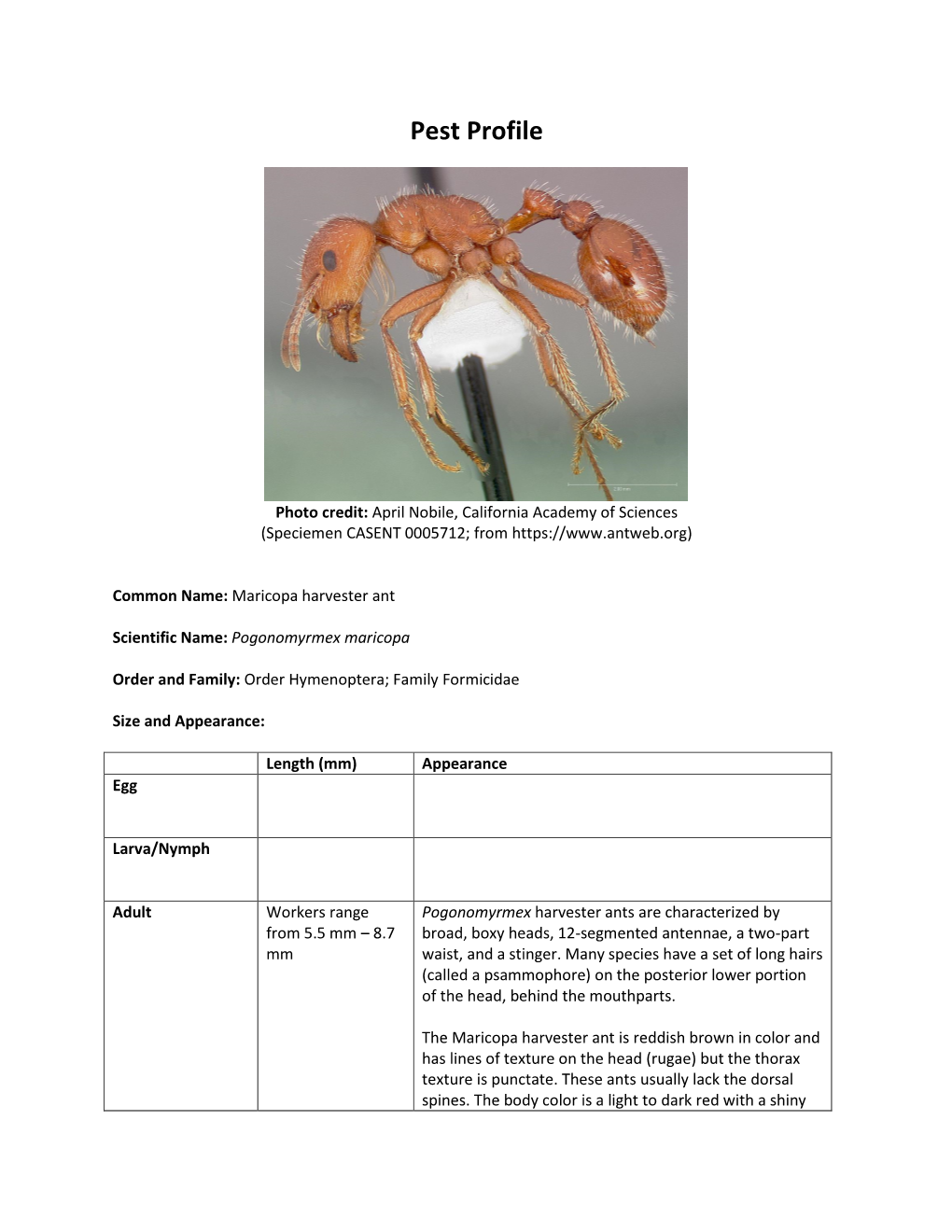
Maricopa Harvester Ant
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Double Mound of the Harvester Ant Pogonomyrmex Occidentalis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae, Myrmicinae)
Great Basin Naturalist Volume 53 Number 4 Article 13 12-28-1993 Double mound of the harvester ant Pogonomyrmex occidentalis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae, Myrmicinae) William H. Clark Orma J. Smith Museum of Natural History, Albertson College of Idaho, Caldwell, Idaho Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/gbn Recommended Citation Clark, William H. (1993) "Double mound of the harvester ant Pogonomyrmex occidentalis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae, Myrmicinae)," Great Basin Naturalist: Vol. 53 : No. 4 , Article 13. Available at: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/gbn/vol53/iss4/13 This Note is brought to you for free and open access by the Western North American Naturalist Publications at BYU ScholarsArchive. It has been accepted for inclusion in Great Basin Naturalist by an authorized editor of BYU ScholarsArchive. For more information, please contact [email protected], [email protected]. Creat Basin Naturalist 53(4), pp. 407-408 DOUBLE MOUND OF THE HARVESTER ANT POGONOMYRMEX OCCLDENTALIS (HYMENOPTERA: FORMICIDAE, MYRMICINAE) William H. ClarkI Key words: ho.rvester ant double mound, Pogonomyrmex occidentalis, ant nest, UUilt. Several species ofPogOlWmynnex, especial County, Utah, approximately 58 Ian NE Moab ly members of the occidentalis complex, have along Highway 128 and about 4 Ian from the nests surmounted by a large, conical mound Colorado River, at an elevation of 1445 m. of soil and gravel in a clearing created by the Voucher specimens from both mounds (WHC ants (Cole 1932, 1968). I report a rare double #8184 and 8185) are deposited in the Orma J. mound of the western halvester ant, Pogono Smith Museum of Natural History, Albertson mymwx oecidentalis (Cresson), having two College ofIdaho, Caldwell (ClDA). -

Wildland Fire in Ecosystems: Effects of Fire on Fauna
United States Department of Agriculture Wildland Fire in Forest Service Rocky Mountain Ecosystems Research Station General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-42- volume 1 Effects of Fire on Fauna January 2000 Abstract _____________________________________ Smith, Jane Kapler, ed. 2000. Wildland fire in ecosystems: effects of fire on fauna. Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-42-vol. 1. Ogden, UT: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. 83 p. Fires affect animals mainly through effects on their habitat. Fires often cause short-term increases in wildlife foods that contribute to increases in populations of some animals. These increases are moderated by the animals’ ability to thrive in the altered, often simplified, structure of the postfire environment. The extent of fire effects on animal communities generally depends on the extent of change in habitat structure and species composition caused by fire. Stand-replacement fires usually cause greater changes in the faunal communities of forests than in those of grasslands. Within forests, stand- replacement fires usually alter the animal community more dramatically than understory fires. Animal species are adapted to survive the pattern of fire frequency, season, size, severity, and uniformity that characterized their habitat in presettlement times. When fire frequency increases or decreases substantially or fire severity changes from presettlement patterns, habitat for many animal species declines. Keywords: fire effects, fire management, fire regime, habitat, succession, wildlife The volumes in “The Rainbow Series” will be published during the year 2000. To order, check the box or boxes below, fill in the address form, and send to the mailing address listed below. -

Metal Acquisition in the Weaponized Ovipositors of Aculeate Hymenoptera
Zoomorphology https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-018-0403-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Harden up: metal acquisition in the weaponized ovipositors of aculeate hymenoptera Kate Baumann1 · Edward P. Vicenzi2 · Thomas Lam2 · Janet Douglas2 · Kevin Arbuckle3 · Bronwen Cribb4,5 · Seán G. Brady6 · Bryan G. Fry1 Received: 17 October 2017 / Revised: 12 March 2018 / Accepted: 17 March 2018 © Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018 Abstract The use of metal ions to harden the tips and edges of ovipositors is known to occur in many hymenopteran species. However, species using the ovipositor for delivery of venom, which occurs in the aculeate hymenoptera (stinging wasps, ants, and bees) remains uninvestigated. In this study, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis was used to investigate the morphology and metal compositional differences among aculeate aculei. We show that aculeate aculei have a wide diversity of morphological adaptations relating to their lifestyle. We also demonstrate that metals are present in the aculei of all families of aculeate studied. The presence of metals is non-uniform and concentrated in the distal region of the stinger, especially along the longitudinal edges. This study is the first comparative investigation to document metal accumulation in aculeate aculei. Keywords Scanning electron microscopy · Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy · EDS · Aculeata · Aculeus · Cuticle · Metal accumulation Introduction with the most severe responses (as perceived by humans) delivered by taxa including bullet ants (Paraponera), taran- Aculeata (ants, bees, and stinging wasps) are the most con- tula hawk wasps (Pepsis), and armadillo wasps (Synoeca) spicuous of the hymenopteran insects, and are known pre- (Schmidt 2016). -

Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera) Intracolonial Genetic Diversity Influences Worker Nutritional Status Bruce J
Honey bee (Apis mellifera) intracolonial genetic diversity influences worker nutritional status Bruce J. Eckholm, Ming H. Huang, Kirk E. Anderson, Brendon M. Mott, Gloria Degrandi-Hoffman To cite this version: Bruce J. Eckholm, Ming H. Huang, Kirk E. Anderson, Brendon M. Mott, Gloria Degrandi-Hoffman. Honey bee (Apis mellifera) intracolonial genetic diversity influences worker nutritional status. Api- dologie, Springer Verlag, 2015, 46 (2), pp.150-163. 10.1007/s13592-014-0311-4. hal-01284439 HAL Id: hal-01284439 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01284439 Submitted on 7 Mar 2016 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Apidologie (2015) 46:150–163 Original article * INRA, DIB and Springer-Verlag France, 2014 DOI: 10.1007/s13592-014-0311-4 Honey bee (Apis mellifera ) intracolonial genetic diversity influences worker nutritional status 1 2 3 3 Bruce J. ECKHOLM , Ming H. HUANG , Kirk E. ANDERSON , Brendon M. MOTT , 3 Gloria DEGRANDI-HOFFMAN 11025 Zylstra Road, Coupeville, WA 98239, USA 2Eurofins Agroscience Services, Inc., 15250 NC Hwy 86 South, Prospect Hill, NC 27314, USA 3Carl Hayden Bee Research Center, USDA-ARS, 2000 East Allen Road, Tucson, AZ 85719, USA Received 9 January 2014 – Revised 10 July 2014 – Accepted 25 July 2014 Abstract – Honey bee queens mate with multiple males resulting in high intracolonial genetic diversity among nestmates; a reproductive strategy known as extreme polyandry. -

Pogonomyrmex Barbatus
Anita. Behav., 1986, 34, 1402-1419 The dynamics of the daily round of the harvester ant colony (Pogonomyrmex barbatus) DEBORAH M. GORDON Museum of Comparative Zoology and Society of Fellows, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, U.S.A. Abstract. Colonies of the red harvester ant, Pogonomyrmex barbatus, do various tasks outside the nest. There is a daily temporal pattern in the numbers of ants engaged in each of five activities: foraging, nest maintenance, patrolling, midden work and convening. Perturbations were carried out in the field to investigate how the daily round changes in response to environmental events and colony needs. Interfering with nest maintenance, foraging or both caused changes in the temporal patterns in all five of the observed activities. Removing nest maintenance workers, foragers or both caused the numbers involved in all five activities to decrease, and there were temporal patterns in the effects of removals. The results of both interference and removal experiments show that the extent to which a worker group does one activity affects the behaviour of other groups. When nest maintenance or foraging is impeded experimentally, these two activities are of reciprocal priority. When both are impeded, foraging is of higher priority than nest maintenance. Harvester ants forage, patrol, maintain the nest speaking, that of an equilibrium state, but the area and foraging trails, collect and arrange dynamics of colony organization are not yet under- pebbles on the nest, and gather in small groups, stood. What events will alter the daily round, by inspecting and grooming each other. The beha- how much, and for how long? Is there more than viour of the colony outside the nest at any moment one equilibrium state? can be described by citing the number of ants This study begins an exploration of the dynamics engaged in each of the five activities. -

Evolution of Colony Characteristics in the Harvester Ant Genus
Evolution of Colony Characteristics in The Harvester Ant Genus Pogonomyrmex Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg vorgelegt von Christoph Strehl Nürnberg Würzburg 2005 - 2 - - 3 - Eingereicht am: ......................................................................................................... Mitglieder der Prüfungskommission: Vorsitzender: ............................................................................................................. Gutachter : ................................................................................................................. Gutachter : ................................................................................................................. Tag des Promotionskolloquiums: .............................................................................. Doktorurkunde ausgehändigt am: ............................................................................. - 4 - - 5 - 1. Index 1. Index................................................................................................................. 5 2. General Introduction and Thesis Outline....................................................... 7 1.1 The characteristics of an ant colony...................................................... 8 1.2 Relatedness as a major component driving the evolution of colony characteristics.................................................................................................10 1.3 The evolution -

TAXONOMIC IDENTITY of "HALLUCINOGENIC" HARVESTER ANT Lpogonomyrmex Calijornicus) CONFIRMED
Journal of Ethnobiology 21(2): 133-144 Winter 2001 TAXONOMIC IDENTITY OF "HALLUCINOGENIC" HARVESTER ANT lPogonomyrmex calijornicus) CONFIRMED KEVIN I' GROARK Department of Anthropology, Un;ocrsity of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90024 ABSTRACf.-The use of California harvester ants (fbgollomyrmex californiClls) for visionary and therapeutic ends was an important but poorly-documented tradi tion in native south-central California. In this brief report, a confirmation of the taxonomic identity of the red ant species used in California is presented, and the descriptive record of its use is supplemented with additional ethnographic ac counts. This taxonomic identification of this species is of particular importance, as visionary red ant ingestion provides the only well-documented case of the widespread use of an insect as an hallucinogenic agent. RESUMEN.-La utilizaci6n de hormigas granivoras rojas (HJgo/wmyrmex califor nicus) con fines alucin6genos y terapeuticos, fue una tradici6n de mucha impor tancia pero mal documentada en el sur y centro-sur de California. Este breve articulo confirma la identidad taxon6mica de dicha especie y la descripci6n de su uso se hace a !raves de datos etnogrMicos adicionales. Esta identificaci6n taxo n6mica es de especial interes, puesto que es el dnico ejemplo etnografico debi damente documentado de un agente alucin6geno derivado de un insecto. REsUME.-L'u!ilisation des fourmis moissonneuses rouges (fbgonomyrmex califor nicus) a des desseins religieux et therapeutiques etait une tradition peu docu mentee mais importante dans la vie de plusieurs groupes autochtones du centre sud de la Californie. Dans ce bref expose on trouve la confirmation de I'identification taxonomique de la fourmi et a la description de la methode de son utilisation s'ajoute des donnees ethnographiques suplementaires. -

Red Harvester Ant (Big Red Ants; Harvester Ants, Red Ants; Barbatus Harvester Ant)
Pest Profile Photo credit: April Nobile, California Academy of Sciences (Specimen CASENT0006306; from https://www.antweb.org) Common Name: Red harvester ant (big red ants; harvester ants, red ants; Barbatus harvester ant) Scientific Name: Pogonomyrmex barbatus Order and Family: Order Hymenoptera; Family Formicidae Size and Appearance: Length (mm) Appearance Egg Larva/Nymph Adult Workers Pogonomyrmex harvester ants are characterized by broad, range from 5 boxy heads, 12-segmented antennae, a two-part waist, a pair mm – 8 mm of dorsal spines and a stinger. Many species have a set of long hairs (called a psammophore) on the posterior lower portion of the head, behind the mouthparts. Workers of the red harvester ant are polymorphic without distinct majors and minors. They vary in color from a light to very deep red and they have texture in the form of lines on the head (rugae). Colonies have one queen (monogynous). Queens are similar to workers but larger with a larger thorax. Female and male reproductive ants have wings. Pupa (if applicable) Type of feeder (Chewing, sucking, etc.): Chewing Host(s): Harvester ants in the genus Pogonomyrmex specialize in seeds but may forage on other foods (generalist and opportunistic). Description of Damage (larvae and adults): Because theses ants primarily eat seeds (up to 90% of the diet), they are pests of agricultural systems, damaging crops but especially grasslands (pasture). They harvest seeds, defoliate plants, and remove young and old plants. Agricultural important plants they affect include corn, oats, alfalfa, cotton, guayule, grapes, date, citrus trees, apple, and pear, as well as more generally pasture (grasses) and shrubs. -

I. Petiole Node II. Tip of Abdomen IV. Length of Antennae Guide to Vineyard Ant Identification III. Shape of Thorax
Guide to Vineyard Ant Identification head abdomen Monica L. Cooper, Viticulture Farm Advisor, Napa County Lucia G. Varela, North Coast IPM Advisor thorax I. Petiole node One Node Two nodes Go to II Subfamily Myrmicinae Go to V II. Tip of abdomen Circle of small hairs present Circle of small hairs absent Subfamily Formicinae Subfamily Dolichoderinae Go to III Argentine Ant (Linepithema humile) III. Shape of thorax Thorax uneven Thorax smooth and rounded Go to IV Subfamily Formicinae Carpenter ant (Camponotus spp.) IV. Length of antennae Antennae not much longer than length of head Antennae much longer than length of head Subfamily Formicinae Subfamily Formicinae Field or Gray Ant (Formica spp.) False honey ant (Prenolepis imparis) head abdomen Petiole with two nodes Subfamily Myrmicinae (V-VIII) thorax V. Dorsal side of Thorax & Antennae One pair of spines on thorax No spines on thorax 12 segmented antennae 10 segmented antennae Go to VI Solenopsis molesta and Solenopsis xyloni VI. Underside of head No brush of bristles Brush of long bristles Go to VII Harvester ants (Pogonomyrmex californicus and P. brevispinosis) VII. Head and Thorax With hairs Without hairs Go to VIII Cardiocondyla mauritanica VIII. Head and Thorax With many parallel furrows Without parallel furrows Profile of thorax rounded Profile of thorax not evenly rounded Pavement ant (Tetramorium “species E”) Pheidole californica Argentine Ant (Linepithema humile), subfamily Dolichoderinae Exotic species 3-4 mm in length Deep brown to light black Move rapidly in distinct trails Feed on honeydew Shallow nests (2 inches from soil surface) Alex Wild Does not bite or sting Carpenter Ant (Camponotus spp.), subfamily Formicinae Large ant: >6 mm in length Dark color with smooth, rounded thorax Workers most active at dusk and night One of most abundant and widespread genera worldwide Generalist scavengers and predators: feed on dead and living insects, nectar, fruit juices and Jack K. -

Red Harvester Ants Bastiaan M
E-402 4-06 Red Harvester Ants Bastiaan M. Drees* ed harvester ants are one of the more Life cycle noticeable and larger ants in open areas in Texas. Eleven species in this group of ants Winged males and females swarm, couple and R mate, especially following rains. Winged forms (genus Pogonomyrmex) are known from the state. are larger than worker ants. Males soon die and However, harvester ants are not nearly as com- females seek a suitable nesting site. After drop- mon today as they were during the earlier 1900s. ping her wings, the queen ant digs a burrow and The decline, particularly in the eastern part of produces a few eggs. Larvae hatch from eggs and the state, has caused some alarm because these develop through several stages (instars). Larvae ants serve as a major source of food for the are white and legless, shaped like a crookneck rapidly disappearing and threatened Texas squash with a small distinct head. Pupation horned lizard. occurs within a cocoon. Worker ants produced by the queen ant begin caring for other develop- Description ing ants, enlarge the nest and forage for food. 1 1 Worker ants are ⁄4 to ⁄2 inch long and red to Pest status dark brown. They have squarish heads and no spines on the body. There are 22 species of har- Worker ants can give a painful, stinging bite, vester ants in the United States, 10 of which are but are generally reluctant to attack. Effects of found in Texas. Seven of these species are found the bite can spread along lymph channels and only in far west Texas. -

A New Ant Genus from Southern Argentina and Southern Chile, Patagonomyrmex (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)
Zootaxa 4139 (1): 001–031 ISSN 1175-5326 (print edition) http://www.mapress.com/j/zt/ Article ZOOTAXA Copyright © 2016 Magnolia Press ISSN 1175-5334 (online edition) http://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4139.1.1 http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:ED6570FE-F499-4B75-B1A3-1386514C3F07 A new ant genus from southern Argentina and southern Chile, Patagonomyrmex (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) ROBERT A. JOHNSON1,3 & CORRIE S. MOREAU2 1School of Life Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-4501, USA 2Field Museum of Natural History, Department of Science and Education, 1400 South Lake Shore Drive, Chicago, IL 60605, USA 3Corresponding author. E-mail: [email protected] Abstract The ant genus Pogonomyrmex (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Myrmicinae) comprises 71 described species that occur in North America, South America, and Hispaniola, and it is the nominal genus in the recently established tribe Pogonomyr- mecini. A molecular phylogeny using 3,647 base pairs from fragments of one mitochondrial gene (cytochrome oxidase I) and five nuclear genes (long-wavelength rhodopsin, elongation factor 1α F1, elongation factor 1α F2, wingless, rudimen- tary) inferred that Pogonomymrex was not monophyletic. The vast majority of species belonged to a monophyletic clade (Pogonomyrmex sensu stricto), whereas species in the Po. angustus-group formed a second lineage outside of Pogono- myrmex and Hylomyrma, the latter being the only other genus in the tribe. To maintain monophyly of Pogonomyrmex, we create the genus Patagonomyrmex gen. n., which consists of the three angustus-group species (Patagonomyrmex angustus comb. n., Patagonomyrmex laevigatus comb. n., and Patagonomyrmex odoratus comb. n.) that are sister to all other pogonomyrmecines. -

Adverse Reactions to Ants Other Than Imported Fire Ants John H
Adverse reactions to ants other than imported fire ants John H. Klotz, PhD*; Richard D. deShazo, MD†; Jacob L. Pinnas, MD‡; Austin M. Frishman, PhD§; Justin O. Schmidt, PhD¶; Daniel R. Suiter, PhDʈ; Gary W. Price, MD**; and Stephen A. Klotz, MD‡ Objective: To identify ants other than Solenopsis invicta and Solenopsis richteri reported to cause adverse reactions in humans. Data Sources: We conducted a literature review to identify reports of medical reactions to ants other than S invicta and S richteri. Our review of medical and entomological literature on stinging ants was generated from MEDLINE and FORMIS, respectively, using the key words stinging ants and ant stings. The search was limited to articles in English published from 1966 to 2004 on MEDLINE and all years on FORMIS. We also present 3 new case reports of severe reactions to stings by 2 different species of ants, Pseudomyrmex ejectus and Hypoponera punctatissima. Study Selection: Articles that concerned anaphylactic (IgE-mediated) or anaphylactic-like (resembling anaphylaxis but mechanism unknown) immediate reactions to ant stings or bites were included in this review. Results: Taken together, our data demonstrate that S invicta and S richteri are not alone in their capability to cause serious allergic or adverse reactions. A diverse array of ant species belonging to 6 different subfamilies (Formicinae, Myrmeciinae, Ponerinae, Ectatomminae, Myrmicinae, and Pseudomyrmecinae) and 10 genera (Solenopsis, Formica, Myrmecia, Tetramorium, Pogonomyrmex, Pachycondyla, Odontomachus, Rhytidoponera, Pseudomyrmex, and Hypoponera) have now been shown to have this capability. Conclusion: Awareness that species other than imported fire ants may cause severe reactions should lead to more rapid evaluation and treatment and further investigation of the medical entomology of these ants.