Recommendations for the Hutt Valley
Conjunctive water management recommendations for the Hutt Valley Conjunctive water management recommendations for the Hutt Valley Mark Gyopari Earth in Mind Ltd For more information, contact the Greater Wellington Regional Council: Wellington Masterton GW/ESC-T-15/77 PO Box 11646 PO Box 41 ISBN-978-1-927217-78-8 (online) ISBN-978-1-927217-77-1 (print) T 04 384 5708 T 06 378 2484 F 04 385 6960 F 06 378 2146 July 2015 www.gw.govt.nz www.gw.govt.nz www.gw.govt.nz [email protected] Report prepared by: Mark Gyopari Earth in Mind Ltd Report reviewed by: M Thompson Senior Environmental Scientist Report reviewed by: N Boyens Team Leader, Hydrology Report approved for release by: G Sevicke-Jones Manager, Environmental Science Date: July 2015 DISCLAIMER This report has been prepared by Environmental Science staff of Greater Wellington Regional Council (GWRC) and as such does not constitute Council policy. In preparing this report, the authors have used the best currently available data and have exercised all reasonable skill and care in presenting and interpreting these data. Nevertheless, GWRC does not accept any liability, whether direct, indirect, or consequential, arising out of the provision of the data and associated information within this report. Furthermore, as GWRC endeavours to continuously improve data quality, amendments to data included in, or used in the preparation of, this report may occur without notice at any time. GWRC requests that if excerpts or inferences are drawn from this report for further use, due care should be taken to ensure the appropriate context is preserved and is accurately reflected and referenced in subsequent written or verbal communications.