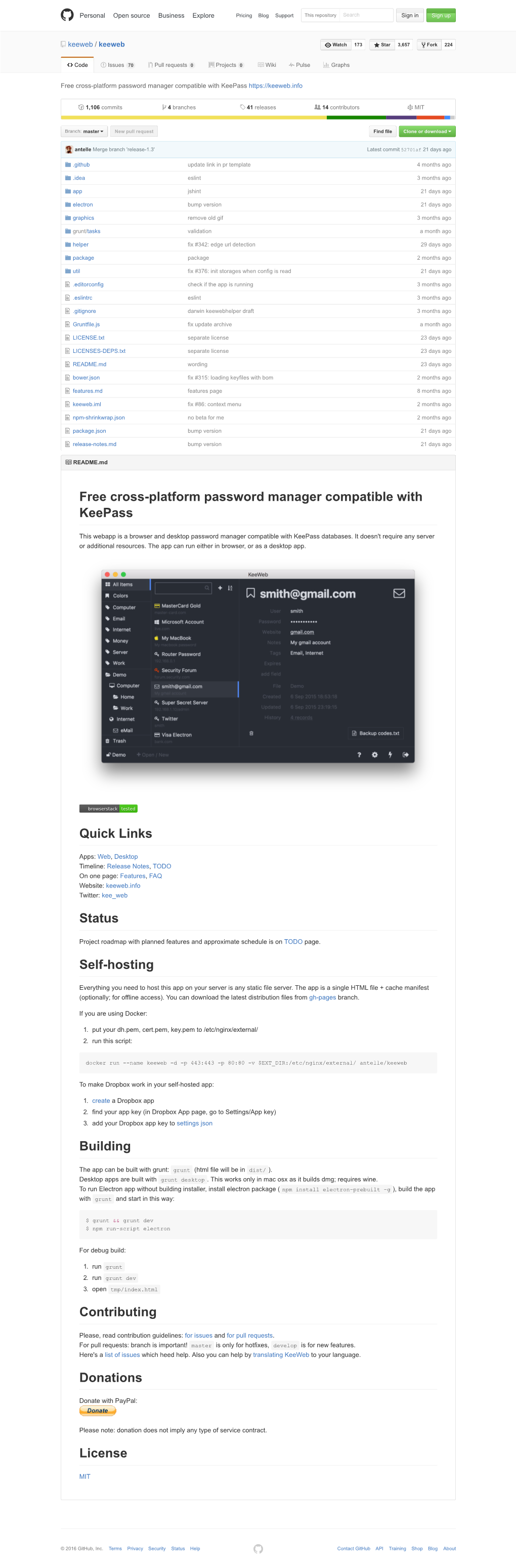
Free Cross-Platform Password Manager Compatible with Keepass
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Privacy and You the Facts and the Myths
Privacy and You The facts and the myths Bill Bowman and Katrina Prohaszka Clarkston Independence District Library 1 Overview ● What is privacy? ● Why should you care? ● Privacy laws, regulations, and protections ● Privacy and libraries ● How to protect your privacy → need-to-know settings 2 “[Privacy is] the right to What is Privacy? be let alone” - Warren & Brandeis, 1890 3 What is Privacy cont’d - Alan Westin (1967) on privacy: - “[privacy is] the right of individuals to control, edit, manage, and delete information about themselves, and to decide when, how, and to what extent information is communicated to others.” - Privacy provides a space for discussion, growth, and learning - Privacy is the ability to control your information and maintain boundaries 4 DEMO → Ghostory 5 What Privacy Is NOT - common myths Myth: Privacy and secrecy Myth: Privacy and security are the same are the same - Privacy is about being - Privacy is about unobserved safeguarding a user’s identity - Secrecy is about intentionally hiding - Security is about something protecting a user’s information & data 6 Evolving Concerns - Persistence of cameras and microphones - Think 1984 by George Orwell - “big brother” is always watching, and “it’s okay” - Social media culture - “Tagging” people without knowledge - Sharing photos without asking - Data as currency - 23andMe, Ancestry.com, Google, etc. 7 “Arguing that you don’t Why should you care about privacy because you have nothing to hide is no different than care? saying you don’t care about free speech because Why -

Keepass Password Safe Help
KeePass Password Safe KeePass: Copyright © 2003-2011 Dominik Reichl. The program is OSI Certified Open Source Software. OSI Certified is a certification mark of the Open Source Initiative. For more information see the License page. Introduction Today you need to remember many passwords. You need a password for the Windows network logon, your e-mail account, your website's FTP password, online passwords (like website member account), etc. etc. etc. The list is endless. Also, you should use different passwords for each account. Because if you use only one password everywhere and someone gets this password you have a problem... A serious problem. He would have access to your e-mail account, website, etc. Unimaginable. But who can remember all those passwords? Nobody, but KeePass can. KeePass is a free, open source, light-weight and easy-to-use password manager for Windows. The program stores your passwords in a highly encrypted database. This database consists of only one file, so it can be easily transferred from one computer to another. KeePass supports password groups, you can sort your passwords (for example into Windows, Internet, My Website, etc.). You can drag&drop passwords into other windows. The powerful auto-type feature will type user names and passwords for you into other windows. The program can export the database to various formats. It can also import data from various other formats (more than 20 different formats of other password managers, a generic CSV importer, ...). Of course, you can also print the password list or current view. Using the context menu of the password list you can quickly copy password or user name to the Windows clipboard. -

Keepass Instructions
Introduction to KeePass What is KeePass? KeePass is a safe place for all your usernames, passwords, software licenses, confirmations from vendors and even credit card information. Why Use a Password Safe? • It makes and remembers excellent passwords for every site you visit. These passwords will be random and long. • It is very dangerous to either try and remember your passwords or re-use the same password on multiple sites. Using KeePass eliminates these problems. • It helps you log into websites • It stores license codes and other critical information from software vendors • It protects all your licenses and passwords with state of the art encryption making it unbreakable as long as you have a good passphrase. I made a 5 minute introductory video screencast . Go ahead and watch it. http://www.screencast.com/t/RgJjbdYF0p Copyright(c) 2011 by Steven Shank Why switch from my OCS Passwords safe to Keepass? Keepass is much better than my program. It is much more secure. My OCS Passwords is not using state of the art encryption. My program is crackable. In addition to being safer, it is even easier to use than my program and has some great extra features. In short, while OCS passwords was a good program in its time, its time has passed. Among the many advanced features, KeePass lets you add fields, copy username and passwords into websites and programs more easily, group your passwords and launch websites directly from KeePass. How Do You Switch from OCS Password to KeePass? What I've done • I worked with a programmer to write a program to convert current password databases into a text file I could import into KeePass. -

Privacy Handout by Bill Bowman & Katrina Prohaszka
Privacy Handout By Bill Bowman & Katrina Prohaszka RECOMMENDED PROGRAM SETTINGS 2 WEB BROWSER SETTINGS 2 WINDOWS 10 4 SMARTPHONES & TABLETS 4 EMAIL 5 SOCIAL MEDIA SETTINGS 5 Instagram 5 TikTok 6 Twitter 6 Snapchat 7 Venmo 7 Facebook 8 RECOMMENDED PRIVACY TOOLS 10 WEB BROWSERS 10 SEARCH ENGINES 10 VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKS (VPNS) 10 ANTI-VIRUS/ANTI-MALWARE 10 PASSWORD MANAGERS 11 TWO-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION 11 ADDITIONAL PRIVACY RESOURCES 12 1 RECOMMENDED PRIVACY TOOLS WEB BROWSERS ● Tor browser -- https://www.torproject.org/download/ (advanced users) ● Brave browser -- https://brave.com/ ● Firefox -- https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/exp/firefox/ ● Chrome & Microsoft Edge (Chrome-based) - Not recommended unless additional settings are changed SEARCH ENGINES ● DuckDuckGo -- https://duckduckgo.com/ ● Qwant -- https://www.qwant.com/?l=en ● Swisscows -- https://swisscows.com/ ● Google -- Not private, uses algorithm based on your information VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKS (VPNS) ● NordVPN -- https://nordvpn.com/ ● ExpressVPN -- https://www.expressvpn.com/ ● 1.1.1.1 -- https://1.1.1.1/ ● Firefox VPN -- https://vpn.mozilla.org/ ● OpenVPN -- https://openvpn.net/ ● Sophos VPN -- https://www.sophos.com/en-us/products/free-tools/sophos-utm-home-edition.aspx ANTI-VIRUS/ANTI-MALWARE ● Malwarebytes -- https://www.malwarebytes.com/ ● Symantec -- https://securitycloud.symantec.com/cc/#/landing ● CCleaner -- https://www.ccleaner.com/ ● ESET -- https://www.eset.com/us/ ● Sophos -- https://home.sophos.com/en-us.aspx ● Windows Defender -- https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/comprehensive-security (built-in to Windows 10) 2 PASSWORD MANAGERS ● Lastpass -- https://www.lastpass.com/ ● KeePass -- https://keepass.info/ ● KeeWeb -- https://keeweb.info/ ● Dashlane -- https://www.dashlane.com/ TWO-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION ● Authy -- https://authy.com/ ● Built-in two-factor authentication (some emails like Google mail, various social media, etc. -

Online Security and Privacy
Security & Privacy Guide Security and Privacy Guide When thinking about security and privacy settings you should consider: What do you want to protect? Who do you want to protect it from? Do you need to protect it? How bad are the consequences if you fail to protect it? How much trouble are you prepared to go to? These questions should be asked whilst considering what information you are accessing (which websites), how you are accessing the information, (what device you are using) and where you are accessing the information (at home, work, public place). Security & Privacy When looking at your Digital Security you are protecting your information against malicious attacks and malware. (Malware is software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer). Digital Privacy is different as you are deciding what information you are prepared to share with a website or App (or its third party partners) that you are already using. Permission to share this information can be implicit once you start using a website or App. Some websites or Apps will allow you to control how they use your information. Security Physical access: How secure is the device you are using? Is it kept in a locked building, at home, or do you use it when you are out and about? Does anyone else have access to the device? Do you require a passcode or password to unlock your device? Virtual access: Have you updated your IOS software (on an iPad) or installed the latest anti-virus software on your device? Most devices will prompt you when an update is available. -

Password Managers an Overview
Peter Albin Lexington Computer and Technology Group March 13, 2019 Agenda One Solution 10 Worst Passwords of 2018 Time to Crack Password How Hackers Crack Passwords How Easy It Is To Crack Your Password How Do Password Managers Work What is a Password Manager Why use a Password Manager? Cloud Based Password Managers Paid Password Managers Free Password Managers How to Use LastPass How to Use Dashlane How to Use Keepass Final Reminder References March 13, 2019 2 One Solution March 13, 2019 3 10 Worst Passwords of 2018 1. 123456 2. password 3. 123456789 4. 12345678 5. 12345 6. 111111 7. 1234567 8. sunshine 9. qwerty 10. iloveyou March 13, 2019 4 Time to Crack Password March 13, 2019 5 Time to Crack Password March 13, 2019 6 Time to Crack Password March 13, 2019 7 Time to Crack Password Time to crack password "security1" 1600 1400 1200 1000 Days 800 Days 600 400 200 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Year March 13, 2019 8 How Hackers Crack Passwords https://youtu.be/YiRPt4vrSSw March 13, 2019 9 How Easy It Is To Crack Your Password https://youtu.be/YiRPt4vrSSw March 13, 2019 10 How Do Password Managers Work https://youtu.be/DI72oBhMgWs March 13, 2019 11 What is a Password Manager A password manager will generate, retrieve, and keep track of super-long, crazy-random passwords across countless accounts for you, while also protecting all your vital online info—not only passwords but PINs, credit-card numbers and their three-digit CVV codes, answers to security questions, and more … And to get all that security, you’ll only need to remember a single password March 13, 2019 12 Why use a Password Manager? We are terrible at passwords We suck at creating them the top two most popular remain “123456” and “password” We share them way too freely We forget them all the time We forget them all the time A password manager relieves the burden of thinking up and memorizing unique, complex logins—the hallmark of a secure password. -

Technical Guides
Technical Guides KeePass Password Manager Tutorial Wireguard Ubuntu Deployment SQM for 1 Gbps Lines With OpenWrt KeePass Password Manager Tutorial Introduction I don't trust online password managers because they are closed source and companies have been hacked in the past. If you look up "lastpass breached" in Google you can see my point. Keepass is open source and offline. Why put your trust in a company when you can create and access the database yourself? An honorable mention is bitwarden. They are also open-source and you have the option of hosting your own bitwarden server at home as an option. If you want to pay and are willing to trust a company and have your passwords encrypted on their cloud they would be your best bet. Downloading Keepass https://keepass.info/download.html Get the Installer for Windows (2.45) aka KeePass-2.45-Setup.exe. After you get it install Keepass. Recommended plugins (.plgx) to download: Keepass has a variety of useful plugins listed here: https://keepass.info/plugins.html I recommend the following below for now. Plugins always have a .plgx file extension. WebAutoType-v6.3.0.zip: https://sourceforge.net/projects/webautotype/files/ YetAnotherFaviconDownloader.plgx: https://github.com/navossoc/KeePass-Yet-Another- Favicon-Downloader/releases After you downloaded the necessary .plgx plugins. Copy or move them into the Plugins folder at C:\Program Files (x86)\KeePass Password Safe 2\Plugins. 1.1.1 Master Password To start off you will be creating a master password which is the masterkey to access all your other passwords. -

That Was Then, This Is Now: a Security Evaluation of Password Generation, Storage, and Autofill in Browser-Based Password Managers∗
That Was Then, This Is Now: A Security Evaluation of Password Generation, Storage, and Autofill in Browser-Based Password Managers∗ Sean Oesch Scott Ruoti University of Tennessee, Knoxville University of Tennessee, Knoxville [email protected] [email protected] Abstract websites [11, 15, 25, 33]. Herley points out that this rejection Password managers have the potential to help users more of security advice by users is rational when the low effectively manage their passwords and address many of the percentage of users affected by breaches is contrasted with concerns surrounding password-based authentication. the effort required [18]. However, the number of data However, prior research has identified significant breaches is on the rise [28], and this situation leaves many vulnerabilities in existing password managers; especially in users vulnerable to exploitation. browser-based password managers, which are the focus of Password managers can help users more effectively manage this paper. Since that time, five years has passed, leaving it their passwords. They reduce the cognitive burden placed unclear whether password managers remain vulnerable or upon the user by generating strong passwords, storing those whether they have addressed known security concerns. To passwords, and then filling in the appropriate password when answer this question, we evaluate thirteen popular password a site is visited. The user is now able to follow the latest managers and consider all three stages of the password security advice regarding passwords without placing a high manager lifecycle—password generation, storage, and cognitive burden on themselves. But password managers autofill. Our evaluation is the first analysis of password are not impervious to attack. -

Password Managers
Password Managers A Higher Education Information Security Council (HEISC) Resource JULY 2019 Password Managers What Is a Password Manager Tool? A password manager tool is software that helps users encrypt, store, and manage passwords. The tool also helps users create secure passwords and automatically log in to websites. Who Might Use a Password Manager Tool, and Why? Users should employ unique passwords for each website or system to help minimize the impact from the breach of one website or system; however, most users cannot remember a separate password for many sites and tend to reuse passwords or write them on a sticky note attached to their computer. Additionally, organizations may have passwords that need to be shared across teams and want a secure method to do so. Password manager tools allow users and teams to more securely manage many distinct passwords and automatically log them in to websites. The Benefits of Using a Password Manager Tool Password manager tools enable users to create and securely store unique passwords for websites, applications, and other systems without having to memorize or write them down. Risks to Consider When Using a Password Manager Tool Special care should be taken to secure the password tool, as it will grant access to all passwords. The “master” password that grants access to the tool should be very strong and unique, and multifactor authentication should be used if possible. Almost all modern commercial password managers allow users to implement some form of multifactor authentication. You will also need to decide whether you want your password management tool to store passwords locally or in the cloud. -

Keepass, Gestionnaire De Mots De Passe
Les guides utilisateur 2020 KEEPASS, GESTIONNAIRE DE MOTS DE PASSE Révision v1.1.1 du 02/10/2020 Keepass, gestionnaire de mots de passe Table des matières Généralités....................................................................................................5 Chiffrez vos mots de passe sur Windows et Mac............................................................................................................5 Un gestionnaire de mot de passe simple et gratuit..........................................................................................................5 Un gestionnaire de mot de passe fiable et sécurisé.........................................................................................................5 Un gestionnaire de mot de passe pour MacOS, Linux, FreeBSD et Windows...............................................................6 Un gestionnaire de mot de passe certifié ANSSI............................................................................................................6 Un gestionnaire de mot de passe recommandé pour sa sécurité.....................................................................................6 Gérez vos mots de passe aussi sur mobile......................................................................................................................7 Une interface en glisser/déposer très facile d’utilisation................................................................................................7 Encore plus simple avec la saisie automatique de mot de passe.....................................................................................7 -

Elcomsoft Distributed Password Recovery Unlocks 1Password, Keepass, Lastpass and Dashlane Vaults
Elcomsoft Distributed Password Recovery Unlocks 1Password, KeePass, LastPass and Dashlane Vaults Moscow, Russia – August 10, 2017 - ElcomSoft Co. Ltd. updates Distributed Password Recovery, enabling the recovery of master keys protecting encrypted vaults of four popular password managers: 1Password, KeePass, LastPass and Dashlane. By attacking a single master password, experts can gain access to the entire database containing all of the user’s saved passwords, authentication credentials and other highly sensitive information. Password managers’ protected vaults may contain images of user’s documents, various identity- related information, payment and loyalty card numbers. “We’re continuing our quest on expanding the types of passwords we can break”, says Vladimir Katalov, ElcomSoft CEO. “This time we are targeting four of the most popular password managers, allowing experts gaining access to protected vaults containing users’ authentication credentials, stored logins, passwords and forms to numerous resources. With today’s password managers this only requires breaking a single master password.” One Password to Rule Them All The idea behind all password management apps is simple: allowing users to securely store, organize and use passwords required to authenticate into various resources. As the user no longer has to remember the many different passwords, the use of password managers effectively cuts password re-use and stimulates the use of strong, unique passwords to protect different resources. Password managers can even automatically generate strong, random passwords that are unique per Web site or resource, rendering both dictionary and brute-force attacks ineffective. These passwords are stored in encrypted vaults, and can be only decrypted once the user enters their master password. -

Today's Howtos Today's Howtos
Published on Tux Machines (http://www.tuxmachines.org) Home > content > today's howtos today's howtos By Roy Schestowitz Created 20/02/2021 - 11:56pm Submitted by Roy Schestowitz on Saturday 20th of February 2021 11:56:06 PM Filed under HowTos [1] How to measure the average CPU utilization of a Linux process [2] Sometimes you may want to know the CPU usage of a particular Linux process. As the CPU usage of a process can fluctuate over its lifetime, you will want to measure the average CPU usage or CPU utilization of the process. For this purpose, a Linux tool set called sysstat may come in handy, which contains a collection of performance monitoring tools for Linux, reporting statistics on disk I/O, CPU, memory, networking, and other system activities. One of the utilities contained in sysstat is pidstat, which can measure the average CPU usage of Linux processes. How to mount USB in Ubuntu Linux [3] Do you have a USB flash drive, USB SD card reader, or USB external hard drive? Want to mount your USB in Ubuntu Linux but can?t figure it out? We can help! Follow along with this guide as we show you how to mount USB devices in Ubuntu Linux! How to play Stardew Valley on Linux [4] Stardew Valley is a simulation RPG developed by Eric Barone. It was released on Microsoft Windows in 2016. Later, it made its way to Mac OS, Linux, PS4, Switch, Xbox One, iOS, Android, and even PlayStation Vita. How to Install Custom Fonts in Linux ? Linux Hint [5] This article will explain how to install custom Fonts in Linux using various graphical and command line tools.