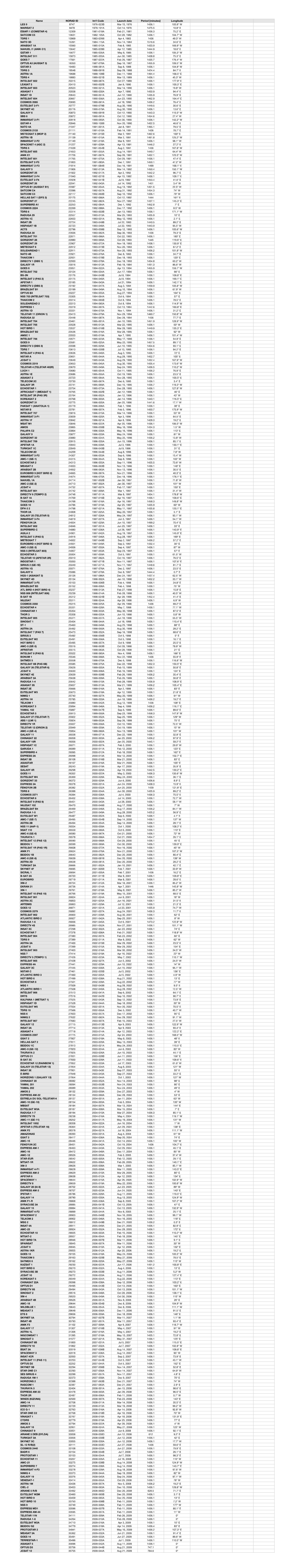
Name NORAD ID Int'l Code Launch Date Period [Minutes] Longitude LES 9 MARISAT 2 ESIAFI 1 (COMSTAR 4) SATCOM C5 TDRS 1 NATO 3D AR
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Project Number: JMW-USC1
Project Number: JMW-USC1 Department of Social Science and Policy Studies THE FUTURE OF UNMANNED SPACE: A SPECULATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE COMMERCIAL MARKET An Interactive Qualifying Project Report: Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Bachelor of Science by ______________________________ Peter Brayshaw ______________________________ Brooks Farnham ______________________________ Jon Leslie December 16, 2004 _____________________________ ________________________________ Professor John M. Wilkes, Advisor Professor Peter Campisano, Co-Advisor Abstract: This report is one of many which deal with the unmanned space race. It is a prediction of who will have the greatest competitive advantage in the commercial market over the next 25 years, based on historical analogy. Background information on Russia, China, Japan, the United States and the European Space Agency, including the launch vehicles and launch services each provides, is covered. The new prospect of space platforms is also investigated. 2 Table of Contents Abstract: ...................................................................................................... 2 Table of Contents ......................................................................................... 3 Introduction ................................................................................................. 5 Literature Review ...................................................................................... 5 Project -

Health of the U.S. Space Industrial Base and the Impact of Export Controls
PRE -DECISIONAL - NOT FOR RELEASE Briefing of the Working Group on the Health of the U.S. Space Industrial Base and the Impact of Export Controls February 2008 1 PRE -DECISIONAL - NOT FOR RELEASE Preamble • “In order to increase knowledge, discovery, economic prosperity, and to enhance the national security, the United States must have robust, effective, and efficient space capabilities. ” - U.S. National Space Policy (August 31, 2006). 2 PRE -DECISIONAL - NOT FOR RELEASE Statement of Task • Empanel an expert study group to [1] review previous and ongoing studies on export controls and the U.S. space industrial base and [2] assess the health of the U.S. space industrial base and determine if there is any adverse impact from export controls, particularly on the lower -tier contractors. • The expert study group will review the results of the economic survey of the U.S. space industrial base conducted by the Department of Commerce and analyzed by the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL). • Integrate the findings of the study group with the result of the AFRL / Department of Commerce survey to arrive at overall conclusions and recommendations regarding the impact of export controls on the U.S. space industrial base. • Prepare a report and briefing of these findings 3 PRE -DECISIONAL - NOT FOR RELEASE Working Group 4 PRE -DECISIONAL - NOT FOR RELEASE Methodology • Leveraged broad set of interviews and data from: – US government • Department of State, Department of Defense (OSD/Policy, OSD/AT&L, DTSA, STRATCOM, General Council), NRO, Department -

23 Mar 2018 2018 Asiasat Reports 2017 Annual Results
MEDIA RELEASE AsiaSat Reports 2017 Annual Results Hong Kong, 23 March 2018 - Asia Satellite Telecommunications Holdings Limited (‘AsiaSat’ – SEHK: 1135), Asia’s leading satellite operator, today announced financial results for the full- year ended 31 December 2017. Financial Highlights: 2017 revenue returned to an upward trend with an increase of 6% to HK$1,354 million from HK$1,272 million in 2016, supported by the lease of the full Ku-band payload of AsiaSat 8 during the year, on-going migration from Standard Definition to High Definition broadcasting and increased demand for data services 2017 profit attributable to owners was HK$397 million (2016: HK$430 million). On a like-for- like basis, after excluding a reversal of tax provision of HK$55 million in 2016, 2017 profit recorded an increase of 6%, HK$22 million compared to 2016 Proposed final dividend of HK$0.20 per share (2016: HK$0.20 per share). Together with the interim dividend of HK$0.18 per share (2016: Nil), the total dividend for the year 2017 is HK$0.38 per share (2016: HK$0.20 per share ) Operational Highlights: AsiaSat enters its 30th year in 2018 with an expanded and upgraded satellite fleet, including the new AsiaSat 9 which became fully operational in November 2017, bringing improved performance to customers and additional capacity to grow company business A lease for the full payload of AsiaSat 4 was secured following successful migration of customers from AsiaSat 4 to AsiaSat 9, the full revenue impact of which will be seen in 2018 Overall payload utilisation -

3640 H 28066 Mpeg2/Fta (Gak Di Acak) Ariana National Satelit
Thaicom 5/6A at 78.5°E (Arah Barat dari Palapa D) 3640 H 28066 Mpeg2/Fta (gak di acak) Ariana National Satelit: Insat 3a (93,5 BT) 4141 V 5150 (C Band) Mpeg2/Fta Beam menjangkau seluruh Indonesia Ke arah barat dari Palapa D, sebelum Measat 3 Telkom 1 (108,5 °E) 3776 H 4280 MPEG2/FTA/BISS HeilongjiangTV (Full Match) Chinasat 6A (125 BT) - Arah Timur dari Palapa D dan Chinasat 6B 3983 H 6880 MPEG2/FTA XJTV5 (Full Match) Chinasat 6A (125 BT) - Arah Timur dari Palapa D dan Chinasat 6B 4121 H 27500 MPEG2/FTA CCTV1 dengan frekuensi : 03840 SymbolRate: 27500 polaritas : H CCTV1 dengan frekuensi 3840 SR 27500 pol H akan menyiarkan bergantian dengan CCT V7 ( frekuensi sama) ?#?SATELIT? & CHANNEL Satelit: ST 2 (88.0°E) ID: SCC TV3 (Iran) 3587 H 12500 (C Band) 11050 V 30000 (Ku Band) MPEG4/SD/BISS SID: 0103/0068 KEY: 1111 1111 1111 1111 Satelit: ST 2 (88.0°E) ID: SCC Varzesh (Ku Band) (Iran) 11050 V 30000 MPEG4/SD/BISS SID: 0116/0117/0075 KEY: 1111 1111 1111 11i11 Satelit: Telkom 1 (108 BT) RTTL (Timor Leste) 3775 H 4280 (C Band) MPEG2/SD/FTA/BISS Satelit: Measat 3 (91,5 BT) TV1 (Malaysia) 3918 H 18385 MPEG4/SD/HD/FTA Satelit: Insat 3a (93,5 BT) Ariana (Afghanistan) 4141 V 5151 (C Band) MPEG2/SD/FTA Satelit: Chinasat 6b (115,5 BT) CCTV 1 (China) 3840 H 27500 (C Band) MPEG2/SD/FTA Satelit: Chinasat 6a (125 BT) CCTV 1 (China) 4080 H 27500 (C Band) MPEG2/SD/FTA Satelit: Chinasat 6a (125 BT) XJTV 5 (China) 4120 H 27500 (C Band) MPEG2/SD/FTA Satelit: Optus D1 (160.0°E) ID: SBS One HD 12390 H 12600 (Ku Band) (MPEG4/HD/FTA) Satelit: Thaicom5 (78,5 BT) CH8 SD, CH8 HD (Thailand) 3800 H 30000 MPEG2/SD/BISS(CH8 HD, Mpeg4/HD/BISS Satelit: Thaicom5 (78,5 BT) BBTV Ch 7 SD, BBTV Ch 7 HD (Thailand) -BBTV Ch 7 SD 3725 H 4700 -BBTV Ch 7 HD 3835 H 8000 MPEG4/HD/BISS 1. -

Satellite Systems
Chapter 18 REST-OF-WORLD (ROW) SATELLITE SYSTEMS For the longest time, space exploration was an exclusive club comprised of only two members, the United States and the Former Soviet Union. That has now changed due to a number of factors, among the more dominant being economics, advanced and improved technologies and national imperatives. Today, the number of nations with space programs has risen to over 40 and will continue to grow as the costs of spacelift and technology continue to decrease. RUSSIAN SATELLITE SYSTEMS The satellite section of the Russian In the post-Soviet era, Russia contin- space program continues to be predomi- ues its efforts to improve both its military nantly government in character, with and commercial space capabilities. most satellites dedicated either to civil/ These enhancements encompass both military applications (such as communi- orbital assets and ground-based space cations and meteorology) or exclusive support facilities. Russia has done some military missions (such as reconnaissance restructuring of its operating principles and targeting). A large portion of the regarding space. While these efforts have Russian space program is kept running by attempted not to detract from space-based launch services, boosters and launch support to military missions, economic sites, paid for by foreign commercial issues and costs have lead to a lowering companies. of Russian space-based capabilities in The most obvious change in Russian both orbital assets and ground station space activity in recent years has been the capabilities. decrease in space launches and corre- The influence of Glasnost on Russia's sponding payloads. Many of these space programs has been significant, but launches are for foreign payloads, not public announcements regarding space Russian. -

Classification of Geosynchronous Objects Issue 12
EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY EUROPEAN SPACE OPERATIONS CENTRE GROUND SYSTEMS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Space Debris Office CLASSIFICATION OF GEOSYNCHRONOUS OBJECTS ISSUE 12 by R. Choc and R. Jehn Produced with the DISCOS Database February 2010 ESOC Robert-Bosch-Str. 5, 64293 Darmstadt, Germany 3 Abstract This is a status report on geosynchronous objects as of the end of 2009. Based on orbital data in ESA’s DISCOS database and on orbital data provided by KIAM the situation near the geostationary ring (here defined as orbits with mean motion between 0.9 and 1.1 revolutions per day, eccentricity smaller than 0.2 and inclination below 30 deg) is analysed. From 1161 objects for which orbital data are available, 391 are controlled inside their longitude slots, 594 are drifting above, below or through GEO, 169 are in a libration orbit and 7 whose status could not be determined. Furthermore, there are 77 uncontrolled objects without orbital data (of which 66 have not been catalogued). Thus the total number of known objects in the geostationary region is 1238. During 2009 twenty-one spacecraft reached end-of-life. Eleven of them were reorbited following the IADC recommendations, one spacecraft was reorbited with a perigee of 225 km - it is not yet clear if it will enter the 200-km protected zone around GEO or not -, six spacecraft were reorbited too low and three spacecraft did not or could not make any reorbiting manouevre at all and are now librating inside the geostationary ring. If you detect any error or if you have any comment or question please contact R¨udiger Jehn European Space Operations Center Robert-Bosch-Str. -

UHD with Asiasat
UHD with AsiaSat Alan WONG Manager, Sales Solutions 23 Jun 2016 AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential Contents • Brief Introduction of AsiaSat • Hands-on Satellite Transmission • Our Engagement with UHD • How we see UHD? • AsiaSat UHD Platform • Next Step AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential UHD with AsiaSat 2 Brief Introduction of AsiaSat Our Background Our Satellite Fleet Our Facilities Our People AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential AsiaSat Corporate Video AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential UHD with AsiaSat 4 Our Background Head-quartered in Hong Kong Established in 1988 Listing in Hong Kong Stock Exchange Regional Satellite Operator • Asia’s leading satellite operator, aiming to provide highest quality satellite communications services in the region Coverage • Across 50 countries in Asia-Pacific • Reaching 2/3 of world's population Customer Profile • International and Regional TV Broadcasters • Telecommunications Service Providers • News Agencies • Corporations and Governments AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential UHD with AsiaSat 5 Our Satellite Fleet C-band Ku-band For more details of our satellite fleet, please visit our web site (http://www.asiasat.com/technology/satellite-fleet). AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential UHD with AsiaSat 6 Our Earth Stations Tai Po Earth Station Stanley Earth Station For more details of our facilities, please visit our web site (http://www.asiasat.com/aboutus/facilities). AsiaSat Proprietary & Confidential UHD with AsiaSat 7 Tai Po Earth Station AsiaSat Tai Po Earth Station is Antennas Services • 1x 1.3m (C) • Uplink Service located at the Tai Po Industrial • 2x 9.0m (C) • Downlink Service Estate in the New Territories, • 3x 7.3m (C) • Occasional Service Hong Kong. • 2x 6.3m (C) • Conditional Access • 1x 6.1m (C) Service • 4x 7.3m (Ku) • Compression Service • 2x 6.3m (Ku) • Playout Service The Station is a two level building • 1x 4.9m (Ku) • Monitoring Service of 5,551 sq.m. -

1998 Year in Review
Associate Administrator for Commercial Space Transportation (AST) January 1999 COMMERCIAL SPACE TRANSPORTATION: 1998 YEAR IN REVIEW Cover Photo Credits (from left): International Launch Services (1998). Image is of the Atlas 2AS launch on June 18, 1998, from Cape Canaveral Air Station. It successfully orbited the Intelsat 805 communications satellite for Intelsat. Boeing Corporation (1998). Image is of the Delta 2 7920 launch on September 8, 1998, from Vandenberg Air Force Base. It successfully orbited five Iridium communications satellites for Iridium LLP. Lockheed Martin Corporation (1998). Image is of the Athena 2 awaiting its maiden launch on January 6, 1998, from Spaceport Florida. It successfully deployed the NASA Lunar Prospector. Orbital Sciences Corporation (1998). Image is of the Taurus 1 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base on February 10, 1998. It successfully orbited the Geosat Follow-On 1 military remote sensing satellite for the Department of Defense, two Orbcomm satellites and the Celestis 2 funerary payload for Celestis Corporation. Orbital Sciences Corporation (1998). Image is of the Pegasus XL launch on December 5, 1998, from Vandenberg Air Force Base. It successfully orbited the Sub-millimeter Wave Astronomy Satellite for the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. 1998 YEAR IN REVIEW INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION In 1998, U.S. launch service providers conducted In addition, 1998 saw continuing demand for 22 launches licensed by the Federal Aviation launches to deploy the world’s first low Earth Administration (FAA), an increase of 29 percent orbit (LEO) communication systems. In 1998, over the 17 launches conducted in 1997. Of there were 17 commercial launches to LEO, 14 these 22, 17 were for commercial or international of which were for the Iridium, Globalstar, and customers, resulting in a 47 percent share of the Orbcomm LEO communications constellations. -

1 Before the Federal Communications Commission Washington, D.C
Federal Communications Commission DA 06-4 Before the Federal Communications Commission Washington, D.C. 20554 In the Matter of ) ) AFRISPACE, INC. ) IB File No. SAT-LOA-20050311- ) 00061 Application for Authority to Launch and ) Operate a Replacement Satellite, AfriStar-2, ) Call Sign: S2666 at 21° E.L. and to Co-locate It with AfriStar-1 ) ) ORDER AND AUTHORIZATION Adopted: January 03, 2006 Released: January 03, 2006 By the Chief, International Bureau: I. INTRODUCTION 1. By this Order, we authorize AfriSpace, Inc. (AfriSpace)1 to launch and operate the AfriStar-2 satellite in the geostationary-satellite orbit (GSO) at the 21° East Longitude (E.L.) orbital location. AfriStar-2 is controlled from the United States and is capable of providing Broadcasting-Satellite Service (sound) (BSS (sound)) to Africa and Europe on a non-common carrier basis. We authorize AfriStar-2 to operate downlinks within 2.6 megahertz of spectrum in each polarization with a center frequency of 1479.5 MHz. We also authorize AfriSpace to utilize feeder links and telecommand links for the AfriStar-2 satellite in the 7025-7075 MHz frequency band, to operate its telemetry link for the AfriStar-2 satellite at a center frequency of 1491.7 MHz, and to co-locate the AfriStar-2 satellite at 21° E.L. with the AfriStar-1 satellite currently in orbit. In addition, we grant AfriSpace a waiver of the Commission’s rule regarding transponder saturation flux densities for the AfriStar-2 satellite.2 These authorizations give AfriSpace the capability to continue to provide service to existing customers despite unanticipated technical difficulties experienced by the AfriStar-1 satellite and to serve new customers, conditioned on AfriSpace complying with the applicable laws, regulations, rules, and licensing procedures of any countries it proposes to serve. -

Spotlight on Asia-Pacific
Worldwide Satellite Magazine June 2008 SatMagazine Spotlight On Asia-Pacific * The Asia-Pacific Satellite Market Segment * Expert analysis: Tara Giunta, Chris Forrester, Futron, Euroconsult, NSR and more... * Satellite Imagery — The Second Look * Diving Into the Beijing Olympics * Executive Spotlight, Andrew Jordan * The Pros Speak — Mark Dankburg, Bob Potter, Adrian Ballintine... * Checking Out CommunicAsia + O&GC3 * Thuraya-3 In Focus SATMAGAZINE JUNE 2008 CONTENTS COVER FEATURE EXE C UTIVE SPOTLIGHT The Asia-Pacific Satellite Market Andrew Jordan by Hartley & Pattie Lesser President & CEO The opportunities, and challenges, SAT-GE facing the Asia-Pacific satellite market 12 are enormous 42 FEATURES INSIGHT Let The Games Begin... High Stakes Patent Litigation by Silvano Payne, Hartley & Pattie by Tara Giunta, Robert M. Masters, Lesser, and Kevin and Michael Fleck and Erin Sears The Beijing Olympic Games are ex- Like it or not, high stakes patent pected to find some 800,000 visitors wars are waging in the global satel- 47 arriving in town for the 17-day event. 04 lite sector, and it is safe to assume that they are here to stay. Transforming Satel- TBS: Looking At Further Diversification lite Broadband by Chris Forrester by Mark Dankberg Internationally, Turner Broadcasting The first time the “radical” concept has always walked hand-in-hand with 54 of a 100 Gbps satellite was intro- the growth of satellite and cable – duced was four years ago, 07 and now IPTV. Here’s Looking At Everything — Part II by Hartley & Pattie Lesser The Key To DTH Success In Asia by Jose del Rosario The Geostationary Operational Envi- Some are eyeing Asia as a haven for ronmental Satellites (GOES) continu- economic safety or even economic ously track evolution of weather over growth amidst the current global almost a hemisphere. -

59864 Federal Register/Vol. 85, No. 185/Wednesday, September 23
59864 Federal Register / Vol. 85, No. 185 / Wednesday, September 23, 2020 / Rules and Regulations FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS C. Congressional Review Act II. Report and Order COMMISSION 2. The Commission has determined, A. Allocating FTEs 47 CFR Part 1 and the Administrator of the Office of 5. In the FY 2020 NPRM, the Information and Regulatory Affairs, Commission proposed that non-auctions [MD Docket No. 20–105; FCC 20–120; FRS Office of Management and Budget, funded FTEs will be classified as direct 17050] concurs that these rules are non-major only if in one of the four core bureaus, under the Congressional Review Act, 5 i.e., in the Wireline Competition Assessment and Collection of U.S.C. 804(2). The Commission will Bureau, the Wireless Regulatory Fees for Fiscal Year 2020 send a copy of this Report & Order to Telecommunications Bureau, the Media Congress and the Government Bureau, or the International Bureau. The AGENCY: Federal Communications indirect FTEs are from the following Commission. Accountability Office pursuant to 5 U.S.C. 801(a)(1)(A). bureaus and offices: Enforcement ACTION: Final rule. Bureau, Consumer and Governmental 3. In this Report and Order, we adopt Affairs Bureau, Public Safety and SUMMARY: In this document, the a schedule to collect the $339,000,000 Homeland Security Bureau, Chairman Commission revises its Schedule of in congressionally required regulatory and Commissioners’ offices, Office of Regulatory Fees to recover an amount of fees for fiscal year (FY) 2020. The the Managing Director, Office of General $339,000,000 that Congress has required regulatory fees for all payors are due in Counsel, Office of the Inspector General, the Commission to collect for fiscal year September 2020. -

Journal of Space Law
JOURNAL OF SPACE LAW VOLUME 24, NUMBER 2 1996 JOURNAL OF SPACE LAW A journal devoted to the legal problems arising out of human activities in outer space VOLUME 24 1996 NUMBERS 1 & 2 EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORS BERGER, HAROLD GALLOWAY, ElLENE Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Washington, D.C. BOCKSTIEGEL, KARL·HEINZ HE, QIZHI Cologne, Germany Beijing, China BOUREr.. Y, MICHEL G. JASENTULIYANA, NANDASIRI Paris, France Vienna. Austria COCCA, ALDO ARMANDO KOPAL, VLADIMIR Buenes Aires, Argentina Prague, Czech Republic DEMBLING, PAUL G. McDOUGAL, MYRES S. Washington, D. C. New Haven. Connecticut DIEDERIKS·VERSCHOOR, IE. PH. VERESHCHETIN, V.S. Baarn, Holland Moscow. Russ~an Federation FASAN, ERNST ZANOTTI, ISIDORO N eunkirchen, Austria Washington, D.C. FINCH, EDWARD R., JR. New York, N.Y. STEPHEN GOROVE, Chairman Oxford, Mississippi All correspondance should be directed to the JOURNAL OF SPACE LAW, P.O. Box 308, University, MS 38677, USA. Tel./Fax: 601·234·2391. The 1997 subscription rates for individuals are $84.80 (domestic) and $89.80 (foreign) for two issues, including postage and handling The 1997 rates for organizations are $99.80 (domestic) and $104.80 (foreign) for two issues. Single issues may be ordered for $56 per issue. Copyright © JOURNAL OF SPACE LAW 1996. Suggested abbreviation: J. SPACE L. JOURNAL OF SPACE LAW A journal devoted to the legal problems arising out of human activities in outer space VOLUME 24 1996 NUMBER 2 CONTENTS In Memoriam ~ Tribute to Professor Dr. Daan Goedhuis. (N. J asentuliyana) I Articles Financing and Insurance Aspects of Spacecraft (I.H. Ph. Diederiks-Verschoor) 97 Are 'Stratospheric Platforms in Airspace or Outer Space? (M.