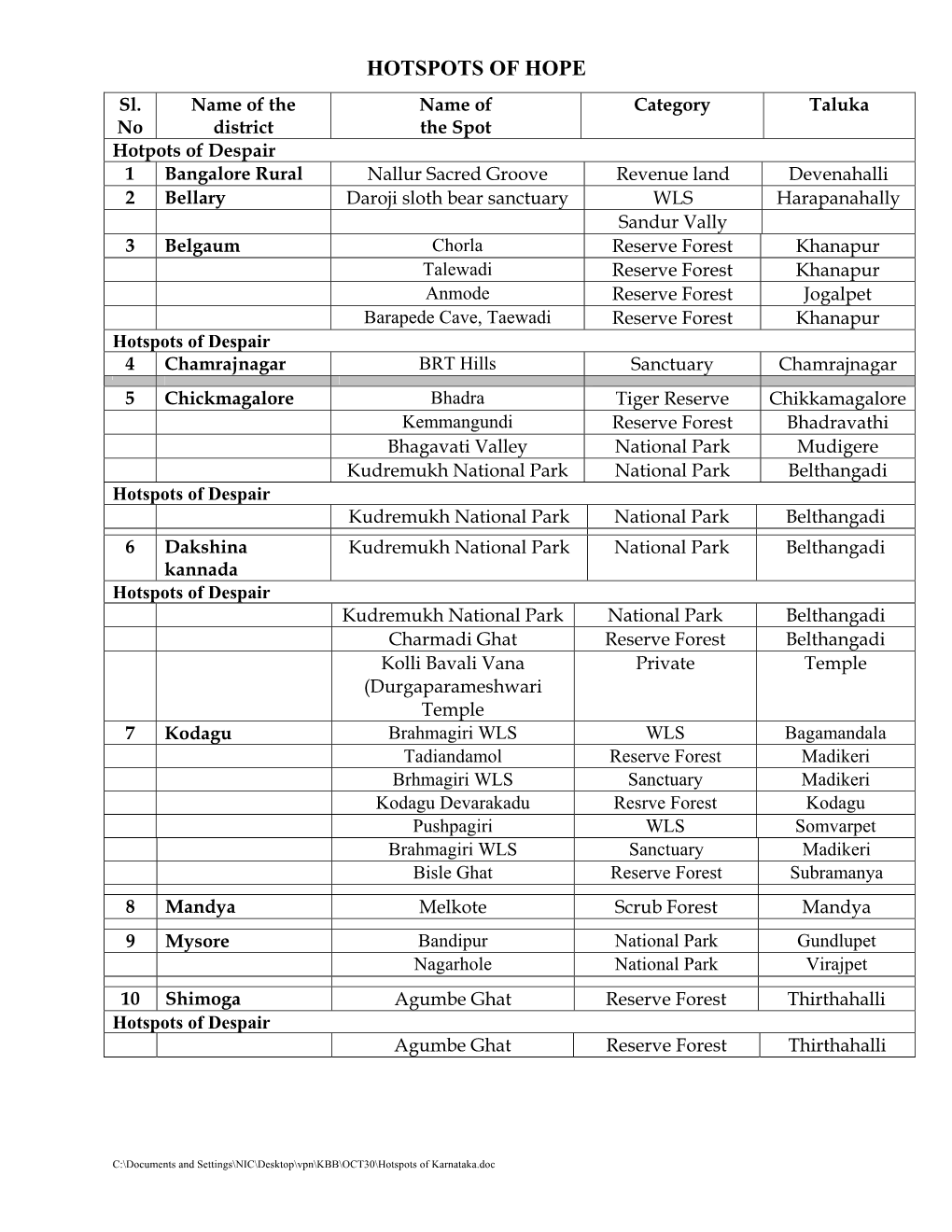
HOTSPOTS of HOPE Sl
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Hampi, Badami & Around
SCRIPT YOUR ADVENTURE in KARNATAKA WILDLIFE • WATERSPORTS • TREKS • ACTIVITIES This guide is researched and written by Supriya Sehgal 2 PLAN YOUR TRIP CONTENTS 3 Contents PLAN YOUR TRIP .................................................................. 4 Adventures in Karnataka ...........................................................6 Need to Know ........................................................................... 10 10 Top Experiences ...................................................................14 7 Days of Action .......................................................................20 BEST TRIPS ......................................................................... 22 Bengaluru, Ramanagara & Nandi Hills ...................................24 Detour: Bheemeshwari & Galibore Nature Camps ...............44 Chikkamagaluru .......................................................................46 Detour: River Tern Lodge .........................................................53 Kodagu (Coorg) .......................................................................54 Hampi, Badami & Around........................................................68 Coastal Karnataka .................................................................. 78 Detour: Agumbe .......................................................................86 Dandeli & Jog Falls ...................................................................90 Detour: Castle Rock .................................................................94 Bandipur & Nagarhole ...........................................................100 -

PROTECTED AREA UPDATE News and Information from Protected Areas in India and South Asia
T PROTECTED AREA UPDATE News and Information from protected areas in India and South Asia Vol. XXI, No. 3 June 2015 (No. 115) LIST OF CONTENTS Maharashtra 9 337 villages from nine talukas in Pune district grant EDITORIAL 3 no-objection to ESZ Tiger conservation and the construction of an Efforts to introduce solar irrigation pumps in Pench ‘urban conservation public’ TR buffer NTCA nod for release of a captive tigress in Pench NEWS FROM INDIAN STATES Tiger Reserve Assam 4 Illegal research carried out on animals at VJBU and 11 poachers killed, 20 arrested in Kaziranga National SGNP in 2001 Park this year Odisha 11 NGT asks Assam government to submit status report 70 lakh Olive ridley hatchlings in Odisha on restraining construction inside Manas NP CFR titles under the FRA distributed to villages in WWF-India and Apeejay Tea partner to reduce the Similipal TR human-elephant conflict in Assam Odisha Mining Corp to get Karlapat bauxite mines, Gujarat 5 part of which are inside the Karlapat WLS FD proposes drone surveillance for Gujarat forests Punjab 12 Jharkhand 6 Punjab to release gharials in Sutlej and Beas rivers Jharkhand working on a comprehensive 24/7 Rajasthan 13 elephant track-and-alert mechanism Tigers from Ranthambore TR moving into MP Karnataka 6 Five tigresses had 22 miscarriages in Sariska TR in NTCA approves tiger reserve status to Kudremukh; seven years state government disagrees Tamil Nadu 13 Dharwad-Belgavi railway line section turns death Plastic waste in elephant dung in Mudumalai, trap for wildlife Sathyamangalam and -

Bhadra Voluntary Relocation India
BHADRA VOLUNTARY RELOCATION INDIA INDIA FOREWORD During my tenure as Director Project Tiger in the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Govt. of India, I had the privilege of participating in voluntary relocation of villages from Bhadra Tiger Reserve. As nearly two decades have passed, whatever is written below is from my memory only. Mr Yatish Kumar was the Field Director of Bhadra Tiger Reserve and Mr Gopalakrishne Gowda was the Collector of Chikmagalur District of Karnataka during voluntary relocation in Bhadra Tiger Reserve. This Sanctuary was notified as a Tiger Reserve in the year 1998. After the notification as tiger reserve, it was necessary to relocate the existing villages as the entire population with their cattle were dependent on the Tiger Reserve. The area which I saw in the year 1998 was very rich in flora and fauna. Excellent bamboo forests were available but it had fire hazard too because of the presence of villagers and their cattle. Tiger population was estimated by Dr. Ullas Karanth and his love for this area was due to highly rich biodiversity. Ultimately, resulted in relocation of all the villages from within the reserve. Dr Karanth, a devoted biologist was a close friend of mine and during his visit to Delhi he proposed relocation of villages. As the Director of Project Tiger, I was looking at voluntary relocation of villages for tribals only from inside Tiger Reserve by de-notifying suitable areas of forests for relocation, but in this case the villagers were to be relocated by purchasing a revenue land which was very expensive. -

Bi-Monthly Outreach Journal of National Tiger Conservation Authority Government of India
BI-MONTHLY OUTREACH JOURNAL OF NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA Volume 3 Issue 2 Jan-Feb 2012 TIGER MORTALITY 2011 AS REPORTED BY STATES Natural & other cause Accident Seizure Inside tiger reserve Outside tiger Eliminated by dept Poaching No. of tiger deaths reserve UTTARAKHAND 14 1 1 1 — 17 8 9 KERALA 3 — — 1 — 4 2 2 ASSAM 3 — — 2 1 6 4 2 MADHYA PRADESH 5 — — — — 5 4 1 RAJASTHAN 1 — — — — 1 1 — ORISSA 1 — — — — 1 1 — TAMIL NADU 3 — — — — 3 1 2 WEST BENGAL 3 — — — — 3 2 1 KARNATAKA 3 — — 3 — 6 6 — MAHARASHTRA 2 — 1 2 1 6 1 5 UTTAR PRADESH — — 1 — — 1 1 — CHHATTISGARH — — — 2 — 2 — 2 BIHAR 1 — — — — 1 — 1 TOTAL 39 1 3 11 2 56 31 25 * One old tiger trophy was seized in Delhi Volume 3 Evaluation Protocol EDITOR Issue 2 Status of Dr Rajesh Gopal Jan-Feb Monitoring tigers in Phase-IV 2012 Western EDITORIAL in tiger Ghats COORDINATOR reserves & Landscape S P YADAV source areas Pg 4 Pg 15 CONTENT COORDINATOR Inder MS Kathuria Photo Tiger FEEDBACK Feature Soldiers Assessment Annexe No 5 Camera Protection Management Bikaner House traps at force gets Effectiveness Shahjahan Road New Delhi work in going in Evaluation Kalakad TR Bandipur, P8 [email protected] Pg 14 Nagarhole Cover photo Pg 18 Bharat Goel BI-MONTHLY OUTREACH JOURNAL OF NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA n o t e f r o m t h e e d i t o r THE new year, with all its freshness, tigers and its prey in each tiger reserves which would commenced with a new set of initiatives complement the once in four year snapshot assess- from NTCA. -

Western Ghats & Sri Lanka Biodiversity Hotspot
Ecosystem Profile WESTERN GHATS & SRI LANKA BIODIVERSITY HOTSPOT WESTERN GHATS REGION FINAL VERSION MAY 2007 Prepared by: Kamal S. Bawa, Arundhati Das and Jagdish Krishnaswamy (Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology & the Environment - ATREE) K. Ullas Karanth, N. Samba Kumar and Madhu Rao (Wildlife Conservation Society) in collaboration with: Praveen Bhargav, Wildlife First K.N. Ganeshaiah, University of Agricultural Sciences Srinivas V., Foundation for Ecological Research, Advocacy and Learning incorporating contributions from: Narayani Barve, ATREE Sham Davande, ATREE Balanchandra Hegde, Sahyadri Wildlife and Forest Conservation Trust N.M. Ishwar, Wildlife Institute of India Zafar-ul Islam, Indian Bird Conservation Network Niren Jain, Kudremukh Wildlife Foundation Jayant Kulkarni, Envirosearch S. Lele, Centre for Interdisciplinary Studies in Environment & Development M.D. Madhusudan, Nature Conservation Foundation Nandita Mahadev, University of Agricultural Sciences Kiran M.C., ATREE Prachi Mehta, Envirosearch Divya Mudappa, Nature Conservation Foundation Seema Purshothaman, ATREE Roopali Raghavan, ATREE T. R. Shankar Raman, Nature Conservation Foundation Sharmishta Sarkar, ATREE Mohammed Irfan Ullah, ATREE and with the technical support of: Conservation International-Center for Applied Biodiversity Science Assisted by the following experts and contributors: Rauf Ali Gladwin Joseph Uma Shaanker Rene Borges R. Kannan B. Siddharthan Jake Brunner Ajith Kumar C.S. Silori ii Milind Bunyan M.S.R. Murthy Mewa Singh Ravi Chellam Venkat Narayana H. Sudarshan B.A. Daniel T.S. Nayar R. Sukumar Ranjit Daniels Rohan Pethiyagoda R. Vasudeva Soubadra Devy Narendra Prasad K. Vasudevan P. Dharma Rajan M.K. Prasad Muthu Velautham P.S. Easa Asad Rahmani Arun Venkatraman Madhav Gadgil S.N. Rai Siddharth Yadav T. Ganesh Pratim Roy Santosh George P.S. -

Nesting Site Studies of White-Bellied Sea Eagle (Haliaeetus Leucogaster Gmelin, 1788) Along Konkan Coast, Dist
Eco. Env. & Cons. 27 (February Suppl. Issue) : 2021; pp. (S108-S115) Copyright@ EM International ISSN 0971–765X Nesting site studies of White-bellied Sea Eagle (Haliaeetus leucogaster Gmelin, 1788) along Konkan Coast, Dist. Ratnagiri, M. S., India Aditi S. Neema1, B. Anjan Kumar Prusty2, Nikunj B. Gajera3 and Poonam N. Kurve4 1,4Department of Biodiversity, Wildlife Conservation and Management BN Bandodkar College of Science, Thane (Univ. of Mumbai), Building 6, Jnanadweepa, Chendani Bunder Road, Thane West, Thane 400 601, Maharashtra 2,3Environmental Impact Assessment Division, Gujarat Institute of Desert Ecology (GUIDE), Bhuj 370 040, Gujarat, India (Received 25 April, 2020; Accepted 12 August, 2020) ABSTRACT Nesting behaviour of White-bellied Sea Eagle has been meagerly studied though; the raptor is widely distributed along the coast of Maharashtra. Present study was carried out by conducting surveys for locating their nesting sites along coast of Ratnagiri district and 12 nests of White-bellied Sea Eagle Haliaeetus leucogaster at different sites along Velas to Dabhol were studied. Various ecological parameters such as nesting tree species, nesting tree height, nesting tree GBH, nest height, geo-coordinates, distance from coast, disturbance level were considered. WBSE was found to be most abundantly nesting (N =12) on Casuarina equisetifolia tree which, accounts to 83% of the total nesting trees and only 02 nests, just 17% of the total nesting trees studied, were on Sterculia foetida. In most cases, it was observed that WBSEs prefer nest trees with larger GBH as compared to same tree species of smaller girth. Location of nest from the supratidal mark was measured to study nesting preference about distance from the sea and we found that, the nearest nest was 30 m away from the coast and the farthest one was at a distance of around 900 m. -

Research Paper Impact Factor: 4.695 Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal IJMSRR E- ISSN
Research Paper Impact Factor: 4.695 IJMSRR Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal E- ISSN - 2349-6746 www.ijmsrr.com ISSN -2349-6738 A STUDY ON PROSPECTS AND PROBLEMS OF HERITAGE TOURISM IN COASTAL KARNATAKA Laxminarayana Karanth, Assistant Professor, Head Department of Economics, MGM College, Udupi Abstract India is a vast country of great beauty and diversity and her tourist potential is equally vast. With her rich cultural heritage as superbly manifest in many of the architectural wonders (palaces, temples, mosques, forts, etc), caves and prehistoric wall paintings, her widely varied topography ranging from the monotonous plains to the loftiest mountains of the world, her large climatic variations ranging from some of the wettest and the driest as well as from the hottest and the coldest parts of the world, beautiful long beaches on the sea coast, vast stretches of sands, gregarious tropical forests and above all, the great variety of the life-style, India offers an unending choice for the tourist. In developing countries like India tourism has become one of the major sectors of the economy, contributing to a large proportion of the National income and generating huge employment opportunities. It has become the fastest growing service industry in the country with great potentials for its further expansion and diversification. Tourism industry is capable to generate employment to both skilled and unskilled workers, directly and indirectly. This paper studied the problem faced by tourism industry in coastal Karnataka . Key Words: Tourism, Development, Problems, Opportunities, Coastal Karnataka. Introduction Tourism isn't associate degree activity for pursuit associate degreed recreation however is an enriching and energizing activity. -

Karnataka, India
Natural Perception by Kodagu communities Georgina Zamora - Karnataka, India- UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Tutor Victoria Reyes-García, ICREA Ethnoecology Laboratory Georgina Zamora Quílez Degree on Environmental Sciences 1 Natural Perception by Kodagu communities Georgina Zamora Detailed Index Advertisement ............................................................................................................. 5 Acknowledgments ....................................................................................................... 6 I. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................ 7 II. LITERATURE REVISION .......................................................................................... 8 1. Natural Capital Origins ............................................................................................. 8 2. Natural Goods and services....................................................................................... 9 2.1 Natural resources............................................................................................... 9 2.2 Ecosystem services ............................................................................................ 9 2.3 NNRR/Ecosystem services and sustainable development ..................................... 10 3 Natural Capital........................................................................................................ 11 3.1 Concept.......................................................................................................... -

Proceedings of Workshop on Coastal Biodiversity
IODIVE B RS A IT K Y A T B A O N A R R D A K PROCEEDING OF THE WORKSHOP ON COASTAL BIODIVERSITY WITH REFERENCE TO COASTAL MANAGEMENT ZONE Organized by: Uttara Kannada Jilla Vijnaana Kendra, Karwar Sponsored by: KARNATAKA BIODIVERSITY BOARD, Ground Floor, ‘Vanavikas’ building, Malleshwaram 18th cross, Bangalore-560 003. Ph : 080- 23448783, Fax : 080-23440535 E-mail : [email protected] Website : www.kbbindia.org June-2009 1 FOREWORD By Dr.R.C.Prajapathi, I.F.S. Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests and Member Secretary, Karnataka Biodiversity Board, Bangalore Mangrove, formation is a tropical phenomenon confined to tropical coastal areas, and some times extend to sub-tropical or slightly beyond that also. The Karnataka part of the Malabar Coasts extends, 320 km and the width ranges from 8 to 25 km towards the inland areas. The West Coast of India in general and the Karnataka coast in particular have no delta worthy of attention. The Sea board of the Karnataka coast possesses headlands, bays, lagoons at irregular intervals. The sea board presents long beaches often intercepted by lateritic rocky headlands, coast parallel estuarine rivers and innumerable lagoons and backwater systems of limited length. The area is intersected by many coast parallel rivers and streams and presents varied and most picturesque scenery. Coastal land form and waters are a very dynamic ecosystem and an extremely valuable natural resource. In fact, they are the ‘critical areas’ and need all attention. The mangroves are highly productive components of the food web of coastal water and estuaries. -

Indian Tourism Infrastructure
INDIAN TOURISM INFRASTRUCTURE InvestmentINDIAN TOURISM INFRASTRUCTUREOppor -tunities Investment Opportunities & & Challenges Challenges 1 2 INDIAN TOURISM INFRASTRUCTURE - Investment Opportunities & Challenges Acknowledgement We extend our sincere gratitude to Shri Vinod Zutshi, Secretary (Former), Ministry of Tourism, Government of India for his contribution and support for preparing the report. INDIAN TOURISM INFRASTRUCTURE - Investment Opportunities & Challenges 3 4 INDIAN TOURISM INFRASTRUCTURE - Investment Opportunities & Challenges FOREWORD Travel and tourism, the largest service industry in India was worth US$234bn in 2018 – a 19% year- on-year increase – the third largest foreign exchange earner for India with a 17.9% growth in Foreign Exchange Earnings (in Rupee Terms) in March 2018 over March 2017. According to The World Travel and Tourism Council, tourism generated ₹16.91 lakh crore (US$240 billion) or 9.2% of India’s GDP in 2018 and supported 42.673 million jobs, 8.1% of its total employment. The sector is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 6.9% to ₹32.05 lakh crore (US$460 billion) by 2028 (9.9% of GDP). The Ministry has been actively working towards the development of quality tourism infrastructure at various tourist destinations and circuits in the States / Union Territories by sanctioning expenditure budgets across schemes like SWADESH DARSHAN and PRASHAD. The Ministry of Tourism has been actively promoting India as a 365 days tourist destination with the introduction of niche tourism products in the country like Cruise, Adventure, Medical, Wellness, Golf, Polo, MICE Tourism, Eco-tourism, Film Tourism, Sustainable Tourism, etc. to overcome ‘seasonality’ challenge in tourism. I am pleased to present the FICCI Knowledge Report “Indian Tourism Infrastructure : Investment Opportunities & Challenges” which highlights the current scenario, key facts and figures pertaining to the tourism sector in India. -

Marine and Coastal Aquatic Biodiversity of Karnataka
MarineMarine andand coastalcoastal aquaticaquatic biodiversitybiodiversity ofof KarnatakaKarnataka Dr.Dr. P.U.P.U. ZachariaZacharia CentralCentral MarineMarine FisheriesFisheries ResearchResearch Institute,Institute, MangaloreMangalore ResearchResearch CentreCentre KarnatakaKarnataka StateState KarnatakaKarnataka StateState hashas aa 300300 kmkm longlong coastlinecoastline andand isis aa frontlinefrontline statestate inin marinemarine fisheriesfisheries development.development. HistoricallyHistorically knownknown asas thethe ‘mackerel‘mackerel coast’,coast’, itit hashas aa continentalcontinental shelfshelf areaarea ofof 25,00025,000 kmkm 2.. AboutAbout 80%80% ofof thethe shelfshelf areaarea lieslies betweenbetween 00 andand 7272 mm depth.depth. ItsIts contributioncontribution toto thethe totaltotal marinemarine fishfish productionproduction ofof thethe countrycountry hashas variedvaried fromfrom 66 toto 1414 %% annually.annually. GeoGeo --locationlocation ofof samplingsampling sitessites Grid No Inter-tidal Lat ( oN) Long ( oE) Code G1 Mangalore 12.99889 74.79389 IT1 G2 Mulki 13.02917 74.78861 IT2 G3 Malpe 13.36556 74.6975 IT3 G4 Kundapura 13.60778 74.67611 IT4 G5 Baindur 13.87333 74.61528 IT5 G6 Murdeshwar 14.09806 74.49083 IT6 G7 Kumta 14.43778 74.38583 IT7 G8 Ankola 14.65889 74.28306 IT8 G9 Karwar 14.88889 74.10278 IT9 Estuary G1 Netravati-Gurupur 12.83972 74.82889 E1 G2 Mulki 13.07361 74.78222 E2 G3 Swarna-Sita 13.33972 74.71056 E3 G4 Chakra-Haladi-Kollur 13.64306 74.65861 E4 G5 Vankatapur 13.98333 74.56167 E5 G7 Saravati-Badgani -

Western Ghats
Western Ghats From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia "Sahyadri" redirects here. For other uses, see Sahyadri (disambiguation). Western Ghats Sahyadri सहहदररद Western Ghats as seen from Gobichettipalayam, Tamil Nadu Highest point Peak Anamudi (Eravikulam National Park) Elevation 2,695 m (8,842 ft) Coordinates 10°10′N 77°04′E Coordinates: 10°10′N 77°04′E Dimensions Length 1,600 km (990 mi) N–S Width 100 km (62 mi) E–W Area 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi) Geography The Western Ghats lie roughly parallel to the west coast of India Country India States List[show] Settlements List[show] Biome Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Geology Period Cenozoic Type of rock Basalt and Laterite UNESCO World Heritage Site Official name: Natural Properties - Western Ghats (India) Type Natural Criteria ix, x Designated 2012 (36th session) Reference no. 1342 State Party India Region Indian subcontinent The Western Ghats are a mountain range that runs almost parallel to the western coast of the Indian peninsula, located entirely in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the eight "hottest hotspots" of biological diversity in the world.[1][2] It is sometimes called the Great Escarpment of India.[3] The range runs north to south along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau, and separates the plateau from a narrow coastal plain, called Konkan, along the Arabian Sea. A total of thirty nine properties including national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and reserve forests were designated as world heritage sites - twenty in Kerala, ten in Karnataka, five in Tamil Nadu and four in Maharashtra.[4][5] The range starts near the border of Gujarat and Maharashtra, south of the Tapti river, and runs approximately 1,600 km (990 mi) through the states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu ending at Kanyakumari, at the southern tip of India.