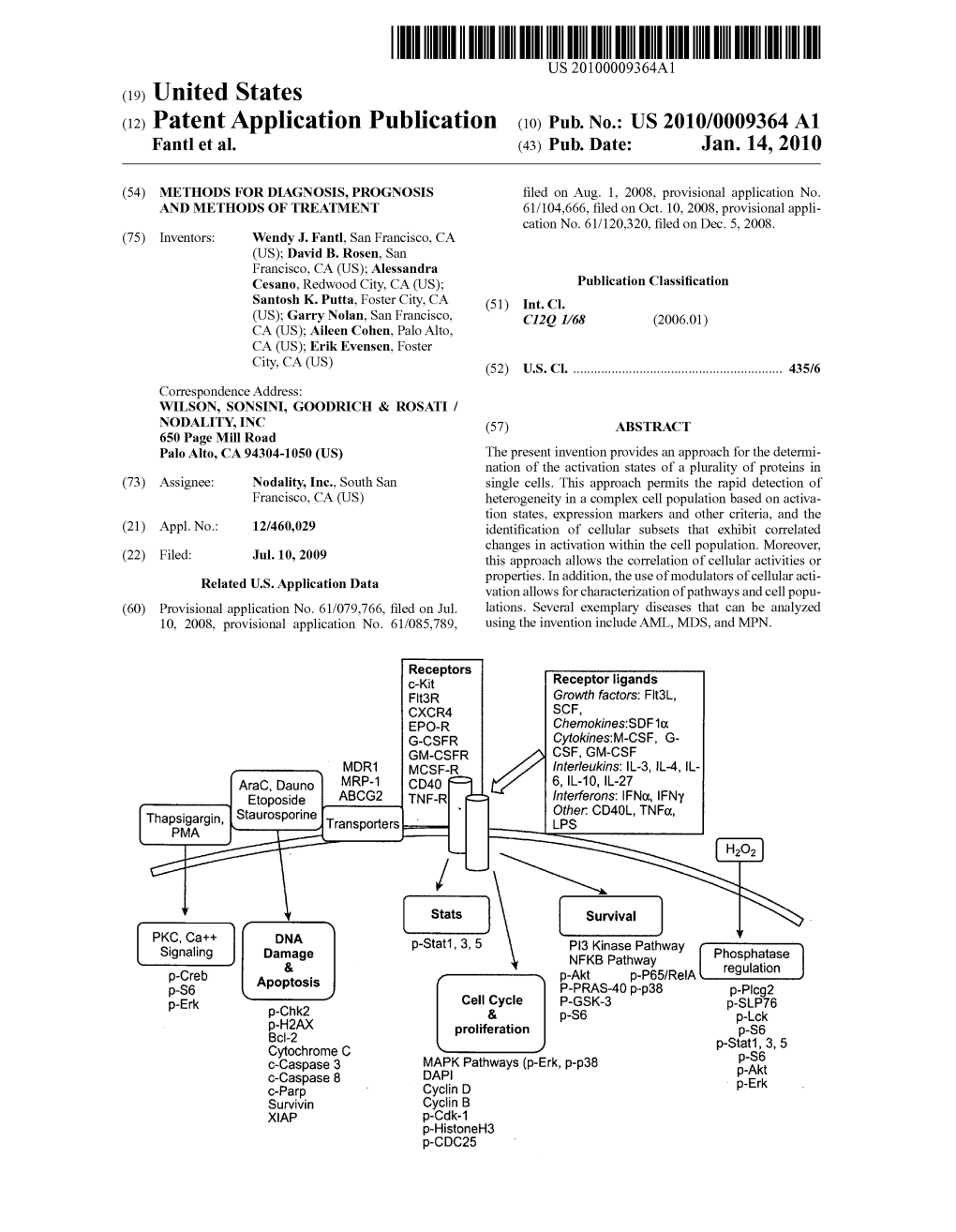
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0009364 A1 Fant Et Al
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Ilamycin C Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Migration and Invasion In
Xie et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2019) 12:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0744-3 RESEARCH Open Access Ilamycin C induces apoptosis and inhibits migration and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer by suppressing IL-6/STAT3 pathway Qing Xie1†, Zhijie Yang2†, Xuanmei Huang1, Zikang Zhang1, Jiangbin Li1, Jianhua Ju2*, Hua Zhang1* and Junying Ma2* Abstract Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive subtype of breast cancer with poor prognosis, and its treatment remains a challenge due to few targeted medicines and high risk of relapse, metastasis, and drug resistance. Thus, more effective drugs and new regimens for the therapy of TNBC are urgently needed. Ilamycins are a kind of cyclic peptides and produced by Streptomyces atratus and Streptomyces islandicus with effective anti-tuberculosis activity. Ilamycin C is a novel compound isolated from the deep South China Sea- derived Streptomyces atratus SCSIO ZH16 and exhibited a strong cytotoxic activity against several cancers including breast cancer cell line MCF7. However, the cytotoxic activity of Ilamycin C to TNBC cells and a detailed antitumor mechanism have not been reported. Methods: CCK-8 assays were used to examine cell viability and cytotoxic activity of Ilamycin C to TNBC, non-TNBC MCF7, and nonmalignant MCF10A cells. EdU assays and flow cytometry were performed to assess cell proliferation and cell apoptosis. Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays were utilized to assess the migratory and invading capacity of TNBC cells following the treatment of Ilamycin C. The expressions of proteins were detected by western blot. Results: In this study, we found that Ilamycin C has more preferential cytotoxicity in TNBC cells than non-TNBC MCF7 and nonmalignant MCF10A cells. -

Thromboxane A2 Receptor Antagonist SQ29548 Attenuates SH‑SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cell Impairments Induced by Oxidative Stress
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOleCular meDICine 42: 479-488, 2018 Thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist SQ29548 attenuates SH‑SY5Y neuroblastoma cell impairments induced by oxidative stress GAOYU CAI1*, AIJUAN YAN2*, NINGZHEN FU3 and YI FU1 1Department of Neurology, Rui Jin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200025; 2Department of Neurology, Xin Hua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200082; 3Department of Pancreatic Surgery, Rui Jin College of Clinical Medicine, Rui Jin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200025, P.R. China Received September 28, 2017; Accepted March 21, 2018 DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3589 Abstract. Thromboxane A2 receptor (TXA2R) serves a vital SQ29548, an antagonist of TXA2R, improved the antioxidant role in numerous neurological disorders. Our previous study capacities of SH-SY5Y cells and reduced the cell apoptosis indicated that SQ29548, an antagonist of TXA2R, attenuated through the inhibition of MAPK pathways. the induced neuron damage in cerebral infarction animals; however, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. Introduction Certain studies revealed a new role of TXA2R in the regula- tion of oxidative stress, which is one of the basic pathological Thromboxane A2 receptor (TXA2R), a member of the G processes in neurological disorders. Thus, the present study protein-coupled receptor family (1), is broadly distributed attempted to examine whether the inhibition of TXA2R with in platelets (2), as well as epithelial (3), smooth muscle (4), SQ29548 helped to protect the nerve cells against oxidative glial and nerve cells in the brain (5). TXA2R is regarded as a stress. SQ29548 was utilized as a TXA2R antagonist, and traditional coagulation and inflammation‑associated receptor, relevant assays were performed to detect the cell viability, which is also closely associated with neurological disorders. -

Supplemetal Materials and Methods Materials Arctiin and Arctigenin
Supplemetal materials and Methods Materials Arctiin and arctigenin were separated and purified by our laboratory and the final product shown an over 98% purity by HPLC detection. Trandrine tablets were provided by Zhejiang Jinhua Conba Bio-Pharm. CO., LTD. China. Silica (SiO2 purity >99%, particle size 0.5-10 μm (approx. 80% between 1-5 μm) was purchased from Sigma, St., Louse, MO, USA. Penicillin G was suppied by North China Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. 2-ketoglutaric acid, pyruvic acid, succinic acid, disodium fumarate, malic acid, stearic acid, 3-hydroxytyramine hydrochloride and mixed amino acid standards were purchased from Sigma, USA. Betaine, allantoin, inosine, taurine, creatinine, L-carnitine, creatine, urea and citric acid were recruited from Aladdin, USA. Sodium lactate, doxifluridine, D-(+)-pantothenic acid calcium salt and 6-hydroxypurine were purchased from the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, China. TNF-α, IL- 1β, NF-κB and TGF-β ELISA kit (FANKEL BIO, Shanghai, China), Hydroxyproline (HYP), ceruloplasmin and lysozyme assay kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). The mitochondrial membrane potential assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China.), reactive oxygen species assay kit (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China.), SDS-PAGE Sample Loading Buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China), BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Antibodies against the following proteins were used: α-SMA, NF-κB, TLR-4, Myd88, NLRP3, ASC, cleaved Caspase-1 (Wanleibio, Shenyang, China), β-actin (Absci, USA), HRP-conjugated goat antirabbit IgG (Wanleibio, Shenyang, China), BeyoECL Plus (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Dose selection The daily dose interval of Fructus Arctii is 6 - 12 g according to Chinese Pharmacopoeia, in which the arctigenin account for 5% of Fructus Arctii. -

Anti-Toxoplasma Gondii Effects of a Novel Spider Peptide XYP1 in Vitro and in Vivo
biomedicines Article Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effects of a Novel Spider Peptide XYP1 In Vitro and In Vivo Yuan Liu 1,†, Yaqin Tang 1,†, Xing Tang 2,†, Mengqi Wu 1, Shengjie Hou 1, Xiaohua Liu 1, Jing Li 1, Meichun Deng 3, Shuaiqin Huang 1 and Liping Jiang 1,4,* 1 Department of Parasitology, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China; [email protected] (Y.L.); [email protected] (Y.T.); [email protected] (M.W.); [email protected] (S.H.); [email protected] (X.L.); [email protected] (J.L.); [email protected] (S.H.) 2 Hunan Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Biological Resources in the Nanyue Mountainous Region, Hengyang Normal University, Hengyang 421008, China; [email protected] 3 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Life Sciences, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China; [email protected] 4 China-Africa Research Center of Infectious Diseases, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +86-731-82650556 † These authors have contributed equally to this work. Abstract: Toxoplasmosis, caused by an obligate intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii, is one of the most prevalent zoonoses worldwide. Treatments for this disease by traditional drugs have shown numerous side effects, thus effective alternative anti-Toxoplasma strategies or drugs are urgently needed. In this study, a novel spider peptide, XYP1, was identified from the cDNA library of the Citation: Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, X.; venom gland of the spider Lycosa coelestis. Our results showed that XYP1 has potent anti-Toxoplasma Wu, M.; Hou, S.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Deng, activity in vitro and in vivo. -

BQ123 Stimulates Skeletal Muscle Antioxidant Defense Via Nrf2 Activation in LPS-Treated Rats
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity Volume 2016, Article ID 2356853, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2356853 Research Article BQ123 Stimulates Skeletal Muscle Antioxidant Defense via Nrf2 Activation in LPS-Treated Rats Agata Kowalczyk,1 Agnieszka JeleN,2 Marta gebrowska,2 Ewa Balcerczak,2 and Anna Gordca1 1 Department of Cardiovascular Physiology, Chair of Experimental and Clinical Physiology, Medical University of Lodz, 6/8 Mazowiecka Street, 92-215 Lodz, Poland 2Laboratory of Molecular Diagnostic and Pharmacogenomics, Department of Pharmaceutical Biochemistry and Molecular Diagnostic, Medical University of Lodz, 1 Muszynskiego Street, 90-151 Lodz, Poland Correspondence should be addressed to Agata Kowalczyk; [email protected] and Anna Gorąca; [email protected] Received 23 July 2015; Revised 24 September 2015; Accepted 11 October 2015 Academic Editor: Ersin Fadillioglu Copyright © 2016 Agata Kowalczyk et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Little is understood of skeletal muscle tissue in terms of oxidative stress and inflammation. Endothelin-1 is an endogenous, vasoconstrictive peptide which can induce overproduction of reactive oxygen species and proinflammatory cytokines. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether BQ123, an endothelin-A receptor antagonist, influences the level of TNF-, IL-6, SOD-1, HO- 1, Nrf2 mRNA, and NF-B subunit RelA/p65 mRNA in the femoral muscle obtained from endotoxemic rats. Male Wistar rats were divided into 4 groups (=6) and received iv (1) saline (control), (2) LPS (15 mg/kg), (3) BQ123 (1 mg/kg), (4) BQ123 (1 mg/kg), and LPS (15 mg/kg, resp.) 30 min later. -

Modes of Action of Herbal Medicines and Plant Secondary Metabolites
Medicines 2015, 2, 251-286; doi:10.3390/medicines2030251 OPEN ACCESS medicines ISSN 2305-6320 www.mdpi.com/journal/medicines Review Modes of Action of Herbal Medicines and Plant Secondary Metabolites Michael Wink Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology, Heidelberg University, INF 364, Heidelberg D-69120, Germany; E-Mail: [email protected]; Tel.: +49-6221-544-881; Fax: +49-6221-544-884 Academic Editor: Shufeng Zhou Received: 13 August 2015 / Accepted: 31 August 2015 / Published: 8 September 2015 Abstract: Plants produce a wide diversity of secondary metabolites (SM) which serve them as defense compounds against herbivores, and other plants and microbes, but also as signal compounds. In general, SM exhibit a wide array of biological and pharmacological properties. Because of this, some plants or products isolated from them have been and are still used to treat infections, health disorders or diseases. This review provides evidence that many SM have a broad spectrum of bioactivities. They often interact with the main targets in cells, such as proteins, biomembranes or nucleic acids. Whereas some SM appear to have been optimized on a few molecular targets, such as alkaloids on receptors of neurotransmitters, others (such as phenolics and terpenoids) are less specific and attack a multitude of proteins by building hydrogen, hydrophobic and ionic bonds, thus modulating their 3D structures and in consequence their bioactivities. The main modes of action are described for the major groups of common plant secondary metabolites. The multitarget activities of many SM can explain the medical application of complex extracts from medicinal plants for more health disorders which involve several targets. -

Overview of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Pharmacokinetic Properties
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018) 39: 787–801 © 2018 CPS and SIMM All rights reserved 1671-4083/18 www.nature.com/aps Review Article Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L Qiong GAO, Mengbi YANG, Zhong ZUO* School of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China Abstract Arctigenin (AR) and its glycoside, arctiin, are two major active ingredients of Arctium lappa L (A lappa), a popular medicinal herb and health supplement frequently used in Asia. In the past several decades, bioactive components from A lappa have attracted the attention of researchers due to their promising therapeutic effects. In the current article, we aimed to provide an overview of the pharmacology of AR and arctiin, focusing on their anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetics properties and clinical efficacies. Compared to acrtiin, AR was reported as the most potent bioactive component of A lappa in the majority of studies. AR exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) via modulation of several cytokines. Due to its potent anti-inflammatory effects, AR may serve as a potential therapeutic compound against both acute inflammation and various chronic diseases. However, pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated the extensive glucuronidation and hydrolysis of AR in liver, intestine and plasma, which might hinder its in vivo and clinical efficacy after oral administration. Based on the reviewed pharmacological and pharmacokinetic characteristics of AR, further pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of AR via alternative administration routes are suggested to promote its ability to serve as a therapeutic agent as well as an ideal bioactive marker for A lappa. -

The Anti-Metastatic Effects of the Phytoestrogen Arctigenin on Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines Regardless of the Status of ER Expression
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 50: 727-735, 2017 The anti-metastatic effects of the phytoestrogen arctigenin on human breast cancer cell lines regardless of the status of ER expression THRESSI MAxwEll, So-YouNg CHuN, KYu-SHIK lEE, SoYouNg KIM and KYuNg-Soo NAM Department of Pharmacology and Intractable Disease Research Center, School of Medicine, Dongguk university, gyeongju-si 780-350, Republic of Korea Received August 8, 2016; Accepted December 12, 2016 DoI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3825 Abstract. Arctigenin is a plant lignan extracted from Arctium were analyzed using western blotting. The activation of Akt, lappa that has been shown to have estrogenic properties. In NF-κB and MAPK (ERK 1/2 and JNK 1/2) was found to be spite of the health benefits of phytoestrogens reducing the risk inhibited. Taken together, these data suggest that arctigenin of osteoporosis, heart disease, and menopausal symptoms, its confers anti-metastatic effects by inhibiting MMP-9 and uPA benefits against the risk of breast cancer have not been fully via the Akt, NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways on breast elucidated. Thus, we investigated the effects of arctigenin cancer, regardless of ER expression. Therefore, we propose on metastasis of breast cancer using both estrogen receptor that the intake of arctigenin could be an effective supplement (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 human for breast cancer patients. breast cancer cell lines to see if the effects are dependent on the status of ER expression. In ER-positive MCF-7 cells, Introduction arctigenin efficiently inhibited 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol- 13-acetate (TPA)-induced cell migration and invasion. -

Investigation of the Antidiabetic Activity Of
INVESTIGATION OF THE ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF CNICUS BENEDICTUS L. IN RATS. RAYMONDE BAMBOUKOU BEKALE (B. Pharm, UWC) A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Magister Pharmaceuticae in the School of Pharmacy, University of the Western Cape SUPERVISOR: PROFESSOR GEORGE J. AMABEOKU NOVEMBER 2016 i DECLARATION I declare that the thesis, Investigation of the antidiabetic activity of Cnicusbenedictus L. in rats, is my own work, that it has not been submitted before for any degree examination in any other University and that all the sources I have used or quoted have been indicated and acknowledged by complete reference. Raymonde BAMBOUKOU BEKALE November 2016 Signed……………………………….. ii DEDICATION I dedicate this thesis to my loving mother, Boubwetata Loba Helene and my family for their sacrifices and endless love, care and encouragement that has got me to where I am today. Thank you for believing in me and supporting me to be the best. iii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First of all, I thank the Almighty God, our Saviour, for His Mercy, Guidance and Protection throughout the years. The completion of this work has come as a product of hard work and I would like to express my sincere gratitude to the following individual and organizations, whose involvement in my life enabled me to complete this thesis: My supervisor, PROFESSOR GEORGE J. AMABEOKU for his commitment, guidance, patience, support, advice and valuable contributions made towards my study. I am privileged to have worked alongside him. The National Research Foundation for financial support. Mrs Eloise for her assistance with laboratory technicalities. MrsVirginaMvula for the maintenance of the animal house and upkeep of the animals. -

Plant. Biotechnol. 30(2)
Plant Biotechnology 30, 97–109 (2013) DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.12.1230a Original Paper A lignan O-methyltransferase catalyzing the regioselective methylation of matairesinol in Carthamus tinctorius Toshiaki Umezawa1,2,*,†, Safendrri Komara Ragamustari1,2,†, Tomoyuki Nakatsubo1, Shohei Wada1, Laigeng Li3,4, Masaomi Yamamura1, Norikazu Sakakibara1,5, Takefumi Hattori1,6, Shiro Suzuki1, Vincent L. Chiang3 1 Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan; 2 Institute of Sustainability Science, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan; 3 Department of Forestry and Environmental Resources, College of Natural Resources, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 27695-7247, USA; 4 Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032, China; 5 Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Kagawa Campus, Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki, Kagawa 769-2193, Japan; 6 Institute of Socio-Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokushima, Tokushima 770-8502, Japan * E-mail: [email protected] Tel: +81-774-38-3625 Fax: +81-774-38-3682 Received December 14, 2012; accepted December 30, 2012 (Edited by T. Aoki) Abstract Lignans are a group of plant phenolic compounds with various biological activities, including antitumor and antioxidant properties. O-Methylation is a critical step in biosynthesis of these compounds. However, little is known about the O-methyltransferase (OMT) enzymes that catalyze lignan O-methylation. We discovered a highly regioselective OMT activity in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) seeds that catalyzed the methylation of matairesinol, a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, into 4′-O-methylmatairesinol (arctigenin) but not 4-O-methylmatairesinol (isoarctigenin). By examining such OMT activity in correlation with OMT transcript abundances during seed development, we cloned a few putative OMT cDNAs and produced their recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. -

Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Colitis: Evidence from Preclinical Studies
Reviews Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Colitis: Evidence from Preclinical Studies Authors ABSTRACT Marília T. Santana, Luana M. Cercato, Janaíne P. Oliveira, Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition whose Enilton A. Camargo treatment includes aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and im- munomodulators. Medicinal plants seem to be an important Affiliation alternative treatment for this condition. They have been the Department of Physiology, Federal University of Sergipe, subject of a great number of studies in recent years. This São Cristóvão, SE, Brazil study was conducted to systematically review the medicinal plants tested in experimental models of ulcerative colitis. We Key words conducted a systematic literature search through specialized ulcerative colitis, medicinal plant, phytotherapy, flavonoid, databases (PUBMED, SCOPUS, EMBASE, MEDLINE, LILACS, terpene SCIELO, and SCISEARCH) and selected articles published be- tween January 2000 and June 21, 2016 by using “medicinal received November 11, 2016 plants” and “ulcerative colitis” as key words. Sixty-eight stud- revised January 17, 2017 ies were included, and the families Asteraceae and Lamiaceae accepted February 20, 2017 presented the largest number of studies, but plants from sev- Bibliography eral other families were cited; many of them have shown DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-104933 good results in experimental animals. However, only a few Published online March 14, 2017 | Planta Med 2017; 83: 588– species (such as Andrographis paniculata and Punica granatum) 614 © Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York | have undergone clinical tests against ulcerative colitis, and ISSN 0032‑0943 the observation that many preclinical studies reviewed are purely descriptive has certainly contributed to this fact. -

Association of Adipose Tissue and Adipokines with Development of Obesity-Induced Liver Cancer
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Review Association of Adipose Tissue and Adipokines with Development of Obesity-Induced Liver Cancer Yetirajam Rajesh 1 and Devanand Sarkar 2,* 1 Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23298, USA; [email protected] 2 Massey Cancer Center, Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM), Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23298, USA * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +1-804-827-2339 Abstract: Obesity is rapidly dispersing all around the world and is closely associated with a high risk of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), leading to carcinogenesis, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It results from an imbalance between food intake and energy expenditure, leading to an excessive accumulation of adipose tissue (AT). Adipocytes play a substantial role in the tumor microenvironment through the secretion of several adipokines, affecting cancer progression, metastasis, and chemoresistance via diverse signaling pathways. AT is considered an endocrine organ owing to its ability to secrete adipokines, such as leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and a plethora of inflammatory cytokines, which modulate insulin sensitivity and trigger chronic low-grade inflammation in different organs. Even though the precise mechanisms are still unfolding, it is now established that the dysregulated secretion of adipokines by AT contributes to the development of obesity-related metabolic disorders. This review focuses on several obesity-associated adipokines and their impact on obesity-related Citation: Rajesh, Y.; Sarkar, D. metabolic diseases, subsequent metabolic complications, and progression to HCC, as well as their Association of Adipose Tissue and role as potential therapeutic targets.