Visiting Mount Umunhum's Summit Audio Tour
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Geologic Map of the Frisco Quadrangle, Summit County, Colorado
Geologic Map of the Frisco Quadrangle, Summit County, Colorado By Karl S. Kellogg, Paul J. Bartos, and Cindy L. Williams Pamphlet to accompany MISCELLANEOUS FIELD STUDIES MAP MF-2340 2002 U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Geologic Map of the Frisco Quadrangle, Summit County, Colorado By Karl S. Kellogg, Paul J. Bartos, and Cindy L. Williams DESCRIPTION OF MAP UNITS af Artificial fill (recent)—Compacted and uncompacted rock fragments and finer material underlying roadbed and embankments along and adjacent to Interstate 70. Also includes material comprising Dillon Dam dt Dredge tailings (recent)—Unconsolidated, clast-supported deposits containing mostly well- rounded to subrounded, cobble- to boulder-size clasts derived from dredging of alluvium for gold along the Blue and Swan Rivers; similar dredge tailings along Gold Run Gulch are too small to show on map. Dredge tailings were mapped from 1974 air photos; most tailings have now been redistributed and leveled for commercial development Qal Alluvium (Holocene)—Unconsolidated clast-supported deposits containing silt- to boulder-size, moderately sorted to well-sorted clasts in modern floodplains; includes overbank deposits. Clasts are as long as 1 m in Blue River channel; clasts are larger in some side-stream channels. Larger clasts are moderately rounded to well rounded. Includes some wetland deposits in and adjacent to beaver ponds along Ryan Gulch. Maximum thickness unknown, but greater than 10 m in Blue River channel Qw Wetland deposits (Holocene)—Dark-brown to black, organic-rich sediment underlying wetland areas, commonly containing standing water and dense willow stands. Maximum thickness estimated to be about 15 m Qav Avalanche deposits (Holocene)—Unsorted, unstratified hummocky deposits at the distal ends of avalanche-prone hillside in Sec. -

Mount Umunhum Environmental Restoration and Public Access Implementation
COASTAL CONSERVANCY Staff Recommendation February 14, 2013 MOUNT UMUNHUM ENVIRONMENTAL RESTORATION AND PUBLIC ACCESS IMPLEMENTATION Project No. 12-036-01 Project Manager: Jeff Melby RECOMMENDED ACTION: Authorization to disburse up to $1,000,000 to the Midpeninsula Regional Open Space District to implement environmental restoration and public access improvements at Mount Umunhum in Santa Clara County. LOCATION: Near the cities of Los Gatos and San Jose, Santa Clara County PROGRAM CATEGORY: San Francisco Bay Area Conservancy EXHIBITS Exhibit 1: Project Location and Site Maps Exhibit 2: Project Photographs Exhibit 3: Final Environmental Impact Report, including public comments received, and Mitigation Monitoring Plan (provided to Conservancy members as a separate CD and otherwise available for review at http://www.openspace.org/plans_projects/mt_umunhum.asp) Exhibit 4: Project Letters RESOLUTION AND FINDINGS: Staff recommends that the State Coastal Conservancy adopt the following resolution pursuant to Sections 31160-31165 of the Public Resources Code: “The State Coastal Conservancy hereby authorizes disbursement of an amount not to exceed one million dollars ($1,000,000) to the Midpeninsula Regional Open Space District (MROSD) to implement environmental restoration and public access improvements at Mount Umunhum in Santa Clara County, subject to the following conditions: A. Prior to the disbursement of Conservancy funds for construction, MROSD shall submit for the review and approval of the Executive Officer of the Conservancy: 1. Evidence that the MROSD has obtained all necessary permits and approvals Page 1 of 12 MOUNT UMUNHUM ENVIRONMENTAL RESTORATION AND PUBLIC ACCESS IMPLEMENTATION 2. A signing plan acknowledging Conservancy participation and identifying the trail to the summit of Mount Umunhum as part of the San Francisco Bay Area Ridge Trail system, as applicable 3. -

Views Fall 17.Prt..2.Indd
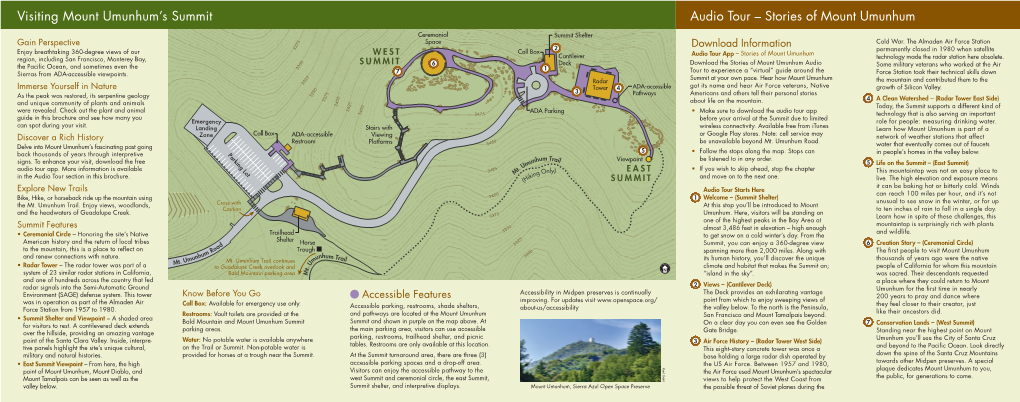
MIDPENINSULA REGIONAL OPEN SPACE DISTRICT Celebrating Over 45 Years of Open Space Preservation QUARTERLYVIEWS NEWS ON OPEN SPACE PRESERVATION AND PROGRAMS • FALL 2017 Find Your Connection Atop Mount Umunhum ount Umunhum’s towering summit opens to the public for the fi rst time this fall thanks to you, local voters, who made it possible by passing M Measure AA. Beginning Monday, September 18 we welcome you to connect with and experience this special place. Gain Perspective Immerse Yourself in Nature Enjoy breathtaking 360-degree views of our region including As the peak is restored its serpentine geology and unique San Francisco, Monterey Bay, the Pacifi c Ocean and sometimes community of plants and animals are revealed. Join our even the Sierras from ADA-accessible viewpoints. docents for a guided look at Mount Umunhum’s natural history. Discover a Rich History Explore New Trails Delve into Mount Umunhum’s fascinating past going back Bike, hike or horseback ride (sorry, no dogs) up to the summit thousands of years through interpretive exhibits. Download from Bald Mountain parking area using the 3.7-mile, the audio tour to hear Air Force veterans, Native Americans newly-constructed Mt. Umunhum Trail. Enjoy views, and others tell their stories about life on the mountain. woodlands and the headwaters of Guadalupe Creek. Know Before You Go at www.mountumunhum.org Prepare for all Weather Bring Water and Snacks Conditions at 3,486 feet can be extreme, even None are available at the summit. on a pleasant day at lower elevations. Get Directions Leave the Dog Home The summit can be reached by Mt. -

The High Deccan Duricrusts of India and Their Significance for the 'Laterite
The High Deccan duricrusts of India and their significance for the ‘laterite’ issue Cliff D Ollier1 and Hetu C Sheth2,∗ 1School of Earth and Geographical Sciences, The University of Western Australia, Nedlands, W.A. 6009, Australia. 2Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. ∗e-mail: [email protected] In the Deccan region of western India ferricrete duricrusts, usually described as laterites, cap some basalt summits east of the Western Ghats escarpment, basalts of the low-lying Konkan Plain to its west, as well as some sizeable isolated basalt plateaus rising from the Plain. The duricrusts are iron-cemented saprolite with vermiform hollows, but apart from that have little in common with the common descriptions of laterite. The classical laterite profile is not present. In particular there are no pisolitic concretions, no or minimal development of con- cretionary crust, and the pallid zone, commonly assumed to be typical of laterites, is absent. A relatively thin, non-indurated saprolite usually lies between the duricrust and fresh basalt. The duricrust resembles the classical laterite of Angadippuram in Kerala (southwestern India), but is much harder. The High Deccan duricrusts capping the basalt summits in the Western Ghats have been interpreted as residuals from a continuous (but now largely destroyed) laterite blan- ket that represents in situ transformation of the uppermost lavas, and thereby as marking the original top of the lava pile. But the unusual pattern of the duricrusts on the map and other evidence suggest instead that the duricrusts formed along a palaeoriver system, and are now in inverted relief. -

Mount Umunhum
A Storied History Mount Umunhum History and Timeline Mount Umunhum How to Get There Sierra Azul Open Space Preserve We invite you to visit Mount Umunhum, as people have done for thousands of years. Learn its rich Mount Umunhum is ONLY accessible via 8,000 BCE–1770s: Native stories steeped in Native American history, gold Hicks Road to Mt. Umunhum Road. Do not A Mountain Made of Stories Americans inhabited the rush-era mining, and the Cold War, and help create take any other route recommended by online region and cared for Los 85 The Natural World Gatos C Mount Umunhum’s next chapter as one of the maps or your GPS device – these directions the land a m San Jose Mount For millions of years, Mount Umunhum has been 9 d Bay Area’s great publicly accessible peaks. This include roads with locked gates. 17 e shaped by close proximity to the San Andreas 1769: First contact between n mountain was sacred to local native people. In Spanish explorers and Avenue Mount Umunhum Summit Parking Area fault system. The unique geology and low-nutrient St. 1850, it was part of California’s first mining claim native tribes El Sereno H Parking is available at the Summit, accessible serpentine soils are home to many rare native Joseph’s ic and was inhabited, explored, and timbered by ks Umunhum from Mt. Umunhum Road. Parking is only plants. The headwaters of several creeks originate R Hill oa settlers. In 1957, the Summit was occupied by the d allowed in designated spaces. on the mountain, and critical reservoirs are tucked Almaden Air Force Station (1957-1980), one of Sierra Azul into its foothills on all sides. -

On the Glaciology of Edgegya and Barentsgya, Svalbard
On the glaciology of Edgegya and Barentsgya, Svalbard JULIAN A. DOWDESWELL and JONATHAN L. BAMBER Dowdeswell J. A. & Bamber. J. L. 1995: On the glaciology of Edgeoya and Barentsoya, Svalbard. Polar Research 14(2). 105-122. The ice masses on Edgeoya and Barentsdya are the least well known in Svalbard. The islands are 42-47% ice covered with the largest ice cap, Edge0yjokulen. 1365 km2 in area. The tidewater ice cliffs of eastern Edgedya are over 80 km long and produce small tabular icebergs. Several of the ice-cap outlet glaciers on Edgeoya and Barentsoya are known to surge, and different drainage basins within the ice caps behave as dynamically separate units. Terminus advances during surging have punctuated more general retreat from Little Ice Age moraines, probably linked to Twentieth Century climate warming and mass balance change. Airborne radio-echo sounding at 60 MHz along 340 km of flight track over the ice masses of Edgeoya and Barentsldya has provided ice thickness and elevation data. Ice is grounded below sea level to about 20 km inland from the tidewater terminus of Stonebreen. Ice thickens from <lo0 rn close to the margins, to about 250 m in the interior of Edgeeiyj~kulen.The maximum ice thickness measured on Barentsjokulen was 270111. Landsat MSS images of the two islands, calibrated to in-band reflectance values, allow synoptic examination of snowline position in late July/early August. Snow and bare glacier ice were identified. and images were digitally stretched and enhanced. The snowline was at about 300111 on the east side of Edgeoyjbkulen, and 50-100 m higher to the west. -

Santa Cruz County San Mateo County
Santa Cruz County San Mateo County COMMUNITY WILDFIRE PROTECTION PLAN Prepared by: CALFIRE, San Mateo — Santa Cruz Unit The Resource Conservation District for San Mateo County and Santa Cruz County Funding provided by a National Fire Plan grant from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service through the California Fire Safe Council. M A Y - 2 0 1 0 Table of Contents Executive Summary.............................................................................................................1 Purpose.................................................................................................................................2 Background & Collaboration...............................................................................................3 The Landscape .....................................................................................................................6 The Wildfire Problem ..........................................................................................................8 Fire History Map................................................................................................................10 Prioritizing Projects Across the Landscape .......................................................................11 Reducing Structural Ignitability.........................................................................................12 x Construction Methods............................................................................................13 x Education ...............................................................................................................15 -

From Decades to Epochs: Spanning the Gap Between Geodesy and Structural Geology of Active Mountain Belts
Journal of Structural Geology 31 (2009) 1409–1422 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Structural Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jsg From decades to epochs: Spanning the gap between geodesy and structural geology of active mountain belts Richard W. Allmendinger a,*, John P. Loveless b, Matthew E. Pritchard a, Brendan Meade b a Department of Earth & Atmospheric Sciences Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853-1504, United States b Department of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, United States article info abstract Article history: Geodetic data from the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), and from satellite interferometric Received 25 March 2009 radar (InSAR) are revolutionizing how we look at instantaneous tectonic deformation, but the signifi- Received in revised form cance for long-term finite strain in orogenic belts is less clear. We review two different ways of analyzing 31 July 2009 geodetic data: velocity gradient fields from which one can extract strain, dilatation, and rotation rate, and Accepted 9 August 2009 elastic block modeling, which assumes that deformation is not continuous but occurs primarily on Available online 14 August 2009 networks of interconnected faults separating quasi-rigid blocks. These methods are complementary: velocity gradients are purely kinematic and yield information about regional deformation; the calcula- Keywords: Geodesy tion does not take into account either faults or rigid blocks but, where GNSS data are dense enough, GPS active fault zones and stable blocks emerge naturally in the solution. Block modeling integrates known Active tectonics structural geometry with idealized earthquake cycle models to predict slip rates on active faults. Future technological advances should overcome many of today’s uncertainties and provide rich new data to mine by providing denser, more uniform, and temporally continuous observations. -

Community Wildfire Protection Plan Prepared By
Santa Cruz County San Mateo County COMMUNITY WILDFIRE PROTECTION PLAN Prepared by: CALFIRE, San Mateo — Santa Cruz Unit The Resource Conservation District for San Mateo County and Santa Cruz County Funding provided by a National Fire Plan grant from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service through the California Fire Safe Council. APRIL - 2 0 1 8 Table of Contents Executive Summary ............................................................................................................ 1 Purpose ................................................................................................................................ 3 Background & Collaboration ............................................................................................... 4 The Landscape .................................................................................................................... 7 The Wildfire Problem ........................................................................................................10 Fire History Map ............................................................................................................... 13 Prioritizing Projects Across the Landscape .......................................................................14 Reducing Structural Ignitability .........................................................................................16 • Construction Methods ........................................................................................... 17 • Education ............................................................................................................. -

Lesson 1: Mount Everest Lesson Plan
Lesson 1: Mount Everest Lesson Plan Use the Mount Everest PowerPoint presentation in conjunction with this lesson. The PowerPoint presentation contains photographs and images and follows the sequence of the lesson. If required, this lesson can be taught in two stages; the first covering the geography of Mount Everest and the second covering the successful 1953 ascent of Everest by Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay. Key questions Where is Mount Everest located? How high is Mount Everest? What is the landscape like? How do the features of the landscape change at higher altitude? What is the weather like? How does this change? What are conditions like for people climbing the mountain? Who were Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay? How did they reach the summit of Mount Everest? What did they experience during their ascent? What did they do when they reached the summit? Subject content areas Locational knowledge: Pupils develop contextual knowledge of the location of globally significant places. Place knowledge: Communicate geographical information in a variety of ways, including writing at length. Interpret a range of geographical information. Physical geography: Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography, including mountains. Human geography: Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including land use. Geographical skills and fieldwork: Use atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Downloads Everest (PPT) Mount Everest factsheet for teachers -

Hydrology Specialist Report
Motorized Travel Plan Hydrology Specialist Report Hydrology Specialist Report Motorized Travel Plan Dixie National Forest Reeds Valley, Cedar City Ranger District Prepared by Bill Goodman, East Zone Hydrologist and Chris Butler, West Zone Hydrologist May 2008 Updated March 2009 1 March 2009 Motorized Travel Plan Hydrology Specialist Report Table of Contents 3.0 Affected Environment.............................................................................................................2 3.1 Existing Conditions ............................................................................................................2 4.0 Environmental Consequences ...............................................................................................9 4.1 Direct and Indirect Effects..................................................................................................9 4.2 Cumulative Effects ...........................................................................................................17 5.0 Project Design Criteria Common to All Action Alternatives..................................................22 6.0 Compliance with Other Laws and Regulations ....................................................................23 6.1 Clean Water Act...............................................................................................................23 6.2 Executive Order 11988 (Protection of Floodplains) of May 24, 1977...............................23 6.3 Executive Order 11990 (Protection of Wetlands) of May 24, 1977..................................23 -

E-Book on Dynamic Geology of the Northern Cordillera (Alaska and Western Canada) and Adjacent Marine Areas: Tectonics, Hazards, and Resources
Dynamic Geology of the Northern Cordillera (Alaska and Western Canada) and Adjacent Marine Areas: Tectonics, Hazards, and Resources Item Type Book Authors Bundtzen, Thomas K.; Nokleberg, Warren J.; Price, Raymond A.; Scholl, David W.; Stone, David B. Download date 03/10/2021 23:23:17 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/11122/7994 University of Alaska, U.S. Geological Survey, Pacific Rim Geological Consulting, Queens University REGIONAL EARTH SCIENCE FOR THE LAYPERSON THROUGH PROFESSIONAL LEVELS E-Book on Dynamic Geology of the Northern Cordillera (Alaska and Western Canada) and Adjacent Marine Areas: Tectonics, Hazards, and Resources The E-Book describes, explains, and illustrates the have been subducted and have disappeared under the nature, origin, and geological evolution of the amazing Northern Cordillera. mountain system that extends through the Northern In alphabetical order, the marine areas adjacent to the Cordillera (Alaska and Western Canada), and the Northern Cordillera are the Arctic Ocean, Beaufort Sea, intriguing geology of adjacent marine areas. Other Bering Sea, Chukchi Sea, Gulf of Alaska, and the Pacific objectives are to describe geological hazards (i.e., Ocean. volcanic and seismic hazards) and geological resources (i.e., mineral and fossil fuel resources), and to describe the scientific, economic, and social significance of the earth for this region. As an example, the figure on the last page illustrates earthquakes belts for this dangerous part of the globe. What is the Northern Cordillera? The Northern Cordillera is comprised of Alaska and Western Canada. Alaska contains a series of parallel mountain ranges, and intervening topographic basins and plateaus. From north to south, the major mountain ranges are the Brooks Range, Kuskokwim Mountains, Aleutian Range, Alaska Range, Wrangell Mountains, and the Chugach Mountains.