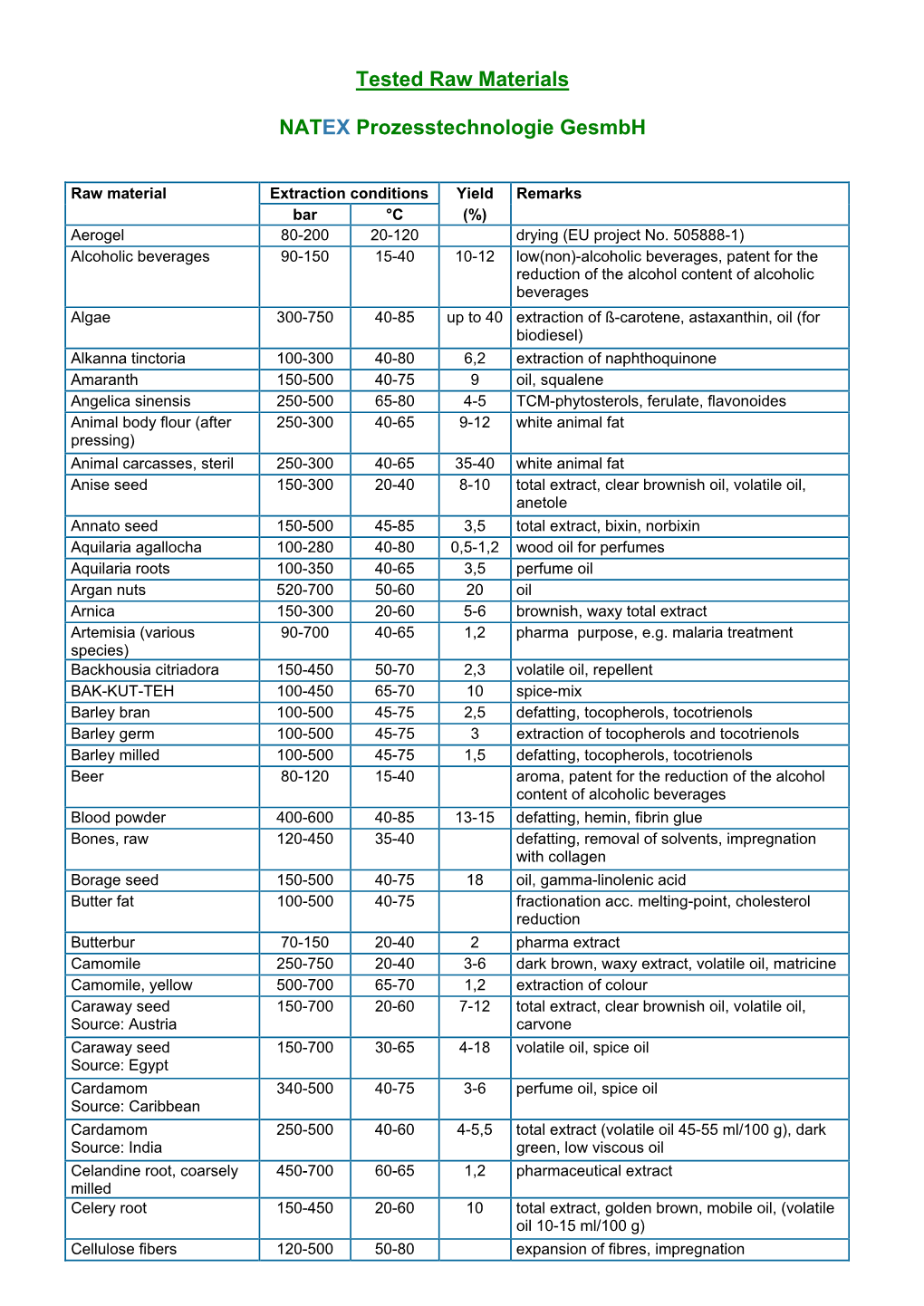
Tested Raw Materials NATEX Prozesstechnologie Gesmbh
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Rise of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Its Materia Medica A
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by University of Bath Research Portal Citation for published version: Williamson, EM, Lorenc, A, Booker, A & Robinson, N 2013, 'The rise of traditional Chinese medicine and its materia medica: a comparison of the frequency and safety of materials and species used in Europe and China', Journal of Ethnopharmacology, vol. 149, no. 2, pp. 453-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.050 DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.050 Publication date: 2013 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication University of Bath General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Download date: 13. May. 2019 Journal of Ethnopharmacology 149 (2013) 453–462 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Ethnopharmacology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jep The rise of traditional Chinese medicine and its materia medica: A comparison of the frequency and safety of materials and species used in Europe and China Elizabeth M. Williamson a,n, Ava Lorenc b,nn, Anthony Booker c, Nicola Robinson b a University of Reading School -

The Maiwa Guide to NATURAL DYES W H at T H Ey a R E a N D H Ow to U S E T H E M
the maiwa guide to NATURAL DYES WHAT THEY ARE AND HOW TO USE THEM WA L NUT NATURA L I ND IG O MADDER TARA SYM PL O C OS SUMA C SE Q UO I A MAR IG O L D SA FFL OWER B U CK THORN LIVI N G B L UE MYRO B A L AN K AMA L A L A C I ND IG O HENNA H I MA L AYAN RHU B AR B G A LL NUT WE L D P OME G RANATE L O G WOOD EASTERN B RA ZIL WOOD C UT C H C HAMOM IL E ( SA PP ANWOOD ) A LK ANET ON I ON S KI NS OSA G E C HESTNUT C O C H I NEA L Q UE B RA C HO EU P ATOR I UM $1.00 603216 NATURAL DYES WHAT THEY ARE AND HOW TO USE THEM Artisans have added colour to cloth for thousands of years. It is only recently (the first artificial dye was invented in 1857) that the textile industry has turned to synthetic dyes. Today, many craftspeople are rediscovering the joy of achieving colour through the use of renewable, non-toxic, natural sources. Natural dyes are inviting and satisfying to use. Most are familiar substances that will spark creative ideas and widen your view of the world. Try experimenting. Colour can be coaxed from many different sources. Once the cloth or fibre is prepared for dyeing it will soak up the colour, yielding a range of results from deep jew- el-like tones to dusky heathers and pastels. -

DN Product Instructions
discovery naturals™ READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE Our products work on ALL HAIR TYPES (African, Asian, Caucasian, Indian, and Latino, chemically colored, bleached, straightened or damaged hair). Hair colors are permanent and normally last 4 - 8 weeks. Our products cannot lighten dark hair. Use as often as desired because the more you use them, the better your results. Below are detailed directions, but you may need to alter the process a bit to achieve your ideal results. Once you find your perfect application technique it will work every time. Remember, your hair, scalp, skin, and health are worth it, plus you'll look great naturally! Sensitivity Test: Sensitivity to our natural plant products is extremely rare. First time users of hair or tattoo products should perform a skin sensitivity test before full application. If any sensitivity occurs it is due to a reaction to one of the natural plants in our formula, or your skin has not healed completely from prior chemical product usage and you’ll need to wait until your skin is fully healed before retrying. Our products DO NOT contain PPD (Para-Phenylenediamine), Amonia, Peroxide, Bleach, Lye, or other nasty chemicals found in traditional hair colors. To perform a sensitivity test, mix a ¼ teaspoon of powder with a few drops of water to form a thick paste. Apply dime sized amount of paste to the inside of the wrist and/or near the hairline. Wrap with plastic wrap to keep moist for 1.5 – 3 hours. Rinse paste off with water. After 24 hours evaluate for sensitivity or redness. -

Henna Powder, Cones, Pastes & Hollywood
HENNA POWDER, CONES, PASTES & HOLLYWOOD INK Please read the following instructions completely before use Sensitivity Test: Sensitivity to this product is extremely rare. First time users should do a spot sensitivity test. For Henna Powder mix a small amount of powder into a paste with water and apply it to the inner wrist and/or near the hairline on the back of the neck. For Cones, Pastes and Hollywood Ink, no mixing is needed. After 2 hours, rinse with warm water. Wait and evaluate for sensitivity or redness after 24 hours. If sensitivity develops, do not use this product. Organic Aloe Vera gel and/or Organic Coconut Oil applied to the skin and scalp may help calm any sensitivity reactions. Henna Powder for Tattoos Prep: Henna Powder 2-4 Tea Bags Bottled or fresh lemon juice (strained) Large plastic or glass bowl for mixing Measuring spoon/measuring cup Sugar or honey (optional) Essential Oils (optional) Large plastic bag or plastic bottle for storage Applicator bottle or cone for applying the henna Saran wrap Paper towels for cleanup Mix: For tattoos, place entire package of henna powder in a glass or ceramic bowl. Boil 2-3 cups of water, then add 2- 4 tea bags, and let steep for 30 minutes or longer. You want the darkest brew possible. Add 2- 4 tablespoons of fresh lemon juice to the powder. While stirring, add the warm tea brew in a little at a time. Mix well and use enough brew so that the mixture is the same consistency as pancake batter. Add 2 teaspoons of an essential oil, and mix well. -

Immunomodulatory Effects of Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulation, Ginseng and Dang Gui Ten Combination (PS10)
Immunomodulatory Effects of Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulation, Ginseng and Dang Gui Ten Combination (PS10) Thesis submitted for the Degree of Master of Science Michael Thomsen N.D., Dip. Bot.Med. Graduate School of Integrative Medicine Swinburne University of Technology 2006 Acknowledgements I wish to sincerely thank my supervisors at the Graduate School of Integrative Medicine at Swinburne University of Technology, Dr Luis Vitetta and head of the school, Prof Avni Sali. I would also like to thank Marilyn Johnson, for without her help I would still have been applying for ethics approval. This study would not have been possible without the support and guidance of the Graduate School of Integrative Medicine. This study would not have been possible without the enormous help I received from Dr Graham Flannery and his team of the Department of Genetics, Faculty of Science, Technology and Engineering, La Trobe University, Bundoora, Victoria. Dr Flannery has helped to pioneer the particular NK cell cytotoxicity test used in the present study. In particular I wish to thank his assistants Rosalia Bruzzese and Maria Mylonas for performing the NK cell assay. In addition, I would like to thank Dr Hijikata from Japan for her assistance in supplying Japanese research papers and sharing her clinical experience in the use of the herbal formulation that was the subject of the present study. I would further like to thank Phytamedica for manufacturing the test medication and to Analytica Laboratory for help with the analytical analysis of the ingredients and the final formulation. Lastly I would like to thank my partner and fellow herbalist, Erin Collins and my children for putting up with me while producing this thesis. -

What Is "Black Henna?" Catherine Cartwright-Jones C 2003
1 2 What is "Black Henna?" Catherine Cartwright-Jones c 2003 Henna is NOT black. However, there are several things marketed as "Black Henna", and some things believed to be "Black Henna". Some are very dangerous. Some are harmless. When para- phenylenediamine black hair dye is used to make black temporary tattoos, often called “black henna”, it can cause blistering, open sores, scarring, and life-ling health problems. PPD “black henna”, two weeks after application, with intense itching and open sores 1) Some people make a black temporary tattoo they call "Black Henna" with synthetic black hair dye, containing para- phenylendiamine. This is NOT HENNA! Black hair dye should never be put straight on your skin, plain, or mixed with other material. Synthetic Black Hair Dye is illegal to put on skin, because that is not approved use. Even when this dye is applied to hair, people must wear gloves, and they try to not get it on the scalp! PPD, para-phenylendiamine can seriously 3 injure people. Para-phenylenediamine is a strong sensitizer, transdermal toxin and potential carcinogen. 2) "Black Henna" was once a term for indigo, when it was sold as hair dye. In the 1800's there was no synthetic hair dye. Henna and indigo were used to dye hair. Henna leaves and twigs that had no, or very low, concentrations of Lawsone (the tannin produced by the henna plant) were sold as neutral henna. Henna leaf buds that had high concentrations of Lawsone were sold as Red Henna or Henna. Indigo was marketed as "black henna". -

Angelica: Part I
August 2008 • w w w. s k i n a n d a l l e rg y n ew s. c o m Aesthetic Dermatology 33 C O S M E C E U T I C A L C R I T I Q U E Angelica: Part I ngelica sinensis, better known as pendently displayed antioxidant activities. dong quai, is a fragrant perennial L. barbarum extract was the strongest, but Aplant that has been used for med- all the extracts inhibited ferric chloride- icinal purposes for more than a thousand ascorbic acid–induced lipid peroxidation in years in China, Japan, and Korea. A. sinen- rat liver homogenate in vitro, and demon- sis is best known as a traditional treat- strated significant superoxide anion-scav- ment for dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, enging activity as well as antisuperoxide menopause, and related conditions in formation activity (Phytother. Res. women. 2004;18:1008-12). The herb is used throughout the world, Another study revealed that the total including the United States, polysaccharide from A. as an unregulated oral sup- sinensis confers antitumor plement and in some topical effects on in vivo murine multibotanical formulations. models and, in vitro, inhibits . C The dried root of A. sinen- invasion and metastasis of N I , sis is included in several herbal hepatocellular cancer cells O T O formulations, typically for (World J. Gastroenterol. H P K amenorrhea, endometriosis 2003;9:1963-7). C O T S I and premenstrual syndrome, In a study of the effects of / A S and as a hormone replace- 14 commonly used herbs on I D A ment therapy alternative, cellular proliferation and © even though Western medi- apoptosis of a hepatic stel- Although little dermatologic research has been done, the Angelica sinensis plant, B Y L E S L I E S . -

Indiana Medical History Museum Guide to the Medicinal Plant Garden
Indiana Medical History Museum Guide to the Medicinal Plant Garden Garden created and maintained by Purdue Master Gardeners of Marion County IMHM Medicinal Plant Garden Plant List – Common Names Trees and Shrubs: Arborvitae, Thuja occidentalis Culver’s root, Veronicastrum virginicum Black haw, Viburnum prunifolium Day lily, Hemerocallis species Catalpa, Catalpa bignonioides Dill, Anethum graveolens Chaste tree, Vitex agnus-castus Elderberry, Sambucus nigra Dogwood, Cornus florida Elecampane, Inula helenium Elderberry, Sambucus nigra European meadowsweet, Queen of the meadow, Ginkgo, Ginkgo biloba Filipendula ulmaria Hawthorn, Crateagus oxycantha Evening primrose, Oenothera biennis Juniper, Juniperus communis False Solomon’s seal, Smilacina racemosa Redbud, Cercis canadensis Fennel, Foeniculum vulgare Sassafras, Sassafras albidum Feverfew, Tanacetum parthenium Spicebush, Lindera benzoin Flax, Linum usitatissimum Witch hazel, Hamamelis virginiana Foxglove, Digitalis species Garlic, Allium sativum Climbing Vines: Golden ragwort, Senecio aureus Grape, Vitis vinifera Goldenrod, Solidago species Hops, Humulus lupulus Horehound, Marrubium vulgare Passion flower, Maypop, Passiflora incarnata Hyssop, Hyssopus officinalis Wild yam, Dioscorea villosa Joe Pye weed, Eupatorium purpureum Ladybells, Adenophora species Herbaceous Plants: Lady’s mantle, Alchemilla vulgaris Alfalfa, Medicago sativa Lavender, Lavendula angustifolia Aloe vera, Aloe barbadensis Lemon balm, Melissa officinalis American skullcap, Scutellaria laterifolia Licorice, Glycyrrhiza -

Herbal Hepatotoxicity an Update on Traditional Chinese Medicine
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Review article: herbal hepatotoxicity – an update on traditional Chinese medicine preparations R. Teschke*, A. Wolff†, C. Frenzel‡ & J. Schulze§ *Department of Internal Medicine II, SUMMARY Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Klinikum Hanau, Academic Teaching Hospital of the Background Medical Faculty of the Goethe Although evidence for their therapeutic efficacy is limited, herbal traditional University Frankfurt/Main, Hanau, Chinese medicine (TCM) preparations increasingly gain popularity. In con- Germany. † trast to other herbal products, adverse effects by herbal TCM including liver Department of Internal Medicine II, toxicity were rarely reported. In recent years, more cases were published, Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectious Diseases, providing new clinical challenges. Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Jena, Germany. Aim ‡ Department of Medicine I, University To summarise comprehensively the literature on herbal TCM hepatotoxicity Medical Center Hamburg Eppendorf, since 2011. Hamburg, Germany. §Institute of Industrial, Environmental and Social Medicine, Medical Faculty, Methods Goethe University Frankfurt/Main, PubMed was searched using key words related to TCM, the results were Frankfurt, Germany. restricted to full English-language publications and abstracts published since 2011. In addition, the database of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and LiverTox was accessed under the topic ‘Drug record: Chinese and other Correspondence to: ’ Dr R. Teschke, Department of Internal Asian herbal medicines . Medicine II, Klinikum Hanau, Academic Teaching Hospital of the Results Goethe University of Frankfurt/Main, Since 2011, new case reports and case series provided evidence for herbal Leimenstrasse 20, D-63450 Hanau, hepatotoxicity by TCM, focusing on nine TCM herbal mixtures and four Germany. individual TCM herbs with potential health hazards. -

The Hennakitten Years
The Hennakitten Years Hennacat’s free henna design book based on work and ideas from 2002 - 2007 Iconic and popular designs which are simple to reproduce and stunning to wear Includes Hennacat’s own henna recipes and instructions for henna body art. 2 Hennacat ‘The Hennakitten Years’ Copyright 2012 Catharine Hinton Cover Graphic by Catharine Hinton Published by Yogaspirit 35 Hotspur Street Shrewsbury Shropshire SY1 2QB All rights reserved. Printed in the United Kingdom No part of this book may be used or reproduced in any manner without written permission except in the case of brief quotations embodied in critical articles or reviews, and within the terms of use as described on page 2. ISBN – To be confirmed Catharine Hinton ‘The Hennakitten Years’ The Hennakitten Years Copyright © 2012 Catharine Hinton Hennacat All rights reserved. Buy body art quality henna and other products from www.Hennacat.com 3 Copyright and terms of Use Hennacat ‘The Hennakitten Years’ Copyright 2012 Catharine Hinton. All rights reserved. This publication is licensed for personal, instructional and educational purposes for five years from the date of download. Terms of use: You must agree to these terms to download, print, and use this publication. You accept the following terms: Hennacat takes all reasonable care to ensure that the information contained on this publication is accurate. However, no warranty or representation is given that the information and materials contained on it are complete or free from errors or inaccuracies. To the extent permitted by applicable laws, Hennacat accepts no liability for any loss or damages or expenses of any kind including without limitation compensatory, direct, indirect or consequential damages, loss of data, income or profit, loss of or damage to property, or claims by third parties howsoever arising in connection with your use of this publication, the copying or use of any information or material contained in or referred to in it. -

Microscopy of Henna the Microscopic Structures of A
Chapter 4: Science and Microscopy: Microscopy of Henna The microscopic structures of a henna leaf This is a quantitative microscopy survey of different brands of henna hair dye products. Henna products in the marketplace frequently contain unlisted additives and adulterants, and the milling and sifting varies with particles from 0.2 mm to over 3 mm. Consumers become frustrated by henna products’ coarse sift, sand, problematic interactions with chemical dyes, and unpredictable, fading results. The public understanding of what is henna is further misinformed by false advertising claims made by by exporters and retailers. Investigation into henna’s agricultural, industrial, and marketing processes was part of my Master’s and PhD dissertations, in contrast to the usual anthropological and folkloric investigations on henna. Through that research, I amassed years of henna, indigo and cassia analysis from a certified independent laboratory, over one hundred henna hair dye products, and declarations by henna exporters. This chapter shows quantitative microscopic comparisons of products sold as ‘henna.’ The above image is are macroscopic view of the ventral side of a 38 mm long henna leaf, 1.5 inches, with the midrib, vein, and lamina indicated.1 The above image shows the dorsal side of four paired young henna leaves; the larger leaves are 20 mm (about 0.8”) long. The above images are scanned, so show natural color from reflected light.2 1 Henna plants raised by Catherine Cartwright-Jones PhD 2 Epson Perfection V600 Photo scanner 1200 DPI “Ancient Sunrise® Henna for Hair,” Chapter 4: Science and Microscopy Part 3, Microscopy of Henna. -

Supplements to Discontinue Before and After Surgery
SUPPLEMENTS TO DISCONTINUE BEFORE AND AFTER SURGERY Nowadays, many patients are taking nutritional supplements in increasing amounts. While generally beneficial and safe, their use around the time of surgery may not be desirable. Certain nutritional supplements may cause adverse reactions during or after surgery, including: prolonged bleeding, interference with anesthesia, cardiovascular disturbances, and interactions with prescription drugs. To ensure surgical safety, please discontinue the use of the following nutritional supplements, two weeks prior to surgery and two weeks after surgery. Bilberry (Vaccinum myrtillus) Ginkgo Biloba (Ginkgo Biloba) Melatonin Contains compounds called anthocyanoside, and One of the oldest living tree specimens and one of A hormone that is secreted by the pineal flavonoid compounds that strengthen blood the best researched herbal medicines. Ginkgo blob gland located in the brain. Since melatonin vessels, improve circulation and can be useful in improves blood circulation by strengthening the controls the body’s sleep-wake cycle, it is treating eye disorders, Bilberry can affect blood vascular system and inhibiting platelet aggregation. cells called platelets and may increase bleeding. Ginkgo is also used to help prevent mental often used to counteract sleeplessness and deterioration in the elderly. Ginkgo has significant jet lag. Melatonin may potentiate the Cayenne (Capsicum frutescens) blood-thinning activity which is three times central nervous system effects of Also known as red pepper, cayenne lowers levels stronger than Vitamin E. barbiturate drugs (produce relaxation and of cholesterol in the blood, which can help to sleep) and general anesthetics. lower blood pressure. Cayenne may affect Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium/Panax ginseng) platelets and an overdose can cause significant Ginseng is a so-called adaptogen (increases Red Clover (Trifolium pretense) drop in body temperature.