NNO. Muscular Genesis
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Science of Synthesis Knowledge Updates 2013/4 © Georg Thieme Verlag KG XVI Table of Contents
XV Table of Contents Volume 2: Compounds of Groups 7–3 (Mn···, Cr···, V···, Ti···, Sc···, La···, Ac···) 2.12 Product Class 12: Organometallic Complexes of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides 2.12.16 Organometallic Complexes of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lan- 2013 thanides J. Hannedouche 2.12.16 Organometallic Complexes of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides .. 1 2.12.16.1 Rare Earth Metal Catalyzed Hydroamination Reactions ...................... 1 2.12.16.1.1 Rare-Earth(II) Complexes ................................................... 1 2.12.16.1.1.1 Synthesis of Rare-Earth(II) Complexes ...................................... 2 2.12.16.1.1.1.1 Method 1: Salt Metathesis ............................................ 2 2.12.16.1.1.2 Applications of Rare-Earth(II) Complexes in Organic Synthesis ............... 3 2.12.16.1.1.2.1 Method 1: Catalytic Intramolecular Hydroamination Reaction of Alkynes 3 2.12.16.1.1.2.2 Method 2: Catalytic Intramolecular Hydroamination Reaction of Alkenes 4 2.12.16.1.2 Cyclooctatetraene–Rare-Earth(III) Complexes ............................... 5 2.12.16.1.2.1 Synthesis of Cyclooctatetraene–Rare-Earth(III) Complexes . .................. 5 2.12.16.1.2.1.1 Method 1: Salt Metathesis ............................................ 5 2.12.16.1.2.2 Applications of Cyclooctatetraene–Rare-Earth(III) Complexes in Organic Syn- thesis ...................................................................... 6 2.12.16.1.2.2.1 Method 1: Catalytic Intramolecular Hydroamination Reaction of Alkynes 6 2.12.16.1.2.2.2 Method 2: Catalytic Intramolecular Hydroamination Reaction of Alkenes 7 2.12.16.1.3 Bis(boratabenzene)yttrium(III) Complexes .................................. 8 2.12.16.1.3.1 Synthesis of Bis(boratabenzene)yttrium(III) Complexes ..................... -

A Manual of Chemistry Physical and Inorganic Chemistry
Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Tirol A manual of chemistry Physical and inorganic chemistry Watts, Henry 1883 Table of Contents urn:nbn:at:at-ubi:2-4741 TABIE OF CONTENTS. PAGE Introdtt CTIOlf * . 1 Table of Elementary Bodies, with their Symbols and Atomic Weights 3 Difference between Chemical Combination and Mixture . 4 Short Sketch of the most important Elementary Bodies . S G-eneral Laws of Chemical Combination — Chemical Nomenclature and Notation 1 Law of Multiples 10 Law of Equivalents 12 Chemical Equations * . 13 PART I. PHYSICS . Or Density astd Specific G-bayitt 15 Methods of determining the Specific Gravities of Liquids and Solids 15 Construction and Application of the Hydrometer . 20 Op the Physicai Constitution oe the Atmosphere , and os G-ases in G-enebai 23 Elasticity of Gases 23 The Air -pump 24 Weight and Pressure of the Air —Barometer . 25 Sprengel ’s Air -pump 26 Law of Boyle or of Mariotte : Eelations of Density and Elastic force : Correction of Volumes of G-ases for Pressure - . 27 Collection, Transference , and Preservation of Gases . • . 29 Heat 32 Expansion —Thermometers 32 Different Rates of Expansion among Solids . 36 Expansion of Liquids —Absolute Expansion of Mercury —Maxi¬ mum Density of Water 37 Expansion of Gases . 40 Conduction of Heat 41 Specific Heat 42 CONTENTS . PAGE Change of State : 1. Fusion and Solidification 46 Determination of Melting Points 47 Latent Heat of Fusion 48 Freezing Mixtures 50 2. Vaporisation and Condensation 50 Latent Heat of Vapours 51 Boiling or Ebullition 51 Elasticity and Latent Heat of Steam 52 Distillation . 54 Tension of Vapours 56- Maximum Density of Vapours . -

Gmelin Catalog
GMELIN Complete Catalog 1997/98 Page Contents Recent Issues 1995/1997 1 Recent Issues 1995/1997 Au Gold Supplement Volume B3 1 Next volumes to appear 1997/98 Gold Supplement Volume B4 2 Reference Table B Boron Compounds, Fourth Supplement 3 Introduction and Explanatory Material Volume lb 4 TYPIX Be Beryllium Supplement Volume B4 5 Alphabetical Index covering all volumes published up Perfluorohalogenoorgano Compounds of to January 1997 F Main Group Elements Second Supple. V. 2 60 Index Volumes Organoiron Compounds Part A11 Facsimile reprint of the First Edition, 1817-1819 Fe GABCOM & GABMET Ga Gallium Supplement Volume C2 Gallium Supplement Volume D2 Gallium Supplement Volume D3 Ge Organogermanium Compounds Part 6 Mn Manganese Volume A3a Manganese Volume A5a Manganese Volume A5bl Mo Molybdenum Supplement Volume B8 Organomolybdenum Compounds Part 10 Organomolybdenum Compounds Part 11 Organomolybdenum Compounds Part 13 N Nitrogen Supplement Volume B6 Ni Organonickel Compounds, First Supplement Part 3 Os Organoosmium Compounds Part B4a Organoosmium Compounds Part B8 Organoosmium Compounds Part B9 P Phosphorus Supplement Volume C2 Phosphorus Supplement Volume C5a Pb Organolead Compounds Part 4 Organolead Compounds Part 5 Re Organorhenium Compounds Part 4 Organorhenium Compounds Part 7 Please note S Sulfur-Nitrogen Compounds Part 11 Every volume or section of the Gmelin Handbook can be Sc,Y, Rare Earth Elements Volume C12a purchased separately. Orders are accepted for volumes which La-Lu Rare Earth Elements Volume E2a are still in preparation. Standing orders for groups of related Si Silicon Supplement Volume B5bl volumes can also be arranged. Please ask for special terms Silicon Supplement Volume B5dl when you order a complete set. -

Nonclassical Imcrs
587 Index a acyl halides 52–55 ab initio calculations 24, 40, 41 O-acyl isoimides 49–51 Acantkella acuta 21 S-acyl isoimides 50, 51 acetals 188, 189, 401 acyl transfer reactions see Mumm acetylenedicarboxylates rearrangements – nonclassical IMCRs 315, 316 acylating agents 129–133 – zwitterions 264–267, 269, 271, 274–277 2-acylbenzazepines 54 achiral isocyanides 1 1-acyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinolines 54 acid addition reactions 49–52 α-acyloxyaminoamides 367 acid-mediated polymerization 25 acylpiperazines 352 acid-promoted condensations 355 2-acylpyrrolines 54 α-acidic isocyanides 75–108 acylthioamides 53, 54 – dihydropyridone MCR 95–97 2-adamantyl isocyanide 37 – 4,5-disubstituted oxazole MCR 83, 84 ADC see acyclic diaminocarbenes – 2-imidazoline MCR 91–95 AFM see atomic force microscopy – isocyanide reactivity 78–80 AIBN see azo-bis-isobutyronitrile – multicomponent reactions 75–108 alcohols – nitropyrrole MCR 83, 84 – carbene coupling reactions – oxazole MCR and in situ Domino process 532–537 88–91 – chiral nonracemic isocyanides 2 – synthesis 76–78 – isocyanide reactivity 64–66 – 2,4,5-trisubstituted oxazole MCR 84–88 – zwitterions 273–275 – 2,6,7-trisubstituted quinoxaline MCR 82, aldazines 204 83 aldehyde-acids 362, 366–371 – union of MCRs 93–95 aldehydes – van Leusen imidazole MCR 81, 82 – amine surrogates 199 acrylonitriles 116 – carboxylic acid surrogates 180–184 activated alkenes – chiral nonracemic isocyanides 4, 5 – isocyanide reactivity 55–58 – isocyanide reactivity 58–60 – α-isocyanoacetic acid derivatives 116, – α-isocyanoacetic -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.256.243 B2 Oikawa Et Al
USOO7256243B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.256.243 B2 Oikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2007 (54) SILICON COMPOUND Shaped Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Polymers' authored by Fukuda et al and published in Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8517-8522.* (75) Inventors: Hisao Oikawa, Chiba (JP); Mikio Abstract for “Modified Cubic Spherosilicates as Macroinitiators for Yamahiro, Chiba (JP); Kazuhiro the Synthesis of Inorganic-Organic Starlike Polymers' authored by Holzinger et al. and published in the Journal of Polymer Science, Yoshida, Chiba (JP); Nobumasa Part A: Polymer Chemistry 2002, 40(21) 3858-3872.* Ootake, Chiba (JP); Kenichi 'Organic/Inorganic Nanocomposite star Polymers via Atom Trans Watanabe, Chiba (JP): Kohji Ohno, fer Radical Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate Using Kyoto (JP); Yoshinobu Tsujii, Kyoto Octafunctional Silsesquioxane Cores' authored by Laine et al. and (JP); Takeshi Fukuda, Kyoto (JP) published in Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5398-5407.* Chunxin Zhang et al., “Hydrosilylation of Allyl Alcohol with (73) Assignee: Chisso Corporation, Osaka (JP) HSiMeOSiOls: Octa(3- hydroxypropyldimethylsiloxy)octasilsesquioxane and Its (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this Octamethacrylate Derivative as Potential Precursors to Hybrid patent is extended or adjusted under 35 Nanocomposites”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 6979-6988, 2000. U.S.C. 154(b) by 266 days. Alan Sellinger et al., “Silsesquioxanes as Synthetic Platforms. 3. Photocurable, Liquid Epoxides as Inorganic/Organic Hybrid Pre (21) Appl. No.: 11/121,120 cursors”, Chem. Mater, vol. 8, No. 8, pp. 1592-1593, 1996. Alan Sellinger et al., “Silsesquioxanes as Synthetic Platforms. (22) Filed: May 4, 2005 Thermally Curable and Photocurable Inorganic/Organic Hybrids'. -

Systematicinorga031822mbp.Pdf
TIGHTBINDINGBOOK > CD 164149 OUH 730 Ii8-*-81 - 10,' 00. OSMANIA UNIVERSITY LIBRARY ' Call Accession No. f~f~ c , 7 06^> Author Title rti M-H+C e^- </ </ This book should be returned on or before the date last marked below Systematic Inorganic Chemistry OF THE FIFTH-AND-SIXTH-GROUP NONMETALLIC ELEMENTS by DON M. YOST frofessor of Inorganic Chemistry California Institute of Technology and HORACE RUSSELL, JR. Instructor in Chemistry California Institute of Technology New York PRENTICE-HALL, 1946 COPYRIGHT, 194-i, PRENTICE-HALL, INC. 70 Fifth Avenue, New York ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. NO PART OF THIS BOOK MAY BE HEPRODt CED IN ANY FORM, BY MIMEOGRAPH OH ANY OTHEK MEANS, WITHOUT PERMISSION IN WRITING FROM THE PUBLISHERS First 1'iintiiiK M:iv, I94J Second Printing \ugust, 1940 PRINTED IN THE 'JNITED STATES OF AMERICA To WILLIAM C. BRAY ABLE SCIENTIST, INSPIRING TKACHEK Preface Inorganic chemistry has undergone a marked transition in the last three decades as it has grown from an almost purely descriptive branch of science to a field in which all of the modern developments of physics and chemistry find application. In this field the quantum theory plays an important role in the establishment of energy states and molecular structures and in the explanation of the periodic law; thermodynamics finds application in the prediction of the degree of completion of chemical reactions at equilibrium; statistical mechanics makes possible the calcu- lation of the thcrmodynamic properties of substances from atomic and molecular data and deepens our insight into the still unsolved problems of the rates of chemical reactions; finally, the phenomena of natural and artificial radioactivity not only increase our knowledge of the funda- mental structure of matter but also, through the use of radio-elements as tracers, greatly extend our understanding of the mechanisms of chemical reactions. -

Patented Feb. 16, 1943 2,311,062
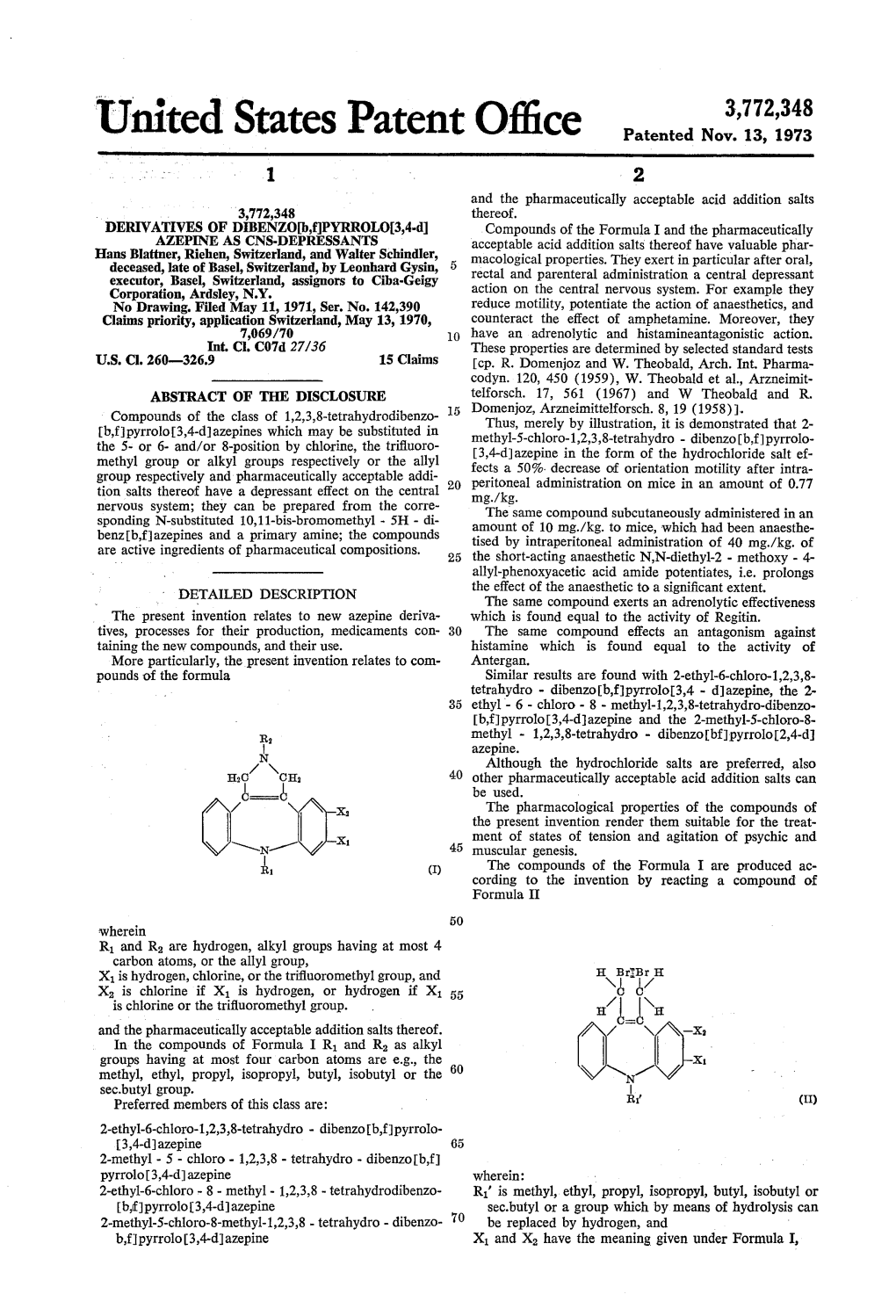
Patented Feb. 16, 1943 2,311,062 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,311,062 HALOGEN SUBSTITUTED ACAMNO SULP BONCACDS Henry Martin, Basel, Hans Heinrich. Zaeslin, Glatthar,Riehen, near and Basel,Alfred and staub, Rudolf Basel, Hirt switter Curt land, assignors to J. R. Geigy A. G., Basel, Switzerland No Drawing. Application June 13, 1939, Serial No. 278,954. In Switzerland June 16, 1938 8 Claims. (C. 260-507) This invention relates to the production of heterocyclic, especially halogen and/or alkyl halogen Substituted acyl amino sulphonic acids, substituted amino Sulphonic acids leads to inter the products being useful for various purposes in esting water-soluble products. But also other industry. e. g., for protecting wool and other sub methods as for example treatment of carbon di stances against damage by moths, the protection Sulphide with the specified amino sulphonic acids being very fast to washing and fulling, and in in the presence of Suitable catalysts, for example Some cases as disinfecting agents, bactericides, hydrogen-peroxide or sulphur, leads to water fungicides, and seed steeping materials. Soluble thio-carbonic acid derivatives. It will be According to the present invention halogen understood that similar products can be obtained Substituted acyl amino sulphonic acids of the 10 by warming, melting or heating, in suitable sol aromatic or heterocyclic series are produced by vents or suspension media, the amino sulphonic the treatment of carbonic acid derivatives or acids with urea or thio-urea or urethanes, with thio-carbonic acid derivatives, or substances or separation of ammonia or alcohol. Furthermore, mixtures of substances forming these com by sulphonating completely condensed, difficultly pounds which may also contain sulphonic acid 5 Soluble or insoluble ureas, thio-ureas and ure groups with isocyclic or heterocyclic amines or thanes, containing at least one halogen atom, aminOSulphonic acids containing replaceable Sulphonic acids with surprisingly good properties hydrogen at the nitrogen atom, the reaction can be obtained.