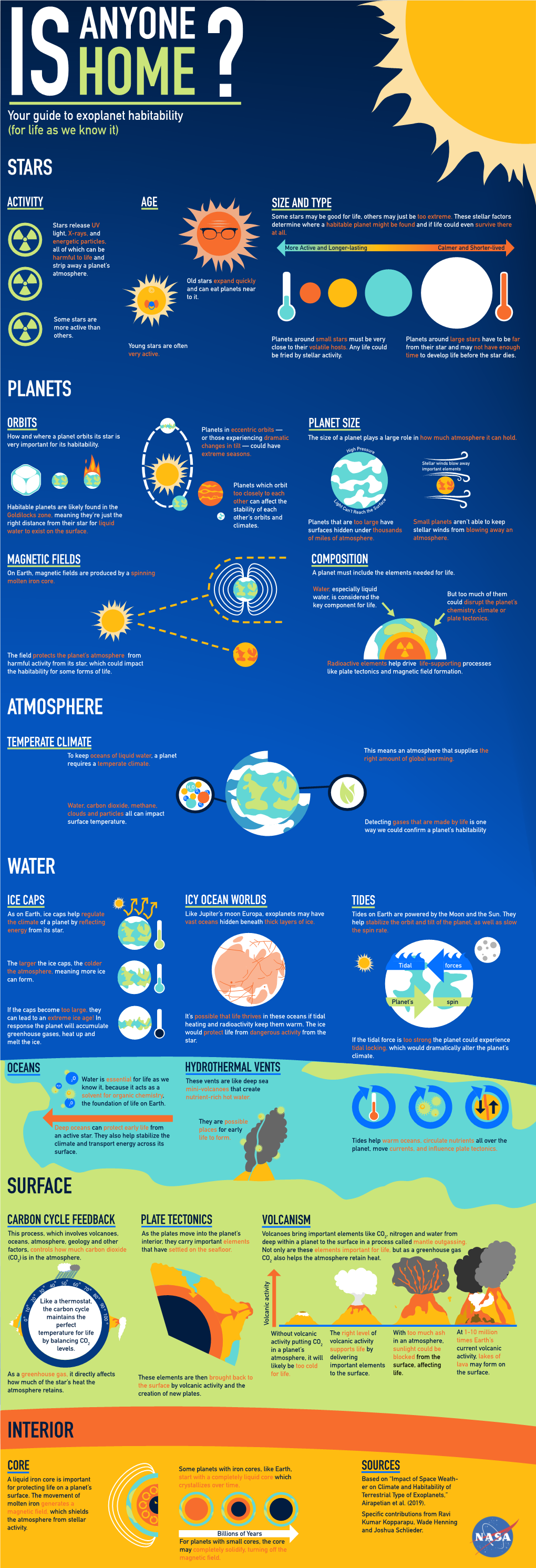
Your Guide to Exoplanet Habitability for Life As We Know It
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Discovery of Exoplanets
L'Univers, S´eminairePoincar´eXX (2015) 113 { 137 S´eminairePoincar´e New Worlds Ahead: The Discovery of Exoplanets Arnaud Cassan Universit´ePierre et Marie Curie Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris 98bis boulevard Arago 75014 Paris, France Abstract. Exoplanets are planets orbiting stars other than the Sun. In 1995, the discovery of the first exoplanet orbiting a solar-type star paved the way to an exoplanet detection rush, which revealed an astonishing diversity of possible worlds. These detections led us to completely renew planet formation and evolu- tion theories. Several detection techniques have revealed a wealth of surprising properties characterizing exoplanets that are not found in our own planetary system. After two decades of exoplanet search, these new worlds are found to be ubiquitous throughout the Milky Way. A positive sign that life has developed elsewhere than on Earth? 1 The Solar system paradigm: the end of certainties Looking at the Solar system, striking facts appear clearly: all seven planets orbit in the same plane (the ecliptic), all have almost circular orbits, the Sun rotation is perpendicular to this plane, and the direction of the Sun rotation is the same as the planets revolution around the Sun. These observations gave birth to the Solar nebula theory, which was proposed by Kant and Laplace more that two hundred years ago, but, although correct, it has been for decades the subject of many debates. In this theory, the Solar system was formed by the collapse of an approximately spheric giant interstellar cloud of gas and dust, which eventually flattened in the plane perpendicular to its initial rotation axis. -

Modeling Super-Earth Atmospheres in Preparation for Upcoming Extremely Large Telescopes
Modeling Super-Earth Atmospheres In Preparation for Upcoming Extremely Large Telescopes Maggie Thompson1 Jonathan Fortney1, Andy Skemer1, Tyler Robinson2, Theodora Karalidi1, Steph Sallum1 1University of California, Santa Cruz, CA; 2Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff, AZ ExoPAG 19 January 6, 2019 Seattle, Washington Image Credit: NASA Ames/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle Roadmap Research Goals & Current Atmosphere Modeling Selecting Super-Earths for State of Super-Earth Tool (Past & Present) Follow-Up Observations Detection Preliminary Assessment of Future Observatories for Conclusions & Upcoming Instruments’ Super-Earths Future Work Capabilities for Super-Earths M. Thompson — ExoPAG 19 01/06/19 Research Goals • Extend previous modeling tool to simulate super-Earth planet atmospheres around M, K and G stars • Apply modified code to explore the parameter space of actual and synthetic super-Earths to select most suitable set of confirmed exoplanets for follow-up observations with JWST and next-generation ground-based telescopes • Inform the design of advanced instruments such as the Planetary Systems Imager (PSI), a proposed second-generation instrument for TMT/GMT M. Thompson — ExoPAG 19 01/06/19 Current State of Super-Earth Detections (1) Neptune Mass Range of Interest Earth Data from NASA Exoplanet Archive M. Thompson — ExoPAG 19 01/06/19 Current State of Super-Earth Detections (2) A Approximate Habitable Zone Host Star Spectral Type F G K M Data from NASA Exoplanet Archive M. Thompson — ExoPAG 19 01/06/19 Atmosphere Modeling Tool Evolution of Atmosphere Model • Solar System Planets & Moons ~ 1980’s (e.g., McKay et al. 1989) • Brown Dwarfs ~ 2000’s (e.g., Burrows et al. 2001) • Hot Jupiters & Other Giant Exoplanets ~ 2000’s (e.g., Fortney et al. -

PEAS: the PLANET AS EXOPLANET ANALOG SPECTROGRAPH. E. C. Martin1 and A
Exoplanets in our Backyard 2020 (LPI Contrib. No. 2195) 3006.pdf PEAS: THE PLANET AS EXOPLANET ANALOG SPECTROGRAPH. E. C. Martin1 and A. J. Skemer1, 1Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA ([email protected]) Introduction: Exoplanets are abundant in our Galaxy • Produce 2D surface maps of Venus, Mars, Jupi- and yet characterizing them remains a technical chal- ter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune lenGe. Solar System planets provide an opportunity to • Produce fiducial measurements that will be used test the practical limitations of exoplanet observations to plan instruments for future exoplanet mis- with hiGh siGnal-to-noise data, and ancillary data (such sions, such as HabEx/LUVOIR and TMT. as 2D maps and in situ measurements) that we cannot Long term: access for exoplanets. However, data on Solar System • Time-series observations of Solar System plan- planets differ from exoplanets in that Solar System ets to explore variability and weather patterns planets are spatially resolved while exoplanets are all on planets unresolved point-sources. • Comparison to historical data (e.g. [4]) There have been several recent efforts to validate techniques for interpreting exoplanet observations by • Study planetary seismoloGy (oscillation modes) binning images of Solar System planets to a single of Solar System planets pixel: For example, Cowan et al. [1] used images from the EPOXI mission to study Earth’s Globally averaGed PEAS Instrument Design Planetary light collect- properties as it rotated; MayorGa et al. [2] used data ed by the telescope will be split into a spectroGraph from the Cassini spacecraft’s fly-by of Jupiter to ob- system and an imaGinG system for simultaneous obser- serve Globally averaGed reflected liGht phase curves; vations. -

The Exoplanet Revolution
FEATURES THE EXOPLANET REVOLUTION l Yamila Miguel – Leiden Observatory, Leiden, The Netherlands – DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/epn/2019506 Hot Jupiters, super-Earths, lava-worlds and the search for life beyond our solar system: the exoplanet revolution started almost 30 years ago and is now taking off. re there other planets like the Earth out discovered the astonishing number of 4000 exoplanets, there? This is probably one of the oldest and counting. Every new discovery shows an amazing questions of humanity. For centuries and diversity that impacts in the perception and understand- Auntil the 90s, we only knew of the existence ing of our own solar system. of 8 planets. But today we live in a privileged time. For the first time in history we know that there are other How to find exoplanets? planets orbiting distant stars. Finding exoplanets is an extremely difficult task. These The first planet orbiting a star similar to the Sun was planets shine mostly due to the reflection of the stellar . Artist’s impression discovered in 1995 -only 24 years ago- and it started light in their atmospheres and their light is incredibly of COROT-7b. a revolution in Astronomy. Today astronomers have weak compared to that of their host stars. For this reason, © ESO/L. Calçada EPN 50/5&6 41 FEATURES THE Exoplanet REVolution observing exoplanets directly is extremely difficult and allows astronomers to calculate the planet’s density, astronomers had to develop indirect techniques that infer important to start assessing planetary compositions the presence of the planet. and diversity. Two of the most successful techniques to discov- er exoplanets are the "Transits" and "Radial Veloci- The Exoplanet Zoo ties" techniques. -

Exploring Exoplanet Populations with NASA's Kepler Mission
SPECIAL FEATURE: PERSPECTIVE PERSPECTIVE SPECIAL FEATURE: Exploring exoplanet populations with NASA’s Kepler Mission Natalie M. Batalha1 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, 94035 CA Edited by Adam S. Burrows, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, and accepted by the Editorial Board June 3, 2014 (received for review January 15, 2014) The Kepler Mission is exploring the diversity of planets and planetary systems. Its legacy will be a catalog of discoveries sufficient for computing planet occurrence rates as a function of size, orbital period, star type, and insolation flux.The mission has made significant progress toward achieving that goal. Over 3,500 transiting exoplanets have been identified from the analysis of the first 3 y of data, 100 planets of which are in the habitable zone. The catalog has a high reliability rate (85–90% averaged over the period/radius plane), which is improving as follow-up observations continue. Dynamical (e.g., velocimetry and transit timing) and statistical methods have confirmed and characterized hundreds of planets over a large range of sizes and compositions for both single- and multiple-star systems. Population studies suggest that planets abound in our galaxy and that small planets are particularly frequent. Here, I report on the progress Kepler has made measuring the prevalence of exoplanets orbiting within one astronomical unit of their host stars in support of the National Aeronautics and Space Admin- istration’s long-term goal of finding habitable environments beyond the solar system. planet detection | transit photometry Searching for evidence of life beyond Earth is the Sun would produce an 84-ppm signal Translating Kepler’s discovery catalog into one of the primary goals of science agencies lasting ∼13 h. -

Another Earth in the Universe
Home / Space/ Special reports Another Earth in the Universe A world similar to the Earth Finally the news we were waiting for, for so long, has arrived. It was only a matter of time. NASA’s Kepler Telescope, has discovered the first Earth-sized extrasolar planet, orbiting in the habitable zone, a region around a star where water in the liquid state can be found. Artist’s concept of Kepler-186f, the exoplanet similar to the Earth discovered with NASA’s Kepler telescope. Credits: Wikipedia The Earth’s “cousin” planet is called Kepler-186f, it is about 500 light years from the Earth, in the constellation of Cygnus. It has been called Kepler-186f because it was discovered with the Kepler telescope, rotating around the star Kepler-186 and is part of a system of five planets (Kepler-186b, Kepler-186c, Kepler-186d, Kepler-186e and Kepler-186f). The Kepler satellite had already discovered various planets orbiting in the habitable zone, however they were all larger, at least 40% larger than the Earth. Image of the planetary system of Kepler-186, which consists of five planets orbiting around the star, Kepler-186. The first four planets have an orbital period of 4,7, 13 and 22 days respectively and are all too hot for life to exist. Kepler-186f has an orbital period of 130 days. Credits: NASA Home / Space/ Special reports The planet system of Kepler-186 instead, consists of five planets; four inner planets, smaller than half our planet, and Kepler-186f, approximately 40% larger than the Earth. -

Exoplanet Exploration Collaboration Initiative TP Exoplanets Final Report
EXO Exoplanet Exploration Collaboration Initiative TP Exoplanets Final Report Ca Ca Ca H Ca Fe Fe Fe H Fe Mg Fe Na O2 H O2 The cover shows the transit of an Earth like planet passing in front of a Sun like star. When a planet transits its star in this way, it is possible to see through its thin layer of atmosphere and measure its spectrum. The lines at the bottom of the page show the absorption spectrum of the Earth in front of the Sun, the signature of life as we know it. Seeing our Earth as just one possibly habitable planet among many billions fundamentally changes the perception of our place among the stars. "The 2014 Space Studies Program of the International Space University was hosted by the École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS) and the École des Hautes études commerciales (HEC), Montréal, Québec, Canada." While all care has been taken in the preparation of this report, ISU does not take any responsibility for the accuracy of its content. Electronic copies of the Final Report and the Executive Summary can be downloaded from the ISU Library website at http://isulibrary.isunet.edu/ International Space University Strasbourg Central Campus Parc d’Innovation 1 rue Jean-Dominique Cassini 67400 Illkirch-Graffenstaden Tel +33 (0)3 88 65 54 30 Fax +33 (0)3 88 65 54 47 e-mail: [email protected] website: www.isunet.edu France Unless otherwise credited, figures and images were created by TP Exoplanets. Exoplanets Final Report Page i ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The International Space University Summer Session Program 2014 and the work on the -

TRAPPIST-1 Press Release
TRAPPIST-1 Press Release Frequently Asked Questions for Informal Learning Environments For additional information, be sure to check out the NASA Exoplanet Exploration FAQ and Glossary. • NASA Exoplanet Exploration FAQ - https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/faq/ • NASA Exoplanet Exploration Glossary - https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/glossary/ TRAPPIST-1 FAQ 1. What makes this disCovery speCial? There are many reasons why this discovery is truly special. The discovery of seven Earth-sized planets in the same star system has profound implications for our search for habitable worlds outside of our solar system. On top of that, this is the first time that people have discovered a star system with more than one planet in the habitable zone that we can examine with transit spectroscopy. Transit spectroscopy is the measurement of a planet’s atmosphere while it transits its host star via studying how the light from the host star behaves as it passes through the planet’s atmosphere. By breaking up this light into its constituent colors via a spectrograph, we can learn about the chemical composition of the planet’s atmosphere. Additionally, the reasonably low activity level of the central star means they are more likely to be able to support life. Finally, the system is really close, only 39 light-years away. That makes it easier for us to learn more with our current observatories – Spitzer, Hubble, Kepler, and ground-based telescopes – and possibly learn the answers to more burning questions with the soon-to-come James Webb Space Telescope. 2. Why is this planetary system Called the TRAPPIST system? The TRAPPIST system is named after the TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope (TRAPPIST) robotic telescopes. -

Exoplanet Biosignatures: a Review of Remotely Detectable Signs of Life
ASTROBIOLOGY Volume 18, Number 6, 2018 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/ast.2017.1729 Exoplanet Biosignatures: A Review of Remotely Detectable Signs of Life Edward W. Schwieterman,1–5 Nancy Y. Kiang,3,6 Mary N. Parenteau,3,7 Chester E. Harman,3,6,8 Shiladitya DasSarma,9,10 Theresa M. Fisher,11 Giada N. Arney,3,12 Hilairy E. Hartnett,11,13 Christopher T. Reinhard,4,14 Stephanie L. Olson,1,4 Victoria S. Meadows,3,15 Charles S. Cockell,16,17 Sara I. Walker,5,11,18,19 John Lee Grenfell,20 Siddharth Hegde,21,22 Sarah Rugheimer,23 Renyu Hu,24,25 and Timothy W. Lyons1,4 Abstract In the coming years and decades, advanced space- and ground-based observatories will allow an unprecedented opportunity to probe the atmospheres and surfaces of potentially habitable exoplanets for signatures of life. Life on Earth, through its gaseous products and reflectance and scattering properties, has left its fingerprint on the spectrum of our planet. Aided by the universality of the laws of physics and chemistry, we turn to Earth’s biosphere, both in the present and through geologic time, for analog signatures that will aid in the search for life elsewhere. Considering the insights gained from modern and ancient Earth, and the broader array of hypothetical exoplanet possibilities, we have compiled a comprehensive overview of our current understanding of potential exoplanet biosignatures, including gaseous, surface, and temporal biosignatures. We additionally survey biogenic spectral features that are well known in the specialist literature but have not yet been robustly vetted in the context of exoplanet biosignatures. -

Astronomers Mull Merger of Missions
NEWS IN FOCUS project along these lines — was indefinitely postponed in 2007, but the agency has contin- ued to put US$6 million a year into developing technology for exoplanet searches. Now planet NASA/JPL-CALTECH hunters think that joining forces with COPAG will be the winning strategy. Jim Kasting, a plan- etary scientist at Pennsylvania State University in University Park who is chair of the exoplanet group, says the two communities would both like to see a 4–8-metre telescope in space that would cost in excess of $5 billion. “Our interests are basically aligned,” he says. Such a mission would compete for top billing in the next decadal survey of astronomy by the US National Academy of Sciences, due in 2020. The big question, which follow-up meetings will consider, is whether the same technology can do both kinds of science. A cosmic-origins mission would need to collect as much ultraviolet and visible light as possible to image intergalactic gas, star formation and Exoplanet hunters want something to replace the postponed Terrestrial Planet Finder. Sun-like stars in nearby galaxies. A planet-hunt- ing probe would need a coronagraph to block SPACE SCIENCE direct light from host stars, and would have to be sensitive to the visible and near-infrared wavelengths that Earth-like planets primar- ily emit. The infrared 6.5-metre James Webb Astronomers mull Space Telescope (JWST), scheduled for launch in 2014, will be able to see larger planets but will not be sensitive to Earth-sized ones. The key to making the joint concept work will be develop- merger of missions ing a reflective coating for the telescope’s mirror that works from the ultraviolet to the infrared ranges and does not distort the incoming light Cosmic-origins scientists convene with exoplanet hunters. -

Who Really Discovered the First Exoplanet?
Who Really Discovered the First Exoplanet? Two Swiss astronomers got a well-deserved Nobel for finding an exoplanet, but there’s an intriguing backstory By Josh Winn The year 1995, like 1492, was the dawn of an age of discovery. The new explorers, instead of using seagoing vessels to discover continents, use telescopes to discover planets revolving around distant stars. Thousands of these extrasolar planets, a term usually shortened to “exoplanets,” have been found, including a few potentially Earth- like worlds, along with bizarre objects that bear no resemblance to any of the planets in our solar system. Two of these exoplanet explorers, Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, were recently awarded half of the Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery they made in 1995. My colleagues and I are united in our admiration for their pioneering work, and in our pride to be continuing what they began. But there is something peculiar about the Nobel Prize citation. It says: “for the discovery of an exoplanet orbiting a solar-type star.” Shouldn’t it say the first exoplanet? After all, hundreds of astronomers have discovered an exoplanet. I’ve helped find a few. Even high school students and amateur astronomers have discovered them. Did the Nobel Committee make a typographical error? No, they did not, and thereby hangs a tale. Just as it is problematic to decide who discovered America (Christopher Columbus? John Cabot? Leif Erikson? Amerigo Vespucci, whose name is the one that stuck? Those who came on foot from Siberia tens of thousands of years ago?) it is difficult to say who discovered the first exoplanet. -

The Tessmann Planetarium Guide to Exoplanets
The Tessmann Planetarium Guide to Exoplanets REVISED SPRING 2020 That is the big question we all have: Are we alone in the universe? Exoplanets confirm the suspicion that planets are not rare. -Neil deGrasse Tyson What is an Exoplanet? WHAT IS AN EXOPLANET? Before 1990, we had not yet discovered any planets outside of our solar system. We did not have the methods to discover these types of planets. But in the three decades since then, we have discovered at least 4158 confirmed planets outside of our system – and the count seems to be increasing almost every day. We call these worlds exoplanets. These worlds have been discovered with the help of new and powerful telescopes, on Earth and in space, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Kepler Spacecraft (artist’s conception, below) and the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) were specifically designed to hunt for new planets. Kepler discovered 2662 planets during its search. TESS has discovered 46 planets so far and has found over 1800 planet candidates. In Some Factoids: particular, TESS is looking for smaller, rocky exoplanets of nearby, bright stars. An earth-sized planet, TOI 700d, was discovered by TESS in January 2020. This planet is in its star’s Goldilocks or habitable zone. The planet is about 100 light years away, in the constellation of Dorado. According to NASA, we have discovered 4158 exoplanets in 3081 planetary systems. 696 systems have more than one planet. NASA recognizes another 5220 unconfirmed candidates for exoplanets. In 2020, a student at the University of British Columbia, named Michelle Kunimoto, discovered 17 new exoplanets, one of which is in the habitable zone of a star.