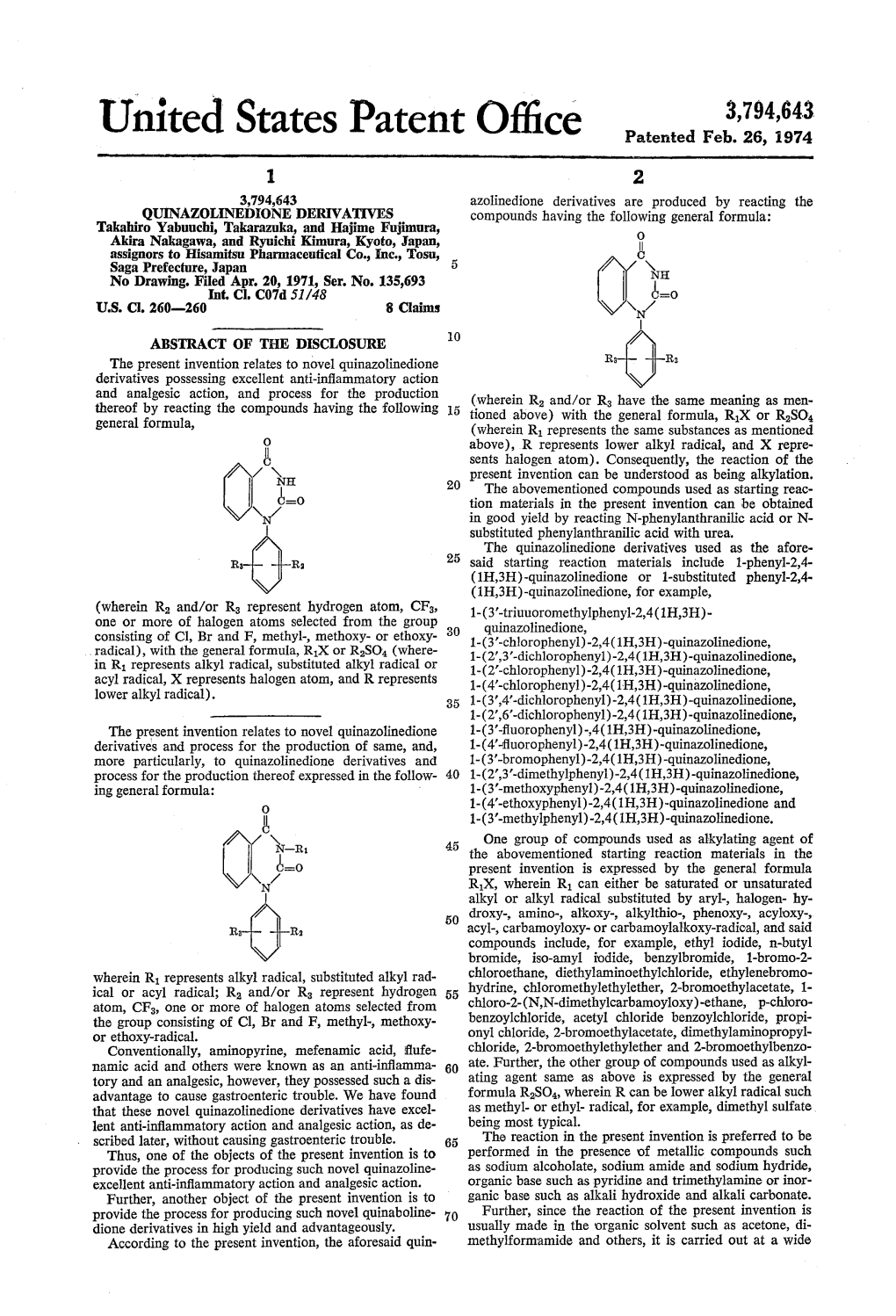
United States Patent Office Patented Feb
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chemistry 234 Chapter 16 Problem Set Electrophilic Aromatic
Chemistry 234 Chapter 16 Problem Set Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 1) Predict the product and draw the mechanism for electrophile generation for each of the following reactions. Cl (a) 2 FeCl3 HNO3 (b) H2SO4 SO (c) 3 H2SO4 2) Explain why reaction of benzene with Br2/FeBr3 results in the product bromobenzne instead of 5,6-dibromo-1,3-cyclohexadiene. 3) Predict the product and draw the active electrophile for each reaction shown below. Cl (a) AlCl3 Cl (b) AlCl3 Cl O (c) AlCl3 Page 1 of 13 Chem. 234 – Chapter 16 Problem Set 4) Explain why each of the following substrates do not undergo Freidel-Crafts reactions. NH2 NO2 N(CH3)3 NH 5) Arrange the following benzene substituents in order of reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. O Cl Ph Ph N Ph Ph H O N H S Ph N Ph Ph Ph O O 6) Predict the maJor products when the following benzene derivatives are treated to nitration conditions (HNO3/H2SO4). a. O Br b. NH2 Br c. NO2 Cl 7) Write the full electron pushing mechanism for the nitration of toluene. Page 2 of 13 Chem. 234 – Chapter 16 Problem Set 8) Predict the product(s) when each of the following benzene derivatives is treated to chloroethane and AlCl3. a. Br b. NH2 Cl c. OH Br d. OH Cl Cl e. NO2 Cl Cl f. Br Br g. SO3H Page 3 of 13 Chem. 234 – Chapter 16 Problem Set 9) Predict the product(s) when the following benzene derivatives are subjected to electrophilic chlorination conditions (Cl2, FeCl3). -

Safety Data Sheet
SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. Identification Product identifier Jump Start® Starting Fluid Other means of identification Product Code No. 05671 (Item# 1003843) Recommended use Starting fluid Recommended restrictions None known. Manufacturer/Importer/Supplier/Distributor information Manufactured or sold by: Company name CRC Industries, Inc. Address 885 Louis Dr. Warminster, PA 18974 US Telephone General Information 215-674-4300 Technical Assistance 800-521-3168 Customer Service 800-272-4620 24-Hour Emergency 800-424-9300 (US) (CHEMTREC) 703-527-3887 (International) Website www.crcindustries.com 2. Hazard(s) identification Physical hazards Flammable aerosols Category 1 Gases under pressure Compressed gas Health hazards Skin corrosion/irritation Category 2 Carcinogenicity Category 2 Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Category 3 narcotic effects Aspiration hazard Category 1 Environmental hazards Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute Category 2 hazard Hazardous to the aquatic environment, Category 3 long-term hazard OSHA defined hazards Not classified. Label elements Signal word Danger Hazard statement Extremely flammable aerosol. Contains gas under pressure; may explode if heated. May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways. Causes skin irritation. May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Suspected of causing cancer. Toxic to aquatic life. Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects. Material name: Jump Start® Starting Fluid SDS US No. 05671 (Item# 1003843) Version #: 01 Issue date: 08-29-2017 1 / 10 Precautionary statement Prevention Obtain special instructions before use. Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. - No smoking. Do not spray on an open flame or other ignition source. -

1,2-DICHLOROETHANE 1. Exposure Data
1,2-DICHLOROETHANE Data were last reviewed in IARC (1979) and the compound was classified in IARC Monographs Supplement 7 (1987a). 1. Exposure Data 1.1 Chemical and physical data 1.1.1 Nomenclature Chem. Abstr. Serv. Reg. No.: 107-06-2 Chem. Abstr. Name: 1,2-Dichloroethane IUPAC Systematic Name: 1,2-Dichloroethane Synonym: Ethylene dichloride 1.1.2 Structural and molecular formulae and relative molecular mass Cl CH2 CH2 Cl C2H4Cl2 Relative molecular mass: 98.96 1.1.3 Chemical and physical properties of the pure substance (a) Description: Colourless liquid with a pleasant odour (Budavari, 1996) (b) Boiling-point: 83.5°C (Lide, 1995) (c) Melting-point: –35.5°C (Lide, 1995) (d) Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; miscible with ethanol, chloroform and diethyl ether (Lide, 1995; Budavari, 1996) (e) Vapour pressure: 8 kPa at 20°C (Verschueren, 1996) (f) Flash-point: 18°C, open cup (Budavari, 1996) (g) Conversion factor: mg/m3 = 4.0 × ppm 1.2 Production and use World production capacities in 1988 for 1,2-dichloroethane have been reported as follows (thousand tonnes): North America, 9445; western Europe, 9830; Japan, 3068; and other, 8351 (Snedecor, 1993). Production in the United States has been reported as follows (thousand tonnes): 1983, 5200; 1990, 6300; 1991, 6200; 1992, 6900; 1993, 8100 (United States National Library of Medicine, 1997). The total annual production in Canada in 1990 was estimated to be 922 thousand tonnes; more than 1000 thousand tonnes were produced in the United Kingdom in 1991 (WHO, 1995). –501– 502 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 71 1,2-Dichloroethane is used primarily in the production of vinyl chloride; 99% of total demand in Canada, 90% in Japan and 88% of total production in the United States are used for this purpose. -

SAFETY DATA SHEET Ethyl Chloride
SAFETY DATA SHEET Ethyl Chloride Section 1. Identification GHS product identifier : Ethyl Chloride Chemical name : chloroethane Other means of : Ethane, chloro-; Ethyl chloride; Muriatic ether; Monochloroethane; Hydrochloric ether; identification ether hydrochloric; 1-CHLOROETHANE; Ethyl chloride (Chloroethane); ethane, chloro; Monochlorethane; R 160 Product type : Liquefied gas Product use : Synthetic/Analytical chemistry. Synonym : Ethane, chloro-; Ethyl chloride; Muriatic ether; Monochloroethane; Hydrochloric ether; ether hydrochloric; 1-CHLOROETHANE; Ethyl chloride (Chloroethane); ethane, chloro; Monochlorethane; R 160 SDS # : 001023 Supplier's details : Airgas USA, LLC and its affiliates 259 North Radnor-Chester Road Suite 100 Radnor, PA 19087-5283 1-610-687-5253 24-hour telephone : 1-866-734-3438 Section 2. Hazards identification OSHA/HCS status : This material is considered hazardous by the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200). Classification of the : FLAMMABLE GASES - Category 1 substance or mixture GASES UNDER PRESSURE - Liquefied gas CARCINOGENICITY - Category 2 AQUATIC HAZARD (LONG-TERM) - Category 3 GHS label elements Hazard pictograms : Signal word : Danger Hazard statements : Extremely flammable gas. Contains gas under pressure; may explode if heated. Suspected of causing cancer. Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects. May cause frostbite. May displace oxygen and cause rapid suffocation. May form explosive mixtures with air. Precautionary statements General : Read and follow all Safety Data Sheets (SDS’S) before use. Read label before use. Keep out of reach of children. If medical advice is needed, have product container or label at hand. Close valve after each use and when empty. Use equipment rated for cylinder pressure. Do not open valve until connected to equipment prepared for use. -

2016 Undetected Chemical Contaminant
2016 Undetected Chemical Contaminant ESTROGENS AND OTHER HORMONES Diethylstilbestrol (DES) Estriol 17alpha-Estradiol Estrone 17beta-Estradiol 17alpha-Ethynl estradiol PERFLUORINATED COMPOUNDS N-ethyl Perfluorooctanesulfonamidoacetic acid Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS) N-methyl Perfluorooctanedsulfonamidoacetic acid Perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) N-methyl Perfluorooctanedsulfonamidoacetic acid Perfluorolauric acid (PFDoA) Perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA) Perfluoromyristic acid (PFTA) Perfluoroheptanoic acid (PFHpA) Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) INORGANIC CHEMICALS Beryllium Lanthanum Cadmium Lead Cerium Lutetium Cesium Mercury Cobalt Molybdenum Cyanide Neodymium Dysprosium Niobium Erbium Osmium Europium Palladium Gadolinium Platinum Germanium Praseodymium Gold Rhenium Hafnium Rhodium Holmium Rhodium Iridium Ruthenium NITROSAMINES N-Nitropyrrolidine (NPYR) N-Nitrosomorpholine N-Nitrosodi-N-butylamine (NDBA) N-Nitrosodiphenylamine N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) N-Nitrosodi-N-propylamine (NDPA) ORGANIC CHEMICALS Acenaphthene 1,2-Dichlorobenzene Acenaphthylene 1,3-Dichlorobenzene Acetaldehyde 1,4-Dichlorobenzene Acetochlor trans-1,2-Dichloro-2-butylene Acetone Dichlorodifluoromethane Acrylonitrile 1,1-Dichloroethane Alachlor 1,2- Dichloroethane Aldicarb (Temik) 1,1-Dichloroethylene Aldicarb sulfone 1,2-Dichloroethylene, cis Aldicarb sulfoxide 1,2-Dichloroethylene, trans Aldrin Di (2-chloroethyl) ether Allyl chloride Dichloromethane (methylene chloride) tert-Amyl Methyl ether 1,2-Dichloropropane Ametryn 1,3-Dichloropropane Anilizine 2,2-Dichloropropane -

Drinking Water Quality Results – Not-Detected Parameters
Drinking Water Quality Results – Not-Detected Parameters The following water quality parameters were monitored in treated drinking water at the water treatment plants, but two-year median values are below laboratory detection limits. In a few cases, the parameter was only monitored at one of the water treatment plants and the two-year median result was non-detect. Pharmaceuticals and Household Products (78) 1,7-Dimethylxanthine Cloxacillin Iopromide Sarafloxacin 4-Nitrophenol Cotinine Lamotrigine Sulfachloropyridazine Acenaphthene DEET Lamotrigine metabolite Sulfadiazine Acetaminophen Dehydronifedipine Lincomycin Sulfadimethoxine Albuterol (Salbutamol) Dextromethorphan Lomefloxacin Sulfamerazine Ampicillin Dextrorphan Lufenuron Sulfamethazine Atenolol Diazepam Mebendazole Sulfamethizole Azithromycin Diclofenac Metformin Sulfamethoxazole BAM (septic additive) Digoxigenin Metoprolol Sulfanilamide Bupropion Digoxin Metroprolol Teflubenzuron Bupropion metabolite Diltiazem Miconazole Triclocarban Butilbatal Diphenhydramine Naproxen Triclosan Caffeine Enrofloxacin Norfloxacin Trimethoprim Carbamazapine Erythromycin Norvenlafaxine Metabolite Tylosin Carbamazepine Erythromycin Anhydrate Ofloxacin Venlafaxine Carbamazepine metabolite Flumequine Oxacillin Venlafaxine metabolite Cefotaxime Fluoxetine Oxolinic Acid Viginiamycin Cimetidine Gabapentin Oxycodone Warfarin Ciprofloxacin Gemfibrozil Ranitidine Clarithromycin Ibuprofen Roxithromycin Pesticides (185) 1,1-Dichloropropene Buprofezin Dinoseb 1,3-Dichloropropene Butachlor Dioxin 2,4,5-TP (Silvex) -

Locating and Estimating Sources of Methyl Chloroform
EPA-454/R-93-045 LOCATING AND ESTIMATING AIR EMISSIONS FROM SOURCES OF METHYL CHLOROFORM Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27711 February 1994 DISCLAIMER This report has been reviewed by the Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, and has been approved for publication. Any mention of tradenames or commercial products is not intented to constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. ii CONTENTS Section Page DISCLAIMER ..................................................... ii LIST OF FIGURES .................................................. v LIST OF TABLES ................................................... vi 1.0 PURPOSE OF DOCUMENT ..................................... 1-1 1.1 Reference for Section 1.0 ................................... 1-5 2.0 OVERVIEW OF DOCUMENT CONTENTS .......................... 2-1 2.1 References for Section 2.0 .................................. 2-5 3.0 BACKGROUND .............................................. 3-1 3.1 Nature of Pollutant ....................................... 3-1 3.2 Regulatory Actions Affecting Methyl Chloroform Production and Use .... 3-4 3.3 Overview of Production and Use .............................. 3-7 3.4 References for Section 3.0 ................................. 3-10 4.0 EMISSIONS FROM METHYL CHLOROFORM PRODUCTION ............ 4-1 4.1 Production Process Descriptions .............................. 4-2 4.1.1 Hydrochlorination of Vinyl Chloride ...................... 4-4 4.1.2 Hydrochlorination -

2. Health Effects
CHLOROETHANE 11 2. HEALTH EFFECTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION The primary purpose of this chapter is to provide public health officials, physicians, toxicologists, and other interested individuals and groups with an overall perspective of the toxicology of chloroethane. It contains descriptions and evaluations of toxicological studies and epidemiological investigations and provides conclusions, where possible, on the relevance of toxicity and toxicokinetic data to public health. A glossary and list of acronyms, abbreviations, and symbols can be found at the end of this profile. 2.2 DISCUSSION OF HEALTH EFFECTS BY ROUTE OF EXPOSURE To help public health professionals and others address the needs of persons living or working near hazardous waste sites, the information in this section is organized first by route of exposure-inhalation, oral, and dermal; and then by health effect-death, systemic, immunological, neurological, reproductive, developmental, genotoxic, and carcinogenic effects. These data are discussed in terms of three exposure periods-acute (14 days or less), intermediate (15-364 days), and chronic (365 days or more). Levels of significant exposure for each route and duration are presented in tables and illustrated in figures. The points in the figures showing no-observed-adverse-effect levels (NOAELs) or lowest-observed-adverseeffect levels (LOAELs) reflect the actual doses (levels of exposure) used in the studies. LOAELS have been classified into “less serious” or “serious” effects. “Serious” effects are those that evoke failure in a biological system and can lead to morbidity or mortality (e.g., acute respiratory distress or death). “Less serious” effects are those that are not expected to cause significant dysfunction or death, or those whose significance to the organism is not entirely clear. -

Jeffrey E. Lucius U.S. Geological Survey This Report Is Preliminary
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND HEALTH EFFECTS OF THIRTY-THREE TOXIC ORGANIC CHEMICALS Jeffrey E. Lucius U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 87-428 August 1987 This report is preliminary and has not been reviewed for conformity with U.S. Geological Survey editorial standards. Any use of trade names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Geological Survey. CONTENTS Page Introduction 4 The Properties 6 Abbreviations 13 Conversion Factors 16 Summary Tables 17 Acetic acid 27 Acetone 31 Benzene 34 Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate 37 Bromoform 39 Carbon tetrachloride 42 Chlorobenzene 46 Chloroethane 49 Chloroform 52 Cyclohexane 55 Di-n-butyl phthalate 58 1.1-Dichloroethane 60 1.2-Dichloroethane 63 1,1-Dichloroethene 66 trans-1,2-Dichloroethene 69 Dimethyl sulfoxide 71 1,4-Dioxane 74 Ethanol 77 Ethylbenzene 81 Ethylene dibromide 84 Methanol 87 Methylene chloride 91 Naphthalene 94 Phenol 97 Quinoline 101 Tetrachloroethene 103 Toluene 106 1,1,1-Trichloroethane 109 Trichloroethene 112 Vinyl chloride 115 Water 118 m-Xylene 121 o-Xylene 124 p-Xylene 127 References and Bibliography 130 SUMMARY TABLES page 1. Ranking of top 20 organic ground water contaminants based on number of sites at which each contaminant was detected. 17 2. Selected toxic organic chemicals ordered by Chemical Abstract Service Registry Number (CAS RN). Those chemicals on the U.S. EPA top 100 hazardous substances list are also noted. 18 3. Selected toxic organic chemicals ordered by number of carbon and hydrogen atoms. 19 4. Ranking of selected toxic organic chemicals by specific gravity at room temperature. -

CHLOROETHANE (C2h5cl) Also Known As Ethyl Chloride Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Number: 75-00-3
CHLOROETHANE (C2H5Cl) also known as Ethyl Chloride Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Number: 75-00-3 General Information Chloroethane is a colorless gas with an ethereal odor. Acute (short-term) inhalation exposure to high levels of chloroethane in humans has resulted in temporary feelings of drunkenness, dizziness, lack of muscle coordination and unconsciousness. Accidental death has resulted from it former medical use as an anesthetic during major surgery. The chronic (long-term) health effects resulting from exposure to chloroethane in humans is not known. Some animal studies indicate effects on the lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart due to chronic exposure to chloroethane. There is no cancer risk data available for human exposure to chloroethane. U.S. EPA has not classified chloroethane for carcinogenicity. Sources Chloroethane is used in the production of ethyl cellulose, use as a solvent, refrigerant, and topical anesthetic, in the manufacture of dyes, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, and as a medication to alleviate pain associated with insect burns and stings. In the past, chloroethane was used in the production of tetraethyl lead, an anti-knock additive to leaded gasoline. Sources of possible chloroethane exposure include the inhalation of contaminated air and ingestion of contaminated drinking water at very low levels. The general population can be exposed to chloroethane by skin contact with consumer products that contain chloroethane such as solvents and refrigerants. Indiana Emissions IDEM collects HAP emissions information for the categories of point sources (large stationary sources like power plants and factories), nonpoint sources (aka area sources - smaller stationary sources like gas stations and dry cleaners), and mobile sources (vehicles, airplanes, marine vessels, etc.).* Estimated statewide emissions of chloroethane totaled 1.20 tons in the 2014 calendar year. -

Chemical Properties Table
Chemical Properties for Calculation of Impact to Ground Water Soil Remediation Standards Chemical CAS Henry’s law Henry’s law Water Diffusion Diffusion Koc or Kd Soil Number constant constant solubility coefficient in coefficient in (L/kg)a Saturation (atm- (dimensionless) (mg/L) air (cm2/sec) water (cm2/sec) Limit m3/mol) (mg/kg) Acenaphthene 83-32-9 1.55E-04 6.36E-03 4.24E+00 4.21E-02 7.69E-06 7.08E+03 - Acenaphthylene 208-96-8 1.11E-04 4.51E-03 1.60E+01 4.40E-02 7.50E-06 2.76E+03 - Acetone (2-propanone) 67-64-1 3.88E-05 1.59E-03 1.00E+06 1.24E-01 1.14E-05 5.75E-01 1.55E+05 Acetophenone 98-86-2 1.10E-05 4.51E-04 6.10E+03 6.00E-02 8.70E-06 3.70E+01 1.39E+03 Acrolein 107-02-8 1.20E-04 4.92E-03 2.10E+05 1.05E-01 1.20E-05 1.00E+00 3.27E+04 Acrylonitrile 107-13-1 1.00E-04 4.10E-03 7.40E+04 1.22E-01 1.30E-05 2.00E+00 1.17E+04 Aldrin 309-00-2 1.70E-04 6.97E-03 1.80E-01 1.32E-02 4.86E-06 2.45E+06 - Aluminum (total) 7429-90-5 - - - - - 1.50E+03 - Anthracene 120-12-7 6.50E-05 2.67E-03 4.34E-02 3.24E-02 7.74E-06 2.95E+04 - Antimony (total) 7440-36-0 - - - - - 4.50E+01 - Arsenic (total) 7440-38-2 - - - - - 2.60E+01 - Atrazine 1912-24-9 2.96E-09 1.21E-07 7.00E+01 2.60E-02 6.70E-06 3.60E+02 - Barium (total) 7440-39-3 - - - - - 1.70E+01 - Benzaldehyde 100-52-7 2.67E-05 1.09E-03 3.00E+03 7.30E-02 9.10E-06 2.90E+01 6.34E+02 Benzene 71-43-2 5.55E-03 2.28E-01 1.75E+03 8.80E-02 9.80E-06 5.89E+01 5.22E+02 Benzidine 92-87-5 3.90E-11 1.60E-09 5.00E+02 3.40E-02 1.50E-05 4.70E+01 - Benzo(a)anthracene (1,2-Benzanthracene) 56-55-3 3.35E-06 1.37E-04 9.40E-03 5.10E-02 -

Toxicological Profile for 1,2-Dichloroethane
TOXICOLOGICAL PROFILE FOR 1,2-DICHLOROETHANE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry September 2001 1,2-DICHLOROETHANE ii DISCLAIMER The use of company or product name(s) is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. 1,2-DICHLOROETHANE iii UPDATE STATEMENT Toxicological profiles are revised and republished as necessary, but no less than once every three years. For information regarding the update status of previously released profiles, contact ATSDR at: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry Division of Toxicology/Toxicology Information Branch 1600 Clifton Road NE, E-29 Atlanta, Georgia 30333 1,2-DICHLOROETHANE vi Disease Registry *Legislative Background The toxicological profiles are developed in response to the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act (SARA) of 1986 (Public law 99-499) which amended the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA or Superfund). This public law directed ATSDR to prepared toxicological profiles for hazardous substances most commonly found at facilities on the CERCLA National Priorities List and that pose the most significant potential threat to human health, as determined by ATSDR and the EPA. The availability of the revised priority list of 275 hazardous substances was announced in the Federal Register on November 17, 1997 (62 FR 61332). For prior versions of the list of substances, see Federal Register notices dated April 29, 1996 (61 FR 18744); April 17, 1987 (52 FR 12866); October 20, 1988 (53 FR 41280); October 26, 1989 (54 FR 43619); October 17, 1990 (55 FR 42067); October 17, 1991 (56 FR 52166); October 28, 1992 (57 FR 48801); and February 28, 1994 (59 FR 9486).