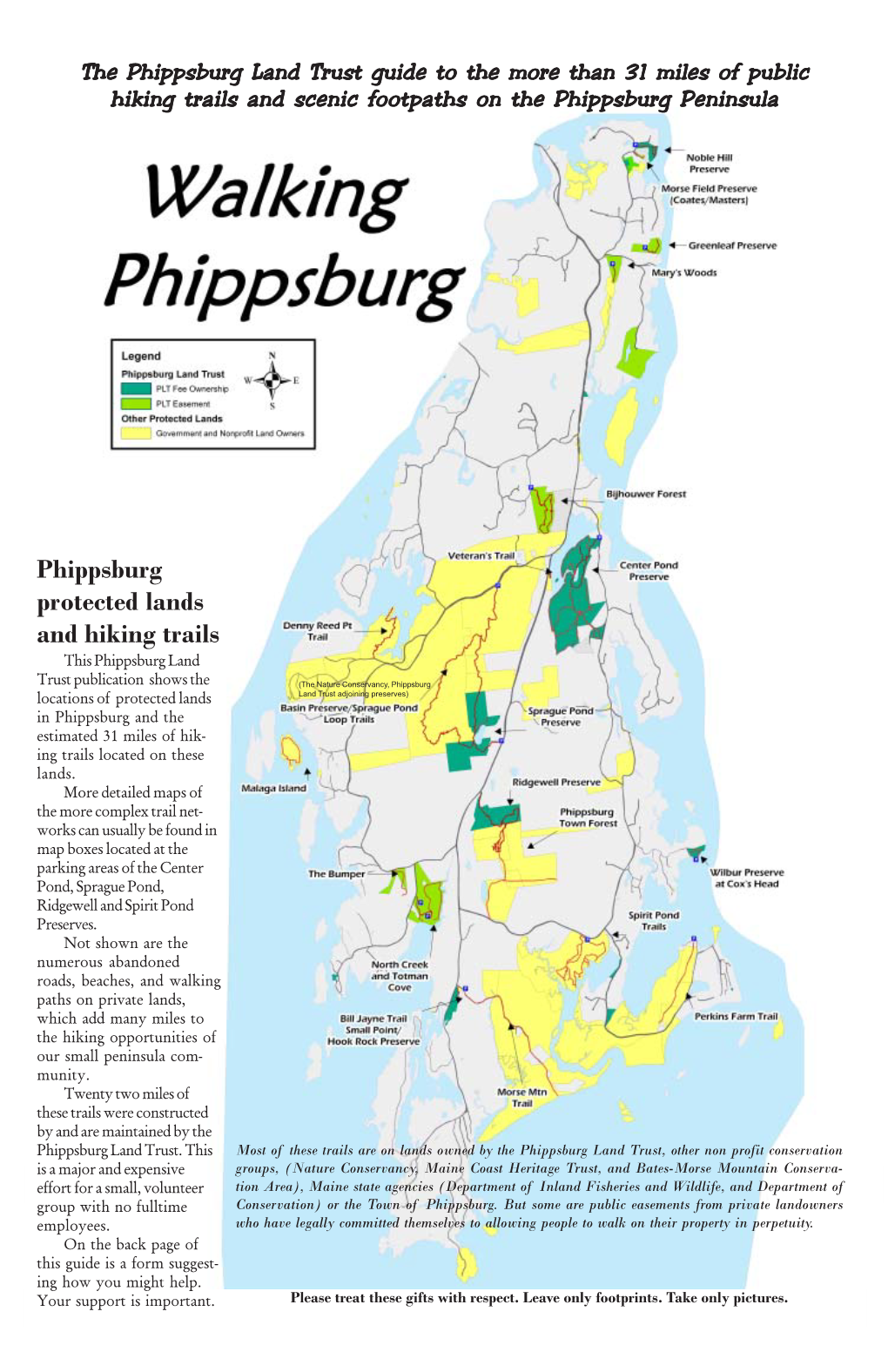
Walking Phippsburg 3Rd Edition Final.Pmd
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Kennebec Estuary Focus Areas of Statewide Ecological Significance Kennebec Estuary
Focus Areas of Statewide Ecological Significance: Kennebec Estuary Focus Areas of Statewide Ecological Significance Kennebec Estuary WHY IS THIS AREA SIGNIFICANT? The Kennebec Estuary Focus Area contains more than 20 percent of Maine’s tidal marshes, a significant percentage of Maine’s sandy beach and associated dune Biophysical Region habitats, and globally rare pitch pine • Central Maine Embayment woodland communities. More than two • Cacso Bay Coast dozen rare plant species inhabit the area’s diverse natural communities. Numerous imperiled species of animals have been documented in the Focus Area, and it contains some of the state’s best habitat for bald eagles. OPPORTUNITIES FOR CONSERVATION » Work with willing landowners to permanently protect remaining undeveloped areas. » Encourage town planners to improve approaches to development that may impact Focus Area functions. » Educate recreational users about the ecological and economic benefits provided by the Focus Area. » Monitor invasive plants to detect problems early. » Find ways to mitigate past and future contamination of the watershed. For more conservation opportunities, visit the Beginning with Habitat Online Toolbox: www.beginningwithhabitat.org/ toolbox/about_toolbox.html. Rare Animals Rare Plants Natural Communities Bald Eagle Lilaeopsis Estuary Bur-marigold Coastal Dune-marsh Ecosystem Spotted Turtle Mudwort Long-leaved Bluet Maritime Spruce–Fir Forest Harlequin Duck Dwarf Bulrush Estuary Monkeyflower Pitch Pine Dune Woodland Tidewater Mucket Marsh Bulrush Smooth Sandwort -

Maine Guide to Camp & Cottage Rentals 1992
MAINE Guide to Camp & Cottage Rentals 1992 An Official Publication of the Maine Publicity Bureau, Inc. MAINE. The Way Life Should Be. Maine Guide to Camp & Cottage Rentals 1992 Publisher/Editor Sherry L. Verrill Production Assistant Diane M. Hopkins TABLE OF CONTENTS South Coast 3-7 Western Lakes and Mountains 8-15 Kennebec Valley/Moose River Valley 16-20 Mid Coast 21-32 Acadia 33-44 Sunrise County 45-50 Katahdin/Moosehead 51-56 Aroostook County 57 Index to Advertisers 58-61 Maine Visitor Information Centers 62 A PUBLICATION OF THE MAINE PUBLICITY BUREAU, INC. P.O. Box 2300, Hallowell, Maine 04347 (207) 582-9300 • • » a The Maine Publicity Bureau, Inc Mail: P.O. Box 2300 209 Maine Avenue Hallowell, Maine 04347-2300 Farmingdale, Maine 04344 FAX 207-582-9308 Tel. 207-582-9300 Dear Friend: Renting a camp or cottage is a delightful way to experience the splendors of Maine. As you browse through these pages, imagine yourself relaxing in your own cozy spot after a day full of Maine enchantment. This guide is a reliable source of camp and cottage rentals. Owners and agents who list properties here are expected to obey The Golden Rule by dealing with others as they would want others to deal with them. We track any complaints about an owner or agent who fails to live up to standards of honesty and fairness. If a pattern develops concerning a listing, it is removed. Tens of thousands of people have used this guide to obtain just the spot they wanted. You, too, can use the guide confidently. -

State of the New Meadows River
Final Report State of the New Meadows River A report on the current environmental and resource status of the New Meadows River and surrounding watershed Prepared for New Meadows River Watershed Project Steering Committee Prepared by Christopher S. Heinig MER Assessment Corporation 14 Industrial Parkway Brunswick, Maine 04011 207.798.7935 [email protected] April 16, 2002 Acknowledgment This project would not have succeeded had it not been for the dedicated participation of the members of the New Meadows River Watershed Project Steering Committee. Over the course of this project the Committee included: Theo Holtwijk (Chairman), Director of Planning and Development, Town of Brunswick, Michael Feldman, Brunswick Town Councilor, Ralph Merry, Town of West Bath Selectman, David Chipman, Town of Harpswell Selectman, Robert Cummings, Town of Phippsburg, Dr. Walter Rosen, Brunswick Conservation Commission, Elsa Martz, Representative for the Town Harpswell, Eric Butler, Brunswick Marine Resources Committee, Roger McNelley and James Hennessey, West Bath Marine Resources Committee, Arthur Dodge, Harpswell Marine Resources Committee, James Upham, City of Bath Planner, George Pollard, City of Bath Planning Board, Edward Benedikt and Anne Hammond, New Meadows Lakes Association, Diane Gould, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Katherine Groves, Casco Bay Estuary Project (CBEP), Todd Janeski, Maine State Planning Office (SPO), Sherry Hanson and Laura Livingston, Maine Department of Marine Resources (DMR), Lee Doggett and Donald Kale, Maine Department of Environmental Protection (DEP), Dr. Edward Laine, and Cathryn Field Bowdoin College, Alan Houston and Steve Walker, Town of Brunswick Natural Resources Planners, Michael Doan and Peter Milholland, Friends of Casco Bay (FOCB), Jon Hentz, Town of West Bath Shellfish Warden. -

A History of Oysters in Maine (1600S-1970S) Randy Lackovic University of Maine, [email protected]
The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Darling Marine Center Historical Documents Darling Marine Center Historical Collections 3-2019 A History of Oysters in Maine (1600s-1970s) Randy Lackovic University of Maine, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/dmc_documents Part of the Aquaculture and Fisheries Commons, History of Science, Technology, and Medicine Commons, and the United States History Commons Repository Citation Lackovic, Randy, "A History of Oysters in Maine (1600s-1970s)" (2019). Darling Marine Center Historical Documents. 22. https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/dmc_documents/22 This Newsletter is brought to you for free and open access by DigitalCommons@UMaine. It has been accepted for inclusion in Darling Marine Center Historical Documents by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@UMaine. For more information, please contact [email protected]. A History of Oysters in Maine (1600s-1970s) This is a history of oyster abundance in Maine, and the subsequent decline of oyster abundance. It is a history of oystering, oyster fisheries, and oyster commerce in Maine. It is a history of the transplanting of oysters to Maine, and experiments with oysters in Maine, and of oyster culture in Maine. This history takes place from the 1600s to the 1970s. 17th Century {}{}{}{} In early days, oysters were to be found in lavish abundance along all the Atlantic coast, though Ingersoll says it was at least a small number of oysters on the Gulf of Maine coast.86, 87 Champlain wrote that in 1604, "All the harbors, bays, and coasts from Chouacoet (Saco) are filled with every variety of fish. -

Inventory of Lake Studies in Maine
University of Southern Maine USM Digital Commons Maine Collection 7-1973 Inventory of Lake Studies in Maine Charles F. Wallace Jr. James M. Strunk Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.usm.maine.edu/me_collection Part of the Biology Commons, Environmental Health Commons, Environmental Indicators and Impact Assessment Commons, Environmental Monitoring Commons, Hydrology Commons, Marine Biology Commons, Natural Resources and Conservation Commons, Natural Resources Management and Policy Commons, Other Life Sciences Commons, and the Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecology Commons Recommended Citation Wallace, Charles F. Jr. and Strunk, James M., "Inventory of Lake Studies in Maine" (1973). Maine Collection. 134. https://digitalcommons.usm.maine.edu/me_collection/134 This Book is brought to you for free and open access by USM Digital Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Maine Collection by an authorized administrator of USM Digital Commons. For more information, please contact [email protected]. INVENTORY OF LAKE STUDIES IN MAINE By Charles F. Wallace, Jr. and James m. Strunk ,jitnt.e of ~lame Zfrxemtiue ~epnrlmeut ~fate Jhtuuiug ®£fit£ 189 ~fate ~treet, !>ugusht, ~nine 04330 KENNETH M. CURTIS WATER RESOURCES PLANNING GOVERNOR 16 WINTHROP STREET PHILIP M. SAVAGE TEL. ( 207) 289-3253 STATE PLANNING DIRECTOR July 16, 1973 Please find enclosed a copy of the Inventory of Lake Studies in Maine prepared by the Water Resources Planning Unit of the State Planning Office. We hope this will enable you to better understand the intensity and dir ection of lake studies and related work at various private and institutional levels in the State of Maine. Any comments or inquiries, which you may have concerning its gerieral content or specific studies, are welcomed. -

Setting the Stage for a Course Change at Popham Beach, Phippsburg
Setting the Stage for a Course Change Maine Geological Survey Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 2011 Setting the Stage for a Course Change at Popham Beach, Phippsburg 43° 44‘ 2.36“ N, 69° 47‘ 39.29“ W Text by Stephen M. Dickson Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Setting the Stage for a Course Change Maine Geological Survey Introduction Popham Beach in Phippsburg, Maine has changed dramatically in the last two decades. As regular visitors to the beach have observed, the beach and dunes are different from one year to the next. In 1990 the beach was backed by an enormous dune field and visitors walked long paths to reach the shoreline. Even in 2005 there were large dunes in the area of Center Beach (Figure 1). Maine Geological Survey From Maine Office Maine of GIS Office From Figure 1. Location map of Popham Beach State Park, adjacent beaches, and water bodies. Note the background air photo was taken in 2005 and shows a large vegetated dune field near Center Beach. The sand bar from the park out to Fox Islands is called a tombolo by geologists. Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 2 Setting the Stage for a Course Change Maine Geological Survey Introduction By 2010 the shoreline was hundreds of feet closer to the parking lot and encroaching on a new bath house. In addition, the last few years have seen hundreds of large pitch pine trees topple onto the beach as a result of erosion driven by the Morse River cutting a long and sinuous path in an easterly direction into the state park before turning south to reach the ocean. -

The Dirty History of Portland Harbor
Reprinted from a 1994 publication The Dirty History of Portland Harbor hen scientists began looking closely at the sediments and at W the bottom of Casco Bay beginning in the early 1980s, they confronted a pollution puzzle. Sediments taken from various locations throughout the Bay, and especially in Portland Harbor, held a wide variety of potentially toxic chemicals. Until we know more about how these heavy metals, pesticides and other compounds affect marine life, it’s hard to know what lasting impact the pollution in Casco Bay may have. But it was decided that the more we know about where those pollutants came from, the better chances we will have in preventing future problems. The Casco Bay Estuary Project (now Casco Bay Early industry was limited by natural energy sources, like this tidal mill at Estuary Partnership) commissioned environmental Stroudwater. (courtesy: Sullivan Train & Photo) historian Edward Hawes to do some detective work, hoping that he could turn up some puzzle pieces from the Casco Bay. Lead, cadmium and mercury concentrations were watersheds that feed the Bay. The industrial legacy he found comparatively high in Back Cove, as were lead and mercury was a surprise to almost anyone who thinks they know the in the inner Fore River. Lead was also relatively high in the Portland area. Presumpscot River estuary. Additional metals — nickel, silver, arsenic, chromium A Pollution Problem and zinc — were evident in lesser concentrations. This widespread contamination was a little mystifying. In this age hen investigators began sampling Casco Bay’s of environmental regulation, how could so much pollution sediments in the 1980s, levels of pollution have landed in the Bay? W were found that merited additional attention. -

Geologic Site of the Month: Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park, Phippsburg, Maine
Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park Maine Geological Survey Maine Geologic Facts and Localities March, 2008 Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park Phippsburg, Maine 43o 44‘ 11.63“ N, 69o 47‘ 46.20“ W Text by Stephen M. Dickson Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park Maine Geological Survey Introduction Popham Beach State Park is one of the State’s most popular parks. It has a large natural dune system and a long stretch of natural beach composed of fine- to medium-grained sand. During the summer, the park is so popular that the parking lot can fill with cars by mid-morning. Views offshore from the park are scenic with several islands including Seguin Island with its high lighthouse. Aerial 2006 Photo, Aerial Northstar Maine Geological Survey Photo by David A. Hamel of of Hamel A. David by Photo Figure 1. A view of Popham Beach State Park in Phippsburg, Maine taken from an aircraft. The park is bound on the westerly side by the Morse River (not shown in the lower edge of the photo) and on the east by the arcuate Hunnewell Beach that is developed with homes. The Kennebec River forms the eastern limit of the beach and dune system. The Fox Islands are in the lower right corner and opposite the State Park parking lot. Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 2 Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park Maine Geological Survey Popham Beach State Park A walk east along the beach from the State Park leads across the developed Hunnewell Beach to the mouth of the Kennebec River about a mile away (Figure 2). -

11Th Workshop Proceedings
Fundy in Flux: Challenges for Science, Policy and Society Proceedings of the 11th BoFEP Bay of Fundy Science Workshop, Fredericton, New Brunswick, 9–11 June 2016 Editors Marianne Janowicz, Blythe Chang, Sarah Chamberlain, Susan J. Rolston, and Peter G. Wells BoFEP Technical Report No. 10 March 2017 This publication should be cited as: M. Janowicz, B. Chang, S. Chamberlain, S.J. Rolston and P.G. Wells (eds.). 2017. Fundy in Flux: Challenges for Science, Policy and Society. Proceedings of the 11th BoFEP Bay of Fundy Science Workshop, Fredericton, New Brunswick, 9–11 June 2016. Bay of Fundy Ecosystem Partnership Technical Report No. 10. Bay of Fundy Ecosystem Partnership, Tantallon, NS. 52 p. Photographs: Sarah Chamberlain, Jack Fife, Fundy Ocean Research Center for Energy (FORCE), Marianne Janowicz, Kimberly Robichaud-Leblanc, Susan Rolston, Peter G. Wells For further information, contact: Bay of Fundy Ecosystem Partnership Secretariat PO Box 3062 Tantallon, Nova Scotia, Canada B3Z 4G9 E-mail: [email protected] www.bofep.org © Bay of Fundy Ecosystem Partnership, 2017 ISBN 978-0-9783120-7-7 2 Table of Contents Preface ........................................................................................................................................................... 4 Acknowledgements ........................................................................................................................................ 5 Workshop Organizers .................................................................................................................................... -

Phippsburg/FOMB Appeal of August Dredging 5-16-11
STATE OF MAINE BOARD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS ) NATURAL RESOURCES PROTECTION ACT Bath and Phippsburg, Sagadahoc County ) COASTAL WETLAND ALTERATION MAINTENANCE DREDGING ) WATER QUALITY CERTIFICATION L-16281-4E-E-N ) APPEAL OF THE DECISION OF THE COMMISSIONER APPROVING THE U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS KENNEBEC RIVER DREDGING PROJCT NOW COME the Town of Phippsburg, the Phippsburg Shellfish Conservation Commission, the Phippsburg Land Trust, the Kennebec Estuary Land Trust, the Friends of Merrymeeting Bay, Bob Cummings, Lawrence Pye, Dean Doyle, Dot Kelly, Captain Ethan DeBery, and Laura Sewall (together as “Appellants”) to appeal the decision of the Commissioner of the Maine Department of Environmental Protection (“Department” or “DEP”) on April 14, 2011 (“Order”), granting to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (“Corps”) a water quality certification pursuant to section 401 of the federal Clean Water Act (“401 Certification”) and a permit under the Natural Resources Protection Act (“NRPA”). The Order authorizes the Corps to conduct out-of-season maintenance and advanced maintenance dredging in August of two locations in the Kennebec River in Bath and Phippsburg, Maine, and to dump approximately 70,000 cubic yards of dredge spoils at two locations in the Kennebec River and near-shore environments in Phippsburg. For the reasons below, Appellants request that the Board of Environmental Protection (“Board”) modify the Order to allow only the minimum out-of-season August dredging necessary, if any, to allow the U.S.S. Spruance to safely transit the Kennebec River in September, and to require that disposal of dredge spoils, if any, occur at upland and/or offshore locations where it will not cause unreasonable impacts to the environment or to Appellants. -

Seawall and Popham Beach Dynamics, Phippsburg
Seawall and Popham Beach Dynamics Maine Geological Survey Maine Geologic Facts and Localities November, 2008 Seawall and Popham Beach Dynamics Phippsburg, Maine 43° 43‘ 56.57“ N, 69° 48‘ 37.22“ W Text by Stephen M. Dickson Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Seawall and Popham Beach Dynamics Maine Geological Survey Introduction Beach dynamics and sand movement along the shoreline at Popham Beach State Park and Seawall Beach is a continuing saga of extreme shoreline change and dune erosion. Here we look at Seawall Beach, the Morse River, and the large sand spit (bar) connected to Seawall Beach that extends seaward of Popham Beach. In fall 2008 an enormous beach spit was connected to Seawall Beach reflecting several years of growth and easterly extension. It currently blocks the Morse River from flowing directly south to the sea and has led to severe dune erosion and loss of mature pitch pine trees in the back dune maritime forest at Popham Beach State Park. For more on the historical location of the Morse River and erosion at the park see the previous MGS web page, Tombolo Breach at Popham Beach State Park, Phippsburg, Maine. Maine Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 2 Seawall and Popham Beach Dynamics Maine Geological Survey Hiking to Seawall Beach to Visit the Morse River Access to the mouth of the Morse River can be from the east via Popham Beach State Park or from the west via Seawall Beach. In order to see the new beach spit first-hand or to walk out on it when the tide is low, a hike from Route 216 will lead to the beach and the spit (Figure 1). -

Shells of Maine: a Catalogue of the Land, Fresh-Water and Marine Mollusca of Maine
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by University of Maine The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Maine History Documents Special Collections 1908 Shells of Maine: a Catalogue of the Land, Fresh-water and Marine Mollusca of Maine Norman Wallace Lermond Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/mainehistory Part of the History Commons This Monograph is brought to you for free and open access by DigitalCommons@UMaine. It has been accepted for inclusion in Maine History Documents by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@UMaine. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Pamp 353 c. 2 Vickery SHELLS OF MAINE Norman Wallace Lermond Thomaston SHELLS OF MAINE. A Catalogue of the Land, Fresh-water and Marine Mollusca of Maine, by Norman Wallace Lermond. INTRODUCTORY. No general list of Maine shells—including land, fresh-water and marine species—-has been published since 1843, when Dr. J. W. Mighels’ list was printed in the Boston Journal of Natural History. Dr. Mighels may be called the “Pioneer” conchologist of Maine. By profession a physician, in his leisure hours he was a most enthusiastic collector and student of all forms of molluscan life. Enthusiasm such as his was “contagious” and he soon had gathered about him a little band of active students and collectors. Of these Capt. Walden of the U. S. Revenue Cutter “Morris” was dredging in deep water and exploring the eastern shores and among the islands, and “by his zeal procured many rare species;” Dr.