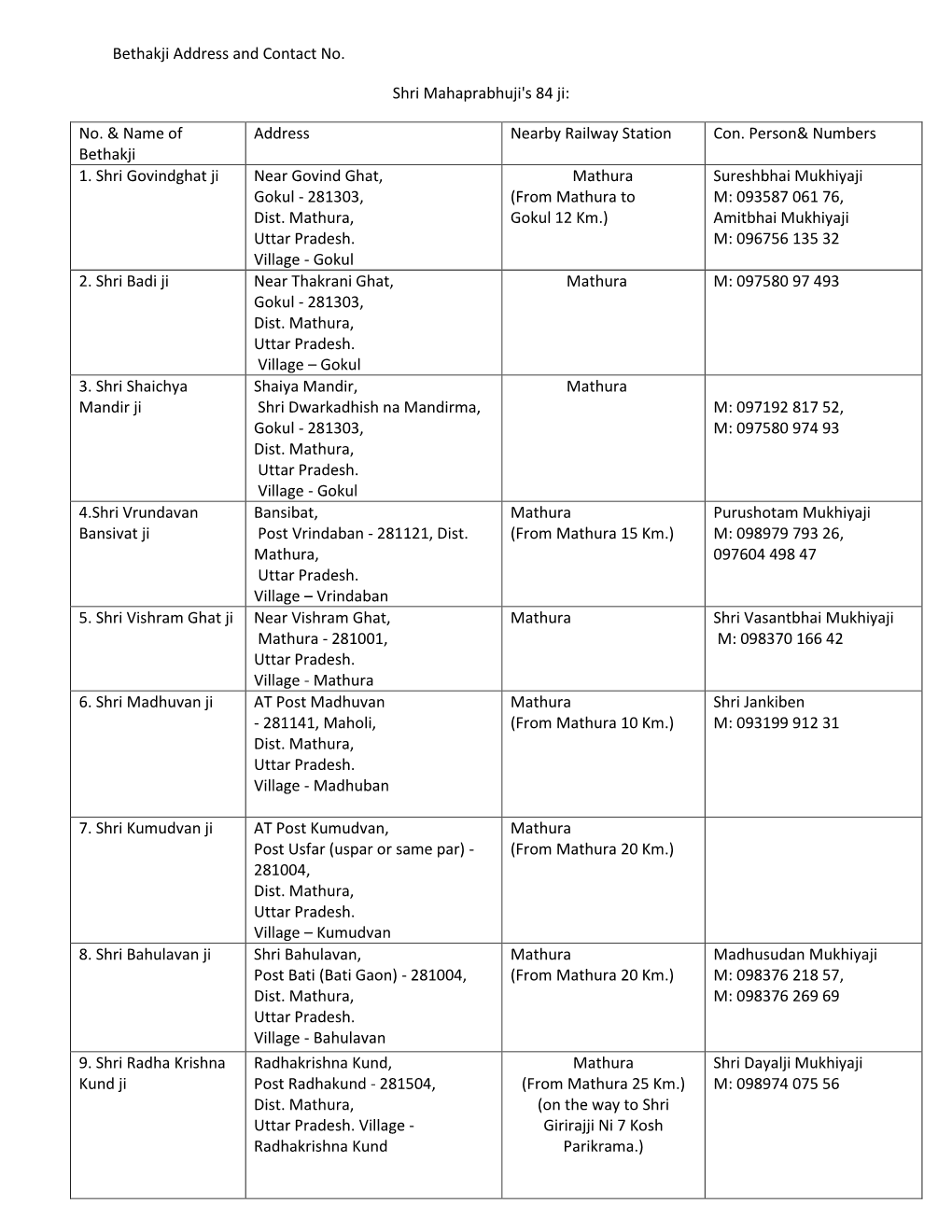
Bethakji Address and Contact No. Shri Mahaprabhuji's 84 Ji
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Tamilnadu.Pdf
TAKING TAMIL NADU AHEAD TAMIL NADU Andhra Pradesh Karnataka TAMIL NADU Kerala The coastal State of Tamil Nadu has seen rapid progress in road infrastructure development since 2014. The length of National Highways in the State has reached 7,482.87 km in 2018. Over 1,284.78 km of National Highways have been awarded in just four years at a cost of over Rs. 20,729.28 Cr. Benchmark projects such as the 115 km Madurai Ramanathapuram Expressway worth Rs. 1,134.35 Cr, are being built with investments to transform the State’s economy in coming years. “When a network of good roads is created, the economy of the country also picks up pace. Roads are veins and arteries of the nation, which help to transform the pace of development and ensure that prosperity reaches the farthest corners of our nation.” NARENDRA MODI Prime Minister “In the past four years, we have expanded the length of Indian National Highways network to 1,26,350 km. The highway sector in the country has seen a 20% growth between 2014 and 2018. Tourist destinations have come closer. Border, tribal and backward areas are being connected seamlessly. Multimodal integration through road, rail and port connectivity is creating socio economic growth and new opportunities for the people. In the coming years, we have planned projects with investments worth over Rs 6 lakh crore, to further expand the world’s second largest road network.” NITIN GADKARI Union Minister, Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Shipping and Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation Fast tracking National Highway development in Tamil Nadu NH + IN PRINCIPLE NH LENGTH UPTO YEAR 2018 7,482.87 km NH LENGTH UPTO YEAR 2014 5,006 km Adding new National Highways in Tamil Nadu 2,476.87 143.15 km km Yr 2014 - 2018 Yr 2010 - 2014 New NH New NH & In principle NH length 6 Cost of Road Projects awarded in Tamil Nadu Yr 2010 - 2014 Yr 2014 - 2018 Total Cost Total Cost Rs. -

Tamil Nadu Government Gazette
© [Regd. No. TN/CCN/467/2012-14 GOVERNMENT OF TAMIL NADU [R. Dis. No. 197/2009. 2018 [Price : Rs. 4.80 Paise. TAMIL NADU GOVERNMENT GAZETTE PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY No. 30] CHENNAI, WEDNESDAY, JULY 25, 2018 Aadi 9, Vilambi, Thiruvalluvar Aandu–2049 Part VI—Section 3(a) Notifi cations issued by cost recoverable institutions of State and Central Governments. NOTIFICATIONS BY HEADS OF DEPARTMENTS, ETC. CONTENTS Pages. JUDICIAL NOTIFICATIONS Insolvency Petitions .. .. .. .. .. .. 76-86 [ 75 ] DTP—VI-3(a)—30 76 TAMIL NADU GOVERNMENT GAZETTE [Part VI—Sec. 3(a) NOTIFICATIONS BY HEADS OF DEPARTMENTS, ETC. JUDICIAL NOTIFICATIONS INSOLVENCY PETITIONS IN THE COURT OF THE SUBORDINATE JUDGE OF BHAVANI (I. P. No. 1/2014) (è.â‡. 383/2018) No. VI-3(a)/65/2018. Nagarajan, Son of Pattappagounder, 65/307-C, Main Road, P. Mettupalayam, P. Mettupalayam Village, Bhavani Taluk, Erode District.—Petitioner/Creditor. Versus M.A. Govindasamy, Son of Andavagounder, 47/297A, Main Road, P. Mettupalayam Village, Bhavani Taluk, Erode District and 60 others—Respondents/Debtors. Notice is hereby given under Section 19(2) of Provincial Insolvency Act that the Petitioner/Debtors have applied to this Court praying to adjudge the petitioner as an Insolvent and that, the said petition stand by posted to 16-8-2018. Sub Court, Bhavani, ââ¡.¡. ïï£èô†²I£èô†²I, 20th July 2018. ꣘¹ cFðF. (I. P. No. 4/2014) (è.â‡. 383/2018) No. VI-3(a)/66/2018. Murugesan, Son of Perumal, 1/57, Kathiriyankadu, Poonachai Village, Anthiyur Taluk Erode District.—Petitioner/Creditor. Versus Ulaganathan, Son of Semmalai, Kathiriyankadu, Poonachi Village, Anthiyur Taluk, Erode District and 13 others— Respondents/Debtors. -

SACRED SPACES and OBJECTS: the VISUAL, MATERIAL, and TANGIBLE George Pati
SACRED SPACES AND OBJECTS: THE VISUAL, MATERIAL, AND TANGIBLE George Pati BRAUER MUSEUM OF ART | APRIL 13 — MAY 8, 2016 WE AT THE BRAUER MUSEUM are grateful for the opportunity to present this exhibition curated by George Pati, Ph.D., Surjit S. Patheja Chair in World Religions and Ethics and Valparaiso University associate professor of theology and international studies. Through this exhibition, Professor Pati shares the fruits of his research conducted during his recent sabbatical and in addition provides valuable insights into sacred objects, sites, and practices in India. Professor Pati’s photographs document specific places but also reflect a creative eye at work; as an artist, his documents are also celebrations of the particular spaces that inspire him and capture his imagination. Accompanying the images in the exhibition are beautiful textiles and objects of metalware that transform the gallery into its own sacred space, with respectful and reverent viewing becoming its own ritual that could lead to a fuller understanding of the concepts Pati brings to our attention. Professor Pati and the Brauer staff wish to thank the Surjit S. Patheja Chair in World Religions and Ethics and the Partners for the Brauer Museum of Art for support of this exhibition. In addition, we wish to thank Gretchen Buggeln and David Morgan for the insights and perspectives they provide in their responses to Pati's essay and photographs. Gregg Hertzlieb, Director/Curator Brauer Museum of Art 2 | BRAUER MUSEUM OF ART SACRED SPACES AND OBJECTS: THE VISUAL, MATERIAL, AND TANGIBLE George Pati George Pati, Ph.D., Valparaiso University Śvetāśvatara Upaniṣad 6:23 Only in a man who has utmost devotion for God, and who shows the same devotion for teacher as for God, These teachings by the noble one will be illuminating. -

Circumambulation in Indian Pilgrimage: Meaning And
232 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOLUME 12, ISSUE 1, JANUARY-2021 ISSN 2229-5518 Circumambulation in Indian pilgrimage: Meaning and manifestation Santosh Kumar Abstract— Our ancient literature is full of examples where pilgrimage became an immensely popular way of achieving spiritual aims while walking. In India, many communities have attached spiritual importance to particular places or to the place where people feel a spiritual awakening. Circumambulation (pradakshina) around that sacred place becomes the key point of prayer and offering. All these circumambulation spaces are associated with the shrines or sacred places referring to auspicious symbolism. In Indian tradition, circumambulation has been practice in multiple scales ranging from a deity or tree to sacred hill, river, and city. The spatial character of the path, route, and street, shift from an inside dwelling to outside in nature or city, depending upon the central symbolism. The experience of the space while walking through sacred space remodel people's mental and physical character. As a result, not only the sacred space but their design and physical characteristics can be both meaningful and valuable to the public. This research has been done by exploring in two stage to finalize the conclusion, In which First stage will involve a literature exploration of Hindu and Buddhist scripture to understand the meaning and significance of circumambulation and in second, will investigate the architectural manifestation of various element in circumambulatory which help to attain its meaning and true purpose. Index Terms— Pilgrimage, Circumambulation, Spatial, Sacred, Path, Hinduism, Temple architecture —————————— —————————— 1 Introduction Circumambulation ‘Pradakshinā’, According to Rig Vedic single light source falling upon central symbolism plays a verses1, 'Pra’ used as a prefix to the verb and takes on the vital role. -

2021 A. Principal Chief Commissioner, Central GST, Ahmedabad Zone S
भारत सरकार GOVERNMENT OF INDIA वित्त मंत्रालय, राजस्व विभाग, Ministry of Finance, Department of Revenue, प्रधान मुख्य आयुक्त का कायाालय, Office of the Principal Chief Commissioner, कᴂद्रीय जीएसटी क्षेत्र, अहमदाबाद, जीएसटी भिन, राजस्व मागग, अम्बािाड़ी अहमदाबाद ३८००१५. Central GST Zone, Ahmedabad, GST Bhavan, Revenue Marg, Ambawadi, Ahmedabad – 380015. दूरभाष Telephone: 079-26302133, 2630 3408, 2630 3418 Fax: 079-26307389, Email: [email protected] For the Quarter ending March - 2021 A. Principal Chief Commissioner, Central GST, Ahmedabad Zone S.No. Office of Principal CPIO Appellate Jurisdiction Notified Chief Commissioner Authority officer for payment of fees 1 Office of the Ms Kriti Shri Ravindra PCCO, Central GST, Chief Principal Chief Pandey, Kumar Tiwari, Ahmedabad Zone Account Commissioner, Assistant Joint Officer, Central GST, Commissioner, Commissioner Central Ahmedabad Zone, Office of the Office of the Tax, 7th Floor, Central Principal Chief Principal Chief Ahmedabad- GST Bhavan, Commissioner, Commissioner, South Ambawadi, Central GST, Central GST, Ahmedabad-380015 Ahmedabad Ahmedabad Zone, Zone, 7th Floor, Central 7th Floor, Central GST Bhavan, GST Bhavan, Ambawadi, Ambawadi, Ahmedabad- Ahmedabad- 380015. 380015 Ph:079-26307587 Tel: 079- Fax 26303402 26304752 Fax: 079- 26306284 Commissionerate: Ahmedabad-South B. Commissioner S. Commission CPIO (Sh./Smt.) Appellate Authority Jurisdiction Notified No. erate (Sh./Smt.) officer for payment of fees 1 Central GST, Shri Aslam Shri Ravindra Kumar Tiwari, Central GST, Chief Ahmedabad- Abdulbhai Mansuri, Joint Commissioner, Office Ahmedabad-South Account South Asst. Commissioner, of the Principal Commissionerate Officer, Office of the Commissioner of Central (Headquarters Central Tax, Principal GST, 7th Floor, Central GST Office) Commissioner of Bhavan, Ambawadi, Ahmedabad Central GST, Ahmedabad- 380015, -South 4th Floor, Central Tel - 079- 26303402 GST Bhavan, E-mail [email protected] Ambawadi, Ahmedabad- 380015 Tel- 079- 26308237, E-mail tech.cgstahdsouth C. -

In the Name of Krishna: the Cultural Landscape of a North Indian Pilgrimage Town
In the Name of Krishna: The Cultural Landscape of a North Indian Pilgrimage Town A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Sugata Ray IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Frederick M. Asher, Advisor April 2012 © Sugata Ray 2012 Acknowledgements They say writing a dissertation is a lonely and arduous task. But, I am fortunate to have found friends, colleagues, and mentors who have inspired me to make this laborious task far from arduous. It was Frederick M. Asher, my advisor, who inspired me to turn to places where art historians do not usually venture. The temple city of Khajuraho is not just the exquisite 11th-century temples at the site. Rather, the 11th-century temples are part of a larger visuality that extends to contemporary civic monuments in the city center, Rick suggested in the first class that I took with him. I learnt to move across time and space. To understand modern Vrindavan, one would have to look at its Mughal past; to understand temple architecture, one would have to look for rebellions in the colonial archive. Catherine B. Asher gave me the gift of the Mughal world – a world that I only barely knew before I met her. Today, I speak of the Islamicate world of colonial Vrindavan. Cathy walked me through Mughal mosques, tombs, and gardens on many cold wintry days in Minneapolis and on a hot summer day in Sasaram, Bihar. The Islamicate Krishna in my dissertation thus came into being. -

VRINDAVAN ECO-CITY in MAKING: Working Together for Sustainable Development
Dr. S. K. Kulshrestha Vrindavan Eco-city in Making 43rd ISOCARP Congress 2007 VRINDAVAN ECO-CITY IN MAKING: Working Together for Sustainable Development INTRODUCTION As a part of the Tenth Five Year Plan, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) initiated the Eco-city Project, in 2002, with grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Environment and Forest (MoEF), Government of India. The German Technical Cooperation (GTZ), under its Indo- German Programme on Advisory Services for Environmental Management (ASEM), extended the technical support to the project. It is a demonstration project and in its first phase covers the following six selected cities in India: 1. Kottayam, Kerala State, a tourist centre; 2. Puri, Orissa State, a town of cultural significance; 3. Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu State, a pilgrimage and tourist centre; 4. Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh State, a pilgrimage centre; 5. Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh State, a heritage and tourist place; and 6. Vrindavan, Uttar Pradesh State, a heritage and tourist place. Under the project, funds are provided to the municipalities by CPCB for the identified and approved project, on 50:50 cost-sharing basis up to a maximum of Rs. 25 million (Euro 0.5 million) per town, wherein 50 per cent of the total budget should come from the municipalities either from their own funds or through financial institutions or any other source including NGOs and CBOs. The total fund for the first phase, including the share of municipalities is Rs.50 million (Euro 1 million at a conversion rate of Rs.50 per Euro, the same rate will be used throughout this paper). -

Apna Nashik-Lo
PROGR AM Designing an effective Air Quality Management (AQM) plan for a city requires robust data on levels of pollution, affected areas, source contributors, peaking trends and possible control mechanisms. The Air Pollution Knowledge Assessment (APnA) City Program seeks to make this database available and also serve as a starting point for understanding air pollution. The program, implemented by Urban Emissions and facilitated by Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation, seeks to create a comprehen- sive, city-specific information pool by pulling together data from disparate sources, surveys, mapping and atmospheric modeling. Policy options based on this information, and their implementation, 3 would be the effective next steps in improving the air quality of our ➜ Modeled annual average PM2.5 concentration (2018) μg/m For urban Nashik, average PM2.5 concentration was 46.0 ± cities. 18.6 μg/m3. This is within the national standard (40) but over four times the WHO guideline (10). 46.0 PM2.5 μg/m3 Agartala / Agra / Ahmedabad / Allahabad / Amritsar / THE AIR POLLUTION Asansol / Aurangabad / Bengaluru / Bhopal / ➜ Air monitoring infrastructure KNOWLEDGE Bhubaneswar / Chandigarh / Chennai / Coimbatore / Dehradun / Dhanbad / Dharwad-Hubli / Gaya / ASSESSMENT (APnA) Guwahati-Dispur / Gwalior / Hyderabad / Imphal / CITY PROGRAM Indore / Jaipur / Jamshedpur / Jodhpur / Kanpur / Kochi 4 1 17 / Kolkata / Kota / Lucknow / Ludhiana / Madurai / Mumbai / Muzaffarpur / Nagpur / Nashik / Panjim / Patna / Puducherry / Pune / Raipur / Rajkot / Ranchi / Shimla / Srinagar / Surat / Thiruvananthapuram / MANUAL STATIONS CONTINUOUS STATIONS REQUIRED STATIONS Tiruchirapalli / Vadodara / Varanasi / Vijayawada / Visakhapatnam ➜ Annual averages from the national ambient monitoring program (2011–2015) µg/m3 PM10 SO2 NO2 84.5 ± 35.8 23.7 ± 6.3 26.4 ± 4.6 NASHIK The city’s PM2.5 concentration is over four ➜ Trend in PM2.5 concentrations, based on satellite observations and global model simulations (1998–2016) µg/m3 times the WHO standards. -

Demographic Structure and Abundance of Asiatic Lions Panthera Leo Persica in Girnar Wildlife Sanctuary, Gujarat, India K Ausik B Anerjee,Yadvendradev V
Short Communication Demographic structure and abundance of Asiatic lions Panthera leo persica in Girnar Wildlife Sanctuary, Gujarat, India K ausik B anerjee,Yadvendradev V. Jhala and B harat P athak Abstract Asiatic lions Panthera leo persica, once confined human interests through predation on livestock and some- to the 1,883 km2 Gir Protected Area in Gujarat, India, have times on people (Saberwal et al., 1994; Karanth & Chellam, in the past 2 decades colonized the adjacent Girnar forest, 2009). Lions have been driven almost to extinction in Asia coastal scrub and agro-pastoral areas covering c. 10,000 km2. (Kinnear, 1920; Pocock, 1930; Divyabhanusinh, 2005). The In May 2008 the Government of Gujarat declared 180 km2 only surviving free-ranging Asiatic lion Panthera leo persica of the sacred Girnar forests a Wildlife Sanctuary. We population is in and around the Gir forests of Gujarat, obtained data on location, age, gender and group composi- India (Divyabhanusinh, 2005). This population has in- tion of lions in Girnar Wildlife Sanctuary from opportunistic creased from c. 20 in 1920 to a current population of c. 360 sightings during March–May 2008 and from systematic (Singh, 2007). 2 surveys in April 2008 (six surveys of 3–4 days each), totalling The population was formerly restricted to the c. 1,883 km 81 lions on 40 occasions. Of the 81 sightings 43% were in the Gir Protected Area (Johnsingh et al., 2007) but during the recruitment age group. Adult sex ratio was 0.87 males : 1 last 2 decades lions have dispersed to establish small female. In the systematic survey we made 26 sightings of breeding units in the districts of Junagadh, Amreli and 2 nine individuals, identified from their vibrissae patterns and Bhavnagar, covering c. -

List of NSH / ICH Intra Circle / L2 Hub Circle Name NSH / L1 Hub Name Name Telangana WARANGAL NSH KARIMNAGAR ICH Khammam ICH
List of NSH / ICH Intra Circle / L2 Hub Circle Name NSH / L1 Hub Name Name Telangana WARANGAL NSH KARIMNAGAR ICH Khammam ICH Telangana HYDERABAD NSH NIZAMABAD ICH NALGONDA ICH ANDHRA PRADESH KURNOOL NSH ANANTAPUR ICH ANDHRA PRADESH TIRUPATHI NSH Cuddapah ICH NELLORE ICH ANDHRA PRADESH VIJAYAWADA NSH GUNTUR ICH ONGOLE ICH ELURU ICH ANDHRA PRADESH VISAKHAPATNAM NSH RAJAHMUNDRY ICH SRIKAKULAM ICH Vizianagaram ICH ASSAM Dibrugarh NSH Jorhat ICH Tinsukia ICH ASSAM GUWAHATI NSH NAGAON SILCHAR TEZPUR BIHAR BARAUNI NSH – BIHAR MUZAFFARPUR NSH – BIHAR PATNA NSH CHHAPRA KIUL BHAGALPUR BIHAR GAYA NSH – CHATTISGARH RAIPUR NSH BILASPUR RAIGARH DURG JAGDALPUR ICH DELHI DELHI NSH – GUJRAT AHMEDABAD NSH HIMATNAGAR MEHSANA PALANPUR BHAVNAGAR BHUJ Dhola ICH GUJRAT RAJKOT NSH JAMNAGAR JUNAGADH SURENDRANAGAR GUJRAT SURAT NSH VALSAD GUJRAT VADODARA NSH BHARUCH GODHARA ANAND HARYANA GURGAON NSH FARIDABAD ICH REWARI ICH HARYANA KARNAL NSH – HARYANA ROHTAK NSH HISAR ICH HARYANA AMBALA NSH SOLAN MANDI HIMACHAL PRADESH SHIMLA NSH SOLAN ICH HIMACHAL PRADESH PATHANKOT NSH KANGRA HAMIRPUR JAMMUKASHMIR JAMMU NSH – JAMMUKASHMIR SRINAGAR NSH – JHARKHAND JAMSHEDPUR NSH JHARKHAND RANCHI NSH DALTONGANJ HAZARIBAGH ROAD JHARKHAND DHANBAD NSH B. DEOGHAR KARNATAKA BENGALURU NSH BALLARI ICH TUMAKURU ICH KARNATAKA BELAGAVI NSH – KARNATAKA KALABURAGI NSH RAICHUR ICH KARNATAKA HUBBALLI-DHARWAD NSH BAGALKOT ICH KUMTA ICH VIJAYAPURA ICH KARNATAKA MANGALURU NSH – KARNATAKA MYSURU NSH – KARNATAKA ARSIKERE NSH – KERALA KOCHI NSH Kottayam ICH KERALA THRISSUR PALAKKAD ICH KERALA TRIVANDRUM -

BHUJ "Ancient Temples, Tall Hills and a Deep Sense of Serenity" Bhuj Tourism
BHUJ "Ancient temples, tall hills and a deep sense of serenity" Bhuj Tourism A desert city with long history of kings and empires make Bhuj one of the most interesting and unique historical places to see. The city has a long history of kings and empires - and hence many historic places to see. The city was left in a state of devastation after the 2001 earthquake and is still in the recovery phase. Bhuj connects you to a range of civilizations and important events in South Asian history through prehistoric archaeological finds, remnants of the Indus Valley Civilization (Harappan), places associated with the Mahabharata and Alexander the Great's march into India and tombs, palaces and other buildings from the rule of the Naga chiefs, the Jadeja Rajputs, the Gujarat Sultans and the British Raj. The vibrant and dynamic history of the area gives the area a blend of ethnic cultures. In a walk around Bhuj, you can see the Hall of Mirrors at the Aina Mahal; climb the bell tower of the Prag Mahal next door; stroll through the produce market; have a famous Kutchi pau bhaji for lunch; examine the 2000-year-old Kshatrapa inscriptions in the Kutch Museum; admire the sculptures of Ramayana characters at the Ramakund stepwell; walk around Hamirsar Lake and watch children jumping into it from the lake walls as the hot afternoon sun subsides; and catch the sunset among the chhatardis of the Kutchi royal family in a peaceful field outside the center of town. This Guide includes : About Bhuj | Suggested Itinerary | Commuting tips | Top places to visit | Hotels | Restaurants | Related Stories Commuting in Bhuj Tuk-tuks (autorickshaws) are the best way to travel within the city. -

Important Lakes in India
Important Lakes in India Andhra Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Kolleru Lake Dal Lake Pulicat Lake - The second largest Manasbal Lake brackish – water lake or lagoon in India Mansar Lake Pangong Tso Assam Sheshnag Lake Chandubi Lake Tso Moriri Deepor Beel Wular Lake Haflong Lake Anchar Lake Son Beel Karnataka Bihar Bellandur Lake Kanwar Lake - Asia's largest freshwater Ulsoor lake oxbow lake Pampa Sarovar Karanji Lake Chandigarh Kerala Sukhna Lake Ashtamudi Lake Gujarat Kuttanad Lake Vellayani Lake Hamirsar Lake Vembanad Kayal - Longest Lake in India Kankaria Sasthamcotta Lake Nal Sarovar Narayan Sarovar Madhya Pradesh Thol Lake Vastrapur Lake Bhojtal Himachal Pradesh www.OnlineStudyPoints.comMaharashtra Brighu Lake Gorewada Lake Chandra Taal Khindsi Lake Dashair and Dhankar Lake Lonar Lake - Created by Metoer Impact Kareri and Kumarwah lake Meghalaya Khajjiar Lake Lama Dal and Chander Naun Umiam lake Macchial Lake Manipur Haryana Loktak lake Blue Bird Lake Brahma Sarovar Mizoram Tilyar Lake Palak dïl Karna Lake www.OnlineStudyPoints.com Odisha Naukuchiatal Chilika Lake - It is the largest coastal West Bengal lagoon in India and the second largest Sumendu lake in Mirik lagoon in the world. Kanjia Lake Anshupa Lake Rajasthan Dhebar Lake - Asia's second-largest artificial lake. Man Sagar Lake Nakki Lake Pushkar Lake Sambhar Salt Lake - India's largest inland salt lake. Lake Pichola Sikkim Gurudongmar Lake - One of the highest lakes in the world, located at an altitude of 17,800 ft (5,430 m). Khecheopalri Lake Lake Tsongmo Tso Lhamo Lake - 14th highest lake in the world, located at an altitude of 5,330 m (17,490 ft).